Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
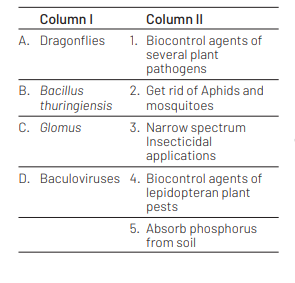
Codes
A B C D
(a) 3 5 4 1
(b) 2 1 3 4
(c) 2 3 4 5
(d) 2 4 5 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Option (d) is the correct match which is as follows
Dragonflies help to get rid of Aphids and mosquitoes. Baccillus thuringiensis acts as biocontrol agent for lepidopteran and plant pests. Glomus is a fungus which forms mycorrhiza to absorb phosphorus from soil. Baculoviruses are used in narrow spectrum insecticidal applications.
Question
A biocontrol agent to be a part of an integrated pest management should be [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) species-specific and symbiotic
(b) free-living and broad spectrum
(c) narrow spectrum and symbiotic
(d) species-specific and inactive on non-target organisms
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
A biocontrol agent to be a part of an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programme should be species-specific and inactive or have no negative impacts on non-target organisms like plants, mammals, birds, fish and even on other non-target insects. It should kill only targeted insects/pests(organisms).
Question
Which of the following can be used as a biocontrol agent in the treatment of plant disease? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Chlorella
(b) Anabaena
(c) Lactobacillus
(d) Trichoderma
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Trichoderma can be used as a biocontrol agent in the treatment of plant disease. It is a filamentous soil fungus having mycoparasitic activity. On the other hand, Anabaena helps in nitrogen-fixation, Lactobacillus helps in the production of organic acid, e.g. lactic acid and Chlorella is a single cell protein which acts as food supplement.
Question
Select the correct group of biocontrol agents. [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Trichoderma, Baculovirus, Bacillus thuringiensis
(b) Oscillatoria, Rhizobium, Trichoderma
(c) Nostoc, Azospirillum, Nucleopolyhedrovirus
(d) Bacillus thuringiensis, Tobacco mosaic virus, Aphids
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The correct group of biocontrol agents is Trichoderma, Baculovirus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Baculovirus are pathogens that attack insects and other arthropods. Most of Boculoviruses used as biocontrol agent belong to the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
Trichoderma is extensively used against pathogenic fungi which causes soil borne diseases.
Bacillus thuringiensis secretes toxin crystals which kill the insect larvae. On the other hand, Rhizobium, Nostoc, Azospirillum and Oscillatoria are used as biofertilisers. Tobacco mosaic virus is a pathogen and aphids are pests that harm crop plants.
Question
Which one of the following is an example of carrying out biological control of pests/diseases using microbes? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Trichoderma sp. against certain plant pathogens
(b) Nucleopolyhedrovirus against white rust in Brassica
(c) Bt cotton to increase cotton yield
(d) Lady bird beetle against aphids in mustard
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Out of the given statement ‘ $c$ ‘ is correct example because $B t$ cotton is Genetically Modified(GM) cotton which has an incorporated gene extracted from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. This gene codes for Bt toxin in plant tissues which is harmful only to a small fraction of insects, most notably the larvae of lepidopterans, moths, butterflies, beetles, flies, etc, and harmless to other forms of life. So, it is used as biological control of pests/diseases.
Question
A common biocontrol agent for the control of plant diseases is[CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Baculovirus
(b) Bocillus thuringiensis
(c) Glomus
(d) Trichoderma
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Trichoderma is a genus of fungi that is present in all soils. Several strains of Trichoderma have been developed as biocontrol agents against fungal diseases of plants. The various mechanisms include antibiosis, parasitism, inducing host-plant resistance and competition.
Most biocontrol agents are from the species T. harzianum, T. viride and T. hamatum. The biocontrol agent generally grows in its natural habitat on the root surface and so, affects root disease in particular but can also be effective against foliar diseases.
Question
The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is widely used in contemporary biology as a/an [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) indicator of water pollution
(b) insecticide
(c)agent for production of dairy products
(d) source of industrial enzyme
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Bacillus thuringiensis is used as an insecticide. It is a Gram-positive, soil dwelling bacterium, also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies.
During sporulation, B. thuringiensis forms crystals of proteinaceous insecticidal\&-endotoxins (cry toxins) which are encaded by cry genes.
It was determined that the cry genes are harbored in the plasmids of $B$.
thuringiensis strains. Cry toxins have specific activities against species of the order-Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies Diptera(flies and mosquitoes) and Coleoptera(beetles). Thus, B. thuringiensis serves as an important reservoir of cry toxins and cry genes for the production of biological insecticides and insect resistant genetically modified crops.
Question
What is true about Bt toxin? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) The inactive protoxin gets converted into active form in the insect gut
(b) Bt protein exists as active toxin in the Bacillus
(c) The activated toxin enters the ovaries of the pest to sterilise it and thus, prevent its multiplication
(d) The concerned Bacillus has antitoxins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Bacillus thuringiensis toxin is an inactive protoxin, which gets converted into active form in the insect gut. It works as an insecticide.
Question
Which of the following is not used as a biopesticide? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Bacillus thuringiensis
(b) Trichoderma harzianum
(c) Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus (NPV)
(d) Xanthomonas compestris
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The bacterium Xanthomonas campestris is the causative agent of plant disease, black rot of cabbage. Bocillus thuringiensis, T. harzianum and NPV are biopesticides.
Question
Main objective of production/use of herbicide resistant GM crops is to [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) eliminate weeds from the field without the use of manual labour
(b) eliminate weeds from the field without the use of herbicides
(c) encourage eco-friendly herbicides
(d) reduce herbicide accumulation in food particles for health safety
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The main abjective of production/use of herbicide resistant Genetically Modified (GM) crops is to reduce herbicide accumulation in food articles for health safety. The chemical substances, which are used to kill or repel pest are called pesticides. The chemical substance which are used to destroy weeds are called herbicides.
Question
Cry-l endotoxins obtained from Bacillus thuringiensis are effective against [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) mosquitoes
(b)flies
(c) nematodes
(d) bollworms
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Cry-l endotoxins obtained from Bacillus thuringiensis are effective against flies (insects). The cry gene of Bacillus thuringiensis produces a protein, which forms crystalline inclusion in the bacterial spores. These crystal proteins are responsible for the insecticidal activities of the bacterial strains.
Question
Which one of the following proved effective for biological control of nemato diseases in plants? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) Pisolithus tinctorius
(b) Pseudomyces lilacinus
(c) Gliocladium virens
(d) Paecilomyces lilacinus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Paecilomyces lilacinus has praved effective for biological control of nematodal disease in plants. It is easily produced in vitro. It attack the eggs of several nematode species and highly effective treatment of plant matter, e.g. seed tuber.
Question
Which one of the following proved effective for biological control of nematode diseases in plants? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) Glicoladium virens
(b) Paecilomces lalacinus
(c) Pisolithus tinctorius
(d) Pseudomonas cepacia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Paecilomyces lilacinus is a fungus which principally infects eggs of root knot nematode (Meloidogyne sp.) land cyst nematodes (Gobodera and Heterodera sp.) It has been considered to have greatest potential for application as a biocontrol agent in sub-tropical and tropical agricultural soils.
Question
The most likely reason for the development of resistance against pesticides in insect damaging a crop is [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) random mutations
(b) genetic recombinations
(c) directed mutations
(d) acquired heritable changes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The most likely reason for the development of resistance against pesticides in insect damaging a crop is random mutations, because environmental stress, i.e. pesticides does not cause direct changes in genome, instead, it simply selects rather persisting mutations which result in phenotypes that are better adapted to the new environment in certain pesticides.
Question
Biological control component is central to advanced agricultural production. Which of the following is used as a third generation pesticide? [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) Pathogens
(b) Pheromones
(c) Insect repellents
(d) Insect hormone analogues
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Insect hormones, i.e. pheromones, are third generation pesticides. Pheromones are the chemical substances which when released into an animal’s surroundings, influence the behaviour ar development of other individuals of the same species. Inorganic substances, oils, plant extracts used as insecticides are called first generation pesticides and synthetic organic compounds as second generation pesticides.
Question
What is agent orange? [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) A biodegradable insecticide
(b) A weedicide containing dioxin
(c) Colour used in fluorescent lamp
(d) A hazardous chemical used in luminous paints
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Agent orange is a weedicide containing diaxin. It is so, called because of distinctive orange stripe on its packaging, combines equal parts of 2 , $4-\square$ and 2, 4, 5-T was later on found to contain a highly poisonous chemical dioxin as impurity.
Question
Suppression of reproduction of one type of organism by utilising some features of its biology or physiology to destroy it or by use of another organism is known as [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a)competition
(b) predation
(c) biological control
(d) physiological control
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Biological contral is the suppression of reproduction of one type of organism by utilising some features of its biology or physiology to destray it or by use of another organism.
Question
One of the major difficulties in the biological control of insect pests is the [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) practical difficulty of intraducing the predator to specific areas
(b) method is less effective as compared with the use of insecticides
(c) predator does not always survive when transferred to a new environment
(d) the predator develops a preference to other diets and may itself become a pest.
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The major difficulties in the biological control of insects pests is that the predator develops a preference to other diets and may itself become a pest. Biological control is mainly refers to the introduction of living organisms which destroy other harmful organisms.
