Question
In the equation GPP $-\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{NPP}, \mathrm{R}$ represents [NEET 2021]
(a) radiant energy
(b) retardation factor
(c) environment factor
(d) respiration losses
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs. Gross primary productivity is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. The overall productivity of a system can be found in an equation, where the Net Primary Productivity or NPP, is equal to the Gross Primary Productivity or GPP, minus the Carbon respiration (respiration losses) or $\mathrm{R}$. The formula is the NPP = GPP $-\mathrm{R}$.
Question
The rate of decomposition is faster in the ecosystem due to following factors except [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) detritus rich in sugars
(b) warm and moist environment
(c) presence of aerobic soil microbes
(d) detritus richer in lignin and chitin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The rate of decomposition is faster in the ecosystem if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars. Warm and moist environment also favour decomposition like wise high temperature and presence of aerobic soil microbes also helps in decomposition. But if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin decomposition rate gets slower. Thus, option (d) is correct.
Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect? [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Biomass decreases from first to fourth trophic level
(b) Energy content gradually increases from first to fourth trophic level
(c) Number of individuals decreases from first trophic level to fourth trophic level
(d) Energy content gradually decreases from first to fourth trophic level
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Statement (b) is incorrect. It can be corrected as The energy content decreases from the first (producer) to fourth (consumer) level. At each level about 90% of energy is lost and only
10% is passed to next level.
Question
Match the trophic levels with their correct species examples in grassland ecosystem. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
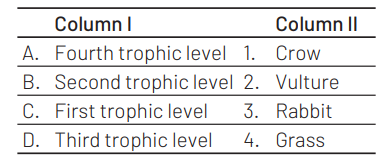
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) 3 2 1 4
(b) 4 3 2 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 2 3 4 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct match is option (d) as in grassland ecosystem grass is the producer (Ist Trophic level). Rabbit is the primary consumer (IInd Trophic level). Crow is secondary consumer (IIIrd Trophic level). Vulture is tertiary consumer (IVth Trophic level). The primary consumers eat the producers. Secondary consumers eat the primary consumers, and so on. Grassland ecosystem is a terrestrial ecosystem. It includes various trophic levels. Grass $\rightarrow$ Rabbit $\rightarrow$ Crow $\rightarrow$ Vulture
Question
In relation to gross primary productivity and net primary productivity of an ecosystem, which one of the following statements is correct? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Gross primary productivity is always more than net primary productivity
(b) Gross primary productivity and net primary productivity are one and same
(c) There is no relationship between gross primary productivity and net primary productivity
(d) Gross primary productivity is always less than net primary productivity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. Net primary productivity is GPP – respiration. Hence, gross primary productivity is always more than NPP.
Question
Most animals that in deep oceanic water are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) primary consumers
(b) secondary consumers
(c) tertiary consumers
(d) detritivores
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Most animals that live in deep oceanic waters and called benthos are scavengers or detritivores. These organisms include crustaceans, polychaetes and some microorganisms.
Question
If $20 \mathrm{~J}$ of energy is trapped at producer level, then how much energy will be available to peacock as food in the following chain? Plant $\rightarrow$ Mice $\rightarrow$ Snake $\rightarrow$ Peacock [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) $0.02 \mathrm{~J}$
(b) $0.002 \mathrm{~J}$
(c) $0.2 \mathrm{~J}$
(d) $0.0002 \mathrm{~J}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
According to $10 \%$ law of energy flow by Raynold Lindeman. The total amount of energy that can be transferred to the next trophic level is the $10 \%$ hence, peacock will receive $0.02 \mathrm{~J}$ of energy as top consumer.
Energy received by other organisms are Plant $\rightarrow 20 \mathrm{~J}$
Mice $\rightarrow 20 \times 10 \%=2 \mathrm{~J}$
Snake $\rightarrow 2 \times 10 \%=0.2 \mathrm{~J}$
Question
Secondary productivity is rate of formation of new organic matter by [NEET 2013]
(a) producer
(b) parasite
(c) consumer
(d) decomposer
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Secondary productivity is the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers. Primary productivity depends on the producers inhabiting a particular area. Decomposers breakdown complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients. Parasitic species feed on the body of other organism.
Question
Identify the likely orgnaisms I, II, III and IV in the food web shown below. [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
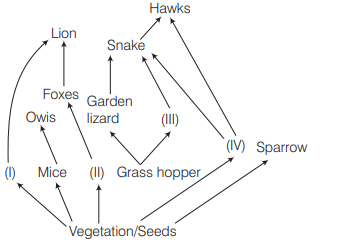
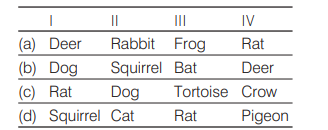
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In the given food web option (a) is correct as producers utilise the radiant energy of sun which is transformed to chemical form during photosynthesis. Thus, green plants occupy the first
trophic level. The herbivores constitute the secondary trophic level and the carnivores the third trophic level. Deer is herbivores, rabbit and rat are also herbivores but frog eats the grasshoppers. Also deer is been eaten by lion.
Question
Identify the possible link ‘ $A^{\prime}$ in the following food chain [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
Plant $\rightarrow$ Insect $\rightarrow$ Frog $\rightarrow{ }^{\prime} A^{\prime} \rightarrow$
Eagle
(a) Rabbit
(b) Wolf
(c) Cobra
(d) Parrot
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The given food chain should be
Plant $\rightarrow$ Insect $\rightarrow$ Frog $\rightarrow$ Cobra $\rightarrow$
Eagle
Question
Mass of living matter at a trophic level in an area at any time is called [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) standing crop
(b) detritus
(c) humus
(d) standing state
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Standing crop is the total amount of living matter in a specified population at a particular time, expressed as biomass (standing biomass) or its equivalent in terms of energy. The standing crop may vary at different times of the year for example in a population of deciduous trees between summer and winter.
Question
Of the total incident solar radiation the proportion of PAR is [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) about $70 \%$
(b) about $60 \%$
(c) less than $50 \%$
(d) more than $80 \%$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The source of energy in all ecosystem is solar energy. About $50 \%$ of the solar energy incident over earth is present in PAR (Photosynthetically active
Radiation). About $1-5 \%$ of incident solar radiation or $2-10 \%$ of PAR is captured by the photosynthetic organisms in the synthesis of organic matter (gross primary productivity).
Roughly $20 \%$ of it is consumed in respiration so that net capture of energy (net primary productivity) is $0.8-4 \%$ of incident radiation or 1.6-8\% of PAR.
Question
The biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and the decomposers is called [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) net primary productivity
(b) secondary productivity
(c) standing crop
(d) gross primary productivity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Net primary productivity is equal to the rate of organic matter created by photosynthesis minus the rate of respiration and other losses. It is the biomass available for consumption by the herbivores and the decomposers.
Question
The correct sequence of plants in a hydrosere is [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Oak $\rightarrow$ Lantana $\rightarrow$ Scirpus $\rightarrow$ Pistia $\rightarrow$ Hydrilla $\rightarrow$ Volvox
(b) Volvox $\rightarrow$ Hydrilla $\rightarrow$ Pistia $\rightarrow$ Scirpus $\rightarrow$ Lantana $\rightarrow$ Oak
(c) Pistia $\rightarrow$ Volvox $\rightarrow$ Scirpus $\rightarrow$ Hydrilla $\rightarrow$ Oak $\rightarrow$ Lantana
(d) Oak $\rightarrow$ Lantana $\rightarrow$ Volvox $\rightarrow$ Hydrilla $\rightarrow$ Pistia $\rightarrow$ Scirpus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The various stages in a hydrosere are well studied in ponds, pools or lakes. The various stages of hydrosere are:
(i) Phytoplankton stage, e.g. some blue-green algae, green algae (Volvox), diatoms and bacteria, etc.
(ii) Rooted submerged stage, e.g. Hydrilla, Vallisneria, etc.
(iii) Floating stage, e.g. Nelumbo, Nymphaea, etc. Some free floating species are Pistia, Azolía, Lemna, etc.
(iv) Red-swamp stage, e.g. species of Scirpus, Typha, etc.
(v) Sedge-meadow stage, e.g.species of Cyperaceae and Gramineae.
(vi) Woodland stage, e.g. Lantana, Salix, Populus, etc.
(vii) Forest stage, e.g. Tropical rain forests, mixed forests of Almus, Acer, Quercus (oak), tropical deciduous forests.
Question
Which one the following types of organisms occupy more than one trophic level in a pond ecosystem? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Phytoplankton
(b)Fish
(c)Zooplankton
(d)Frog
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In a pond ecosystem, fishes occupy more than one trophic levels. Small fishes act as secondary consumer. They feed on primary consumer. Large fishes act as Tertiary consumer. They feed on smaller fish.
Question
Consider the following statements concerning food chains. [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
I. Removal of $80 \%$ tigers from an area resulted in greatly increased growth of vegetation
II. Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deers
III. The length of food chains is generally limited to $3-4$ trophic levels due to energy loss
IV. The length of food chains may vary from 2 to 8 trophic levels
Which of the two above statements are correct?
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) III aqnd IV
(d) I and IV
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Statements II and III are correct. A simple food chain consists of producers, herbivores and carnivores. The length of food chain is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to the energy loss. In grazing food chain the producers (i.e. plants) are eaten by herbivores (i.e. rabbit, deer, cow, etc) and the herbivores are eaten by carnivores. Therefore, the removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deers.
Question
Which of the following ecosystem types has the highest annual net primary productivity? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Tropical rain forest
(b) Tropical deciduous forest
(c) Temperate evergreen forest
(d) Temperate deciduous forest
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Productivity of tropical rain forest is highest. The tropical rain forest cover $300,000 \mathrm{~km}^2$ area. They contain more than $50 \%$ of total flora and fauna of the world.
Question
Which of the following is expected to have the highest value $\left(\mathrm{gm} / \mathrm{m}^2 / \mathrm{yr}\right.$ ) in a grassland ecosystem? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Secondary Production (SP)
(b) Tertiary Production (TP)
(c) Gross Production (GP)
(d) Net Production (NP)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The rate of total capture of energy or the rate of total production of organic material is gross primary productivity while the balance or biomass remaining after meeting the cost of respiration of producers is net primary productivity. Hence, gross productivity has highest value in grassland ecosystem.
Question
Bamboo plant is growing in a far forest then what will be the trophic level of it? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) First trophic level ( $\left.T_1\right)$
(b) Second trophic level $\left(T_2\right)$
(c) Third trophic level $\left(\mathrm{T}_3\right)$
(d) Fourth trophic level $\left(T_4\right)$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Plants, being photosynthetic, occupy first trophic level$ (T_1 )$ in the food chain.
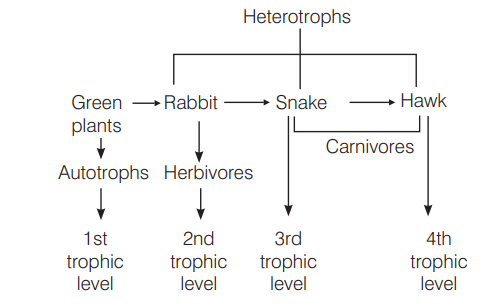
A trophic level is a step in the flow of energy through an ecosystem, such as the step at which plants manufacture food or the step at which carnivores feed on other animals.
Question
The transfer of energy from one trophic level to another is governed by the 2 nd law of thermodynamics. The average efficiency of energy transfer from herbivores to carnivores is [CBSE AIPMT 1999, 96]
(a) $5 \%$
(b) $10 \%$
(c) $25 \%$
(d) $50 \%$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
According to 10\% law of Lindeman, only $10 \%$ of energy is transferred from one trophic level to another, i.e. from herbivores to carnivores.
Question
The rate at which light energy is converted into chemical energy of organic molecules is the ecosystem’s [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) net primary productivity
(b) gross secondary productivity
(c) net secondary productivity
(d) gross primary productivity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Plants, found in an ecosystem are known as producers, because they can prepare food for themself by the process of photosynthesis. The energy fixed by the autotrophs during photosynthesis gets incorporated into organic compounds. The rate at which organic molecules are formed in a green plant (or a population of green plants) is called gross primary productivity.
Question
Which of the following ecosystem has the highest gross primary productivity? [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Grasslands
(b)Coral reefs
(c) Mangroves
(d) Equatorial rain forest
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the total amount of organic matter produced by it’s producers, i.e. autotrophs. Coral reefs have maximum and deserts have lowest productivity.
Question
In a biotic community, the primary consumers are [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) carnivores
(b)omnivores
(c) detritivores
(d)herbivores
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In a biotic community, the primary consumers or first order consumers are herbivores, they feed on producers. They are also called key industry animals because they convert plant material into animal material, e.g. rat, deer, rabbit, cattle, goat, sheep, insects etc.
Question
If we completely remove the decomposers from an ecosystem, its functioning will be adversely affected, because [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) energy flow will be blocked
(b) herbivores will not receive solar energy
(c) mineral movement will be blocked
(d) rate of decomposition will be very high
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Decomposers like fungi, bacteria and Actinomycetes are also called mineralisers as they release minerals trapped in organic matter. Thus, they help in recycling of minerals, so if we completely remove decomposers the mineral movement will be blocked.
Question
In grass-deer-tiger food chain, grass biogass is one tonne. The tiger biomass shall be [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) $100 \mathrm{~kg}$
(b) $10 \mathrm{~kg}$
(c) $200 \mathrm{~kg}$
(d) $1 \mathrm{~kg}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
According to 10\% law of Lindemann, if 1 tonne $(1000 \mathrm{~kg})$ biomass is present in grass, only $10 \%$ of it means $100 \mathrm{~kg}$ will go into deer and in tiger the biomass will be only $10 \mathrm{~kg}$, i.e. $10 \%$ of deer’s biomass.
Question
Second most important trophic level in a lake is [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a)zooplankton
(b) phytoplankton
(c) benthos
(d) neuston
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In a lake ecosystem, the first trophic level is occupied by phytoplankton and then in second trophic level there are zooplanktons which are primary consumers.
Question
Food chain in which microorganisms breakdown the food formed by primary producers are [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) parasitic food chain
(b) detritus food chain
(c) consumer food chain
(d) predator food chain
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Detritus food chain goes from dead organic matter to detritivores protozoan, bacteria, fungi and then to organisms feeding on detritivores, e.g. insect larva, nematodes. This food chain is also called as saprophytic food chain.
Question
Pick up the correct food chain. [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) Grass $\rightarrow$ Chameleon $\rightarrow$ Insect $\rightarrow$ Bird
(b) Grass $\rightarrow$ Fox $\rightarrow$ Rabbit $\rightarrow$ Bird
(c) Phytoplankton $\rightarrow$ Zooplankton $\rightarrow$ Fish
(d) Fallen leaves $\rightarrow$ Bacteria $\rightarrow$ insect larvae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct food chain is:
Phytoplankton $\rightarrow$ Zooplankto $\rightarrow$ Fish
i.e. Producers $\rightarrow$ Primary consumer
$\rightarrow$ Secondary consumer
Question
Upper part of sea/aquatic ecosystem contains [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) plankton
(b) nekton
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) benthos
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Planktons are passively floating organisms living in the surface layers of water due to absence of locomotory organs, they are of two types: Phytoplankton (photosynthetic plankton) and zooplankton.
While nektons are actively floating organisms and benthos are found in the bottom and are usually sessile.
