Question
a. The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
Classify vitamins $A, C$ and $D$ as either mainly fat- or water-soluble, using section 35 of the data booklet.

b(i)The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
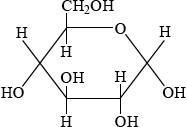
Deduce the straight chain structure of deoxyribose from its ring structure drawn in section 34 of the data booklet.
b(ii)The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
Draw the nitrogenous base that is paired with guanine in DNA, showing the hydrogen bonds between the bases. Use section 34 of the data booklet.
c. The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
Retinal is the key molecule involved in vision. Explain the roles of cis- and trans-retinal in vision and how the isomers are formed in the visual cycle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.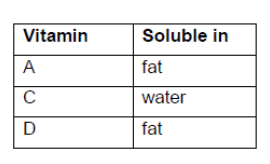
all three correct
b(i).
– $\mathrm{CH}_2$ – must be placed next to CHO AND $2 \mathrm{OH}$ s on central carbons must be on same side (LHS or RHS) Accept crosses in place of $\mathrm{C}$ on three middle carbons.
b(ii).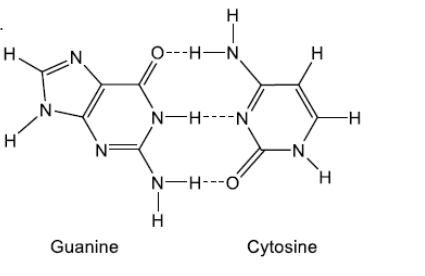
cytosine drawn
appropriate representation of three hydrogen bonds AND between correct atoms
Structure of cytosine must be given for M1.
Ignore missing hydrogens on carbon atoms in cytosine.
Dashed lines (horizontal or vertical) OR dots can be used to represent hydrogen bonds.
Only award M2 if M1 correct.
c. Any three of:
cis-retinal binds to «the protein» opsin
OR
cis-retinal «binds to opsin and» forms rhodopsin
opsin extends conjugation in retinal
OR
conjugation in rhodopsin is larger/more extended/involves more atoms than that in retinal OR
rhodopsin allows absorption of visible/blue/green light
when visible light is absorbed cis-retinal changes to trans-retinal
change «to trans-retinal» triggers an electrical/nerve signal
trans-retinal detaches from opsin $A N D$ is converted back to cis-retinal
OR
trans-retinal is converted back to cis-retinal through enzyme activity
Question
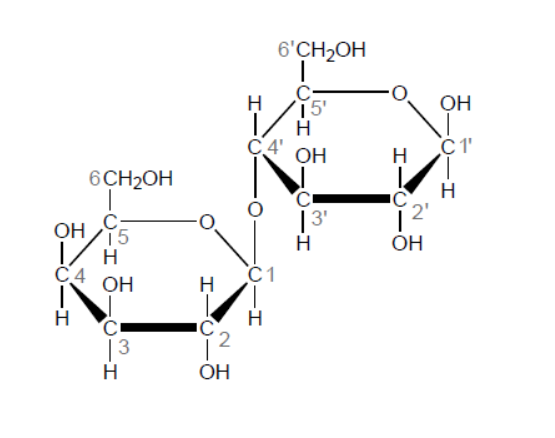
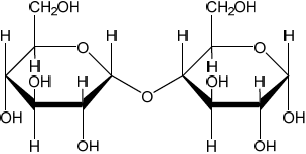
b. Outline how the two monomer structures, galactose and glucose, differ.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «1,4-»glycosidic
Do not accept “glucosidic”.
b. $\mathrm{H}$ and $\mathrm{OH}$ are reversed/in different positions on $\mathrm{C}-4$
C-4 must be specified.
Do not penalize if reference is made to $\mathrm{H}$ and $\mathrm{OH}$ above and below ring/in alpha and beta positions on $\mathrm{C}-4$ incorrectly.
Question
Starch is a natural polymer of glucose.
a. Draw the structure of the repeating unit of starch and state the type of linkage formed between these units.
Type of linkage:
b. Formulate the equation for the complete hydrolysis of a starch molecule, $\left(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{10} \mathrm{O}_5\right)_n$.
c. Calculate the energy released, in $\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{g}^{-1}$, when $3.49 \mathrm{~g}$ of starch are completely combusted in a calorimeter, increasing the temperature of $975 \mathrm{~g}$ of water from $21.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $36.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
d. Explain how the inclusion of starch in plastics makes them biodegradable.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.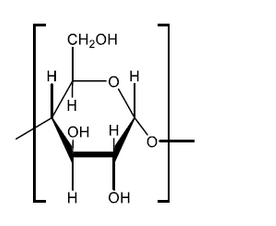
continuation bonds $A N D$-O- attached to just one end $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ both $\mathrm{H}$-atoms on end carbons must be on the same side [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
Note: Square brackets not required.
Ignore ” $n$ ” if given.
Mark may be awarded if a polymer is shown but with the repeating unit clearly identified.
Type of linkage:
glycosidic [ $\sim]$
Note: Accept “ether”.
b. $\left(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{10} \mathrm{O}_5\right) n(\mathrm{~s})+n \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l}) \rightarrow n \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_6(\mathrm{aq})[\sim]$
Note: Accept “(n-1) $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ “.
Do not award mark if ” $n$ ” not included.
c. $q=« m c \Delta T=975 \mathrm{~g} \times 4.18 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~g}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1} \times 15.0 \mathrm{~K}=» 61100$ « $» / 61.1$ «J»] [ ]
«heat per gram $=\frac{61.1 \mathrm{~kJ}}{3.49 \mathrm{~g}}=» 17.5 « \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~g}^{-1} »[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Award [2] for correct final answer.
d. Any two of:
carbohydrate grains swell/break plastic into smaller pieces [ $\checkmark]$
inclusion of carbohydrate makes the plastic more hydrophilic/water soluble $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
carbohydrates are broken down/hydrolysed/digested by bacteria/micro-organisms [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
plastic becomes more accessible to bacteria as holes/channels are created in it $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
«presence of» carbohydrate weakens intermolecular/London/dispersion forces between polymer chains in the plastic [ $\boldsymbol{\nu}$ ]
Note: Accept “starch” for “carbohydrate” throughout. Do not accept carbohydrates are broken down/hydrolyzed.
Question
Sucrose is a disaccharide.
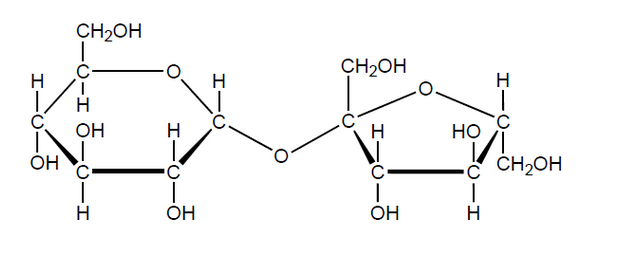
a. State the name of the functional group forming part of the ring structure of each monosaccharide unit.
b. Sketch the cyclic structures of the two monosaccharides which combine to form sucrose.
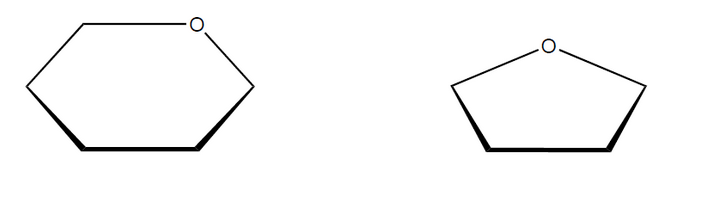
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. acetal
OR
ether $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
Note: Accept “glycosidic bond/linkage” but not “glucosidic”.
Do not accept “hemiacetal”.
b.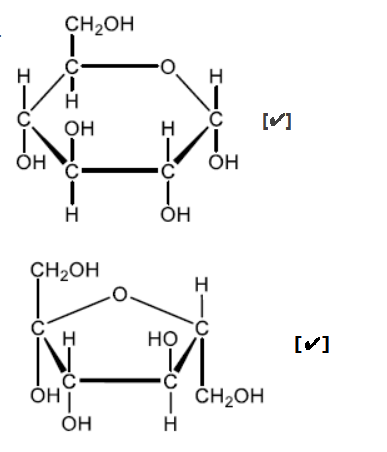
Question
Vitamins are organic compounds essential in small amounts.
a. State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of the data booklet.
b. Explain the biomagnification of the pesticide DDT.
c. Explain why maltose, $\mathrm{C}_{12} \mathrm{H}_{22} \mathrm{O}_{11}$, is soluble in water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. hydroxyl
NOTE: Accept “hydroxy” but not “hydroxide”.
Accept “alkenyl”.
Do not accept formula.
b. accumulates in fat/tissues/living organisms
OR
cannot be metabolized/does not break down «in living organisms»
OR
not excreted / excreted «very» slowly
passes «unchanged» up the food chain
OR
increased concentration as one species feeds on another «up the food chain»
NOTE: Accept “lipids” for “fat”.
c. “solubility depends on forming many» $\mathrm{H}$-bonds with water
maltose has many hydroxyl/OH/oxygen atom/O «and forms many $\mathrm{H}$-bonds»
NOTE: Reference to “with water” required.
Accept “hydroxy” for “hydroxyl” but not “hydroxide/OH”.
Reference to many/several $\mathrm{OH}$ groups/O atoms required for $M 2$.
Question
Malnutrition can be caused by starvation, dieting or a person eating an excess of highly processed food.
Describe the structural composition of the following nutrients:
fats and oils
monosaccharides.
Liver is a source of arachidonic acid, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{(CH=CHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}\), and fish oils are a source of linolenic acid. With reference to the structure of linolenic acid in Table 22 of the Data Booklet, explain why arachidonic acid has a much lower melting point compared to linolenic acid, even though it contains two more carbon atoms.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(tri)esters/contains COO group/(tri)glycerides;
(three) fatty acid chains joined to glycerol/propan-123-triol / OWTTE;
Accept long-chain carboxylic acid and glycerine.
empirical formula is \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) / general formula is \({{\text{C}}_n}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}n}}{{\text{O}}_n}\);
contains one carbonyl/C=O group and at least two/several hydroxyl/OH groups;
four C=C bonds in arachidonic acid and three C=C bonds in linolenic acid / greater unsaturation/number of C=C bonds in arachidonic acid;
presence of double bonds prevents close-packing/kinks in structure / extra double bond decreases ability of arachidonic acid molecules to align themselves together / OWTTE;
(so) van der Waals’/London/dispersion/intermolecular forces weaker in arachidonic acid;
Examiners report
The descriptions of structure in (b) often lacked the essential points – perhaps some candidates did not know how to interpret “structural composition”.
the descriptions of structure in (b) often lacked the essential points – perhaps some candidates did not know how to interpret “structural composition”.
The effect of double bonds on the intermolecular forces in unsaturated fats was well known in (c), and thankfully few candidates referred to the breaking of covalent bonds.
Question
Simple sugars are nutrients and are also described as monosaccharides.
State three characteristic features of all monosaccharide molecules.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
they have the empirical formula CH2O;
they contain one carbonyl/C=O group;
they contain at least two hydroxy/–OH groups;
Examiners report
Many candidates stated physical properties of monosaccharides rather than structural features. Those who stated structural features often only gave one or two rather than the three required.
Question
Foods such as rice, bread and potatoes are rich in carbohydrates. There are three main types of carbohydrate – monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Glucose, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\), is a monosaccharide. When 0.85 g of glucose was completely combusted in a calorimeter, the temperature of 200.10 g of water increased from 20.20 °C to 27.55 °C. Calculate the energy value of glucose in \({\text{J}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}\).
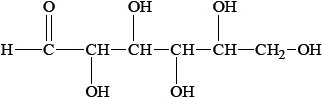
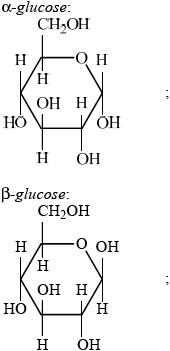
(i) Draw the straight chain structure of glucose.
(ii) Draw the structural formula of \(\alpha \)-glucose.
(iii) Distinguish between the structures of \(\alpha \)- and \(\beta \)-glucose.
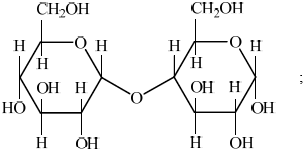
(iv) Two \(\alpha \)-glucose molecules condense to form the disaccharide maltose. Deduce the structure of maltose.
One of the major functions of carbohydrates in the human body is as an energy source. State one other function of a carbohydrate.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\Delta T = 7.35\) (K/°C);
\(q( = mc\Delta T = {\text{200.10 g}} \times {\text{4.18 J}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}{{\text{K}}^{ – 1}} \times {\text{7.35 K}}) = 6.15 \times {10^3}{\text{ J}}\) (per 0.85 g of glucose heated);
energy value \( = 7.2 \times {10^3}{\text{ (J}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}{\text{)}}\);
Award [3] for correct final answer.
(i) 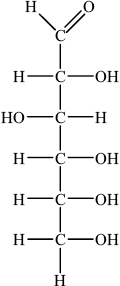
Accept CHO, CH2OH and OH groups on either side of the carbon chain provided OH on C3 is on the opposite side to OHs on C2, C4 and C5.
(ii) 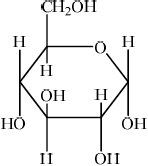 ;
;
Accept CH2OH and OH groups on either face, as long as OH on C3 is on the opposite face to the OH’s on C1, C2 and C4.
No mark awarded if HOCH2 is written, with H bonded to C or if HO is written for hydroxyl groups, with H bonded to C. Penalize this once only in (i), (ii) and (iv).
(iii) the OH on carbon-1/C-1 is inverted / difference in position of OH on carbon-1/C-1;
(iv) 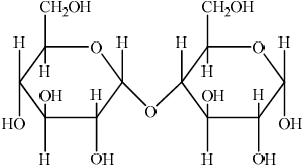 ;
;
energy reserve / can act as precursors in large number of metabolic reactions/for other biologically important molecules;
Examiners report
In (a) SD’s proved the major issue. Most candidates scored the mark for \(\Delta T\). The candidates who struggled made the following errors: incorrect mass (0.85 g) of water was used in \(q = mc\Delta T\), and failure to convert to J per g by dividing \(q\) by 0.85.
In (b)(i) many candidates struggled to draw the straight chain structure of glucose. In many instances the –OH groups were positioned incorrectly and some candidates were careless with bonding writing ‘-C–HO’ rather than ‘-C–OH’.
In (ii) a significant number of candidates mixed up the positions of the substituents on the two faces. In (iii) C1 was commonly omitted. It was surprising to see that quite a few candidates could not draw the structure of maltose in (iv). The most common mistake involved an incorrect linkage
Part (c) was answered well by the vast majority.
Question
A healthy diet consists of a range of food groups in the right proportions that provide the energy for the body to function, grow and repair itself.
Examples of straight-chain fatty acids include \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{39}}}}{\text{COOH}}\), \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{31}}}}{\text{COOH}}\) and \({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{29}}}}{\text{COOH}}\).
State the empirical formula and structural features of monosaccharides.
Deduce the structural formula of a triester formed from three long-chain carboxylic acid molecules, RCOOH, and one propane-1,2,3-triol molecule, \({\text{HO–C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CH(OH)–C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}\). Identify one of the ester linkages in the structure by drawing a rectangle around it.
Deduce the number of C=C bonds present in one molecule of each fatty acid.
\({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{39}}}}{\text{COOH}}\):
\({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{31}}}}{\text{COOH}}\):
\({{\text{C}}_{{\text{19}}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{29}}}}{\text{COOH}}\):
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\);
Accept (CH2O)n
one carbonyl/C=O and (at least two) hydroxyl/OH groups;
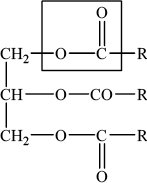
Award [1] for structure that shows unambiguously how the atoms are arranged together.
Award [1] for identifying one of the three ester linkages – must not include R and/or CH2.
\({{\text{C}}_{19}}{{\text{H}}_{39}}{\text{COOH}}\): 0
\({{\text{C}}_{19}}{{\text{H}}_{31}}{\text{COOH}}\): 4
\({{\text{C}}_{19}}{{\text{H}}_{29}}{\text{COOH}}\): 5
All three [2], any two [1], any one [0].
Examiners report
The vast majority of candidates were able to state the empirical formula of monosaccharides, but a good number were not able to state its structural features.
It was surprising to see that only about half could deduce the structure of the triester correctly and identify the ester linkage.
About half of the candidates were able to deduce the number of C=C bonds correctly from the list of fatty acids.
Question
The straight chain form of glucose is represented below.
Fructose is an isomer of glucose, but they differ with regard to one functional group and hence in their redox properties.
Glucose is mainly present in one of two cyclic forms: \(\alpha \)-glucose and \(\beta \)-glucose. Distinguish between the two cyclic forms by completing the diagrams below.
(i) Identify the functional group present in glucose, but not fructose.
(ii) Identify the functional group present in fructose, but not glucose.
(iii) Identify the sugar that acts as a reducing agent.
Outline how the structure of cellulose is related to that of glucose.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\alpha \): C-1 OH below plane
 ;
;
\(\beta \): C-1 OH above plane
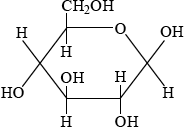 ;
;
(i) aldehyde/alkanal/CHO;
(ii) ketone/alkanone/CO;
(iii) glucose;
cellulose is (condensation) polymer of \(\beta \)-glucose;
(rings in cellulose) joined by \(\beta \)-1,4 linkages;
Examiners report
Part (a) was generally well answered with full marks awarded to more than half of the candidates. Those who did not score full marks usually reversed OH on carbon 4. Glucose has an aldehyde functional group which can undergo oxidation and this was covered in Topic 10. The fact that cellulose is a polymer of glucose and has beta-1,4 linkages seemed to have been overlooked by many candidates.
Glucose has an aldehyde functional group which can undergo oxidation and this was covered in Topic 10.
The fact that cellulose is a polymer of glucose and has beta-1,4 linkages seemed to have been overlooked by many candidates.
Question
Most foods are complex mixtures and many components of them are nutrients.
Identify the types of nutrients A, B and C.
A 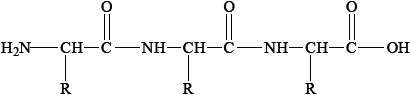
B 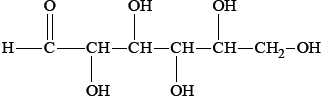
C 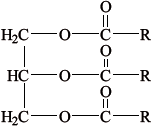
State the names of two types of nutrient other than those shown in part (b).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A: protein / polypeptide/tripeptide;
B: carbohydrate / sugar / monosaccharide / glucose;
C: lipid / triglyceride / vegetable oil / fat;
vitamins;
minerals;
water;
Examiners report
This question was generally well answered by many candidates. Though most had a general idea of the difference between a food and a nutrient, many did not appreciate the distinction between an “unhealthy” food and one that isn’t a nutrient.
This question was generally well answered by many candidates. Though most had a general idea of the difference between a food and a nutrient, many did not appreciate the distinction between an “unhealthy” food and one that isn’t a nutrient.
Question
Monosaccharides and disaccharides are classes of carbohydrates.
Describe the structural features of monosaccharides.
Draw the structures of \(\alpha \)-glucose and \(\beta \)-glucose.
\[\alpha {\text{ – glucose}}\quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \beta {\text{ – glucose}}\]
Two \(\alpha \)-glucose molecules condense to form the disaccharide maltose. Draw the structure of maltose.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
contain carbonyl (group)/C=O;
have at least two hydroxyl/OH (groups);
Do not accept hydroxide instead of hydroxyl.
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) empirical formula;
Do not accept CxH2yOy or C6H12O6.
Award [1 max] if position of OH is correct in both structures at C1 but other groups/moieties (eg, CH2OH) or H are missing.
Award [1 max] if the alpha and beta structures are labelled in reverse.
Examiners report
Only some of the candidates described a monosaccharide correctly in part (a) although its features are given in the programme guide. Drawing alpha and beta glucose was also a discriminating question.
About a third of candidates were able to score full marks on part (b)(i).
Similarly, drawing maltose in part (d)(ii) was a challenge for the majority of candidates. Many had missing hydrogen atoms or an incorrect orientation of bonds around the linkage.
Question
Foods such as pasta are rich in carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides are a type of carbohydrate.
State why a professional cyclist would eat pasta before a race.
(i) Fructose, a monosaccharide, is found in honey. Draw the straight-chain structure of fructose.
(ii) Draw the five-membered ring structure of \(\beta \)-fructose.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(source of) energy;
(i) 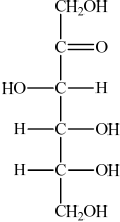 ;
;
Accept any six-carbon linear structure in which the second carbon is a carbonyl and there is one OH on all other carbons.
(ii) 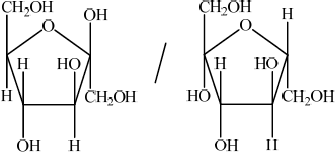 ;
;
Correct orientation of groups is required.
Allow Haworth projection, ie,
Examiners report
Almost all candidates related pasta to energy.
(i) Only a few candidates were able to draw the straight-chain structure of fructose.
(ii) About a quarter of the candidates were able to draw the five-membered ring structure of \(\beta \)-fructose. Many candidates had the orientation that suggested they drew the structure by referring to the structure of sucrose in the Data Booklet. A common mistake was missing the –OH at the position of the glycosidic link in sucrose.
Question
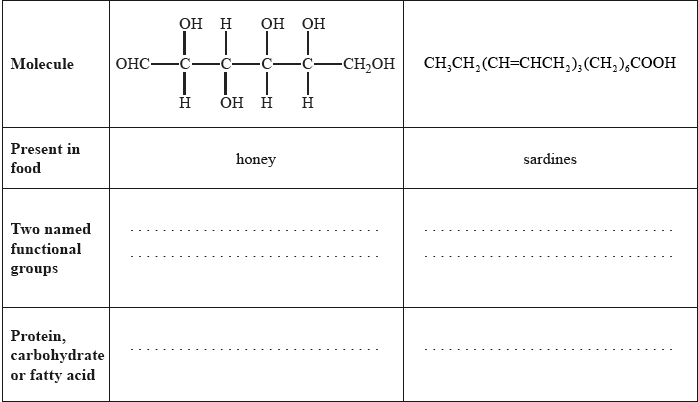
Food chemistry and nutritional science are two important scientific fields to which the general public relate.
State two named functional groups present in each of the following molecules found in two different food products (honey and sardines). Identify each molecule as a protein, a carbohydrate or a fatty acid.
Butter is an example of a saturated fat and olive oil is an example of an unsaturated fat. Describe the main structural difference between these two types of fat.
Linoleic acid, whose structure is given in Table 22 of the Data Booklet, is present in peanut oil. The oil can be converted to a semi-solid using hydrogen gas. Predict the structural formula of the compound formed from the partial hydrogenation reaction of linoleic acid, and state a suitable catalyst for this reaction.
Structural formula:
Catalyst:
Partial hydrogenation can sometimes produce trans fats. Suggest why trans fats are considered unhealthy.
Olestra, with one of its structures shown below, has been used to prepare snacks such as crisps (potato chips). Deduce the type of compound that can undergo an esterification reaction involving carboxylic acid to produce olestra.
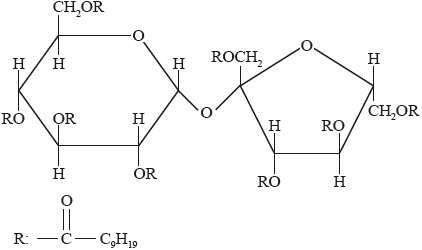
Olestra
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
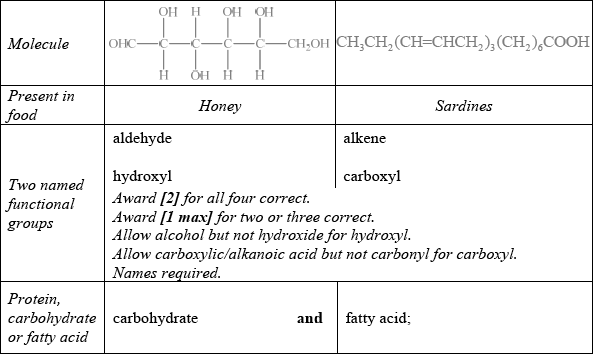
Saturated fat: no carbon-carbon double bonds/no C=C/all single carbon-carbon bonds/ all C–C and Unsaturated fat: carbon-carbon double bonds/C=C/alkene groups;
Mention of carbon-carbon or alkene necessary for mark.
Structural formula:
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{)}}_4}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CH}}\)=\({\text{CH(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{)}}_7}{\text{COOH}}\) /
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{)}}_4}{\text{CH}}\)=\({\text{CHC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{)}}_6}{\text{COOH}}\);
Catalyst: nickel/Ni / palladium/Pd / platinum/Pt / copper/Cu / zinc/Zn;
decrease (blood) levels of HDL/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (which protects from heart disease) / increase levels of LDL/low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (increasing risk of heart disease) / less easily digested/metabolized / leads to blocked arteries;
carbohydrate / disaccharide;
Allow sucrose / sugar.
Examiners report
Well answered with most candidates gaining two marks. The most common mistake was failing to recognize OHC– as an aldehyde.
The majority of candidates distinguished between saturated and unsaturated fats correctly.
The catalyst was usually well suggested but the structural formula was only provided by the strongest candidates. Some candidates gave the saturated product not taking note of the word “partial” in the question.
Another question better answered than in previous sessions. Many candidates related trans fats to LDL cholesterol.
This was a discriminating question. Only a few candidates recognized the compound as a carbohydrate.
Question
Carbohydrates are energy-rich molecules which can be synthesized in some plant cells from inorganic compounds.
State the raw materials and source of energy used in the process described above.
The structures of two molecules, X and Y, are shown below.
(i) Justify why both these molecules are carbohydrates.
(ii) Distinguish between these molecules in terms of their functional groups.
Amylose is an unbranched polysaccharide composed of repeating units of glucose.
(i) Draw the structure of the repeating unit of amylose. Use section 34 of the data booklet.
(ii) Amylose is a major component of starch. Corn starch can be used to make replacements for plastics derived from oil, especially for packaging. Discuss one potential advantage and one disadvantage of this use of starch.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
CO2 AND H2O AND sun
Accept names.
Accept “sunlight/light/photons” instead of “sun”.
i
both have formula Cx(H2O)y
OR
both contain several OH/hydroxyl «groups» AND a C=O/carbonyl «group»
Accept “both have the formula CnH2nOn /empirical formula CH2O” but do not accept “both have same molecular formula/have formula C3H6O3”.
Accept “aldehyde or ketone” for “carbonyl”.
ii
Accept “alkyl” for “R”.
Accept “X: aldose/aldehyde AND Y: ketose/ketone”.
Accept “CO” for “C=O”.
i
continuation bonds AND open O on either but not both ends
Brackets are not necessary for the mark.
Do not accept β-isomer.
Mark may be awarded if a polymer is shown but with the repeating unit clearly identified.
3-D representation is not required.
ii
Advantage:
Any one of:
biodegradable / break down naturally/by bacteria
Do not accept just “decompose easily”.
compostable
does not contribute to land-fill
renewable/sustainable resource
starch grains swell AND help break up plastic
lower greenhouse gas emissions
uses less fossil fuels than traditional plastics
less energy needed for production
Disadvantage:
Any one of:
land use «affects biodiversity/loss of habitat»
growing corn for plastics instead of food
«starch» breakdown can increase acidity of soil/compost
«starch» breakdown can produce methane «especially when buried»
sensitive to moisture/bacteria/acidic foods
«bioplastics sometimes» degrade quickly/before end of use
cannot be reused
poor mechanical strength
eutrophication
increased use of fertilizers/pesticides/phosphorus/nitrogen «has negative environmental effects»
Ignore any reference to cost.
Accept “prone to site explosions/fires” or “low heat resistance” for disadvantage.
Only award [1 max] if the same example is used for the advantage and disadvantage.
Question
Lipids and carbohydrates contain the same elements but have different properties.
List the building blocks of triglycerides and carbohydrates.
The drain pipe of a kitchen sink can become clogged by fatty acids, such as linoleic acid, C18H32O2, but not by the trisaccharide, raffinose, C18H32O16, containing the same number of carbon atoms.
Explain why raffinose is far more water soluble than linoleic acid.
Solid fat triglycerides can also clog kitchen sink drains.
Explain how sodium hydroxide unblocks the drain.
The amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates determine the energy content of foods.
Explain why linoleic acid, C18H32O2, is a more efficient energy storage molecule than raffinose, C18H32O16.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Triglycerides:
organic acid/fatty acid and glycerol/propane-1,2,3-triol
AND
Carbohydrates:
monosaccharides
Accept simple sugars.
[1 mark]
«water/aqueous solubility depends on forming many» H-bonds with water
raffinose has many hydroxyl/O–H/oxygen atoms/O «and forms many H-bonds» AND linoleic acid has few/one hydroxyl/O–H/oxygen atom/O/carboxyl group/ COOH/is largely non-polar «and cannot form many H-bonds»
Accept statement which implies comparison.
[2 marks]
«base» hydrolysis/saponification
OR
«produces glycerol and» soap/salt of the «fatty» acid
«products are» water soluble «and drain away»
Accept condensed formulas.
Accept non-balanced equation.
Accept “RCOONa”.
[2 marks]
linoleic acid/C18H32O2 combustion/oxidation more exothermic «per mol»
linoleic acid/C18H32O2 has lower proportion/number of O atoms
OR
linoleic acid/C18H32O2 is less oxidized
Accept converse arguments.
[2 marks]
Question
Sugars exist in both straight chain and ring forms.
Biodegradable plastics produced from starch present one solution to the environmental problem created by the use of large quantities of plastics.
Deduce the straight chain structure of ribose from its ring structure drawn in section 34 of the data booklet.
Using the partial structure given, complete the structural formula of the molecule formed from the condensation of two cyclic \(\alpha \)-glucose molecules.
Constructing models that allow visualizations of the stereochemistry of carbohydrates is essential to understand their structural roles in cells.
Describe how Haworth projections help focus on the position of attached groups.
State one advantage of starch based polymers besides being biodegradable.
Biodegradable boxes made from polylactic acid, PLA, disintegrate when exposed to water.
State the formula of the product formed when water reacts with PLA.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
All OH groups must be on the same side.
Accept structures with chiral carbon atoms shown as C or C* instead of crosses.
[1 mark]
Accept –O– in a straight line provided both H’s are above the plane.
[1 mark]
«allow» 3-D perspective of structures «of cyclic monosaccharide molecules»
OR
«show» cis/same side arrangement of «attached» groups
OR
«show» trans/opposite side arrangement of «attached» groups
OR
«make» carbon and hydrogen implicit
[1 mark]
abundant/renewable/allows use of «local» vegetation
OR
less use of fossil fuel/oil based plastics
OR
air permeable/better breathing of products
OR
«can be» mixed/blended with synthetic polymers
Do not accept answers related to biodegradable examples.
Ignore any reference to cost.
Accept “carbon neutral/do not contribute to global warming”.
Accept “require less energy to produce”.
Accept “do not produce toxic products”.
[1 mark]
HO–CH(CH3)–COOH/CH3CH(OH)COOH
Do not accept C3H6O3.
Do not accept OH–CH(CH3)–COOH.
[1 mark]
Question
Monosaccharides can combine to form disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Identify the functional groups which are present in only one structure of glucose.
Sucrose is a disaccharide formed from \(\alpha \)-glucose and β-fructose.
Deduce the structural formula of sucrose.
Starch is a constituent of many plastics. Suggest one reason for including starch in plastics.
Suggest one of the challenges scientists face when scaling up the synthesis of a new compound.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Only in straight chain form:
carbonyl
OR
aldehyde
Only in ring structure:
hemiacetal
Accept functional group abbreviations (eg, CHO etc.).
Accept “ether”.
[2 marks]
correct link between the two monosaccharides
Correct 1,4 beta link AND all bonds on the 2 carbons in the link required for mark.
Ignore any errors in the rest of the structure.
Penalize extra atoms on carbons in link.
[1 mark]
plastic «more» biodegradable/degrades into nontoxic products
OR
plastic can be produced using green technology/renewable resource
OR
reduces fossil fuel use/petrochemicals
OR
easily plasticized
OR
used to form thermoplasts
[1 mark]
minimize «negative» impact on environment
OR
minimize waste produced
OR
consider atom economy
OR
efficiency of synthetic process
OR
problems of side reactions/lower yields
OR
control temperature «inside large reactors»
OR
availability of starting/raw materials
OR
minimize energy costs
OR
value for money/cost effectiveness/cost of production
[1 mark]
Question
Lactose is a disaccharide formed by the condensation reaction of the monosaccharides galactose and glucose.
Describe what is meant by a condensation reaction.
Draw the structure of galactose on the skeleton provided.
Explain how the inclusion of carbohydrates in plastics makes them biodegradable.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«reaction in which» two reactants/molecules/functional groups bond/react «to form a larger molecule/single main product»
small/tiny molecule
OR
H2O formed
Accept formula or name of a specified small molecule other than water such as ammonia, ethanoic/acetic acid,
ethanol, hydrogen sulfide etc. for M2.
Do not accept just “molecule formed”.
Award [1 max] for an example giving an equation of a condensation reaction such as the formation of a disaccharide.
Accept “alpha” or “beta” form of galactose.
Any two of:
makes the plastic more hydrophilic/water soluble
carbohydrates are broken down/hydrolysed by bacteria/microorganisms
makes plastic more accessible to bacteria as holes/channels are created
OR
plastic of lower density is more permeable/susceptible to water/oxygen/heat/pressure
weakens intermolecular/London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces «between polymer chains in the plastic»
Accept “van der Waals/vdW” for “London” forces.
[Max 2 Marks]
Question
Polymers of α-glucose include the disaccharide maltose and the polysaccharide amylose, a type of starch. The cyclic structure of α-glucose is shown in section 34 of the data booklet.
State the specific type of linkage formed between α-glucose fragments in both maltose and amylose.
A person with diabetes suffering very low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) may be advised to consume glucose immediately and then eat a small amount of starchy food such as a sandwich. Explain this advice in terms of the properties of glucose and starch.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«α-1,4-»glycosidic
Accept «α-1,4-»glycoside.
Accept “ether”.
[1 mark]
Glucose:
readily passes through intestine wall/dissolves in blood
OR
is immediately available for energy/respiration
OR
transported rapidly around body
Starch:
must be hydrolysed/broken down «into smaller molecules» first
[2 marks]
Question
Lipids provide energy and are an important part of a balanced diet.
Identify the type of chemical reaction that occurs between fatty acids and glycerol to form lipids and the by-product of the reaction.
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid found in peanut oil.
Determine the number of carbon–carbon double bonds present if the iodine number for the compound is 334. (Arachidonic acid Mr = 304.5)
Deduce the structure of the lipid formed by the reaction between lauric acid and glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) using section 34 of the data booklet.
Outline one impact food labelling has had on the consumption of foods containing different types of lipids.
Determine, to the correct number of significant figures, the energy produced by the respiration of 29.9 g of C5H10O5.
ΔHc (C5H10O5) = 205.9 kJ mol−1
Explain why lipids provide more energy than carbohydrates and proteins.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Type of reaction:
condensation
OR
esterification/triesterification
OR
nucleophilic substitution/nucleophilic displacement/SN2
By-product:
water/H2O
Do not accept just “substitution/displacement”.
[2 marks]
ALTERNATIVE 1
«\(\frac{{334}}{{253.8}}\) =» 1.32 AND «\(\frac{{100}}{{304.5}}\) =» 0.328
«\(\frac{{1.32}}{{0.328}}\) ≈» 4
ALTERNATIVE 2
«334 × \(\frac{{304.5}}{{100}}\) ≈» 1017
«\(\frac{{1017}}{{253.8}}\) ≈» 4
Award [2] for correct final answer.
[2 marks]
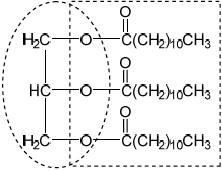
glycerol backbone
ester formula AND linkage
Accept a skeletal structure.
Penalize missing hydrogens or incorrect bond connectivities once only in Option B.
Accept condensed formula for ester.
[2 marks]
has affected consumption of trans-fats/cis-fats/saturated fats/unsaturated fats/hydrogenated/artificially altered fats
OR
reduce/eliminate trans-fats/increase in cis-fats
OR
reduce/eliminate saturated fats
OR
increase unsaturated fats
Do not accept “decrease in fat” alone.
Accept “lipid” for “fats”.
[1 mark]
«\(\frac{{29.9{\text{ g}}}}{{150.15{\text{ g mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\) =» 0.199 «mol»
«0.199 mol × 205.9 kJ mol–1 =» 41.0 «kJ»
Ignore significant figures in M1.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Award [1 max] for incorrect significant figures in final answer.
[2 marks]
ratio of oxygen to carbon in lipids lower
OR
lipids less oxidized
OR
lipids more reduced
more energy per mass/g released when lipids are oxidized
Accept “«average» oxidation number of carbon in linoleic acid is lower” for M1.
[2 marks]

