Question
Which of the following secretes the hormone, relaxin, during the later phase of pregnancy? [NEET 2021]
(a) Graafian follicle
(b)Corpus luteum
(c) Foetus
(d) Uterus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Corpus luteum is formed in ovary after the ovulation and degenerates if pregnancy does not occur.
In later phase of pregnancy the corpus luteum secretes relaxin hormone.Relaxin dilates the cervix and helps in parturition. Graafian follicle, uterus and foetus has no role in relaxin secretion.
Question
Which of these is not an important component of initiation of parturition in humans? [NEET 2021]
(a) Increase in oestrogen and progesterone ratio
(b) Synthesis of prostaglandins
(c) Release of oxytocin
(d) Release of prolactin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Prolactin hormone is not important for initiation of parturition because it is released after the parturition in order to secrete the milk from the mammary gland. Parturition is usually initiated by the release of oxytocin hormone from the maternal pituitary.
This hormone increases the concentration of uterine muscles. Prostaglandins are synthesised and released in response to the oxytocin hormone which induces stronger contraction resulting in expulsion of baby. During parturition there is an increase in oestrogen and progesterone ratio in the female body.
Question
In human beings, at the end of 12 weeks (first trimester) of pregnancy, the following is observed. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Eyelids and eyelashes are formed
(b) Most of the major organ systems are formed
(c) The head is covered with fine hair
(d) Movement of the foetus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In human beings, at the end of 12 weeks (first trimester), most of the major organ systems are formed, e.g. the limbs and external genital organs gets well-developed.
Question
Select the correct sequence of events [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Gametogenesis $\rightarrow$ Gamete transfer $\rightarrow$ Syngamy $\rightarrow$ Zygote $\rightarrow$ Cell division (Cleavage) $\rightarrow$ Cell differentiation $\rightarrow$ Organogenesis
(b) Gametogenesis $\rightarrow$ Gamete transfer $\rightarrow$ Syngamy $\rightarrow$ Zygote $\rightarrow$ Cell divison (Cleavage) $\rightarrow$ Organogenesis $\rightarrow$ Cell differentiation
(c) Gametogenesis $\rightarrow$ Syngamy $\rightarrow$ Gamete transfer $\rightarrow$ Zygote $\rightarrow$ Cell division (Cleavage) $\rightarrow$ Cell differentiation $\rightarrow$ Organogenesis
(d) Gametogenesis $\rightarrow$ Gamete transfer $\rightarrow$ Syngamy $\rightarrow$ Zygote $\rightarrow$ Cell differentiation $\rightarrow$ Cell division (Cleavage) $\rightarrow$ Organogenesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The correct sequence of events are Gametogenesis (i.e. production of gametes) $\rightarrow$ Gamete transfer (i.e. movement of gamete at the site of fertilisation) $\rightarrow$ Syngamy (i.e. the fusion of gametes) $\rightarrow$ Zygote (i.e. a eukaryotic cell formed by fertilisation of gametes) $\rightarrow$ Cell division (cleavage) $\rightarrow$ Cell differentiation (i.e the process where a cell changes from one cell type to another) $\rightarrow$ Organogenesis (i.e. the process of formation of three germ layers).
Question
Which of the following hormones is responsible for both the milk ejection reflex and the foetal ejection reflex? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Destrogen
(b) Prolactin
(c) Oxytocin
(d) Relaxin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Oxytocin hormone is responsible for both, the milk ejection reflex and foetal ejection reflex. It is a peptide hormone normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland.
Question
Colostrum, the yellowish fluid, secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation is very essential to impart immunity to the new born infants because it contains [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) monocytes
(b) macrophages
(c) immunoglobulin A
(d) natural killer cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Colostrum, the yellowish fluid, secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation is very essential to impart immunity to the newborn infants because it contains immunoglobulin $A$. The type of immunity provided by colostrum is natural passive immunity. As IgA is secreted in mother’s milk, it is also called secretory immunoglobulin. Monocytes are a type of white blood cell having simple oval nucleus. Macrophages are cells of the immune system. These cells can engulf bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites.
Natural killer cells are lymphocytes and are a component of innate immune system.
Question
The amnion of mammalian embryo is derived from [NEET 2018]
(a) mesoderm and trophoblast
(b) endoderm and mesoderm
(c) ectoderm and mesoderm
(d) ectoderm and endoderm
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Amnion of mammalian embryo is derived from ectoderm and mesoderm. It is one of the extraembryonic membrane which is formed by the amniogenic cells of ectodermal origin on inner side and somatopleuric extraembryonic mesoderm on outer side. This membrane acts as a shock absorber for the foetus, regulates foetal body temperature and prevents desiccation. The origin of other extraembryonic membranes is as follows
Chorion Trophoectoderm and mesoderm.
Allantois and Yolk sac Outer mesoderm and inner endoderm.
Question
Hormones secreted by the placenta to maintain pregnancy are [NEET 2018]
(a) hCG, hPL, progestogens, estrogens
(b) hCG, hPL, estrogens, relaxin, oxytocin
(c) hCG, hPL, progestogens, prolactin
(d) hCG, progestogens, estrogens, glucocorticoids
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The hormones secreted by the placenta to maintain pregnancy are hCG, $\mathrm{hPL}$, progestogens and estrogens. Placenta is the intimate connection between the foetus and uterine wall of the mother to exchange the materials. It has endocrine function and secretes the following hormones
(i) Human Chorionic Gonadotropins (hCG) It stimulates and maintains the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone until the end of pregnancy.
(ii) Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) It is also known Human Chorionic Somatomam- motropin (HCS), it stimulates the growth of mammary glands during pregnancy.
(iii) Progesterone and estrogen support foetal growth, maintain pregnancy, inhibit uterine contractions, etc.
On the other hand, the sources of other hormones are as follows
Oxytocin Secreted by posterior lobe of pituitary gland during foetal ejection reflex. Glucocorticoid Secreted by adrenal gland of foetus to induce foetal ejection reflex.
Relaxin Secreted by corpus luteum to increase flexibility of pubis symphysis.
Prolactin Secreted by anterior lobe of pituitary, helps in the secretion of milk.
Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option using the codes given below. [NEET 2016, Phase II]
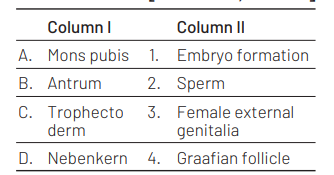
Codes
A B C D
(a) 3 4 2 1
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 1 4 3 2
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The carrect match are
(a) Mona pubis-female external genitalia
(b) Antrum-Graafian follicle
(c) Trophectoderm-Embryo development
(d) Nebenkern-Sperm
Concept Enhancer Nebenkern is a mitochondrial structure present in the sperm of certain insects.
Question
Several hormones like hCG, hPL. oestrogen, progesterone are produced by [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) ovary
(b) placenta
(c) Fallopian tube
(d) pituitary
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Several hormanes like-hCG, hPL, oestrogen, progesterone are produced by placenta. It is a structural and functional connectivity between the developing embryo (foetus) and the maternal body. It is connected to embryo through an umblical cord which helps in transport of substances to and from the embryo. Placenta also acts as an endocrine tissue by producing the above mentioned hormanes.
Question
Which one of the following is not the function of placenta? It [NEET 2013]
(a) facilitates supply of oxygen and nutrients to embryo
(b) secretes aestrogen
(c) facilitates removal of carbon dioxide and waste material from embryo
(d) secretes oxytocin during parturition
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Pituitary secretes oxytocin during parturition. The functions of placenta are supply of oxygen and nutrients to embryo. It aslo secretes estrogen, facilitates removal of carbon dioxide and waste materials from embryo.
Question
Signals for parturition originate from [CBSE AIPMT 2012, 10]
(a) both placenta as well as fully developed toetus
(b) coxytocin released from maternal pituitary
(c) placenta only
(d) fully developed toetus only
Answer/Explanation
Ans.(a)
The process of delivery of the foetus (childbirth) is called parturition which is induced by a complexneuroendocrine mechanism. The signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta which induce mild uterine contractions called foetal ejection refiex.
This triggers release of oxytocin fram maternal pituitary. Oxytocin causes stronger uterine contractions which in turn stimulate further secretion of axytocin. The stimulatory reflex between the uterine contraction and axytocin secretion continues resulting in stranger and stronger contractions. This leads to expulsion of the baby out of the uterus through the birth canal, i.e. parturition.
Question
The first movements of the foetus and appearance of hair on its head are usually observed during which month of pregancy? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Fourth month
(b) Fifth month
(c) Sixth month
(d) Third month
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
During development of toetus in human by week 20, hair begin to grow including eyebrows and eyelashes, tingerprints develop. Fingemails and toe nails grow. Firm hand grip. Between 16 and 20 weeks the tirst movements of the foetus are observed.
Question
Which extra-embryonic membrane in humans prevents desiccation of the embryo inside the uterus? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) Chorion
(b)Allantois
(c) Yolk sac
(d)Amnion
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Amnion is an extra embryonic membrane that surrounds embryo in reptiles, birds and mammals. It provides a kind of private aquarium to the embryo and protects it from mechanical shock and desiccation. Chorion (serosa] is the outermost extra embryonic membrane in reptiles, birds and mammals. It surrounds the whole embryonic system of embryo.
Yoik sac contains yolk in reptiles and birds. In mammals yolk sac is also know umbilical vesicle. It is connected to enteron of embryo by a slender yolk stalk.
Question
During embryonic development, the establishment of polarity along anterior/ posterior, dorsal/ventral or medial/lateral axis is called [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) anamorphosis
(b) pattern formation
(c) arganiser phenomena
(d) axis formation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Embryonic axis are formed very early in development and sametimes by the polarity of the egg.
Question
Extra-embryonic membranes of the mammalian embryo are derived from [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) inner cell mass
(b) trophoblast.
(c)formative cells
(d) follicle cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Extra-embryonic membranes are formed outside the embryo from the trophoblast in amniotes(reptiles, birds and mammals) and pertorm specitic function. These are yolk sac, amnion, allantois and chorion.
Question
Gonads develop from embryonic [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) ectoderm
(b) endoderm
(c)mesoderm
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Gonads develop from mesoderm. Beside gonads mesoderm also forms muscles, connective tissue, dermis of skin, bones and cartilages, peritoneal layers, coelom, circulatory system (heart, blood vessels, blood, lymphatic system). Kidneys, ureters and adrenal cortex.
Question
Cells become variable in morphology and function in different regions of the embryo. The process is [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) differentiation
(b) metamorphosis
(c) organisation
(d) rearrangement
Answer/Explanation
Ans.(a)
After formation of three primary germ layers [i.e., ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderml, cells of these three layers become variable in morphology, shape, size and more specified to form organs so as to meet out the future functional needs of the foetus, this process is called differentiation.
