Definition of Limit
The statement
\(\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}f(x)=L\)
means f approaches the limit L as x approaches c.
Which is read “the limit of f (x), as x approaches c, equals L .”
Basic Limits
1. If f is the constant function f (x) = k , then for any value of c,
\(\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}f(x)=\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}k=k\).
2. If f is the polynomial function \(f(x)=x^{n}\), then for any value of c,
\(\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}f(x)=\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}x^{n}=c^{n}\).
Finding Limits Graphically
Consider the graph of the function \(f\left ( x \right )=\frac{x^{3}+1}{x+1}\). The given function is defined for all real numbers x except x = -1. The graph of f is a parabola with the point (-1,3) removed as shown below. Even though f (-1) is not defined, we can make the value of f (x) as close to 3 as we want by choosing an x close enough to −1 .
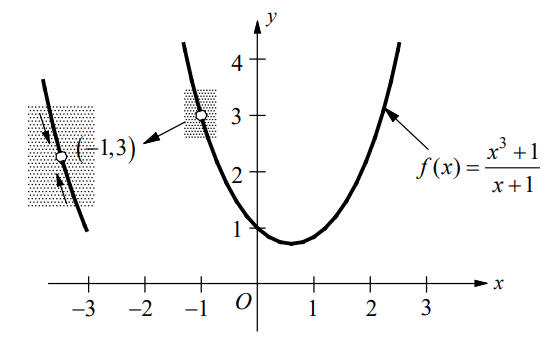
Although f (x) is not defined when x = -1, the limit of f (x) as x approaches -1 is 3, because the definition of a limit says that we consider values of x that are close to c , but not equal to c .
One Sided Limits
The right-hand limit means that x approaches c from values greater than c.
This limit is denoted as
\(\underset{x\rightarrow c^{+}}{lim}f(x)=L\).
The left-hand limit means that x approaches c from values less than c.
This limit is denoted as
\(\underset{x\rightarrow c^{-}}{lim}f(x)=L\).
The Existence of a Limit
The limit of f (x) as x approaches c is L if and only if
\(\underset{x\rightarrow c^{+}}{lim}f(x)=L\) and \(\underset{x\rightarrow c^{-}}{lim}f(x)=L\)
Limits That Fail to Exists
Some limits that fail to exists are illustrated below.
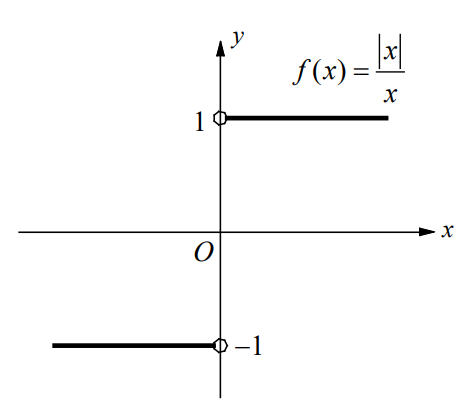
The left limit and the right limit is different. \(\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{lim}\frac{\left | x \right |}{x}=1\), if x > 0 and \(\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{lim}\frac{\left | x \right |}{x}=-1\), if x < 0.
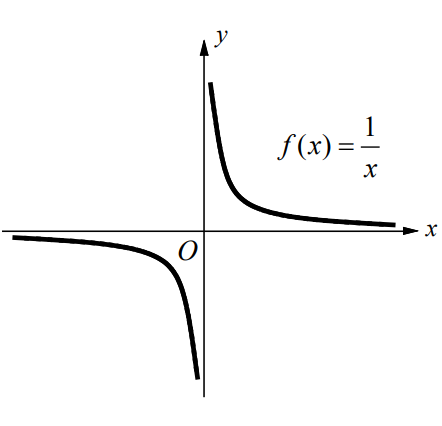
As approaches 0 from the right or the left, f (x) increases or decreases without bound.
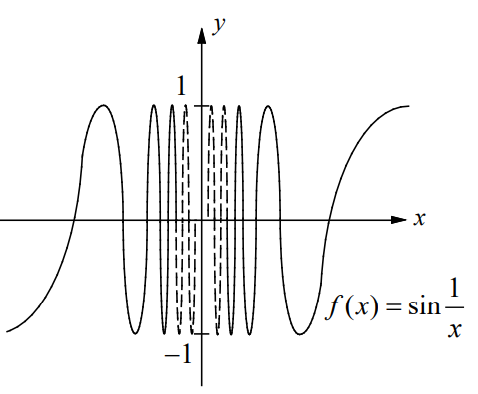
The values of f (x) oscillate between -1 and 1 infinitely often as x approaches 0.
Example 1
- Find the limit.
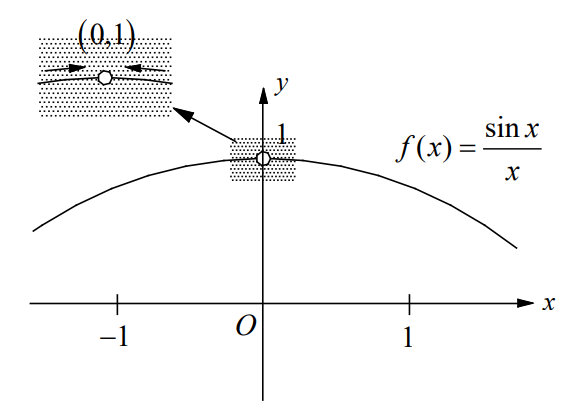
(a) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 2}{lim}\left ( 7 \right )\) (b) \(\underset{x\rightarrow -1}{lim}\left ( x^{3}-2x \right )\) (c) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{lim}\frac{sin x}{x}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution
(a) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 2}{lim}\left ( 7 \right )=7\) \(\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}k=k\)
(b) \(\underset{x\rightarrow -1}{lim}\left ( x^{3}-2x \right )=\left ( -1 \right )^{3}-2\left ( -1 \right )=1\) \(\underset{x\rightarrow c}{lim}x^{n}=c^{n}\)
(c) The function f (x) is not defined when x = 0 . Find the Limit Graphically. Graph \(y=\frac{sinx}{x}\) using a graphing calculator. The limit of \(f\left ( x \right )=\frac{sinx}{x}\) as x approaches 0 is 1.
Example 2
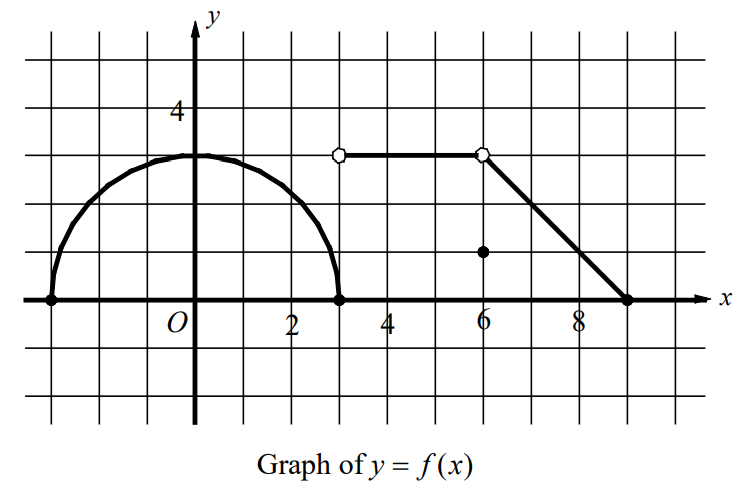
- The graph of the function f is shown in the figure below. Find the limit or value of the function at a given point.
(a) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{-}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\) (b) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{+}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\) (c) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\)
(d) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 6}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\) (e) f (3) (f) f (6)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution
(a) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{-}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=0\)
(b) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{+}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=3\)
(c) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{-}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\) does not exists since \(\underset{x\rightarrow 3^{-}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\neq \underset{x\rightarrow 3^{+}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\).
(d) \(\underset{x\rightarrow 6}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=3\), because \(\underset{x\rightarrow 6^{-}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=3= \underset{x\rightarrow 6^{+}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\).
(e) \(f\left ( 3 \right )=0\)
(f) \(f\left ( 6 \right )=1\)
Example 3
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{lim}lnx\), if it exists.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution
As x approaches to 0, ln x decreases without bound. Since the value of f (x) does not approach a number, \(\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{lim}lnx\) does not exists.
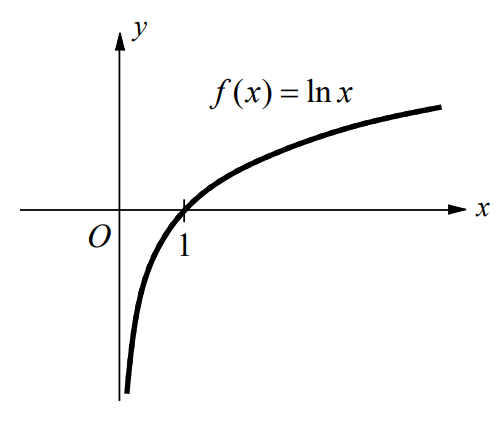
Exercises – The Limit of a Function and One Sided Limits
Multiple Choice Questions
Question
1. \(\underset{x\rightarrow \frac{\pi }{6}}{lim}sec^{2}x=\)
(A) \(\frac{3}{4}\) (B) \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\) (C)\(\frac{4}{3}\) (D)\(\frac{2\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1. C
Question
- 2. If \(f\left ( x \right )=\left\{\begin{matrix}x^{2}+3, & x\neq 1\\1, & x= 1\end{matrix}\right.,\) then \(\underset{x\rightarrow 1}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=\)
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2. D
Question
- \(\underset{x\rightarrow 1}{lim}\frac{\left | x-1 \right |}{\left | 1-x \right |}=\)
(A) −2 (B) −1 (C) 1 (D) nonexistent
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
3. D
Question
- 4. Let f be a function given by \(f\left ( x \right )=\left\{\begin{matrix}3-x^{2}, & if & x< 0\\2-x, & if & 0\leq x< 2.\\\sqrt{x-2}, & if & x> 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Which of the following statements are true about f ?
I. \(\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=2\)
II. \(\underset{x\rightarrow 2}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=0\)
III. \(\underset{x\rightarrow 1}{lim}f\left ( x \right )=\underset{x\rightarrow 6}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\)
(A) I only (B) II only (C) II and III only (D) I , II, and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
4. B
Free Response Questions
Questions 5-11 refer to the following graph.
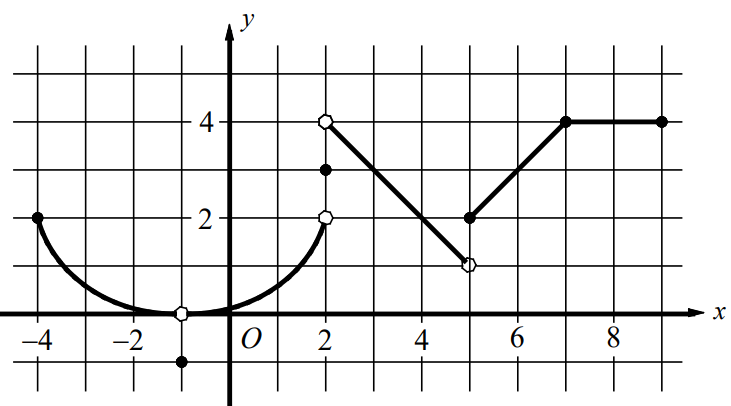
The figure above shows the graph of y = f (x) on the closed interval [−4,9] .
Question
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow -1}{lim}cos\left ( f\left ( x \right ) \right )\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
5. 1
Question
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow 2^{-}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
6. 2
Question
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow 2^{+}}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
7. 4
Question
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow 2}{lim}f\left ( x \right )\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
8. DNE
Question
- Find f (2) .
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
9. 3
Question
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow 5^{-}}{lim}\) arctan (f(x)).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
10. \(\frac{\pi }{4}\)
Question
- Find \(\underset{x\rightarrow 5^{+}}{lim}\left [ x f\left ( x \right ) \right ]\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
11. 10
