Forces
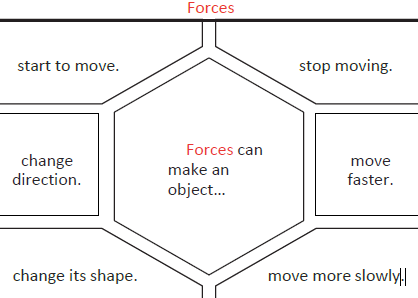
Forces can make an object…
- start to move.
- change direction.
- change its shape.
- stop moving.
- move faster.
- move more slowly.
Mass V/s Weight
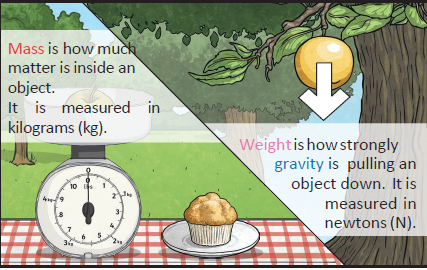
Mass is a measurement of the number of atoms in an object. Mass is typically measured in kilograms or grams. Mass reflects the amount of matter (i.e., electrons, protons and neutrons) an object contains.
Weight is how strongly gravity is pulling an object down. It is measured in newtons (N).
The Moon has a smaller mass than Earth so the gravitational pull on the Moon is smaller than it is on Earth.
Jupiter has a greater mass than Earth so the gravitational pull on Jupiter is stronger than on Earth.

Theory of gravity

Simplified explanations of Newton’s law of universal gravitation and general relativity that are suitable for a Year 5 student:
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation: All objects in the universe attract each other with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Different types of force:
Contact— Contact forces are forces that require contact to push or pull another object e.g. friction and air, water and surface resistance.
Non-contact— Forces acting at a distance are forces that do not require direct contact between the objects to be able to push or pull them. Two examples are gravity and magnetism
Friction—Friction is a ‘sticking’ force – the resistance that a surface or object encounters when moving over another surface or object.
Air resistance—Air resistance is the force on an object moving through air. Air resistance affects how fast or slowly objects move through the air.
Water resistance— Water resistance is the force on objects floating on or moving in water.
Gravity— Gravity is the pulling force acting between the Earth and a falling object. Gravity pulls objects to the ground
Unbalanced forces— can cause an object to change its motion. If an object is at rest and an unbalanced force pushes or pulls the object, it will move
Balanced forces— do not cause a change in motion. When two forces are the same strength but act in opposite directions, they are called balanced forces.
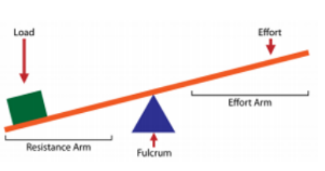
Levers
A way to lift heavy weights using the least amount of effort. The longer the easier it is to lift. The fulcrum is where the lever pivots in order to lift the load. The closer the fulcrum is to the load the easier it is to lift
Pulleys
Used like levers to lift loads with less effort Rope is passed through a pulley and then is returned back round to be pulled.

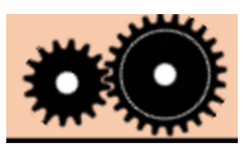
Gears
Used to transmit power from one part of a machine to another. Connected gears can increase speed, increase force. When joined, the direction of rotation of the driven gear is the opposite of the drive gear.
Focus Scientist
Isaac Newton

- Isaac Newton studied Science and philosophy at the University of Cambridge
- He discovered the idea of forces acting upon objects on Earth.
- Discovered gravity acts upon objects on Earth
- For every action there is and equal and opposite reaction.
Galileo

- Was a professor of mathematics in Italy.
- Discovered the idea of air resistance and how it effects the rate the objects fall.
- He discovered that all objects, no matter their mass, would fall at the same rate in a vacuum.
Archimedes

- He was a philosopher and mathematician , who lived in Greece.
- He discovered the idea of water resistance, density and water displacement and how it effects objects moving through water.
Key Vocabulary
force: a force is an interaction which can change the motion of an object.
gravity: the force which causes things to drop to the ground.
air resistance: Air resistance is a type of friction between air and another material ).
water resistance: a force that slows things down that are moving through water.
friction: the force that makes it difficult for things to move freely when they are touching each other.
upthrust: an upward push or thrust.
mass: A measure of the amount of matter in an object (measured in grams and kilograms). It will the same whether you are on Earth or in space
weight: Is the force of gravity on an object. This changes whether you are on Earth or in space. Measured in Newtons
gears: A toothed wheel that works with others to increase speed.
mechanisms: a part, often consisting of a set of smaller parts, which performs a particular function
pulleys: A machine with a wheel and a fixed axle (pin) .
buoyancy: the ability that something has to float on a liquid or in the air.
fulcrum: The point where a lever turns (also called a pivot)
lever: A rigid bar that rests on a fulcrum. It is used to lift/move heavy objects.
