ASTROPHYSICS
- Astrophysics is the study of stars, planets, moons and other celestial bodies, including their satellites.
- Celestial bodies include stars, planets, moons, satellites etc.
- Stars are huge masses of fire that are constantly burning. They fuse gasses and pro vide light and heat.
- Planets are, according to the International Astronomical Union, celestial bodies that:
- Orbit a star around a circular/ovalthike path.
- Are (nearly) round
- Are not any other planet’s mon
- Do not have debris around their orbit.
- There are an estimated $10^{24}$ planets in the observable universe. There are 2 types of planets:
- Terrestialismall and Rocky
- Jovian: Giant, made of gasses
- There are 36 sub-categories of planets.
- Terrestrial planets have a smaller size and mass. They have a heavy molten core and topological features like volcanoes and craters. Examples inclu de Earth. Mars etc. They make up the inner part of our Solar System. They are rocky.
- Jovian Planets have larger sizes. They only have small amounts of rooks in cores, and are mostly made of gasses (Hydrogen and telium in atmosphere. They include Jupiter, Saturn etc. (outer planets).
- All planets revolve around a star and rotate on different axes. scientists stay that planets continue to rotate in the same manner in which they were when they collided, due to inertia.
- Dwarf Planets are the same as normal Planets, except they have debris in their outer surroundings.
- Scientists say planets were formed by the collision and vibration of rocky substances. Due to their great masses, they turned circular.
- A satellite is a moon, planet or star that orbits a planet or star. Moons are generally regarded as “Natural satellites”.
- There are many types of satellites:
- Natural Solellifes $\rightarrow$ Naturally orbit stars or planets
- Low Earth Orbits $\rightarrow 160 \mathrm{~km}$ away from Earth. Complete an or bit in 90 minutes. Used by military to locate tanks.
- Geosynchronous $\rightarrow 24$ hours for an orbit. Used for communication at high altitudes.
- Geo stationary $\rightarrow$ majority of communication satellites Orbit once in 24 hours, $14788 \mathrm{~km}$ above the Earth.
- Sun-synchronous $\rightarrow 15-16$ orbits daily. They in polar orbits make weather predictions, being fixed relative to the sun.
- Satellites work by reflecting signals back to barth. An uplink is sent from earth to the satellite, after which data is processed. Transponder’s are used to avoid incoming and outgoing signals. Finally, a downlik is used to send the data from the Satellites back to Earth.
- Everything, according to the Big Bang Theory, came into existence about 13.7 billion years ago. It says that at the time there was infinitely dense and small “dot” that “burst “into existence. It also states that all galaxies are spreading apart from one another. After the do “burst”, it was spreading. There was no actual explosion, just the stretching of the universe. That dot stretched into gluons, then quarks, and matter was able to “triumph over antimatter. Then, the yessential forces were formed (Electromagnetic, Strong \& weak Nuclear and gravity).
- Within $10^{-9}$ seconds of the event, the universe was already a billion $\mathrm{km}$ in diameter. Quarks Started producing neutrons and protons. Within a second, the universe had already spreat over a 100 billion $\mathrm{km}$, and synthesized the first atom -Hydrogen. It was around 10 billion’ $\mathrm{C}$ at the time. within a few minutes, atoms formed stars, ga laxies, planets etc.
- Some people question as to what existed before the Big Bang. It is important that we understand that the Big Bang did not just create Space, but Space – Time. Meaning that time did n ot exist before the Big Bang.
“Scientists “travel back inline” to the Big Bang using the Redshift Theory. This suggests that as. - galaxies spread out, their wavelengths become larger. Scientists reversed this to “see in the past”
- A telescope is an optical instrument that makes distant objects (celestial) bodies) appear to be nearer. It contains an arrangement of lenses and mirrors, and focuses rays onto one point. Types of telescopes.
- Astrograph: for photographing distant astronomical objects
- Comet Seeker: Searching co mes
- Go To: Automatically points to distant objects /celestial bodies.
- Infrared Uses infrared rays.
- Etc.
- There are two main categories of telescopes: Refractive and Reflective.
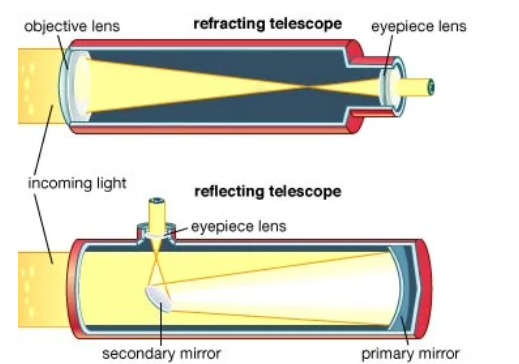
- A telescope basically works by gathering light. The “ob jective” is the lens that collects light. The bigger it is, the more light is collect ad. If there is more light, one can see far then.
- Solar system ( 4.5 billion years old):
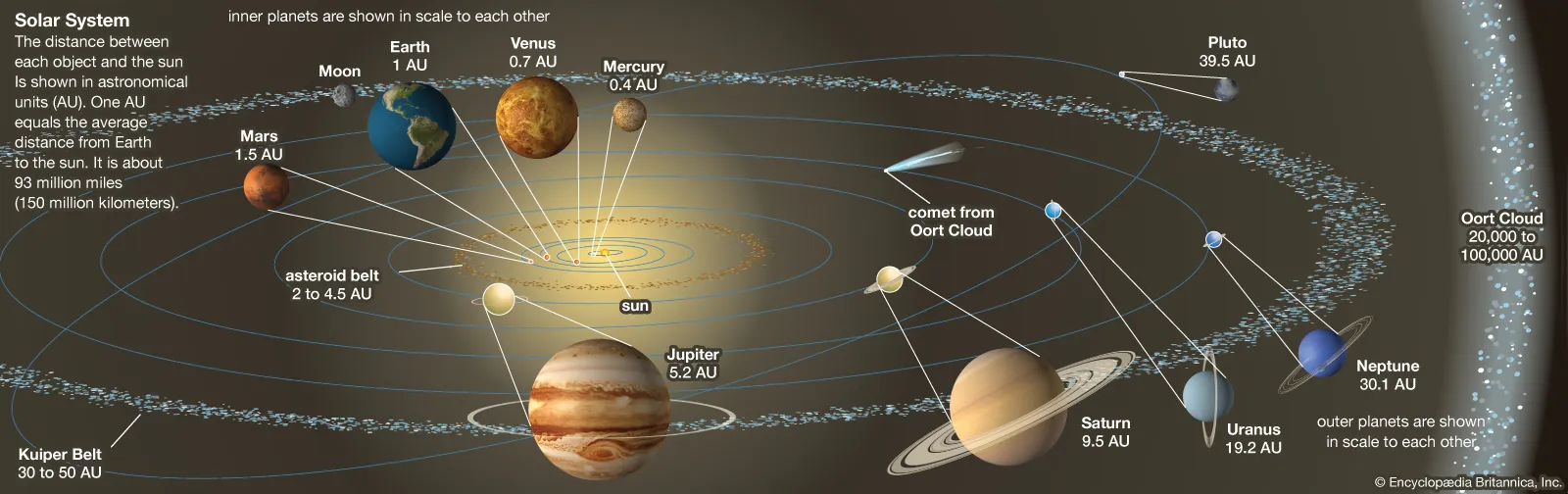
- Mercury, Venus, Garth, Mars, Asteroid Belt, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
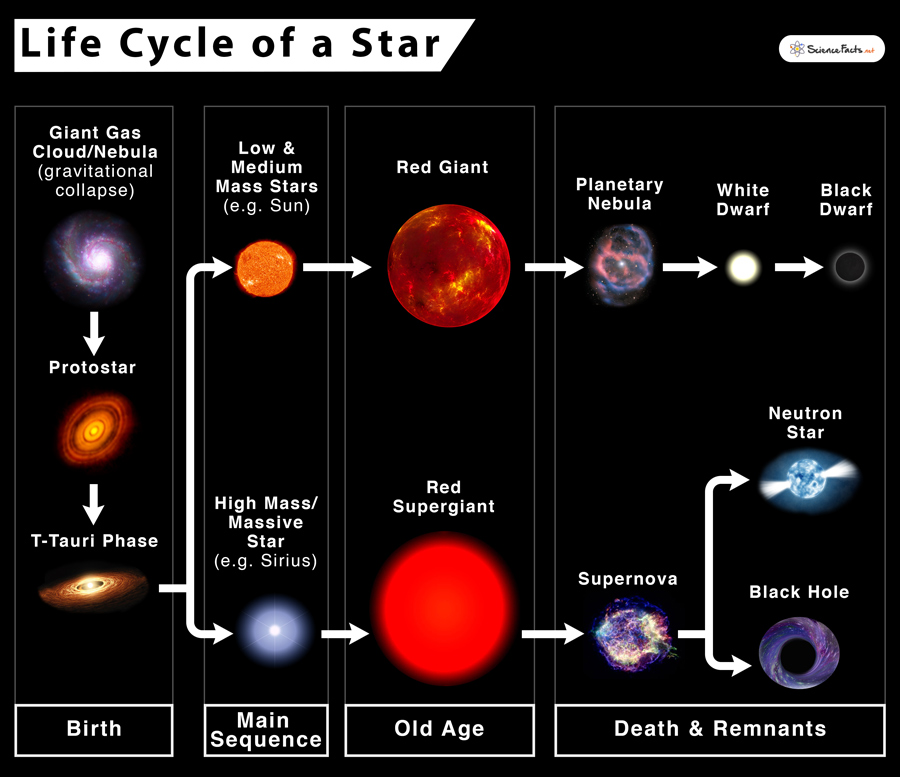
Life Cycle of a star: