Reproductive Health : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of Reproductive Health
- Master File Reproductive Health
- NCERT Book chapter Reproductive Health
- NCERT Solutions for – Reproductive Health
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for – Reproductive Health
- Revision Note of Reproductive Health
- Past Many Years Question papers and Answer of Reproductive Health
- Mind Map of Reproductive Health
Examples and Exercise
- Reproductive Health : Practice Paper 1
- Reproductive Health : Practice Paper 2
- Reproductive Health : Practice Paper 3
4. REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
According to World Health Organisation (WHO), Reproductive health is a total well-being in all aspects of reproduction i.e., physical, emotional, behavioural & social.
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH: PROBLEMS & STRATEGIES
India initiated reproductive health programmes (family planning) in 1951.
Now wider reproduction-related areas are in operation under Reproductive & Child Health Care (RCH) programmes.
Such programmes deal the following:
- Give awareness about reproduction related aspects for creating a reproductively healthy society.
- Educate people about birth control, care of pregnant mothers, post-natal care of mother and child, importance of breast feeding, equal opportunities for male & female child etc.
- Awareness of problems due to population explosion, social evils like sex-abuse and sex-related crimes, etc.
- To provide right information about sex-related aspects. It helps to avoid sex-related myths and misconceptions.
- To give proper information about reproductive organs, adolescence and related changes, safe and hygienic sexual practices, sexually transmitted diseases (STD), AIDS etc.
POPULATION STABILIZATION & BIRTH CONTROL
In 1900, world population was about 2 billion. By 2000, it rocketed to about 6 billion and 7.2 billion in 2011.
In India, population was nearly 350 million at the time of independence. It reached 1 billion by 2000 and crossed 1.2 billion in May 2011. It means every sixth person in the world is an Indian.
According to the 2011 census report, our population growth rate was less than 2% (i.e. 20/1000/year), a rate at which our population could increase rapidly.
- Increased health facilities and better living conditions.
- Rapid decline in death rate, maternal mortality rate (MMR) and infant mortality rate (IMR).
- Increase in number of people in reproducible age.
- Scarcity of basic requirements (e.g. food, shelter & clothing).
- Motivate smaller families by using contraceptive methods.
- Aware peoples about a slogan Hum Do Hamare Do (we two, our two). Many couples have adopted a ‘one child norm’.
- Statutory rising of marriageable age of females (18 years) and males (21 years).
- User-friendly, easily available, effective and reversible.
- No or least side-effects.
- It should not interfere with sexual drive, desire & sexual act.
CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS
Avoid chances of ovum and sperms meeting. It includes
- Periodic abstinence: Avoid coitus from day 10 to 17 (fertile period) of the menstrual cycle to prevent conception. Fertile period is the period having chances of fertilization.
- Coitus interruptus (withdrawal): Withdraw penis from the vagina just before ejaculation to avoid insemination.
- Lactational amenorrhea: It is the absence of menstrual cycle & ovulation due to intense lactation after parturition. Fully breastfeeding increases lactation. This method helps to prevent conception. This is effective up to 6 months following parturition.
Natural methods has no side effect. But chances of failure are high.
They prevent physical meeting of sperm & ovum. E.g.
Condoms (E.g. Nirodh):
Made of rubber/latex sheath.
Condoms for male: Cover the penis.
Condoms for female: Cover the vagina & cervix.
Condoms are used just before coitus. They prevent the entry of semen into female reproductive tract.
Condoms are very popular because:
- It protects the user from STDs and AIDS.
- Easily available and disposable.
- It can be self-inserted and thereby give privacy to user.
Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults:
Made of rubber and are inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix during coitus.
They block the entry of sperms through the cervix.
They are reusable.
Spermicidal creams, jellies & foams are used along with these barriers to increase contraceptive efficiency.
These are inserted by doctors or nurses in the uterus through vagina. They increase phagocytosis of sperms.
IUDs are ideal method to delay pregnancy or space children.
Types of IUDs:
- Non-medicated IUDs: They retard sperm motility. Also have spermicidal effect. E.g. Lippes loop.
- Copper releasing IUDs: Cu ions suppress motility and fertilising capacity of sperms. E.g. CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375.
- Hormone releasing IUDs: They make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to the sperms. E.g. Progestasert, LNG-20.

Oral administration of progestogens or progestogen–oestrogen combinations in the form of tablets (pills).
Pills are taken daily for 21 days starting within the first five days of menstrual cycle. After a gap of 7 days (menstruation period), it should be repeated in the same pattern till the female desires to prevent conception.
They inhibit ovulation and implantation and thicken cervical mucus to prevent entry of sperms.
Pills are very effective with lesser side effects.
Saheli: New oral contraceptive for the females. It is developed by Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI) in Lucknow. It contains a non-steroidal preparation. It is a ‘once a week’ pill with very few side effects and high contraceptive value.
Progestogens or Progestogens-oestrogen combination are used by females as injections or implants under skin.
Their mode of action is like that of pills and their effective periods are much longer.
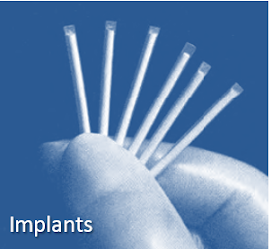
It helps to block gamete transport and thereby prevents conception. It is very effective but reversibility is very poor.
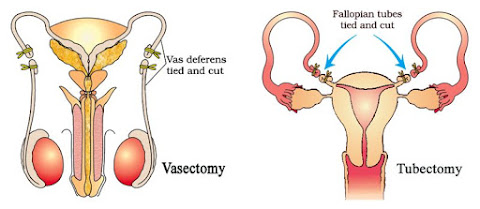
Vasectomy: Sterilization procedure in males. In this, a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small incision on the scrotum.
Tubectomy: Sterilization procedure in females. In this, a small part of the fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through vagina.
Side effects of anti-natural contraceptives:
Nausea, abdominal pain, breakthrough bleeding, irregular menstrual bleeding, breast cancer etc.
MEDICAL TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY (MTP)
45 to 50 million MTPs are performed in a year all over the world (i.e. 1/5th of total number of conceived pregnancies).
MTP helps to decrease the population.
Many countries have not legalised MTP due to emotional, ethical, religious and social issues.
Government of India legalised MTP in 1971 with some strict conditions to check illegal female foeticides.
Importance of MTP
- To avoid unwanted pregnancies due to casual intercourse or failure of the contraceptive used during coitus or rapes.
- It is essential in cases where continuation of pregnancy could be harmful to the mother or to the foetus or both.
Problems related with MTP
- Majority of the MTPs are performed illegally.
- Misuse of amniocentesis test for foetal sex determination. If the foetus is female, it is followed by MTP. Such practices are dangerous for the young mother and foetus.
Government of India enacted The Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2017 to reduce illegal abortion and consequent maternal mortality and morbidity.
According to this Act, a pregnancy may be terminated within the first 12 weeks on the opinion of a registered medical practitioner. If the pregnancy is between 12 – 24 weeks, two registered medical practitioners must be of the opinion.
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (STDs)
Diseases or infections transmitted through sexual intercourse are called Sexually transmitted diseases/infections (STDs or STIs)/Venereal diseases (VD) or Reproductive tract infections (RTI).
Hepatitis-B & HIV are also transmitted
- By sharing of injection needles, surgical instruments etc.
- By transfusion of blood.
- From infected mother to foetus.
Early symptoms: Itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swellings, etc. in the genital region.
Absence or less significant early symptoms and the social stigma deter the infected persons to consult a doctor. This leads to pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID), infertility, ectopic pregnancies, abortions, still births, cancer of the reproductive tract etc.
All persons are vulnerable to STDs. These are very high among persons in the age group of 15-24 years.
Prevention:
- Avoid sex with unknown partners/multiple partners.
- Always use condoms during coitus.
- In case of doubt, go to a qualified doctor for early detection and get complete treatment.
INFERTILITY
The reasons for this may be physical, congenital, diseases, drugs, immunological or even psychological.
ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGIES (ART)
These are the technologies used to correct the infertility problems.
1. In vitro fertilisation (IVF) or Test tube baby programme
ET is 2 types:
- Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer (ZIFT): Transfer of zygote or early embryo (with up to 8 blastomeres) into fallopian tube.
- Intra Uterine Transfer (IUT): Transfer of embryo with more than 8 blastomeres into the uterus.
2. Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT)
3. Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
4. Artificial insemination (AI) technique
Artificial insemination into the uterus is known as intra-uterine insemination (IUI).
This technique is useful for the male partner having inability to inseminate female or low sperm counts etc.
Problems of ART
- It requires specialized professionals and expensive instrumentation. Therefore, these facilities are available only in very few centres.
- Emotional, religious and social problems.
1 Marks Questions
1. Give the term for prenatal diagnostic technique aimed to know the sex of developing foetus and to detect congenital disorders.
Ans. Amniocentesis.
2. After a successful in vitro fertilisation, the fertilised egg begins to divide. Where is this egg transferred before it reaches the 8-celled stage and what is this technique called?
Ans. Fallopian tube; Zygote intra fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
3. Give the term for rapid population growth.
Ans. Population explosion.
4. Name the fluid from which foetal cells are extracted for chromosomal analysis.
Ans. Amniotic fluid.
5. Give technical name of female used to bring up in vitro fertilized egg to maturity.
Ans. Surrogate mother.
6. Name the oral contraceptive developed by CDRI, Lucknow.
Ans. Saheli
7. What is the WHO’s interpretation of reproductive health?
Ans. WHO defines reproductive health as total well being in all respects of reproduction including physical, emotional, behavioural and social.
8. Why has the Government imposed a statutory ban on amniocentesis?
Ans. The Government has banned amniocentesis to check on the incidences of female foeticides.
9. Expand MTP and ICSI.
Ans. MTP: Medical Termination of Pregnancy.
ICSI: Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection.
10. What is lactational amenorrhoea?
Ans. It refers to absence of menstruation during period of intense lactation.
11. Write the scientific name of causative agents of :–
i) Syphillis
ii) Gonorrhoea.
Ans. (i) Treponema Pallidum
(ii) Neisseria Gonorrhoea
12. Name the technique by which one can disorder any possible chromosomal or metabolic disorders in foetus.
Ans. Amniocentesis.
13. Expand the following :–
i) GIFT
ii) ICSI
iii) IUCD
Ans. (i) Gamete Intrafallopian transfer.
(ii) Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm injection
(iii) Intra uterine contraceptive devices.
2 Mark Questions
Chapter 4
Reproductive Health
2 Marks Questions
1. Lactational Amenorrhea is a method of contraception Justify. What is the maximum effectiveness of this method in terms of period/duration?
Ans. (a) Ovulation and menstrual cycle do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition. Therefore, as the mother breast feeds, chances of conception are nil.
(b) It is effective only upto a maximum period of six months following parturition.
2. How are non medicated IUDS different from hormone releasing IUDS? Give examples.
Ans. (a) Non medicated IUDs = Lippes loop, Copper releasing IUDS (CuT, Multiload 375) ® These increase phagocytosis of sperms within uterus and release copper ions which suppress sperm motility and fertilizing capacity of sperm.
(b) Hormone releasing IUDs – Progestasert, LNG-20 -These makes uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to sperms.
3. What are implants? How do they help in preventing fertilisation?
Ans. The structures which contain hormones like progesterone and estrogen and are placed under the skin.
4. Briefly explain two natural barriers for birth control.
Ans. Periodic abstinence couple should avoid coitus from 10th to 17th day of menstrual cycle. Coitus interruptus Male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation of semen.
5. Enlist any four possible reasons for infertility in human beings.
Ans. Physical, congenital disease, Drugs, Immunological and even psychological (any four).
6. What does GIFT represent?
Ans. It is the introduction of two unfertilized oocytes and several sperms into the fallopian tube of a woman desirous to be a mother through laproscope. The eggs may be hers or a donor’s. The sperms may be of her husband’s or of a donor. Fertilisation occurs in vivo and the development of the foetus takes place through natural process.
7. How does Cu- T act as a contraceptive?
Ans. It is an intrauterine device having ionized copper. The copper diffuses into the uterus and brings about the release of toxic cytokines. They inhibit sperm motility and therefore fertilization of ovum.
8. Mention any four probable reasons for the rapid rise of population in our country?
Ans. The probable reasons could be:
- Steady decline in the death rate due to improved health services.
- Early marriages especially in certain rural areas.
- Lack of education among the poor and they fail to understand the ill effects of a large family.
- Longer life span.
9. Identify the device used for the following methods of birth control: Barrier, IUD, Surgical technique and Administering hormone.
Ans. Barrier: Condom, IUD: Copper –T, Surgical technique: Vasectomy or Tubectomy, Administering Hormone : Oral Pill.
10. What are STDs? Mention any two of it.
Ans. Diseases or infections transmitted through sexual intercourse are collectively called Sexually Transmitted Diseases or STDs. Ex: Syphilis and Gonorrhoea.
11. “Removal of Gonads cannot be a contraceptive option”. Why?
Ans. Because in this methods, gonads are surgically removed it will lead to infertility & both male & female will be dependent on hormones in their remaining life to regulate functioning of many reproductive org.
12. What are MTPs ? Under what conditions MTPs are legally permitted?
Ans. MTP refers to as medical termination of pregnancy. It is legalized in our country only:-
- in case of rape.
- in case of casual unprotected intercourse
- in case pregnancy is harmful for foetus or for mother.
13. Describe the technique which is used for sex determination in foetus?
Ans. Amniocentesis is the prenatal diagnosis in which sample of amniotic fluid from womb of a pregnant women is taken during early stages of foetal development, the cells are cultured & analyzed to determine the sex of foetus.
14. What are test tube babies? Are they different from normal babies?
Ans. The baby produced lay conceiving eggs & sperms in a culture tube (envitro fertilization) & nursing in the uterus is called a test – tube baby. They are same as normal babies only the fertilization for such zygote occurs in in-vitro conditions.
15. Mention any four objectives of RCHC.
Ans. RCHC refers to a popular programme called “Reproductive & child health care (RCHC) & the major tasks under these programmes are :-
- Creating awareness about various reproduction related aspects eg. STDs, birth control methods.
- Providing facilities & support for building up reproductive healthy society.
- Educating people about care of pregnant women, important of breast feeding.
- awareness about sex abuse & sex related crimes
3 Mark Questions
Chapter 4
Reproductive Health
3 Marks Questions
1. Give another name for sexually transmitted diseases. Name two sexually transmitted diseases which are curable and two diseases which are not curable.
Ans. Veneral disease (VD)/Reproductive tract infection (RTI)
Curable : Syphilis, Gonorrhoea
Non Curable : Hepatitis B, AIDS, Genital herpes
2. Differentiate between Vasectomy and Tubectomy.
Ans.
| Vasectomy | Tubectomy | ||
| 1. 2. 3. | Method of sterilisation in males Vasa defferentia of both sides are cut and tied Prevents movement of sperms at cut end. | 1. 2. 3. | Method of sterilisation in females. Fallopian tube of both sides are cut and tied. Prevent movement of egg at cut end. |
3. Name the techniques which are employed in following cases :
(a) Transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce ova but can provide suitable environment for fertilisation and development.
(b) Embryo is formed in laboratory in which sperm is directly injected into ovum.
(c) Semen collected either from husband or a healthy donor is artificially introduced either into vagina or uterus.
Ans. (a) Gamete intra fallopian transfer.
(b) Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection
(c) Intra uterine insemination.
4. Mention the various precautions one has to take in order to protect himself/herself form STDs.
Ans. (i) Avoid blood transfusion from an infected person.
(ii) Avoid sex with an unknown partner or multiple partners.
(iii) Always use condom.
(iv) Avoid sharing of injections needles and syringes and surgical instruments.
5. What are the disturbing trends observed regarding MTP?
Ans. Majority MTPs performed illegally by unqualified quacks, missuse for female foeticide.
6. Enlist any three causes of infertility in men and women.
Ans. Reasons for infertility in men and women are:
7. State the consequences of over population.
Ans. The consequences of overpopulation are :
- An increase demand and therefore pressure on the natural resources.
- An increase in the level of pollution.
- More number of unemployment, poor infrastructure and pressure on the country’s economy.
8. Differentiate between natality rate and mortality rate.
Ans.
| Natality rate ( Birth rate) | Mortality rate ( Death rate) |
| 1. It is the number of births per one thousand individuals per year. | 1. It is the number of deaths per one thousand individuals per year. |
| 2. It is the rate at which the new members are added to the population by reproduction. | 2. it is the rates at which the individuals die out. |
| 3. It increases population size and population density. | 3. It decreases population size and population density. |
9. Explain any one natural method of birth control.
Ans. One of the natural methods of birth control is Periodic abstinence or Rhythm method. The couple avoids or abstains from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle because ovulation occurs during this period and therefore the period is highly fertile. The method is based on the facts the ovum remains alive for 1-2 days and the sperm remains alive for about 3 days. The effectiveness of this method is limited as most of the women have irregular menstrual cycle.
10. Give three differences between tubectomy and vasectomy.
Ans.
| Vasectomy | Tubectomy |
| 1. It is a sterilization technique for men. | 1. It is a sterilization technique for women. |
| 2. The two vasa differentia are cut and tied up. | 2. The two oviducts are cut and tied up. |
| 3. Passage of sperms is prevented. | 3. Passage of ova is prevented. |
11. Describe the three manners in which fertilization of human ovum by sperm can be prevented?
Ans. I. NATURAL METHODS : avoiding chances of meeting between the gametes.
- Periodic Abstinence :-couples avoid coitus from 10-17th day of menstrual cycle when ovulation is expected.
- Lactational Amenorrhoea :- absence of menstruation during intense lactation.
II. BARRIER METHODS :- ovum & sperms are prevented from coming closer with the help of barriers.
- Condoms :- barriers made up of thin rubber or latex sheath to cover penis in makes or cervix in females.
- Diaphragms cervical caps :- made up of rubber & are reusable
- Spermicidal creams along with these barriers
- SURGICAL METHODS :- blocks transport of gametes & thereby conception.
- Vasectomy :- small portion of vas deferens is removed or tied up through incision in scrotum.
- Tubectomy :- small portion of fallopian tube is removed or tied up through vagina.
12. Suggest some methods to assist infertile couples to have children?
Ans. Three are special techniques called Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) to help infertile couples to have children:-
- Test tube Baby Programme :- In this method, ova from wife or donor female & Sperm from husband are allowed to fuse under simulated conditions in the laboratory it is called In-vitro fertilization (IVF). The zygote is then transferred into uterus or fallopian tube this process is called embryo transfer (ET)
- Gamete Intra fallopian Transfer (GIFI) :- It involves transfer of an ovum collected from a donor female into another female who cannot produce ova but can provide suitable condition for fertilization
- Artificial Insemination: – In this method semen is collected from the husband or a healthy donor & is artificially introduced into vagina or uterus.
13. Briefly explain the various reproductive technologies to assist an infertile couple to have children.
Ans. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) includes in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer (IVF-ET), gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT), zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT), and frozen embryo transfer (FET). These techniques also apply to oocyte donation and gestational carriers. Approximately 99 percent of ART cycles performed are IVF-ET. IVF-ET has helped many couples conceive successfully. ART may be recommended when other treatments (such as intrauterine insemination) have not been successful or when there is severe male factor infertility, severe endometriosis or tubal obstruction.
Reproductive Health Class 12 Biology MCQs
1. Which of the following is hormonereleasing?
(a) Multiload 375
(b) LNG-20
(c) Lippes loop
(d) Cu 7
Answer
Answer: b
2. Which among the following is commonly called withdrawal method?
(a) Lactational amenorrhoea
(b) Coitus interruptus
(c) Periodic abstinence
(d) Rhythm method
Answer
Answer: b
3. In which of the following ARTs, does in vivo fertilisation occur?
(a) ZIFT
(b) GIFT
(c) ICSI
(d) IVF
Answer
Answer: b
4. Surgical methods, also called sterilisation techniques are fool-poof methods be prevent pregnancy. But, it is the last option for many couples, because
(a) it is nearly irreversible.
(b) of lack of sufficient facilities in many parts of the country.
(c) of fear that it will reduce sexual drive.
(d) all of these
Answer
Answer: d
5. Emergency contraceptives are effective if
used within [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) 72 hrs of coitus.
(b) 72 hrs of ovulation.
(c) 72 hrs of menstruation.
(d) 72 hrs of implantation.
Answer
Answer: a
6. Condoms are one of the most popular contraceptives because of the following reasons [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) these are effective barriers for insemination.
(b) they do not interfere with coital act.
(c) these help in reducing the risk of STDs.
(d) all of the above.
Answer
Answer: d
7. Intensely lactating mothers do not generally conceive due to the [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) suppression of gonadotropins.
(b) hyper secretion of gonadotropins.
(c) suppression of gametic transport.
(d) suppression of fertilisation.
Answer
Answer: a
8. The method of directly injecting a spenn into ovum in assisted reproductive, technology is called [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) GIFT
(b) ZIFT
(c) ICSI
(d) ET
Answer
Answer: c
9. The oral contraceptive pills mainly contain the hormones
(a) estrogen and luteinising hormone.
(b) progesterone and estrogen.
(c) estrogens and follicle-stimulating hormone.
(d) progesterone and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Answer
Answer: b
10. Diaphragms are the contraceptive devices used by females. Choose the correct option about them.
(a) They are reusable.
(b) They block the entry of sperms.
(e) They are placed to cover the cervix.
(d) All of these.
Answer
Answer: d
11. ZIFT is transfer of
(a) zygote into fallopian tube.
(b) a mixture of sperms and ova into the fallopian tube.
(c) a mixture of sperms and ova into the uterus.
(d) embryo into the uterus.
Answer
Answer: a
12. ‘Sahelr is a/an
(a) oral contraceptive for females.
(b) surgical/sterilisation method for females.
(c) diaphragm for females.
(d) surgical/sterilisation method for males.
Answer
Answer: a
13. _______ is the sterilisation procedure carried out in males.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Vasectomy.
14. The incidences of STPs are reported to be very high among persons in the age group of _____ years.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 15 – 24.
15. The world population was around ______ in 1900.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 2 billion/2000 million.
16. According to the 2001 census report, the population growth rate in India is ______ per year.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 17/1000 or 1.7 per cent.
17. ______ methods work on the principle of avoiding the chances of meeting of ovum and sperm.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Barrier.
18. ______ is the oral contraceptive for female containing non-steroidal preparation.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Saheli.
19. The statutory ban on _____ is to legally check the female foeticide.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Amniocentesis.
20. Day ______ of the menstrual cycle are called fertile period.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 10-17.
21. Embryo with more than 32 blastomeres is transferred into the _______ .
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Uterus.
22. Surgical methods of contraception are highly effective but their _______ is poor.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Reversibility.
Directions (Q23 and Q24): Match the items of Column I with those of Column II.
23.
| Column 1 | Column 11 |
| A. Copper – releasing IUD | 1. Sterilisation in males. |
| B. Hormone – releasing IUD | 2. Progesterone- estrogen combination. |
| C. Vasectomy | 3. Progestasert. |
| D. Oral contraceptive | 4. Multiload 375. |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: A – 4, B – 3, C – 1, D – 2
24.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Lactational amenorrhoea | 1. Directly injecting a sperm into the ovum. |
| B. ICSI | 2. Suppressing ovulation and implantation. |
| C. Tubectomy | 3. Suppression of gonadotropins. |
| D. Oral contraceptive | 4. Blocking the transport of gametes. |
| 5. Implant under the skin. |
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: A – 3, B – 1, C – 4, D – 2
25. Contraceptive pills prevent ovulation and implantation. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
26. MTPs are considered relatively safe during the first 18 weeks of pregnancy. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
27. Hepatitis-B, AIDS and genital herpes are the STDs that can be cured. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
28. Sterilisation process in males, is called vasectomy and that in females, is called tubectomy. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: True.
29. Saheli is an imported oral pill. [True/False]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: False.
Directions (Q30 to Q33): Mark the odd one in each of the following groups.
30. Diaphragm, Vaults, Progestasert, Cervical caps
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Progestasert.
31. Coitus interruptus, Vasectomy, Periodic abstinence, Lactational amenorrhoea.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Vasectomy.
32. Cu 7, CuT, LNG-20, Multiload
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: LNG-20.
33. ZIFT, GIFI, IUI, MTP
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: MTP.
34. What is meant by reproductive health according to WHO?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: According to WHO, reproductive health means a total, well-being in physical, emotional, behavioural and social aspects of reproduction.
35. Mention one positive and one negative application of amniocentesis. [Delhi 2010]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Positive application:
– Any genetic disorder of the foetus can be detected.
Negative application:
– It is misused for sex determination and female foeticide.
36. Government of India has raised the marriageable age of female to 18 years and of males to 21 years. Suggest any two more measures adopted by Government for the purpose. [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
The other methods include:
– Motivation to have smaller families by using various contraceptive methods.
– Advertisements in the media and posters showing a happy couple with two children with a slogan ‘Hum Do, Hamare Do’.
– Incentives given to the couples with small families. (any two)
37. State one reason why breast feeding the baby acts as a natural contraceptive, for the mother? [AI2014C; HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) The events of menstrual cycle are absent during the period of intense lactation.
(ii) In the absence of ovulation, there is no question of fertilisation and conception.
38. Why is the period between day 10 and 17 of the menstrual cycle, called ‘fertile period’? [HOTS]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Ovulation occurs during this period and chances of fertilisation are high; hence this period is called ‘fertile period’.
39. What is the principle behind the barrier methods of birth control?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: In these methods, the ovum and sperms are prevented from physically meeting each other.
40. Name any two barriers used by human females for birth control.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Cervical caps, diaphragms, vaults, (any two)
41. What are the advantages of using condoms?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Condoms act as barriers for the meeting of sperm and ovum and prevent conception.
(ii) They also protect the user from contracting STDs.
42. Name an IUD that you would recommend to promote the cervix hostility to the sperms. [Delhi 2014C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Hormone-releasing IUDs like LNG-20 or progestasert.
43. Mention any two events that are inhibited by the intake of oral contraceptive pills to prevent pregnancy in humans.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Ovulation and implantation.
44. How can pregnancy due to rape or casual unprotected intercourse be prevented?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
Pregnancy due to rape or casual unprotected intercourse can be prevented by
(i) administration of progestogens or progestogen-estrogen combination within 72 hours of coitus.
(ii) administration of IUDs within 72 hours of coitus.
45. Why is tubectomy considered a contraceptive method? [Foreign 2010]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
In tubectomy, the surgical intervention blocks the transport of ova and hence the conception; so it is considered a contraceptive method.
46. What is MTP?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: MTP refers to the intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term under the care of a medical practitioner.
47. When was MTP legalised by the Indian government?
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: In the year 1971.
48. Our government has intentionally imposedstrict conditions for MTP in our country. Justify giving a reason. [Delhi 2017]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: The restrictions are mainly to check the indiscriminate and illegal female foeticides.
49. Name two sexually transmitted diseases caused by bacteria.
Or
Name two curable STDs.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Syphilis and gonorrhoea.
50. Name two STDs which can be transmitted through contaminated blood.
Or
Name two sexually transmitted diseases that do not specifically affect the reproductive organs.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: Hepatitis B and AIDS.
51. Give two reasons why a person infected with a venereal disease does not go for timely detection and treatment of it.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) The early symptoms of venereal diseases are less significant and cannot be detected.
(ii) The social stigma attached to the disease.
52. Mention the age group where STDs are reported to be very high.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: 15-24 years is the age group.
53. Name two STDs that are not curable.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: AIDS, genital herpes, Hepatitis-B. (any two)
54. Mention the primary aim of the ARTs.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination: The primary aim oftheARTs is the diagnosis and corrective treatment of the causes of infertility and enable the couples to have children.
55. Name any two assisted reproductive technologies that help infertile couples to have children. [Delhi 2012C]
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
Explaination:
(i) Test Tube Baby Programme
(ii) Gamete Intra-Fallopian Transfer (GIFT)
(iii) Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
(iv) Artificial Insemination. (any two)
