Question
In which one of the following processes $\mathbf{C O}_2$ is not released? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Aerobic respiration in plants
(b) Aerobic respiration in animals
(c) Alcoholic fermentation
(d) Lactate fermentation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
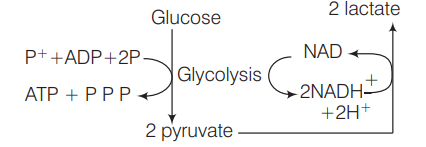
Lactic acid fermentation is process by which glucose, fructose and sucrose are corverted into energy and the metabolite lactate. It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells and allows glycolysis to continue by ensuring that $\mathrm{NADH}$ is returned to its oxidised state $\left(\mathrm{NAD}^{+}\right)$.
Question
The energy-releasing metabolic process in which substrate is oxidised without an external electron acceptor is called [CBSE AIPMT 2010, 08]
(a) glycolysis
(b) fermentation
(c) aerobic respiration
(d) photorespiration
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Fermentation takes place in the lack of oxygen (when the electron transport chain is unusable)and becomes the cell’s primary means of ATP(energy) production. It turns NADH and pyruvate in the glycolysis into $\mathrm{NAD}^{+}$and various small molecules depending on the type of fermentation. In the presence of $\mathrm{O}_2$, NADH and pyruvate are used to generate ATP in respiration. It is called oxidative respiration.
Question
In alcoholic fermentation [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) axygen is the electron acceptor
(b) triose phosphate is the electron donor while acetaldehyde is the electron acceptor
(c) triose phosphate is the electron donor while pyruvic acid is the electron acceptor
(d) there is no electron donor
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In alcoholic fermentation,
(a) $\mathrm{NADH}$ (formed during conversion of triose-3 phosphate to 3 phosphoglycerate] is oxidised to $\mathrm{NAD}^{-}$
(b) electrons are accepted by acetaldehyde formed by decarboxylation of pyruvate.
Question
Fermentation is anaerobic production of [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Protein and acetic acid
(b) alcohol, lactic acid or similar compounds
(c) ethers and acetones
(d) alcohol and lipoproteins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Fermentation is defined as anaerobic break down of carbohydrates and other organic compounds to form aldehyde, alcohol and organic acids (lactic acid) with the help of microorganisms or their enzymes.
Question
Fermentation products of yeast are [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{D}+\mathrm{CO}_2$
(b) methyl alcohol $+\mathrm{CO}_2$
(c) methyl alcahol $+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
(d) ethyl alcohol $+\mathrm{CO}_2$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Yeast cells undergo alcoholic fermentation in which glucose is first. converted into pyruvic acid. In the presence of pyruvic decarboxylase, it is changed into acetaldehyde. Alcohol dehydrogenase changes it to ethyl alcohol and $\mathrm{CO}_2$.
Question
Life without air would be [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) reductional
(b) free from oxidative damage
(c) impossible
(d)anaerobic
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Anaerobic means ‘in the absence of molecular axygen’, so life without air would be anaerobic. The atmosphere of earth at the time of origin of life was without free oxygen atoms, so the primitive atmosphere was reducing.
Question
Out of 36 ATP molecules produced per glucose molecule during respiration [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) 2 are produced outside glycolysis and 34 during respiratory chain
(b) 2 are produced outside mitochondria and 34 inside mitochondria
(c) 2 during glycolysis and 34 during Krebs’ cycle
(d) all are formed inside mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
A total of 38 ATP molecules are produced per glucose molecule during respiration. Out of which, 2 ATP are produced outside mitochondria (i.e. glycolysis in cytoplasm) and 36 ATP inside mitochondria (i.e. 2 ATP through Krebs’ cycle and 34.ATP from NADH/FADH ${ }_2$ through respiratory. chain). In contrast, in some cells the number of ATP produced inside mitochondria equals to 34 and thus, there is a net synthesis of 36 ATP molecules.
