Question
Polybutadiene, used in truck tyres, is a polymer of buta-1,3-diene. The spatial arrangement of atoms in the polymer depends on the type of catalyst used.
a. Outline two differences between heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts.
b. Suggest, giving a reason, how elastomers used for the tyre tread can increase the traction between the tyre and the road.
c(i).Tyre fires emit trace quantities of polychlorinated dibenzofurans and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin.
Outline, using section 31 of the data booklet, why polychlorinated dibenzofuran is not classed chemically as a dioxin but considered “dioxin-like”. c(ii)The trace quantities of dioxins from tyre fires are rarely inhaled and instead settle on the ground.
Describe why this is a health concern▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any two of:
heterogeneous catalyst is in different phase than reactants AND homogeneous catalyst in same phase [ $\checkmark$ ]
homogeneous catalysts chemically change/react and are reformed at end of reaction OR
reactants adsorb onto heterogenous catalyst and products desorb [ $\checkmark]$
heterogeneous catalysts are more easily removed than homogenous catalysts $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
heterogeneous catalysts can function at higher temperatures $[\boldsymbol{\nu}]$
homogeneous catalysts are «generally» more selective $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
homogeneous catalysts offer a broader range of reactions $[\boldsymbol{\nu}]$
Note: Accept “state” for “phase”.
Accept “heterogeneous catalyst provides a surface to activate reaction”.
b. elastomers bend under force «and return to original form when force is released»
OR
elastomers make tyre more flexible [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
allows greater contact with road $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
c(i)does not contain heterocyclic ring with 2 oxygen atoms
OR
middle ring has only 1 oxygen atom $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
produces similar toxic effects to dioxins $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
Note: Accept “does not contain dioxin ring” for M1.
c(ii)taken up by plants, which are eaten by animals «and then further dispersed»
OR
passed on in food chain $[\boldsymbol{W}]$
Note: Accept “do not break down and can be remobilised as dust”.
Question
Polymers have a wide variety of uses but their disposal can be problematic.
a. Draw a section of isotactic polychloroethene (polyvinylchloride, PVC) showing all the atoms and all the bonds of four monomer units.
b. The infrared (IR) spectrum of polyethene is given.
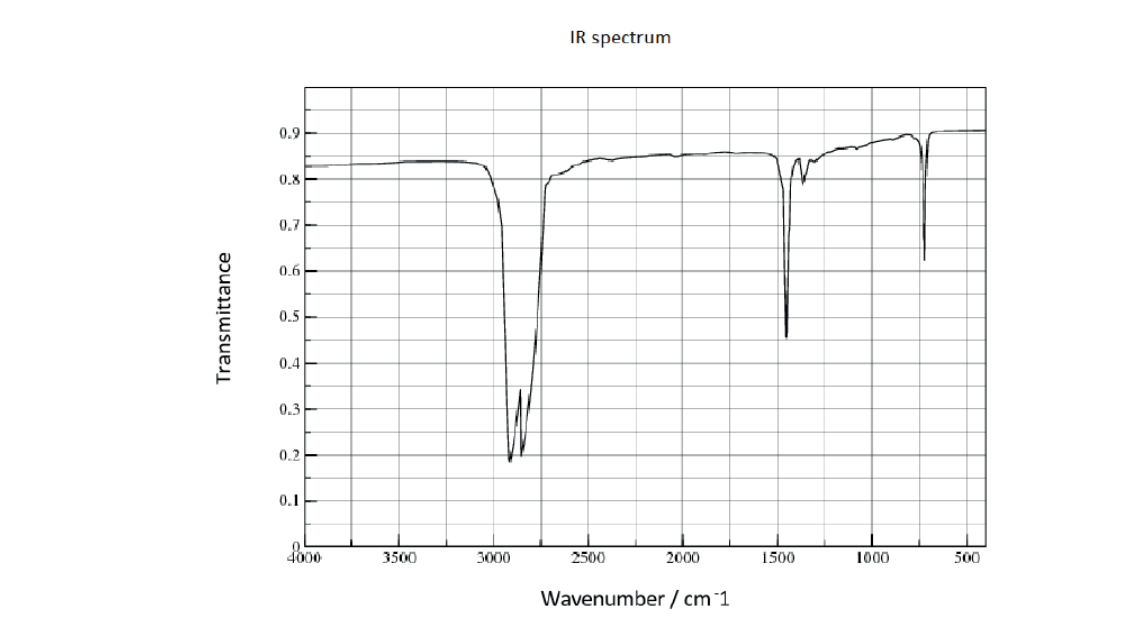
Suggest how the IR spectrum of polychloroethene would differ, using section 26 of the data booklet.
c. Identify a hazardous product of the incineration of polychloroethene.
d. Explain how plasticizers affect the properties of plastics.
e. Suggest why the addition of plasticizers is controversial.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.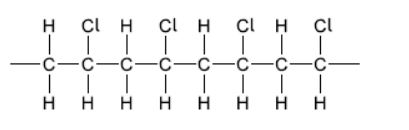
correct bonding $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
$\mathrm{Cl}$ atoms all on same side and alternate $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Continuation bonds must be shown.
Award [1 max] if less than or more than four units shown.
Accept a stereo formula with all atoms and bonds shown.
b. «strong additional» absorption at $600-800$ «cm$^{-1}$ » $\left.\boldsymbol{\sim}\right]$
c. Any one of:
$\mathrm{HCl}[\circlearrowleft]$
$\mathrm{Cl}_2[\boldsymbol{\vee}]$
dioxins $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
$\mathrm{c}[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
$\mathrm{CO}[\boldsymbol{\nu}]$
d. Any two of:
embedded/fit between chains of polymers [ $\checkmark]$
keep polymer strands/chains/molecules separated/apart [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}$ ]
increase space/volume between chains $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
weaken intermolecular/dipole-dipole/London/dispersion/instantaneous dipoleinduced dipole/van der Waals/vdW forces «between chains» [ $\boldsymbol{\wedge}$ ]
increase flexibility/durability/softness $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
make polymers less brittle $[\boldsymbol{\nu}]$
e. leach into foodstuffs/environment
OR
«unknown» health/environmental consequences [ $\checkmark$ ]
Note: Accept “plasticizers cannot be recycled”.
Question
Polypropene is used to make many objects including carpets, stationery and laboratory equipment.
a. Draw a section of an isotactic polypropene polymer chain containing four repeating units.
b. Predict, with a reason, whether isotactic or atactic polypropene has the higher melting point.
c. Polypropene is a thermoplastic. Outline what is meant by thermoplastic.
d. Discuss why the recycling of plastics is an energy intensive process.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.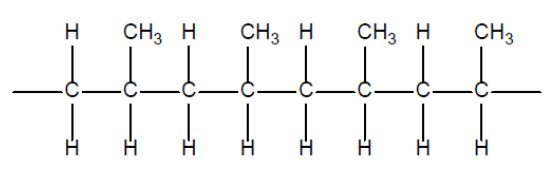
NOTE: Continuation bonds must be shown.
Ignore square brackets and ” $n$ “.
Do not accept one repeating unit in square brackets with a subscript of 4.
Accept condensed structure provided all $\mathrm{C}$ to $\mathrm{C}$ bonds are shown and $\mathrm{CH}_3$ groups on same side.
Accept
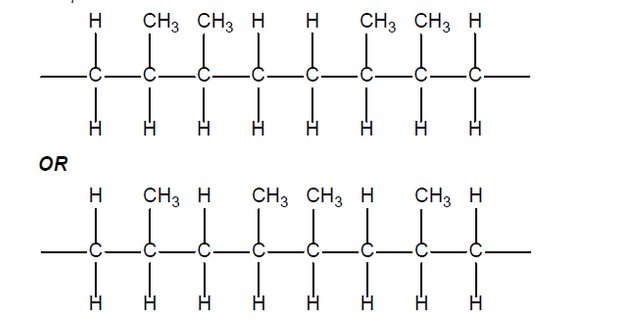
Do not accept syndiotactic (alternating orientation of the $\mathrm{CH}_3$ groups).
b. isotactic «has higher melting point» $A N D$ ordered chains pack more closely
OR
isotactic «has higher melting point» AND stronger intermolecular/London/dispersion forces
NOTE: Accept “van der Waals’ forces”/”vdW”.
c. softens when heated «and hardens when cooled»
d. Any two of:
collection/transportation of plastic waste
separation of different types «of plastic»
OR
separation of plastic from other materials
melting plastic
processing/washing/cleaning/drying/manufacture of recycled plastic
Question
One way of classifying materials is based on the type of bonding present.
One reaction to convert cyclohexanone to caprolactam using concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst is shown.
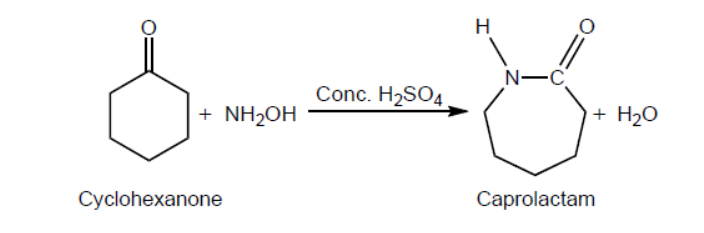
a. Outline why this type of classification is not entirely satisfactory by using magnesium diboride, $\mathrm{MgB}_2$, as an example. Refer to sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
b.i.Structures of poly(methyl acrylate), PMA, and Bakelite ${ }^{\circledR}$ are shown.
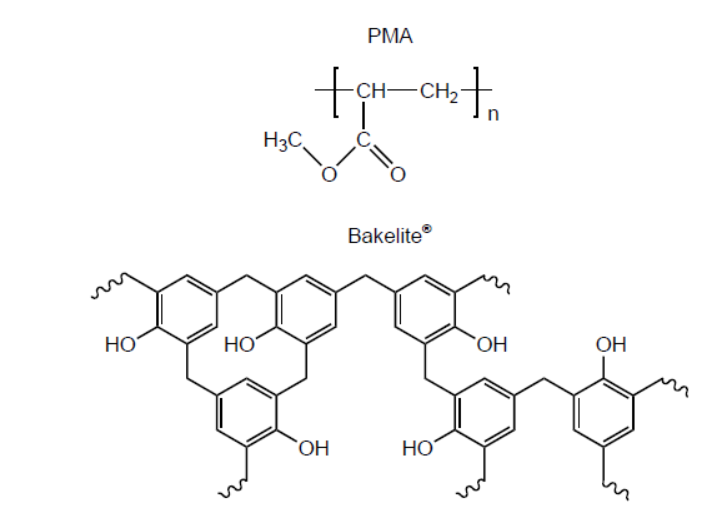
Suggest, giving reasons, which is the thermoplastic polymer and which is the thermosetting polymer.

b.ii.In an incomplete combustion of the polyvinyl chloride, PVC, it was found that hydrogen chloride, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water vapour were released.
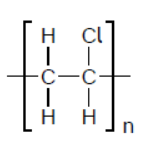
Formulate an equation for this reaction using the formula of the PVC repeating unit.
c.i. A zeolite is an alternative catalyst for this reaction.
Explain how zeolites act as selective catalysts.
c.ii.Identify another advantage of using a zeolite instead of concentrated sulfuric acid.
d. Repeating units of several polymers are listed.
The infrared (IR) spectrum of one of these polymers is shown.
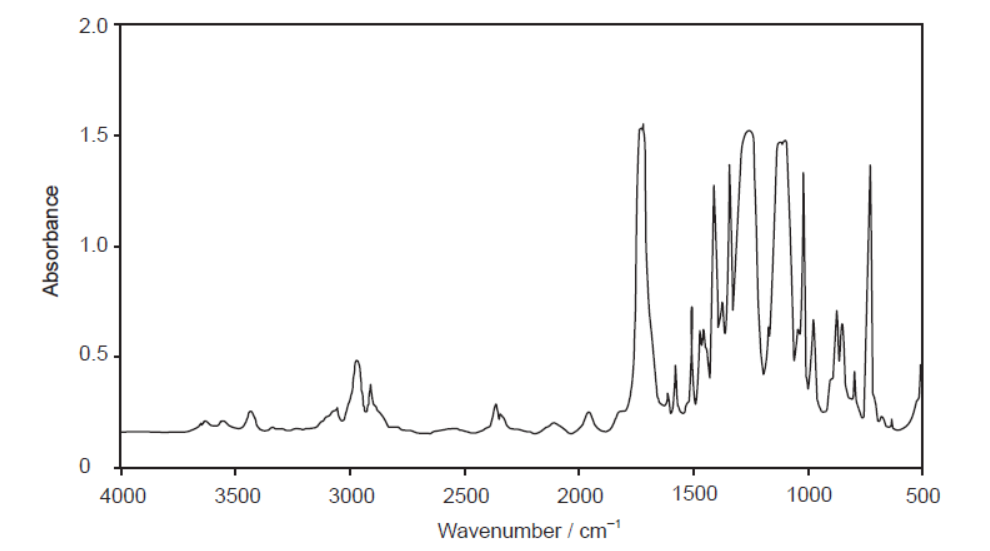
Deduce, giving a reason, the name of this polymer and its Resin Identification Code (RIC), using sections 26 and 30 in the data booklet.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. $\Delta \chi=0.7$ AND average $\Delta \chi=1.7$
bonding between metallic and ionic
OR
more than one type of bonding present
OR
bond type difficult to determine as close to several regions/several types/named bonding types «eg ionic and covalent etc.»
OR
bond is mostly covalent «based on \% covalent scale on diagram»
OR
bond has « $\frac{0.7}{3.2} \times 100=» 22 \%$ ionic character
Accept “EN” for ” $\chi$ “.
Accept “bond is ionic but close to several regions/several types/other named bonding type(s) (eg covalent, metallic and covalent etc.)”.
Do not accept just “bond is ionic”.
Accept any value for $\%$ ionic character in range $15-24 \%$ or $\%$ covalent character in range $76-85 \%$.
b.i. Thermoplastic polymer:
PMA AND «weak» intermolecular/IMFs/London/dispersion/van der Walls/vdW/dipole-dipole forces «between layers/chains»
OR
PMA AND no/few cross-links «between layers/chains»
Thermosetting polymer:
Bakelite ${ }^{\circledR}$ AND «strong» covalent bonds «between layers/chains»
OR
Bakelite ${ }^{\circledR}$ AND extensive cross-links «between layers/chains»
Do not accept “hydrogen bonding” for M1.
Award [1 max] for correct reasons for both polymer classes even if named polymers are incorrectly classified.
b.ii. $\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHCl}(\mathrm{s})+2 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})$
OR
$\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CHCl}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{g})+2 \mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})$ AND $2 \mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})$
Accept any correctly balanced equation that includes the products specified.
c.i. pores/cavities/channels/holes/cage-like structures «in zeolites» have specific shape/size
only reactants «with appropriate size/geometry» fit inside/go through/are activated/can react
c.ii.does not require corrosive acid/«concentrated» sulfuric acid/ $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4$
OR
zeolite can be recycled «more easily»
OR
product can be «more» easily separated from a zeolite «than from sulfuric acid»
OR
minimal/less impact on environment
OR
synthesis of specific isomers as products
d. Name and reason:
PET/PETE $A N D$ peak for $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ «at $1700-1750 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1} »$
$R I C$ :
1
Accept “PET/PETE AND peak for C-O «at 1050-1410 cm-1»” for M1.
Accept “PET/PETE AND peak(s) for COO” for M1.
Accept name or abbreviation for polymer.
No ECF for $M 2$.
Question
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethene are both polymers made from crude oil.
Explain why PVC is less flexible than polyethene.
State how PVC can be made more flexible during its manufacture and explain the increase in flexibility on a molecular level.
PVC can exist in isotactic and atactic forms. Draw the structure of the isotactic form showing a chain of at least six carbon atoms.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C–Cl bond / molecule is polar;
stronger intermolecular/van der Waals’/London/dispersion forces/dipole-dipole attraction;
addition of plasticizers;
Allow misspelling within reason.
get between polymer chains / keeps chains further apart and reduces attraction (between the chains);
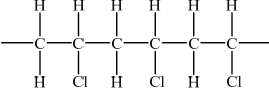 ;
;
Accept any structure with all the Cl atoms shown on the same side.
Continuation bonds at end of structure not needed.
Hydrogen atoms must be included.
Examiners report
Most answers in (a) did not mention the polarity of the C–Cl bond.
The explanation of PVC’s flexibility in (b) did not usually refer to the polymer chains being pushed apart.
A significant number of candidates drew the isotactic form of polypropene instead of PVC in response to (c).
Question
Use high-density poly(ethene) and low-density poly(ethene) as examples to explain the difference that branching can make to the properties of a polymer.
During the formation of poly(styrene), a volatile hydrocarbon such as pentane is often added. Describe how this affects the properties of the polymer and give one use for this product.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
in HDPE there is little branching / in LDPE there is branching/side chains;
long chains can pack closely together/have greater forces of attraction so (HDPE) is more dense/more rigid/stronger;
side chains make (LDPE) more flexible/ideal for film products (such as food wrapping);
Accept opposite statements for marking points 2 and 3.
makes the polymer low density/good thermal insulator/expanded/softer/better shock absorber;
packaging/insulation;
Award [1 max] if thermal insulation given for both answers.
Examiners report
Most candidates had difficulty explaining the difference between HDPE and LDPE in terms of branching. Many mixed up the branching and properties, for example stating that increased branching led to a higher density.
Part (b), which required candidates to explain why pentane is added to poly(styrene) to improve its thermal insulation properties, was also difficult for most candidates.
Question
Addition polymers are extensively used in society. The properties of addition polymers may be modified by the introduction of certain substances.
(a) For two different addition polymers, describe and explain one way in which the properties of addition polymers may be modified.
Polymer one:
Polymer two:
(b) Describe and explain how the extent of branching affects the properties of poly(ethene).
(c) Discuss two advantages and two disadvantages of using poly(ethene).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(a) Accept two of the following four pairs of answers.
plasticizers in polyvinyl chloride;
the more plasticizer the more flexible the plastic;
OR
volatile hydrocarbons in the formation of (expanded) polystyrene;
volatile hydrocarbons vaporize during the formation of the polystyrene and reduce the density of (expanded) polystyrene / improving insulating properties;
OR
sulfur added to diene/2-methyl-1,3-butadiene/rubber (produces cross-link polymer);
maintains its spring/softness (for longer periods of time);
OR
blowing air/steam during the polymerisation to form polyurethane;
reduces density/increases springiness
(b) high degree of branching produces low density polyethene;
small degree of branching produces high density polyethenes;
HDPE/low branching is stiffer/stronger/more resistant to heat and corrosion/less permeable to gases / LDPE/high branching is more flexible/weaker/less resistant to heat and corrosion/more permeable to gases;
(c) Advantages:
polymer’s properties can be customized / OWTTE
can be recycled/reused
cheap
chemically inert
transparent
non-toxic
Any two correct answers scores [1].
Disadvantages:
rely on non-renewable energy sources
volume occupied by plastics in landfill
non-biodegradability
burning produces toxic gases
burning produces carbon dioxide (greenhouse gas)
burning printed polyethene can release toxic (heavy) metals/substances
may cause suffocation/death of animals
Any two correct answers scores [1].
Examiners report
The way in which the properties of addition polymers depend on their structure and methods for modifying this appeared to be very poorly understood, with only a handful of candidates scoring well on any parts of this question. In Part (b) many candidates discussed the difference between isotactic and atactic polymers rather than the effects of branching.
Question
Catalytic cracking uses heterogeneous catalysts.
The initial products of the fractional distillation of oil often undergo cracking. This can be carried out in a number of ways. State the major reason for choosing each of the following techniques.
Catalytic cracking:
Thermal cracking:
Steam cracking:
Explain how these differ from homogeneous catalysts.
Identify one disadvantage of using heterogeneous catalysts.
Many of the compounds produced by cracking are used in the manufacture of addition polymers. State the essential structural feature of these compounds and explain its importance.
The polymers often have other substances added to modify their properties. One group of additives are plasticizers. State how plasticizers modify the physical properties of polyvinyl chloride and explain at the molecular level how this is achieved.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Catalytic cracking:
used to produce moderate length alkanes (for fuels) / lower temperature / lower energy consumption / more control of product;
Thermal cracking:
used to crack very long chain starting material;
Steam cracking:
used to produce low molar mass alkenes (for petrochemicals);
heterogeneous catalysts in a different phase to the reactants / homogeneous catalysts in the same phase as reactants;
easily poisoned / efficiency decreases over time / forms clumps / only effective on surface / require high surface area;
carbon-carbon double bond;
breaks allowing addition reaction / allows monomers/molecules to join together/polymerize;
make the polymer more flexible;
fits between/increases separation between polymer chains / allow polymer chains to slide past each other more easily / weaken intermolecular attraction;
Examiners report
Few candidates appear to have any knowledge of the different cracking techniques, though more appeared familiar with issues relating to catalysts. Quite a number of candidates were aware carbon-carbon double bonds were needed for addition polymerization, though the nature and effect of plasticizers was less well known
Few candidates appear to have any knowledge of the different cracking techniques, though more appeared familiar with issues relating to catalysts. Quite a number of candidates were aware carbon-carbon double bonds were needed for addition polymerization, though the nature and effect of plasticizers was less well known
Few candidates appear to have any knowledge of the different cracking techniques, though more appeared familiar with issues relating to catalysts. Quite a number of candidates were aware carbon-carbon double bonds were needed for addition polymerization, though the nature and effect of plasticizers was less well known
Few candidates appear to have any knowledge of the different cracking techniques, though more appeared familiar with issues relating to catalysts. Quite a number of candidates were aware carbon-carbon double bonds were needed for addition polymerization, though the nature and effect of plasticizers was less well known
Few candidates appear to have any knowledge of the different cracking techniques, though more appeared familiar with issues relating to catalysts. Quite a number of candidates were aware carbon-carbon double bonds were needed for addition polymerization, though the nature and effect of plasticizers was less well known
Question
The two major acids that cause acid rain originate from different sources.
State an equation that shows why rain water is naturally acidic.
Outline the process responsible for the production of each acid and state an equation to show its formation.
Acid rain has caused damage to limestone buildings and marble statues. State an equation to represent the reaction of acid rain with limestone or marble.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}/{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^ + } + {\text{HCO}}_3^ – \);
Do not penalize absence of reversible sign.
Do not accept CO2 + H2O \( \to \) 2H+ + CO32–.
Acid 1:
\({\text{(HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}\) high temperature in internal combustion/jet engine;
reaction between \({{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\) and \({{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) at high temperature/lightning;
Accept either of the above for first mark.
\({\text{2N}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3} + {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_2}/{\text{4N}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {\text{4HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}\);
Acid 2:
\({\text{(}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{/}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{)}}\) from burning of coal / smelting plants / sulfuric acid plants / volcanic activity;
Do not accept combustion of fossil fuels.
\({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}/{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}\);
Allow H2SO3/H2SO4 to be Acid 1 and HNO2/HNO3 to be Acid 2.
\({\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{2HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} \to {\text{Ca(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\);
Accept equation with H2SO3 or H2SO4 or ionic equations.
Do not accept equations with H2CO3.
Examiners report
Most candidates correctly identified carbon dioxide as the source of natural water acidity and wrote an acceptable equation. Many also identified sources of nitric and sulphuric acid, though these equations often proved trickier, with many candidates writing equations for the formation of the oxide from which the acid is derived. Balanced equations for the reaction with limestone also proved to be a challenge, with carbonic acid often appearing as a product.
Most candidates correctly identified carbon dioxide as the source of natural water acidity and wrote an acceptable equation. Many also identified sources of nitric and sulphuric acid, though these equations often proved trickier, with many candidates writing equations for the formation of the oxide from which the acid is derived. Balanced equations for the reaction with limestone also proved to be a challenge, with carbonic acid often appearing as a product.
Most candidates correctly identified carbon dioxide as the source of natural water acidity and wrote an acceptable equation. Many also identified sources of nitric and sulphuric acid, though these equations often proved trickier, with many candidates writing equations for the formation of the oxide from which the acid is derived. Balanced equations for the reaction with limestone also proved to be a challenge, with carbonic acid often appearing as a product.
Question
Since the accidental discovery of polyethene in the 1930s, polymers have played an essential role in daily life because of their wide range of properties and uses.
Titanium compounds are used as catalysts in the manufacture of high-density polyethene (HDPE). Discuss two factors scientists would have considered in choosing these catalysts.
Describe a structural feature of low-density polyethene (LDPE) that explains why LDPE has a different melting point from that of HDPE.
State one environmental impact of the disposal of these polyethenes by using incineration.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
no other product formed (except HDPE);
expensive but effective;
little or no environmental/health impact;
not easily poisoned by impurities;
cause (considerable) increase in rate;
ability to work under mild/severe conditions;
side-chains / branching present (in LDPE);
limits closer packing / chains further apart / OWTTE;
less van der Waals’/dispersion/London forces / OWTTE;
Award mark for less intermolecular forces. Do not accept weaker.
low(er) melting point (than HDPE);
No mark for different melting point.
Accept reverse argument for HDPE.
\({\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}\) is a greenhouse gas / causes climate change / global warming / formation of soot/particulates / melting of polar ice caps / rising sea levels / OWTTE;
Accept CO produced is toxic/poisonous.
Examiners report
(a) was surprisingly poorly answered, with very few candidates understanding how to discuss two factors in choosing catalysts, although they should have studied several factors.
(b) was answered well.
(c) was answered well.
Question
Nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide are two air pollutants.
Nitrogen dioxide is formed in a two-stage process. Describe one anthropogenic (man-made) source of nitrogen dioxide and state the two chemical equations for its formation.
Both of these air pollutants also contribute to acid deposition. State one chemical equation for each gas to describe how each forms an acidic solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
combustion of fuels (at high temperature);
Accept internal combustion/aircraft/jet engines.
\({{\text{N}}_2} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{2NO}}\) and \(2{\text{NO}} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{2N}}{{\text{O}}_2}\);
\({\text{2N}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}/{\text{4N}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{4HN}}{{\text{O}}_3}\);
\({\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}/{\text{2S}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}\);
Examiners report
The man-made source of nitrogen oxide was generally very well answered, although the equations for its formation proved demanding.
The chemical equation for the formation of sulfuric acid was given correctly by many candidates, but it was surprising to see that a significant number of candidates did not know the chemical formula for nitric acid.
Question
Ethene can be polymerized to form high-density poly(ethene), HDPE, or low-density poly(ethene), LDPE, depending on the reaction conditions. Describe the main structural difference between HDPE and LDPE and explain how this accounts for their different properties.
(i) The repeating unit of poly(propene) has the formula:
–[–\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{–CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}\)–]–
Draw a section of the polymer containing five repeating units to illustrate atactic
poly(propene).
(ii) Explain why isotactic poly(propene) is tough and can be used to make car bumpers (fenders), whereas atactic poly(propene) is soft and flexible making it suitable for sealants.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
HDPE has little branching whereas LDPE has branching/side chains / OWTTE;
HDPE is stronger/more rigid / LDPE is weaker/more flexible/resilient;
HDPE chains pack more closely together / LDPE chains pack less closely together; HDPE has stronger van der Waals’ forces / LDPE has weaker van der Waals’ forces;
(i) 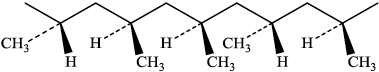 ;
;
There must be five –CH3 groups and they must be shown in random orientation.
Allow the following structure:
(ii) isotactic has all methyl groups oriented/pointing in the same direction/has a more regular structure / atactic has the methyl groups oriented/pointing in different directions/arranged randomly/has an irregular structure;
in isotactic the chains can pack more closely together (making it more crystalline/tough) / in atactic the chains pack less closely together (making it soft/flexible);
isotactic has stronger van der Waals’ forces / atactic has weaker van der Waals’ forces;
Examiners report
In (a) most candidates were aware of the differences between HDPE and LDPE, but often failed to fully score as they referred to intermolecular forces in a rather vague, instead of specific, manner.
Most candidates found it difficult to draw the structure of atactic poly(propene) in part (b)(i). Most candidates were very familiar with the difference in structure of isotactic and atactic poly(propene), but many failed to fully score as their responses lacked the required specificity for the intermolecular forces.
Question
The two diagrams below show the arrangement of molecules in two different types of polyethene, labelled A and B.

Predict which type of polyethene (A or B) has the strongest intermolecular forces, highest density and greatest flexibility.
(i) Strongest intermolecular forces:
(ii) Highest density:
(iii) Greatest flexibility:
The polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC), also known as poly(chloroethene), is hard and brittle when pure. Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, how adding a plasticizer to PVC modifies the properties of the polymer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) A;
(ii) A;
(iii) B;
closely packed molecules with crystalline structure;
(plasticizers) separate the PVC molecules/polymer chains / disrupt crystalline structure;
decrease/weaken intermolecular forces/intermolecular dipole-dipole interactions/van der Waals’/London Dispersion;
Do not accept mention of H-bonding
makes it (PVC) softer/more flexible/more easily moulded;
Examiners report
Many candidates were able to score three marks in (a) and most gave a good account of (b). Many, however, neglected to mention intermolecular forces, specifically requested in the question.
Many candidates were able to score three marks in (a) and most gave a good account of (b). Many, however, neglected to mention intermolecular forces, specifically requested in the question.
Question
Poly(propene) has different forms. Isotactic poly(propene) is tough, while atactic poly(propene) is flexible.
State the difference in the structure of the two polymers.
Isotactic:
Atactic:
Explain how the difference in structure results in the different properties of isotactic and atactic poly(propene).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Isotactic: methyl groups all oriented on same side of polymer chain and
Atactic: methyl groups oriented randomly;
Diagram alone is not sufficient – unless difference stated in words.
closer packing of isotactic chains;
isotactic has stronger van der Waals’/London/dispersion/intermolecular forces (than atactic);
Accept opposite statements for atactic.
Allow vdW as abbreviation for van der Waals’ or FDL for London/dispersion.
Examiners report
The orientations of methyl groups in isotactic and atactic poly(propene) were known by more than half of the candidates, but the explanations of the properties did not involve intermolecular forces for the majority of candidates.
The orientations of methyl groups in isotactic and atactic poly(propene) were known by more than half of the candidates, but the explanations of the properties did not involve intermolecular forces for the majority of candidates.
Question
Poly(ethene) can be produced in a low density (LDPE) or a high density (HDPE) form.
Describe how the two forms differ in their chemical structure.
Explain in terms of their structures how the flexibility of the two forms of poly(ethene) differ.
Describe why pentane is sometimes added during the formation ofpoly(phenylethene), also known as polystyrene.
State one use for the product formed from this process.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
HDPE/high density polyethene has little/no branching/side chains and low density has (many) branches/side chains;
branching in LDPE/ low density polyethene prevents chains fitting closely together;
weaker intermolecular/van der Waals’/London/dispersion forces so more flexible;
Accept opposite statements for HDPE/high density polyethene.
vaporizes causing it to expand/form expanded polystyrene / OWTTE;
(thermal) insulator / packaging material / absorb shock;
Do not accept just cups.
Examiners report
The answers to this often betrayed a confusion between isotactic and atactic polypropene. That being said the link between packing and the strength of the dispersion forces was relatively well understood at least to the extent of gaining one of the marks. Most candidates were aware of the role of pentane and even the weakest were scoring the mark for a use of expanded polystyrene.
The answers to this often betrayed a confusion between isotactic and atactic polypropene. That being said the link between packing and the strength of the dispersion forces was relatively well understood at least to the extent of gaining one of the marks. Most candidates were aware of the role of pentane and even the weakest were scoring the mark for a use of expanded polystyrene.
The answers to this often betrayed a confusion between isotactic and atactic polypropene. That being said the link between packing and the strength of the dispersion forces was relatively well understood at least to the extent of gaining one of the marks. Most candidates were aware of the role of pentane and even the weakest were scoring the mark for a use of expanded polystyrene.
The answers to this often betrayed a confusion between isotactic and atactic polypropene. That being said the link between packing and the strength of the dispersion forces was relatively well understood at least to the extent of gaining one of the marks. Most candidates were aware of the role of pentane and even the weakest were scoring the mark for a use of expanded polystyrene.
Question
Polyacrylonitrile is an important polymer used in the manufacture of carbon fibres. The monomer has the structure below.
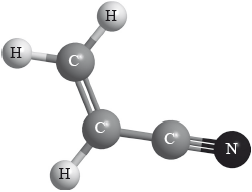
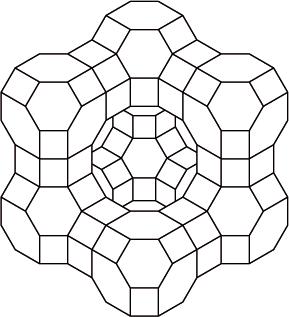
The rate of the polymerization reaction from the gaseous monomer is increased in the presence of a zeolite with the cage structure shown.
A new range of light batteries has been developed that uses open carbon nanotubes, covered with silicon, as electrodes.
Polyacrylonitrile is similar to polypropene and can exist in two forms.
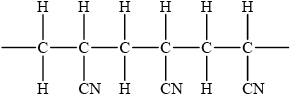
Draw the structure of the isotactic form of polyacrylonitrile showing three repeating units.
Polyacrylonitrile is similar to polypropene and can exist in two forms.
Explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for the manufacture of strong fibres.
Identify the role of the zeolite in the reaction.
Suggest an explanation for its efficiency in favouring the production of the crystalline polymer.
Outline the structure of the open carbon nanotubes.
State a property of these nanotubes that makes them suitable for this use.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
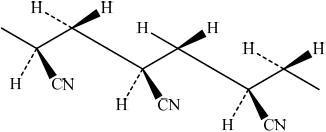 /
/
 ;
;
Continuation bonds at end of structure needed.
Hydrogen atoms must be included.
Award [1] for chain with CN groups on alternate carbons.
Award [2] for correct chain with CN on alternate carbons with same orientation.
chains pack together better;
strong intermolecular/attractive forces between chains;
chains do not move past each other easily (so fibre strong/rigid);
catalyst;
(selective) because of dimensions/shape/size (of cage);
Accept “large surface area”.
cylinder with hexagons of carbon (atoms);
Accept suitable diagram.
Do not award mark if pentagons are also mentioned.
(electrical) conductor;
Accept low density.
Do not accept light.
Examiners report
Some very strange polymers were suggested in (a) (i) with the –CN group becoming integrated into the carbon backbone. Candidates were, however, able to explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for fibres. The role of the zeolite in (b) was usually correctly identified but it was not known that the dimensions, size or shape of the cage were an explanation for its efficiency. Most were able to give a good account of carbon nanotubes although some introduced pentagons at the end. This was specifically ruled out in the question – open carbon nano-tubes.
Some very strange polymers were suggested in (a) (i) with the –CN group becoming integrated into the carbon backbone. Candidates were, however, able to explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for fibres. The role of the zeolite in (b) was usually correctly identified but it was not known that the dimensions, size or shape of the cage were an explanation for its efficiency. Most were able to give a good account of carbon nanotubes although some introduced pentagons at the end. This was specifically ruled out in the question – open carbon nano-tubes.
Some very strange polymers were suggested in (a) (i) with the –CN group becoming integrated into the carbon backbone. Candidates were, however, able to explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for fibres. The role of the zeolite in (b) was usually correctly identified but it was not known that the dimensions, size or shape of the cage were an explanation for its efficiency. Most were able to give a good account of carbon nanotubes although some introduced pentagons at the end. This was specifically ruled out in the question – open carbon nano-tubes.
Some very strange polymers were suggested in (a) (i) with the –CN group becoming integrated into the carbon backbone. Candidates were, however, able to explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for fibres. The role of the zeolite in (b) was usually correctly identified but it was not known that the dimensions, size or shape of the cage were an explanation for its efficiency. Most were able to give a good account of carbon nanotubes although some introduced pentagons at the end. This was specifically ruled out in the question – open carbon nano-tubes.
Some very strange polymers were suggested in (a) (i) with the –CN group becoming integrated into the carbon backbone. Candidates were, however, able to explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for fibres. The role of the zeolite in (b) was usually correctly identified but it was not known that the dimensions, size or shape of the cage were an explanation for its efficiency. Most were able to give a good account of carbon nanotubes although some introduced pentagons at the end. This was specifically ruled out in the question – open carbon nano-tubes.
Some very strange polymers were suggested in (a) (i) with the –CN group becoming integrated into the carbon backbone. Candidates were, however, able to explain why the isotactic form is more suitable for fibres. The role of the zeolite in (b) was usually correctly identified but it was not known that the dimensions, size or shape of the cage were an explanation for its efficiency. Most were able to give a good account of carbon nanotubes although some introduced pentagons at the end. This was specifically ruled out in the question – open carbon nano-tubes.
Question
Crude oil (petroleum) is initially separated into its components by fractional distillation, but subsequent cracking of the heavier fractions is usually required.
Ethene can be polymerized to form poly(ethene) and, depending on the conditions used, either high-density poly(ethene) (HDPE) or low-density poly(ethene) (LDPE) is formed.
State a balanced equation for the thermal cracking of \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{20}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{42}}}}\) in which octane and ethene are products.
(i) Other than density, state two differences in the physical properties of HDPE and LDPE.
(ii) Outline how the differences in (b)(i) relate to differences in their chemical structure.
It has been said that bitumen and heavy fuel oils are too valuable a resource to use for road surfacing and electricity generation. Comment on this statement.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({{\text{C}}_{20}}{{\text{H}}_{42}} \to {{\text{C}}_8}{{\text{H}}_{18}} + {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4} + {{\text{C}}_{10}}{{\text{H}}_{20}}/{{\text{C}}_{20}}{{\text{H}}_{42}} \to {{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{18}}}} + {\text{6}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\)
Accept any correctly balanced equation that includes octane and at least one ethene molecule as products.
correct reactants and products;
balanced equation;
M2 can only be scored if M1 is correct.
(i) Award [1] for any two.
HDPE has higher mp;
HDPE is more rigid / less flexible;
HDPE is stronger;
Accept opposite statements for LDPE.
(ii) HDPE has straight chain and LDPE has branched chain / LDPE has more branched chains;
more valuable for (cracking to provide) chemical precursors/petrochemicals / may be cracked to produce same substances now obtained from lighter fractions / OWTTE;
Examiners report
Only about a third of the candidates were able to score both marks by giving a balanced equation producing octane and ethene. Others scored one mark as they failed to balance the equation.
(i) Less than half the candidates gave two physical properties that differed between LDPE and HDPE.
(ii) A small number of candidates attributed the difference to the branching in the chains.
The answers were mostly unsatisfactory as they failed to recognize the value of cracking products for the petrochemical industry.
Question
The development and application of plastics was one of the most important technological developments of the last century.
The diagram below represents a section of a polymer.
Identify the two functional groups in the monomer from which this polymer is manufactured.
An expanded form of the plastic is often used in packaging. Describe how this is manufactured.
Discuss two advantages and one disadvantage of using the expanded form as a packaging material.
Two advantages:
One disadvantage:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
alkenyl/C=C and phenyl/–\({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_5}\);
Accept alkene and benzene ring/aromatic ring/arene but not benzene.
pentane/volatile hydrocarbon added (during polymerization process);
heating causes pentane/volatile hydrocarbon to evaporate/vaporize/produce bubbles of gas (expanding the polystyrene);
Accept other suitable identified blowing agents such as carbon dioxide.
Advantages:
Any two for [2 max]:
low/reduced density;
Accept “small mass”.
Do not accept “light”.
can be shaped (around object);
good shock absorber;
insulator;
Disadvantage:
Award [1] for disadvantage:
disposal takes up a lot of space (in landfill);
Accept “non-biodegradable/polluting/hazardous to wildlife”.
Examiners report
Some candidates identified two functional groups in the monomer.
About half of the candidates described how the expanded form of the plastic could be manufactured.
Most candidates were able to score one or two marks. “Good shock absorber” was a popular answer. Candidates should be encouraged to use precise terminology such as “has low density” instead of “light”.
Question
Chloroethene undergoes polymerization with a free-radical initiator to produce the atactic form of polychlorethene (PVC).
Sketch the atactic form of polychloroethene showing four units.
(i) Explain, in molecular terms, why PVC becomes more flexible and softer when a plasticizer is added.
(ii) State one type of compound which can be used as a plasticizer.
Suggest an environmental issue associated with the use of PVC.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct structure with random orientation of Cl atoms
Accept 2-dimensional diagrams.
Accept any random arrangement of Cl atoms providing the monomer units originate from chloroethene and Cl atoms are on alternate carbons.
Continuation bonds are necessary for the mark.
(i)
«plasticizer molecules» fit between chains
OR
«plasticizer molecules» prevent chains from forming crystalline regions
OR
«plasticizer molecules» keeps strands/chains/molecules separated
OR
«plasticizer molecules» increase space/volume between chains
weakens intermolecular/dipole-dipole/London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole/van der Waals/vdW forces
Do not accept “«plasticizer molecules» lower density”.
(ii)
ester/phthalate/citrate
Accept other general or specific names of plasticizers.
does not degrade/biodegrade/break down «easily»
occupies more space in landfills
incineration produces dioxins/hydrochloric acid/HCl «which can contribute to acid rain»
Accept “plasticizer added to PVC can be a health hazard”.
Accept “combustion” for “incineration”.
Do not accept simply “toxic compounds” for M3
Question
Polymers are made up of repeating monomer units which can be manipulated in various ways to give structures with desired properties.
(i) Draw the structure of 2-methylpropene.
(ii) Deduce the repeating unit of poly(2-methylpropene).
Deduce the percentage atom economy for polymerization of 2-methylpropene.
(i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
i
OR
H2C=C(CH3)2
ii
OR
−CH2C(CH3)2−
Continuation bonds needed for mark.
No penalty if square brackets present or “n” appears after the bracket/formula.
«same mass of product as reactant, thus» 100«%»
Accept “less than 100%” only if a reason is given (eg, the catalyst is not converted into the product, or other reasonable answer).
i
due to stability of plastics/strong covalent bonds
OR
low volatility preventing good mixing with oxygen «gas»
OR
lack of/insufficient oxygen
OR
plastics are often parts of devices with non-combustible components «which mechanically prevent the combustion of plastic components»
OR
PVC already partly oxidised «because some C–H bonds are replaced with C–Cl bonds», so it cannot produce enough heat for complete combustion
OR
many industrial/household materials contain additives that reduce their flammability/act as flame retardants
ii
weakly bound to the PVC/no covalent bonds to PVC/only London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces between DEHP and PVC AND leach/evaporate «from PVC» to atmosphere/food chain
OR
has low polarity/contains non-polar hydrocarbon chains AND fat-soluble/deposits in the fatty tissues
OR
has unusual structural fragments/is a xenobiotic/difficult to metabolise AND stays in the body for a long time
Question
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is often used for the identification of polymers, such as PETE, for recycling.
LDPE and high density polyethene (HDPE) have very similar IR spectra even though they have rather different structures and physical properties.
Below are the IR spectra of two plastics (A and B); one is PETE, the other is low density polyethene (LDPE).
Deduce, giving your reasons, the identity and resin identification code (RIC) of A and B using sections 26 and 30 of the data booklet.
Describe the difference in their structures.
Explain why the difference in their structures affects their melting points.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A RIC: 1 AND B RIC: 4
ALTERNATIVE 1:
«only» PETE contains carbonyl/C=O/ester/COO groups
carbonyl groups absorb at 1700–1750 «cm–1»
ALTERNATIVE 2:
LDPE contains more C–H bonds «than PETE»
C–H bonds absorb at 2850–3090 «cm–1»
For either, accept specific frequencies in these ranges (eg 1735 «cm–1» or 2900 «cm–1»).
[3 marks]
HDPE less branched
OR
LDPE more branched
Accept “no branching in HDPE AND branching in LDPE”.
[1 mark]
HDPE «polymer» chains/molecules can pack together more closely «than LDPE chains»
OR
HDPE «polymer» chains/molecules have a higher contact surface area «than LDPE chains»
stronger intermolecular/dispersion/London/van der Waals’ forces in HDPE AND higher melting point
Accept converse arguments.
[2 marks]
Question
Polymer nanocomposites often have better structural performance than conventional materials. Lithographic etching and metal coordination are two methods of assembling these nanocomposites.
Nanoparticles anchor plasticizers in PVC so that they cannot escape from the polymer as easily.
State the two distinct phases of a composite.
Identify the methods of assembling nanocomposites by completing the table.
Explain how the structure of plasticizers enables them to soften PVC.
Suggest a reason why nanoparticles can better anchor plasticizers in the polymer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
reinforcing «phase»
«embedded in» matrix «phase»
[2 marks]
Award [2] for all 4, [1] for 2 or 3 correct.
[2 marks]
Any three of:
contain a polar group «which locks into the polymer»
a non-polar group «which weakens the forces between chains»
embedded between chains of polymers
«plasticizer molecules» fit between chains
«plasticizer molecules» prevent chains from forming crystalline regions
«plasticizer molecules» keeps strands/chains/molecules separated
«plasticizer molecules» increase space/volume between chains
weakens intermolecular/dipole-dipole/London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole/van der Waals/vdW forces
Do not accept “«plasticizer molecules» “lower density” or “softer”.
[3 marks]
more places «for plasticizers» to bond
OR
increased surface area
[1 mark]
Question
The development of materials with unique properties is critical to advances in industry.
Low density polyethene (LDPE) and high density polyethene (HDPE) are both addition polymers.
Outline two properties a substance should have to be used as liquid-crystal in a liquid-crystal display.
Describe how the structures of LDPE and HDPE affect one mechanical property of the plastics.
One of the two infrared (IR) spectra is that of polyethene and the other of polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE).
Deduce, with a reason, which spectrum is that of PTFE. Infrared data is given in section 26 of the data booklet.
Many plastics used to be incinerated. Deduce an equation for the complete combustion of two repeating units of PVC, (–C2H3Cl–)2.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
ability to form a LC phase
chemically stable
«LC phase that is» stable over suitable temperature range
polar
OR
being able to change orientation with applied electric field
rapid switching speed «responds to changes of voltage quickly»
Accept “ability of molecules to transmit light under certain conditions” OR “rodshaped molecules” OR “stable to light/not light sensitive”.
[Max 2 Marks]
branching in LDPE prevents close packing «of chains»
LDPE is more flexible/less rigid
OR
LDPE has lower «tensile» strength
Do not accept “difference in density”.
Award [1 max] for stating “branching in LDPE AND little/no branching in HDPE”.
B AND absence «of absorption of» C–H at 2850–3090 «cm–1»
OR
B AND presence of «absorption of» C–F at 1000–1400 «cm–1»
(–C2H3Cl–)2 (s) + 5O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + 2HCl (g)
correct species in reactants and products
balanced
Accept “(–C2H3Cl–)2 (s) + 5.5O2 (g) → 4CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l) + Cl2 (g)”.
Award M2 only if M1 correct.
Question
Both HDPE (high density polyethene) and LDPE (low density polyethene) are produced by the polymerization of ethene.
Both of these are thermoplastic polymers. Outline what this term means.
Compare and contrast the structures of HDPE and LDPE.
State one way in which a physical property of HDPE, other than density, differs from that of LDPE as a result of this structural difference.
The production of HDPE involves the use of homogeneous catalysts. Outline how homogeneous catalysts reduce the activation energy of reactions.
Trace amounts of metal from the catalysts used in the production of HDPE sometimes remain in the product. State a technique that could be used to measure the concentration of the metal.
Suggest two of the major obstacles, other than collection and economic factors, which have to be overcome in plastic recycling.
Suggest why there are so many different ways in which plastics can be classified. HDPE can, for example, be categorized thermoplastic, an addition polymer, having Resin Identification Code (RIC) 2, etc.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
soften/melt when heated
OR
can be melted and moulded
Accept “low melting point” OR “can be moulded when heated”.
[1 mark]
both have «long» hydrocarbon chains
OR
both have chains comprising CH2 units
HDPE has little/no branching AND LDPE has «more» branching
Accept “CH2–CH2 units”.
Accept “HDPE more crystalline”.
[2 marks]
HDPE is more rigid/less flexible
OR
HDPE has a higher melting point
OR
HDPE has greater «tensile» strength
Accept “HDPE has lower ductility”.
[1 mark]
form «temporary» activated complexes/reaction intermediates
Accept “consumed in one reaction/step AND regenerated in a later reaction/step”.
Accept “provides alternative mechanism”.
[1 mark]
inductively coupled plasma/ICP spectroscopy using mass spectroscopy/mass spectrometry/MS/ICP-MS
OR
inductively coupled plasma/ICP spectroscopy using optical emission spectroscopy/OES/ICP-OES
Accept “atomic absorption/aa spectroscopy” or “MS/massspectroscopy/mass spectrometry”.
[1 mark]
Any two of:
many types «of plastics» exist
OR
«plastics» require sorting «by type»
«plastics» need to be separated from non-plastic materials
OR
«often» composites/moulded on/bound to non-plastic/other components
Accept other valid factors such as thermal decomposition of some plastics, production of toxic fumes, etc.
[2 marks]
«different classifications are appropriate for» different properties/applications/purposes
[1 mark]
Question
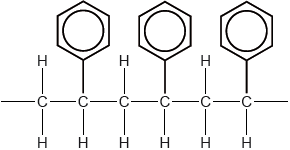
Propene can polymerize to form polypropene.
Propene monomer: 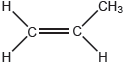
Sketch four repeating units of the polymer to show atactic and isotactic polypropene.
State the chemical reason why plastics do not degrade easily.
Compare two ways in which recycling differs from reusing plastics.
Civilizations are often characterized by the materials they use.
Suggest an advantage polymers have over materials from the iron age.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
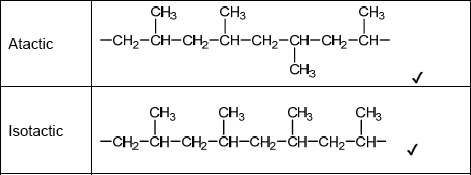
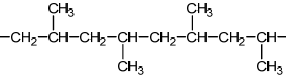
Do not accept syndiotactic (alternating orientation of the CH3 groups), eg,
for M1 or M2.
Accept any correct atactic ordering of CH3 groups.
Penalize missing hydrogens or incorrect bond connectivities once only.
Accept skeletal structures.
Ignore continuation bonds, brackets and “n” indices in structures.
[2 marks]
strong covalent bonds
Accept “moisture cannot get inside the plastic matrix, and bacteria cannot live without moisture, so they cannot attack the polymer chains”.
Accept “bacteria lack the enzymes required to break down the hydrocarbon chains”.
[1 mark]
Any two of:
Recycling: shredded/melted/reformed AND Reuse: used in its current form
recycling is more energy intensive «than reusing»
recycling degrades the quality of plastic but reusing «typically» does not
recycling breaks down original product to form a new product whereas reuse extends product life
[2 marks]
more pliable/flexible materials
OR
more durable/non-corrosive/longer-lasting materials
OR
greater variety of materials
OR
lower density
OR
can be clear/translucent
Accept “more adaptable”.
Do not accept just “more useful”.
[1 mark]

