Question
Match the Column -I with Column-II. [NEET 2021]
Choose the correct answer from options given below.
A B C D
(a) 2 4 1 3
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 4 3 2 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
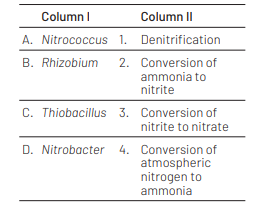
(A) -(2), (B)-(4), (C)-(1), (D)-(3)
Nitrification is the process of conversion of ammonia into nitrites and nitrites into nitrates. It is facilitated by microorganism like
Nitrococcus and Nitrobacter.
Rhizobium is involved in biological nitrogen fixation, i.e. it converts atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia.
These are symbiotically associated with the roots of leguminous plants.
Thiobacillus are involved in conversion of nitrate to nitrogen gas by the process called denitrification
Question
In Glycine max, the product of biological nitrogen fixation is transported from the root nodules to other parts as [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) ammonia
(b) glutamate
(c) nitrates
(d) ureides
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In Glycine max (Soyabean), the product of biological nitrogen fixation is transported from the root nodules to other parts as nitrate.
Question
The product(s) of reaction catalysed by nitrogenase in root nodules of leguminous plants is/are [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) nitrate only
(b) ammonia and oxygen
(c) ammonia and hydrogen
(d) ammonia only
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The products of reaction catalysed by nitrogenase in root nodules of leguminous plants are ammonia and hydrogen. The reaction is as follows $\mathrm{N}_2+8 \mathrm{e}^{-}+8 \mathrm{H}^{++}+16 \mathrm{ATP} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NH}_3+\mathrm{H}_2$ $+16 A D P+16 P_i$
Symbiotic Rhizobium bacteria invade the roots of leguminous plants and form root nodules in which they fix nitrogen, supplying both to the bacteria and the plants.
Question
Which of the following bacteria reduces nitrate in soil into nitrogen? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Nitrobacter
(b) Nitrococcus
(c) Thiobacillus
(d) Nitrosomonas
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Thiobacillus reduces nitrate in soil into nitrogen. The process is called denitrification. On the other hand, Nitrosomonas and Nitrococcus oxidise ammonia into nitrite. The bacterium, Nitrobacter oxidises nitrite to nitrate. These processes together are known as nitrification.
Question
Thiobacillus is a group of bacteria helpful in carrying out [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) chemoautotrophic-fixation
(b) nitrification
(c) denitrification
(d) nitrogen-fixation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Thiobacillus bacteria help to carry out denitrification during nitrogen cycle.
This bacteria brings about the reduction of nitrate to free nitrogen $\left(\mathrm{N}_2\right)$. Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter are chemoautotrophs that cause nitrification.
Question
Select the mismatch. [NEET 2017]
(a) Frankia – Alnus
(b) Rhodospirillum – Mycorrhiza
(c) Anabaena – Nitrogen fixer
(d) Rhizobium – Alfa-alfa
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Among the given options, only option (b) is mismatched. Rhodospirillum is a free living nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Mycorrhiza is the symbiotic association of a fungus with the root of a higher plant.
Question
During biological nitrogen fixation, inactivation of nitrogenase by oxygen poisoning is prevented by [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) leghaemoglobin
(b) xanthophyll
(c) carotene
(d) cytochrome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During biological nitrogen fixation, inactivation of nitrogenase by oxygen poisioning is prevented by leghaemoglobin.
It is a red-pigment that is filled outside the peribacteroid space in the cytosol of nodule cells. It is similar to haemoglobin of red blood cells. It has the ability to combine very rapidly with oxygen and thus acts as a very efficient $\mathrm{O}_2$ scavenger.
Question
The first stable product of fixation of atmospheric nitrogen in leguminous plants is [NEET 2013]
(a) $\mathrm{NO}_2^{-}$
(b) ammonia
(c) $\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}$
(d) glutamate
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The process of conversion of nitrogen $\left(\mathrm{N}_2\right)$ to ammonia is termed as nitrogen fixation. In reductive animation ammonia reacts with $\alpha$-ketoglutaric acid and forms glutamic acid
$\alpha$-ketoglutaric acid $+\mathrm{NH}_4^{+}+$NADPH $\underset{\text { Dehygrogenae }}{\stackrel{\text { Clutamate }}{\longrightarrow}}$ Glutamate $+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}+$ NADP
Question
Which one the following helps in absorption of phosphorus from soil by plants? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Frankia
(c) Anabaena
(d) Glomus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Glomus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, which form symbiotic relationships with plant roots. It is a longest Genus of AM fungi but it is currently defined as non-monphylactic. Mo, $\mathrm{Zn}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ are micronutrients.
Question
The function of leghaemoglobin in the root nodules of legumes is [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) oxygen removal
(b) nodule differentiation
(c) expression of nif gene
(d) inhibition of nitrogenase activity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Leghaemoglobin is an oxygen scavenger. It protects the nitrogen fixing enzyme nitrogenase from oxygen.
Question
Nitrifying bacteria [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) convert free nitrogen to nitrogen compounds
(b) convert proteins into ammonia
(c) reduce nitrates to free nitrogen
(d) oxidise ammonia to nitrates
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Nitrifying bacteria(one of the chemosynthetic bacteria) which oxidise ammonia to nitrites and obtain energy for the preparation of food. This oxidation occurs in two steps. In the first step, ammonia is oxidised to nitrite by nitrite bacteria (e.g. Nitrosomonas and Nitrococcus). In the second step, nitrite is oxidised to nitrate by nitrate bacteria(e.g. Nitrocystis and Nitrobacter).
Question
An element playing important role in nitrogen fixation is [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) molybdenum
(b) copper
(c) manganese
(d) zinc
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Molybdenum is absorbed as molybdate by plants. It is involved in nitrogen metabolism including nitrogen fixation. It is a component of enzyme nitrogenase and acts as enzyme activator. Its deficiency causes chlorosis and necrosis, whiptail of cauliflower and premature leaf fall. Copper is absorbed by the plant in ionic form. Its deficiency causes necrosis, die back in Citrus, reclamation in legumes. Manganese is absorbed by the plants as bivalent ion. It acts as enzyme activator. Its deficiency causes interveinal chlorosis as well as yellowing of starch and their subsequent degenerate.
Zinc is needed for biosynthsis of IAA and also acts as enzyme activator. Its deficiency causes chlorosis, little leaf,rosette, white bud of maize and mottling of leaves.
Question
The common nitrogen-fixer in paddy fields is [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Azospirillum
(c) Oscillatoria
(d) Frankia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Azospirillum is a nitrogen fixing bacterium in paddy fields. It is very useful soil and root bacterium. It is associative symbiotic $\mathrm{N}_2$-fixing bacteria. When it is added to the soil, it multiplies in millions and can supply $20-40 \mathrm{Kg}$ of nitrogen per hectare per season. It also producess growth promoting substances like Indole Acetic Acid (IAA), gibberellins $\left(\mathrm{GA}_3\right)$ and promotes root proliferation. These substances improve the plant growth and yield.
Question
Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of Alnus is brought about by [CBSE AIPMT 2009, 08]
(a) Bradyrhizobium
(b) Clostridium
(c) Frankia
(d) Azorhizobium
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Nitrogen is the most critical element. Certain non-leguminous plants also form nodules to fix nitrogen. The best known example in temperate region is alder (Alnus sp). The bacteria involved in nodule formation is an Actinomycetes the Frankia. Clostridium is anaerobic, saprotrophic free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria. Bradyrhizobium sp are symbiont in plants of Paraspania and soyabean. The Azorhizobium forms both stem and root nodules in Sesbania(aquatic plant).
Question
Which of the following is a flowering plant with nodules containing filamentous nitrogen fixing microorganism? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Casuarina equisetifolia
(b) Crotalaria juncea
(c) Cycas revoluta
(d) Cicer arietinum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The Casuarina tree has nitrogen fixing root nodules that harbor a filamentous actinomycete nitrogen fixing organism called Frankia.
Question
A free living, nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium which can also form symbiotic association with the water fern Azolla is [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Tolypothrix
(b) Chlorella
(c) Nostoc
(d) Anabaena
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Anabaena is a free living, nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium which can form symbiotic association with water fern Azolla.
Question
Enzyme involved in nitrogen assimilation [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) nitrogenase
(b) nitrate reductase
(c) transferase
(d) transaminase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In the process of biological nitrogen fixation, the dinitrogen molecule is reduced by the addition of pairs of hydrogen in the presence of enzyme nitrogenase. Enzyme nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase come into picture at later stage (for nitrate assimilation).
Question
In plants inulin and pectin are [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) reserved food material
(b) wastes
(c) secretory material
(d) insect attracting material
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Inulin a polymer of fructose, is used as a food store, particularly in roots and tubers of family-Compositae. Pectin is a mucopolysaccharide which is found in cell wall of plants. During the time of food ripening, the pectin becomes hydrolyse and gives rise the constituents of sugar.
Question
Which aquatic fern performs nitrogen fixation? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Azolla
(b) Nostoc
(c) Salvia
(d) Salvinia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The leaves of Azolla contain colonies of Anabaena azollae which have the capacity to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Question
Which of the following is a free living aerobic non-photosynthetic nitrogen fixer? [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Azotobacter
(c) Azospirillum
(d) Nostoc
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Azotobacter is a free living, aerobic non-photosynthetic, i.e. saprophytic bacteria. It retains the capability of fixing atmospheric nitrogen, i.e. fixation of atmospheric dinitrogen into ammonia.
Question
Which of the following can fix atmospheric nitrogen? [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Albugo
(b) Cystopus
(c) Saprolegnia
(d) Anabaena
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Blue-green algae (BGA) are the only organisms, capable of performing oxygenic photosynthesis and fixation of nitrogen, e.g. Anabaena, Nostoc which produce a specialized type of cell, called heterocyst within which $\mathrm{N}_2$ fixation occurs.
Question
Minerals absorbed by roots move to the leaf through [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) xylem
(b) phloem
(c) sieve tubes
(d) None of these
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Mineral ions accumulated in the root. hairs passes into the cortex and finally reach the xylem from where these are carried along with water to other parts of the plant along the transpiration stream. Like organic solutes, minerals can move upwards, downwards (bidirectional movement) as well as laterally.
