Question
Consider the structures of medicinal molecules in section 37 of the data booklet.
a. Explain how zanamivir works as a preventative agent against flu viruses.
b(i)Circle the side-chain in penicillin on the structure below.
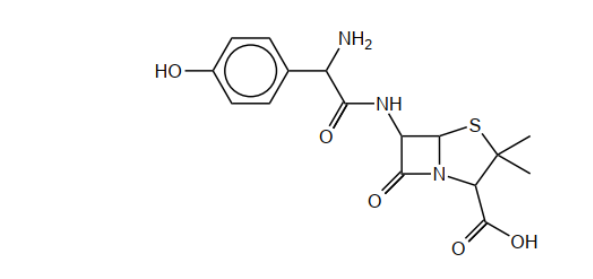
b(iiExplain, with reference to the action of penicillin, why new penicillins with different side-chains need to be produced.
c(i)State and explain the relative solubility of codeine in water compared to morphine and diamorphine.
c(ii) State the natural source from which codeine, morphine and diamorphine are obtained.
d. Circle two chiral carbons in the section of the Taxol structure below.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «drug» blocks/inhibits «viral» enzyme/neuraminidase/NA «activity» prevents virus from leaving/escaping host cells «thus cannot infect other cells»
Do not accept other anti-viral methods (as question is specific to Zanamivir).
b(i).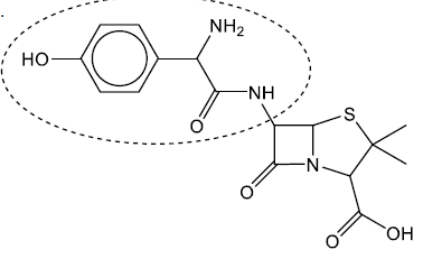
Accept a circle that does not surround the amido group.
Do not accept a circle that only surrounds the phenol group.
b(iibacterial resistance «to older penicillins/antibiotics»
prevent penicillinase/beta-lactamase/enzyme in bacterium to deactivate/open penicillin/beta-lactam ring
Accept “antibiotic resistant bacteria” but not “antibiotic resistance” for M1.
Accept “reduce allergic reactions from penicillin” for M2.
Award [1 max] for “increased efficiency” OR “increased stability in GIT”.
Do not accept “bacteria develop tolerance”.
c(i)codeine less soluble «in water» than morphine $A N D$ more soluble than diamorphine
OR
morphine > codeine > diamorphine «in terms of solubility in water»
more/stronger/greater hydrogen/ $\mathrm{H}$ bonding «due to more hydroxyl groups leads to greater solubility»
c(ii)pium poppy/plants/seeds
Accept “poppy” OR “opioid”.
d.
any two chiral carbons identified
Question
Aspirin can be obtained from salicylic acid.
Unreacted salicylic acid may be present as an impurity in aspirin and can be detected in the infrared (IR) spectrum.
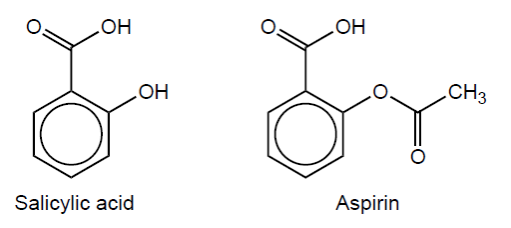
Name the functional group and identify the absorption band that differentiates salicylic acid from aspirin. Use section 26 of the data booklet.
Name:
Absorption band:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Name:
hydroxyl [ $\checkmark]$
Absorption band:
$3200-3600 \ll \mathrm{cm}^{-1} »[V]$
Note: Accept “phenol” OR “alcohol” but not “hydroxide”.
Question
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infections have been successfully treated with penicillin and penicillin derivatives.
a. Identify the feature in penicillin responsible for its antibiotic activity.
$\mathrm{b}(\mathrm{i})$ The widespread use of penicillin and its derivatives has led to the appearance of resistant $S$. aureus strains.
Outline how these bacteria inactivate the antibiotics.
$\mathrm{b}(\mathrm{ii}$ Putline how the structure of penicillin has been modified to overcome this resistance.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «four-membered» beta-lactam ring $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Note: Accept a diagram showing a structural representation of the beta-lactam ring.
b(i)produce penicillinase/enzyme that deactivates penicillin [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
b(iiside-chain changed «preserving beta-lactam ring» [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Note: Accept “R group changed”.
Question
\text { A student synthesized aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, in a school laboratory. }
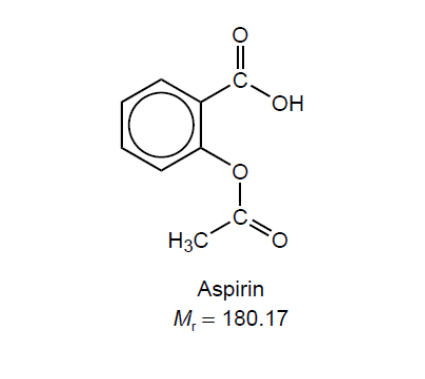
$0.300 \mathrm{~g}$ of crude aspirin was dissolved in ethanol and titrated with sodium hydroxide solution, $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})$.
$$
\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{C}_9 \mathrm{H}_8 \mathrm{O}_4(\text { in ethanol }) \rightarrow \mathrm{NaC}_9 \mathrm{H}_7 \mathrm{O}_4(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})
$$
a. Predict one absorption band present in an infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin, using section 26 of the data booklet.
$b(i)$ Determine the mass of aspirin which reacted with $16.25 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of $0.100 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3} \mathrm{NaOH}$ solution.
$b$ (iiDetermine the percentage purity of the synthesized aspirin.
c. Outline how aspirin can be chemically modified to increase its solubility in water.
d. State why aspirin should not be taken with alcohol.
e. Outline two factors which must be considered to assess the greenness of any chemical process.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any one of:
$1050-1410 \ll \mathrm{cm}^{-1}$ due to C-O»[ [
1700-1750 «cm ${ }^{-1}$ due to $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ in acids and esters» [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}$ ]
2850-3090 «cm ${ }^{-1}$ due to $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ in alkanes and arenes» [ $\boldsymbol{V}$ ]
$\mathrm{b}(\mathrm{i}) \mathrm{n}($ aspirin $) «=\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{NaOH})=\frac{16.25 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{1000} \times 0.100 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3} »=1.625 \times 10^{-3}$ «mol»[ [ ]
$\mathrm{m}\left(\right.$ aspirin) «= $1.625 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~mol} \times 180.17 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} »=0.293$ «” [
Note: Award [2] for correct final answer.
c. convert to a salt
OR
react with sodium hydroxide/ $\mathrm{NaOH}[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept other reactions forming soluble salts.
Accept “to ionize” but not “more polar”.
d. synergistic effect/increased toxicity
OR
increased risk of stomach/intestines bleeding/ulcers/heartburn
OR
increased risk of liver toxicity/damage
OR
increased risk of nausea/vomiting $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
e. Any two of:
energy requirements «during production» $[\checkmark]$
use of toxic materials «during production» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
use of solvents «that are not recycled» $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
emission of toxic by-products $[\boldsymbol{\sim}$ ]
quantity of waste produced
OR
atom economy $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Note: Accept “E-factor/carbon efficiency/\% of carbon in reactants vs products” for M1.
Accept references to materials being/not being recycled for $M 3$.
Question
\text { The structure of aspirin is shown in section } 37 \text { of the data booklet. }
a. Suggest one reactant used to prepare aspirin from salicylic acid.
b. Aspirin, $\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_4\left(\mathrm{OCOCH}_3\right) \mathrm{COOH}$, is only slightly soluble in water.
Outline, including an equation, how aspirin can be made more water-soluble. Use section 37 in the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.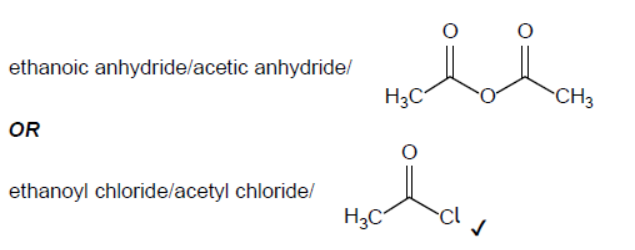
NOTE: Accept condensed structural formulas.
Accept “ethanoic acid/acetic acid/ $\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}^{\mathrm{CO}}$ “
Accept ” $\mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_6 \mathrm{O}_3$ ” OR ” $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{OCl}$ “.
b. react with sodium hydroxide/ $\mathrm{NaOH} /$ «strong» base
OR
convert to «ionic» salt
NOTE: Accept other suitable bases (eg, $\mathrm{KOH} / \mathrm{NaHCO}_3 / \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{CO}_3$ ) with corresponding equation for chosen base for $\mathrm{M} 2$.
Accept ” $\mathrm{CaCO}_3$ “, although calcium salicylate is not water soluble.
Accept ionic equation.
$\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_4\left(\mathrm{OCOCH}_3\right) \mathrm{COOH}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq}) \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_4\left(\mathrm{OCOCH}_3\right) \mathrm{COONa}(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ (I)
NOTE: Award [2] for M2.
Question
Infectious diseases can be caused by bacteria or viruses.
a. State one difference between bacteria and viruses.
b. Discuss two difficulties, apart from socio-economic factors, associated with finding a cure for AIDS.
c. The discovery of penicillins contributed to the development of antibiotics.
Explain how the beta-lactam ring is responsible for the antibiotic properties of penicillin. Refer to section 37 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any one of:
bacteria perform living functions «on their own and viruses do not without host cell»
OR
bacteria have cell walls «and viruses do not»
OR
bacteria do not have a capsid «and viruses do»
OR
bacteria larger than viruses
OR
bacteria reproduce by fission/budding «and viruses reproduce within a living host cell»
OR
bacteria affected by antibiotics «while viruses are not»
NOTE: Accept “bacteria have flagella/cytoplasm/ribosome “and virus can have head/protein tail/double stranded RNA/single stranded DNA»”
Accept “asexual reproduction” for bacteria.
Accept other specific structural differences between bacteria and viruses, and examples of living functions that bacteria perform (such as excretion, reproduction etc.) that viruses do not.
Accept “bacteria are living and viruses are not”
b. Any two of:
HIV difficult to detect/remains dormant
HIV mutates rapidly/quickly
NOTE: Do not accept “AIDS mutates” without mention of the HIV/virus.
HIV replicates rapidly/quickly
HIV destroys «T-» helper cells/white blood cells/lymphocytes
OR
HIV attacks immune system
HIV has several «significantly different» strains/subtypes $\checkmark$
NOTE: Accept “virus” for “HIV”.
Penalize the use of “AIDS” for “HIV” once only.
Accept “HIV metabolism linked to that of host cell” OR “drugs harm host cell as well as HIV”.
c. ring is «sterically» strained
OR
angles of $90^{\circ}$ instead of $109.5 / 109 / 120^{\circ}$ angles
OR
angles smaller than 109.5/109/120\%/tetrahedral/trigonal planar/triangular planar angle
NOTE: Accept arguments using correct descriptions of hybridization for M1.
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amido/amide group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
«irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of «bacterial» cell walls
NOTE: Do not accept “breaks/binds to cell walls” – a reference to the enzyme is needed for alternatives 1 and 2 for M3.
Do not accept “cell membrane” for “cell wall” for M3.
Question
Analgesics are used to relieve pain in the body. Aspirin and paracetamol (acetaminophen) are both mild analgesics.
The structures of the strong analgesics morphine and heroin (diamorphine) can be found in Table 20 of the Data Book
Compare how mild and strong analgesics relieve pain in the body.
Identify the amine functional group in the morphine molecule below by drawing a ring around it.
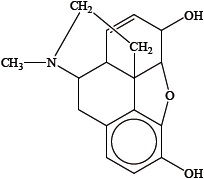
State the name of the functional group found in heroin but not in morphine.
State one advantage and one disadvantage of using morphine as a strong analgesic.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
mild analgesics function by intercepting the pain stimulus at the source / interfere with the production of substances that cause pain/prostaglandins;
strong analgesics work by bonding to receptor sites in the brain / prevent the transmission of pain impulses without depressing the central nervous system;
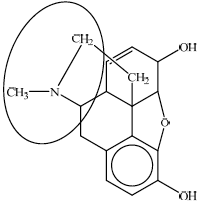
any circle around the nitrogen atom / the nitrogen atom and its three neighboring atoms;
ester;
Advantage: antidiarrheal/constipation (in treatment of diarrhea) / reduces coughing;
Disadvantage: addiction / tolerance / risk of overdose;
Examiners report
Most candidates were able to distinguish between the ways mild analgesics and strong analgesics relieve pain in part (b).
A substantial number of candidates failed to identify the tertiary amine in the structure of morphine. Candidates were inaccurate in drawing a circle around the amine group in part (c). Either just the nitrogen atom or nitrogen atom with its three neighbouring atoms should have been circled.
A large number of candidates confused the ester with an ether or carbonyl group as the functional group found in heroin but not in morphine.
Most candidates recognized the disadvantage of using morphine but they had extreme difficulty in stating a specific advantage for using morphine as a strong analgesic.
Question
Antibacterials are drugs that kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms that cause infectious diseases. The general structure of penicillin, an antibacterial, is given below.
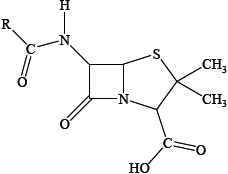
With reference to the structure above, state what the letter R represents and discuss how penicillins can be made more resistant to the penicillinase enzyme.
Describe and explain one effect of overprescription of antibacterials.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
side chain/alkyl group;
Accept hydrocarbon chain.
modify side chain / use different R groups;
Ignore reference to functional groups.
may wipe-out helpful/useful/beneficial bacteria (in the alimentary canal);
destroyed bacteria may be replaced by more harmful bacteria;
leads to resistance / makes penicillin less effective;
resistant bacteria grow / pass on their immunity/mutation/trait to succeeding generations / OWTTE;
Examiners report
Most candidates knew that R is a side chain, although some identified it as a functional group.
Some candidates got confused with over-prescription of antibiotics and answered that the body becomes resistant or dependent.
Question
Alexander Fleming, Howard Florey and Ernst Chain shared the Nobel Prize for “the discovery of penicillin and its curative effect in various infectious diseases”.
Ampicillin is a semi-synthetic penicillin used to treat lung infections. The structure of the antibiotic is shown below.
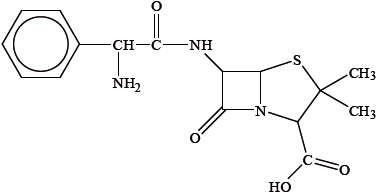
Describe the mode of action of penicillins in treating infectious diseases.
Identify two functional groups present in the side chain (R) of ampicillin by comparing its structure to that of penicillin in Table 20 in the Data Booklet.
Explain why it is important to continue to develop semi-synthetic penicillins.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
interfere with cell wall formation (in bacteria) / prevent formation of crosslinks within cell wall;
Accept “destroys cell wall”.
size/shape of cell cannot be maintained / water enters the cell / osmosis occurs / cell bursts/disintegrates;
benzene/aromatic ring/ C6H5 /phenyl;
Accept the circle-in-hexagon or Kekule symbols
Do not allow benzene or arene.
amine/ NH2 / amino;
Do not award mark if reference to secondary/tertiary given.
to overcome the resistance that bacteria develop to existing antibiotics / increases resistance to penicillinase enzyme / OWTTE;
Do not accept “over prescription”.
prevents penicillinase enzyme from destroying penicillin / molecules have different shape/stability/solubility/side-chain / OWTTE;
Examiners report
The mode of action of penicillin in treating infectious diseases was generally well understood although some candidates referred to viruses instead of bacteria in their answers.
The two functional groups were usually correctly identified in (b) although some candidates lost marks due to imprecise answers: benzene instead of benzene ring, amide instead of amine.
Similarly explanations in (b) (ii) were often vague and failed to score the marks.
Question
Aspirin, paracetamol (acetaminophen), morphine and diamorphine (heroin) are all pain killers. Their structures are given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet.
Aspirin is thought to interfere with the production of prostaglandins. Explain how this produces an analgesic effect.
Explain how morphine can prevent pain.
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is generally considered to be safe to use as an analgesic in small doses. Other than the possibility of death, outline the problems associated with taking larger doses of paracetamol.
State one important use for aspirin other than the relief of pain and fever.
Explain what is meant by the term tolerance and suggest why this is a particular problem for heroin users.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
prostaglandins are involved in the transmission of pain impulses (to the brain) / OWTTE;
morphine (temporarily) bonds to/inhibits receptor sites in the brain (without depressing central nervous system) / OWTTE;
causes blood disorders;
causes damage to kidney;
causes damage to liver;
causes damage to brain;
preventing (recurrence of) heart attacks/strokes / reduces blood clotting / thins the blood / anti-inflammatory;
tolerance: more of the drug needs to be taken to achieve the initial effect / OWTTE;
in order to achieve the desired effect heroin users may reach/exceed the lethal dose / heroin users are more likely to commit crimes to pay for gradually increasing doses of the drug / OWTTE;
Examiners report
This question was generally answered very well compared with other sections of the paper. In part (a) most candidates knew that prostaglandins is involved in the transmission of pain impulses to the brain.
In part (b) there was some confusion between signals and receptors when describing how morphine can prevent pain.
In part (c) most candidates could outline problems associated with larger doses of paracetamol (acetaminophen), although some candidates confused aspirin and paracetamol and incorrectly referred to Reye’s syndrome or stomach bleeding.
Most candidates stated a use for aspirin other than relief of pain or fever in part (d).
In part (f) most candidates successfully stated the meaning of tolerance and suggested why it is a particular problem for heroin users.
Question
The first penicillin to be used was benzylpenicillin (Penicillin G), its structure is shown below.
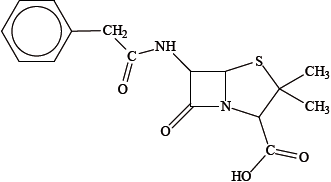
Explain how penicillins are able to act as antibacterials.
Modern penicillins have a similar structure to Penicillin G but a different side-chain.
State two advantages of modifying the side-chain.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
penicillins interfere with the enzymes that bacteria need to make cell walls / interfere with formation of bacterial cell wall / OWTTE;
the increased osmotic pressure causes the bacterium to die / the bacterial cells absorb too much water and burst / OWTTE;
resistant to penicillinase enzyme / more resistant to bacteria breaking it down / effective against bacteria which are resistant (to penicillin G);
resistance to breakdown by stomach acid (so can be taken orally) / OWTTE;
Examiners report
In part (a) there were some very good, very detailed explanations of how penicillins act as antibacterials, and some very vague statements.
Many candidates scored only half marks for part (b) by correctly referring to resistance, although they correctly discussed the use of a cocktail of antibiotics to treat tuberculosis in part (c).
Question
Mild analgesics such as aspirin, and strong analgesics such as opiates, differ not only in their potency but also in the ways they act on the central nervous system.
(a) Describe how mild and strong analgesics provide pain relief.
Mild analgesics:
Strong analgesics:
(b) Discuss two advantages and two disadvantages of using morphine and other opiates for pain relief.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(a) Mild analgesics:
suppress the production of prostaglandins/pain-sensitizing substances / intercept the pain stimulus at the source;
Strong analgesics:
bind to (opioid) receptors in the CNS/central nervous system/brain / suppress the transmission of pain impulses to the brain / OWTTE;
(b) Advantages: [2 max]
strong(er) analgesics / relieve acute/extreme pain;
wide therapeutic window / OWTTE;
relieve anxiety / induce relaxation / improve the quality of life;
intravenous/faster distribution of drug;
Disadvantages: [2 max]
euphoria / lack of self-control / dangerous behaviour;
addiction/dependence / withdrawal symptoms;
tolerance / increased risk of overdose upon prolonged use;
kidney/renal failure;
risks associated with intravenous drug administration;
Accept other side-effects (including drug-specific for different opiates).
Examiners report
Many candidates displayed good knowledge about the differences in the mode of action of weak and strong analgesics, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the latter.
Question
State one difference between viruses and bacteria.
Discuss three methods in which the activities of humans has created an increase in the resistance to penicillin in bacteria populations.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
viruses smaller than bacteria;
viruses do not have a nucleus/cytoplasm/cell membrane/cell wall/ribosomes;
viruses are not cells;
viruses do not feed/excrete/grow;
Allow viruses are not living/alive.
overuse of antibiotics has increased proportion of resistant bacteria;
use of penicillin in animal feedstock has introduced antibiotics into human food chain (increasing proportion of resistant bacteria);
patients not completing course of antibiotics increases proportion/spread of resistant bacteria;
Examiners report
Most candidates scored the mark in (a).
A number of journalistic responses were given in part (b) where candidates did not discuss the activities of humans that have created an increase in resistant bacteria. Some candidates misread the question and discussed how penicillin had been modified to combat resistant bacteria. Overuse and developing resistance was generally the only valid reason given.
Question
Aspirin and paracetamol (acetaminophen) are mild analgesics.
Morphine is a strong analgesic which is administered parenterally.
Explain why it is dangerous to take aspirin when ethanol has also been consumed.
State the meaning of the term parenteral.
Explain how a strong analgesic such as morphine prevents pain.
The structures of morphine and diamorphine (heroin) are shown in Table 20 of the Data Booklet. State the name of a functional group present in diamorphine (heroin) but not in morphine.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
increased risk of stomach bleeding;
administered by injection;
(temporarily) bond to receptor sites in the brain/CNS;
prevent the transmission of pain impulses;
ester;
Examiners report
Most candidates were very familiar with analgesics and the synergistic effect of ethanol and aspirin.
Many of the weaker candidates thought that parenteral administration of morphine required supervision by parents or authorities. Assessment statement D.1.3 outlines the meaning of this technique.
Many candidates gave good descriptions of how morphine prevents pain.
[N/A]
Question
Antibiotics treat infections by stopping the growth of bacteria or destroying them.
Identify the side-chain by drawing a circle around the side-chain in the structure of benzyl penicillin given below (the structure of penicillin is given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet).
Discuss two problems associated with the overprescription of penicillin and explain how these are overcome.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
No mark if circle includes CO or just O.
Award [1] if it includes 7 C atoms but misses out on attached H atoms.
overprescription can lead to allergic reaction;
may wipe-out harmless/helpful/beneficial bacteria (in the alimentary canal)/destroyed bacteria may be replaced by more harmful bacteria;
(may pass on genetic) resistance/immunity;
[1] each for any two.
modify R group/side chain to change penicillin effectiveness / form penicillin that is more resistant to penicillinase enzyme;
Examiners report
Many candidates scored the mark in (a) by correctly identifying the side-chain, but a surprising number of candidates only circled the aromatic ring without including the \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\). The general structure of penicillin is given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet, so if all candidates referred to the table they should have scored the mark.
Many candidates did not recognise the loss of beneficial bacteria in the problems associated with over prescription of penicillin. A surprising number were not able to explain the modification of the side chain/R group to change the effectiveness of penicillin.
Question
Many diseases are the result of infection of the body by either bacteria or viruses.
(i) State the name of one disease caused by each.
Bacteria:
Viruses:
(ii) Discuss the differences between bacteria and viruses.
Describe two misuses of antibiotics that have led to some bacteria becoming resistant.
It is much more difficult to produce effective antiviral drugs than drugs that kill bacteria. Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) Bacteria:
tuberculosis/TB / syphilis / cholera / salmonella / bronchitis / botulism / lyme disease / (stomach) ulcers / anthrax / diptheria / meningitis / MRSA / gonorrhea / chlamydia / septicaemia;
Viruses:
influenza / common cold / AIDS / herpes / rabies / small pox / polio / rubella / yellow fever / measles / mumps / encephalitis / chicken pox / shingles / mononucleosis;
Do not accept name of an organism (such as e-coli) rather than a disease.
(ii) bacteria larger than viruses / viruses are smaller than bacteria;
bacteria are cells / viruses comprise DNA in a protein coat;
bacteria have cell wall/nucleus/cytoplasm / viruses do not have cell components;
bacteria can reproduce without a host / viruses require host/cell for replication/reproduction;
bacteria are not always harmful/parasitic / viruses are always parasitic;
patient non-compliance / not completing courses / OWTTE;
overprescription;
use for animals/in animal feedstock;
Accept overuse.
Do not accept overdose.
becomes part of DNA of virus / alters virus DNA/genetic material / blocks enzyme (polymerase) which builds DNA;
changes the cell membrane so that it inhibits the virus entry/bonding to the cell;
prevents virus from leaving the cell (after reproduction);
prevents virus from using cell to multiply/reproduce/replicate;
Examiners report
Many candidates stated the correct name of one bacterial and one viral disease but some had problems stating differences between bacteria and viruses. Candidates must realize that AIDS is a viral disease not HIV.
In part (c), the terms “over dosage” and “over prescription” were often used interchangeably.
In part (d), the method of action of anti-viral was poorly explained. It seemed candidates, at times, learned several key phrases without clearly understanding their meaning and so used them in inappropriate context.
Question
The discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928 is often given as an example of serendipity in science.
Explain how penicillin works and why it is necessary to continue to develop new forms of penicillin with modified side chains.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Two of these for first two marks:
interferes with enzymes/chemicals that bacteria need to make (normal) cell walls / interferes with cell wall formation (in bacteria);
osmotic pressure causes (weakened) cell wall to break/burst / water enters cell causing it to burst / OWTTE;
\(\beta \)-lactam ring is strained/reactive;
Required for final mark:
bacteria become resistant to penicillins/produce the enzyme penicillinase / OWTTE
Examiners report
In (c) many candidates gave detailed descriptions of the interference of penicillin in the formation of cell walls, but it was not rare to see this connected with the bursting of the cell or the statement that this led to increased osmotic pressure without taking water into consideration. It was rather uncommon to find answers including \(\beta \)-lactam ring‘s reactivity. The vast majority of candidates were aware of problems related to bacteria becoming resistant.
Question
Creating a new pharmaceutical product is a long and complex process. Outline the main stages of this process in the correct order.
There are various ways to administer drugs to a patient. One of the common methods, parenteral, is also known as injection. State and describe two other methods of administering drugs.
The efficiency of certain drugs is strongly dependent on the frequency and regularity of their administration. Explain the importance of patient compliance when the patient is treated with antibacterials.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
drug design/discovery/screening/identifying lead compound;
preparation of analogues through combinatorial chemistry;
characterization of the new compound / in vitro testing / drug formulation/delivery/stability studies;
pre-clinical (toxicology and pharmacokinetics) tests / tests on animals/bacteria/cell cultures / LD50 / OWTTE;
clinical tests/tests on humans;
ED50 to show improvements over existing drugs / OWTTE;
Penalize for incorrect order once only.
oral – by mouth / swallowing pills/powders / drinking liquids/mixtures / OWTTE;
inhalation – administering drugs into respiratory tract / inhaling gases/vapours/sprays/powders;
rectal – introducing drugs into the rectum/colon via the anus / using suppositories/enemas;
transdermal – diffusion through the skin/skin patches/ointments/therapeutic baths;
Accept other methods/variations with appropriate descriptions.
Award [1 max] if only two correct names or two correct descriptions are given.
irregular/interrupted treatment allows more bacteria to survive (and mutate) / failure to complete full course / OWTTE;
surviving bacteria develop/pass on resistance (to the drug);
Do not accept superbugs.
Examiners report
Part (a) was generally well answered although a lot of candidates seem to think that ED50 is established on animals and a few, even more worryingly, linked LD50 with human trials!
In part (b), descriptions were often missing but in (c) most understood the importance of frequency and regularity of drug administration.
In part (b), descriptions were often missing but in (c) most understood the importance of frequency and regularity of drug administration.
Question
Analgesics can be either mild or strong.
Morphine, codeine and diamorphine (heroin) are all examples of strong analgesics. Their structures are found in Table 20 of the Data Booklet.
Explain how mild and strong analgesics prevent pain.
Mild analgesics:
Strong analgesics:
State a reason why it is dangerous to use aspirin while consuming alcohol.
Deduce from the structures the names of two functional groups present in all three analgesics.
Deduce the name of one functional group present in diamorphine (heroin) but not in morphine or codeine.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Mild analgesics:
intercept pain stimulus at source / inhibit release of substances/prostaglandins that cause pain/swelling/fever / OWTTE;
Strong analgesics:
(temporarily) bond to receptor sites in brain / prevent transmission of pain impulses in central nervous system/CNS / OWTTE;
Award [1 max] if states that mild analgesics act at source and strong analgesics act at brain/CNS.
increased risk of stomach bleeding;
Any two for [1]
amine
benzene ring
alkene
ether
Allow benzene or phenyl (group) but not arene.
ester;
Names of functional groups must be stated for both marks in part (d).
Do not apply ECF in (d) if formulas (for example, C=C) given instead of names.
Examiners report
The mode of action of mild and strong analgesics in part (a) was well known by most candidates; however, the terminology used was sometimes inaccurate and reflected confusion. For example, some candidates talked about intercepting pain receptors on site of injury for mild analgesics.
Part (c) was well answered by the majority of candidates (increased risk of stomach bleeding when alcohol is consumed with aspirin), and two-thirds of the candidates identified the functional groups correctly in part (d). A common mistake was using the term esther which was not clear whether it was meant to indicate ether or ester.
Question
The structures of aspirin and diamorphine (heroin) are given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet.
Other than the benzene (aromatic) ring, state the name of the functional group that is common to both aspirin and diamorphine.
Describe the different ways in which aspirin and diamorphine function when they relieve or prevent pain.
Aspirin:
Diamorphine:
Other than the prevention of pain and/or the reduction of fever, state one reason why aspirin is often prescribed or recommended to some people for daily use.
Discuss one advantage and one disadvantage of taking diamorphine rather than morphine to relieve pain.
Advantage:
Disadvantage:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ester;
Accept ethanoate/acetate.
Do not accept formula.
Aspirin:
Intercepts pain stimulus at source / blocks/interferes with production of substances/prostaglandins that cause pain/swelling/fever / OWTTE;
Diamorphine:
(temporarily) bonds to/blocks/interferes with receptor sites/synapses in the brain / prevent transmission of pain impulses (without depressing central nervous system/CNS) / OWTTE;
Award [1 max] if answer states that mild analgesic acts at source and strong analgesics act in the brain/CNS.
prevent stroke/heart attack/disease / thin blood / reduces risk of blood clots / antiinflammatory;
Advantage:
stronger pain killer / lower dose required / quicker acting;
Disadvantage:
more addictive / easier to build up tolerance and exceed lethal dose / smaller therapeutic window/index / OWTTE;
Examiners report
This was well answered. Most students could correctly identify the group common to both analgesics and could explain the differences in their modes of action, though the terms used often lacked precision. The reasons for regularly taking low doses of aspirin and the advantages and disadvantages of morphine and heroin, were also well known.
Question
Ethanol is a depressant.
The presence of ethanol in the breath can be detected by blowing into a “bag” through a tube containing acidified potassium dichromate(VI). The half-equation for the dichromate reaction is:
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 – }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{14}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{6}}{{\text{e}}^ – } \to {\text{2C}}{{\text{r}}^{3 + }}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{7}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\]
Describe the colour change observed when the dichromate ion reacts with the ethanol.
State the name of the organic product formed during the reaction.
In order to quantify exactly how much ethanol is present in the blood, a person may be required to give a blood sample or may be asked to blow into an intoximeter. Explain the chemistry behind the techniques for determining the ethanol content in a blood sample and by using an intoximeter.
Blood sample:
Intoximeter:
Ethanol may exert a synergistic effect when taken with other medicines. State the meaning of the term synergistic effect.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
from orange to green;
ethanal/acetaldehyde/CH3CHO / ethanoic acid/acetic acid/CH3COOH;
Do not accept aldehyde / carboxylic acid.
Blood sample:
gas(-liquid) chromatography/GLC/GC / high pressure/performance liquid chromatography/HPLC;
No credit for just “chromatography”.
column separates the alcohol/ethanol from the other components in the blood / retention time identifies alcohol/ethanol / (the amount of alcohol/ethanol in the blood is) compared with a known sample / by measuring the area under the eluted peaks / OWTTE;
Intoximeter:
infrared spectroscopy/infrared light passed through;
the absorption of the C–H/C–O bond is measured (and compared with a calibrated sample) / OWTTE;
OR
fuel cell;
an electric current/voltage is generated (proportional to the concentration of alcohol/ethanol in the breath) / OWTTE;
enhances the effect/causes a stronger/different effect of another drug (present in the body at the same time);
Examiners report
This question produced significantly lower marks. In the first part candidates often confused moderate and high dose symptoms and the latter were often confused with chronic effects. The colour change and product were widely known though, as in the past, some students forgot that a colour change involves stating both the initial and final colour and some gave the class of compound (aldehyde/carboxylic acid) rather than the specific product from ethanol. Only a handful of students gained any of the marks for specific techniques used to assess blood alcohol levels, with IR methods being the best known. Many knew what a “synergistic effect” was, but many struggled to convey this in appropriate language rather than just quoting an example of this type of activity.
Question
Two different antibacterials are sodium piperacillin and doxycycline. Sodium piperacillin is a type of penicillin and doxycycline belongs to a class of drugs known as the tetracyclines.
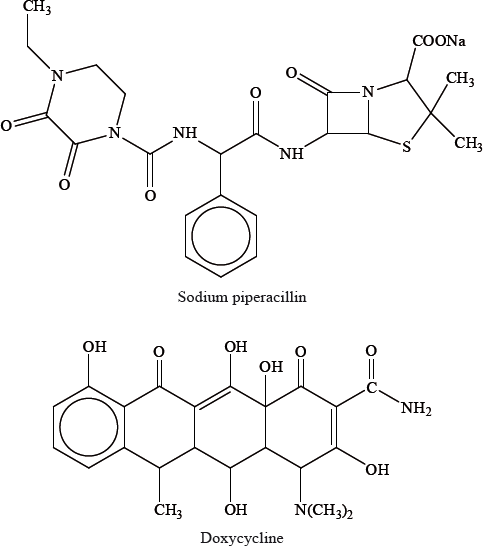
Explain how penicillins are able to cure certain diseases caused by bacteria.
Sodium piperacillin has a different side chain to the original penicillin developed by Florey and Chain. State one advantage of changing the side chain.
Explain why it may be necessary to give a mixture of several different types of antibacterials (such as penicillins and tetracyclines) to patients suffering from diseases such as tuberculosis (TB) or MRSA (a disease caused by the presence of the staphylococcus aureus bacterium).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
prevents the growth/ multiplication of bacteria (causing disease);
Accept “kills bacteria”.
interferes with the enzymes that bacteria need to make normal cell walls / prevents normal cell wall formation;
Do not accept “Destroys cell walls”.
cells absorbs water (by osmosis) and ruptures/bursts;
does not need to be injected / not broken down by stomach acid / resistant to penicillinase;
Accept “overcomes resistance of bacteria” / OWTTE;
Do not accept “immune” rather than “resistant”.
some bacteria may be resistant to just one antibiotic / can make \(\beta \)-lactamase/penicillinase (which can degrade penicillin);
few bacteria resistant to all the antibiotics / prevents the risk of further resistance developing;
Unless penalised in D3 (b), do not accept “immune” rather than “resistant”.
Examiners report
Many students knew that penicillins affected the walls of bacteria, though many wrongly stated that it destroyed the cell wall, rather than hindering its formation. The effects of changing the side chain were generally appreciated, but once again, in the final part of the question, students often failed to express the reasons for using multiple antibacterials clearly enough to gain full credit. In the last two parts candidates often, incorrectly, referred to bacteria being “immune” or “tolerant” rather than “resistant” – another example of a failure to use precise vocabulary correctly.
Question
Each capsule of Solpadol®, a commercial analgesic, contains 500 mg of paracetamol (acetaminophen) and 30 mg of codeine (in the form of codeine phosphate hemihydrate).
Diamorphine (heroin) is an even stronger painkiller than codeine. The structures of codeine and diamorphine are given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet. Discuss, in terms of named functional groups, how the structure of diamorphine differs from the structure of codeine.
A normal aspirin tablet taken to relieve pain contains about 300 mg of aspirin. Certain adults who are not in pain are recommended by doctors to take a smaller 75 mg dose of aspirin each day. State one reason for this recommendation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
codeine contains a hydroxyl group;
Allow alcohol/hydroxy but not hydroxide.
codeine contains one methoxy group/two ether groups;
Allow codeine contains one additional ether group but not codeine contains the ether group.
diamorphine contains ester/acetoxy/ethanoate group(s);
Names required not functional group formulas.
Allow acetyl group.
prevents (the recurrence of) heart attack/stroke / reduces ability of blood to clot;
Examiners report
Majority of the candidates were familiar with the mode of action of mild and strong analgesics in part (a) however, there was some inaccurate use of the terminology. There was some confusion about signal interception and transmitting signals. For example, some candidates talked about prostaglandins released at the source and reducing pain perception in the brain. Most candidates answered the part (b) correctly; a few did not use functional group names but used bonds or diagrams instead. Many candidates missed stating two ether groups and were not able to score the third mark. The majority of candidates stated correct advantages and disadvantages of paracetamol over aspirin in part (b). Part (c) was well answered by the majority of candidates; some gave the only reason as aspirin thins blood and lost the mark; almost all candidates were able to provide one reason for answer to part (d) correctly. Many candidates missed to identify both, codeine as a strong analgesic and addictive, and did not score the mark.
Question
A commonly used mild analgesic is aspirin, 2-acetoxybenzoic acid, whose structure is given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet.
One form of soluble aspirin is \({\text{Ca(}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{9}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\).
Morphine, codeine and diamorphine (heroin) are examples of strong analgesics. Their structures are given in Table 20 of the Data Booklet.
Describe how mild analgesics function.
(i) Outline why this substance is more soluble than standard aspirin in water.
(ii) Deduce the balanced ionic equation for the reaction that occurs between soluble aspirin and the acid in the stomach.
(i) Deduce two named functional groups present in both aspirin and diamorphine.
(ii) Deduce one named functional group present in morphine but not in diamorphine.
(iii) State two short-term advantages and two long-term disadvantages of using codeine as a strong analgesic.
Short-term advantages
Long-term disadvantages:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
intercepts pain stimulus at source / inhibits release of substances/prostaglandins that cause pain/swelling/fever;
(i) ionic compound (which dissociates);
(ii) \({{\text{C}}_9}{{\text{H}}_7}{\text{O}}_4^ – {\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to {{\text{C}}_9}{{\text{H}}_8}{{\text{O}}_4}{\text{(aq)}}\);
Ignore state symbols
Ignore arrow.
(i) phenyl/benzene ring;
Do not allow just benzene or arene or the formula C6H6.
ester;
Do not allow –COO– or carbonyl/CO.
(ii) hydroxyl / phenol;
Allow alcohol/hydroxy but not hydroxide.
Do not allow –OH.
(iii) Award [1] for any two short-term advantages from:
strong/powerful (pain reliever);
fast-acting / effective;
has a wide safety margin;
can quickly stop diarrhoea;
can be used in cough mixtures/medicines / antitussive properties;
works effectively with paracetamol/acetaminophen;
Award [1] for any two long-term disadvantages from:
(regular use) can lead to addiction/dependence/withdrawal symptoms;
tolerance can lead to toxic dosages;
can result in depression / apathy;
can cause mental health problems;
can result in constipation;
can result in sterility/sexually related problems;
memory loss;
serious health risk to babies who are breastfed;
Award [1 max] for one correct advantage and one correct disadvantage.
Examiners report
While many candidates scored the mark, some candidates offered vague and/or inaccurate descriptions of how mild analgesics functioned.
(i) Few candidates scored here. Very often the answers would attribute the solubility to the presence of calcium.
(ii) A highly discriminating question. A substantial number of candidates ignored the request for an ionic equation. Those who attempted one mostly failed to give the correct products.
(i) Many correct answers. A few candidates stated “benzene” without “ring” which did not score the mark. Another mistake was using “esther” where it was not clear if “ester” or “ether” was meant.
(ii) A well answered question.
(iii) A good number of candidates scored at least one mark, often as a result of stating one short-term and one long-term advantage of using codeine.
Question
The development of new and improved medications for the reduction and management of pain is an important part of 21st-century medicine.
Explain the way that mild and strong analgesics prevent pain.
Mild analgesics:
Strong analgesics:
The structure of morphine and diamorphine (heroin) are shown in Table 20 of the Data Booklet. State the name of the functional group present in diamorphine that is not present in morphine.
Discuss two advantages and two disadvantages of the medical use of morphine and its derivatives.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Mild analgesics:
mild analgesics work by intercepting pain stimulus at source;
suppress production of prostaglandins/pain sensitizing substances / OWTTE;
Strong analgesics:
strong analgesics work directly on opioid/pain receptors in brain;
suppress transmission of pain impulses in brain/CNS / OWTTE;
ester;
Accept alkanoate/ethanoate/acetoxy.
Advantages:
Award [1 max] for any two of:
strong pain relief / strong analgesic;
sedation / OWTTE;
treatment of diarrhoea;
relieve coughing;
Disadvantages:
Award [1 max] for any two of:
addiction;
tolerance;
dependence;
constipation;
depresses respiratory drive;
Accept “criminals/drug addicts might get access to strong analgesics intended for medical use” / OWTTE.
Award [1 max] if one advantage and one disadvantage are given.
Examiners report
Although the question on mild and strong analgesics, (a), is a question that has been asked previously a myriad of times, few surprisingly scored all four marks. Candidates occasionally discussed types of medication rather than mode of action. For mild analgesics many did not state the fact that these analgesics work by intercepting the pain stimulus at the source itself. The suppression of the production of prostaglandins often was not alluded to. For strong analgesics the most common mistake involved candidates not referring to opioid receptors in the brain.
(b) proved no problem for candidates though some stated incorrect functional groups or classes (alcohol and carboxylic acid were common incorrect answers). Please note that to prepare new candidates for the 2016 syllabus, the markscheme was later altered to include the correct naming of functional groups following IUPAC guidelines.
In (c), most candidates scored at least one mark. For the advantage few stated the fact that morphine is a strong analgesic.
Question
The first commercially available antibiotic came from a class of compounds known as the penicillins.
Explain how penicillins work and why it is necessary to continually modify the side-chain.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
penicillins interfere with (enzymes involved with) development of cell wall/(cross-link) structure of bacteria;
(due to damage) cells absorb water (by osmosis) and burst / OWTTE;
modifying side-chain overcomes resistance (by bacteria) / OWTTE;
Examiners report
In (b) the most common mistake seen was claims that penicillin breaks down cell walls. This is totally incorrect – penicillin does not break down existing cell walls – it only interferes with the production of new ones. Many candidates also did not mention the fact that due to damage cells absorb water and burst. Most knew that modification of the side-chain overcomes resistance by bacteria.
Question
The properties of four analgesics are summarized below.
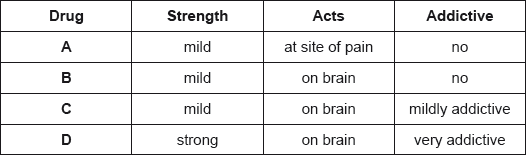
Deduce which drugs could be morphine, aspirin and codeine.
Morphine:
Aspirin:
Codeine:
Compare the structures of diamorphine (heroin) and morphine. Their structures are given in table 20 of the data booklet.
Two similarities:
One difference:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Morphine: D;
Aspirin: A;
Codeine: C;
Award [2] for all three correct, [1] for two correct.
Similarities:
Award [1 max] for any two:
benzene ring/aromatic ring/−C6H2;
Accept “phenyl” or “arene” but not C6H5– or benzene/C6H6.
(tertiary) amino/−NRR’/NRR’R”;
Accept “(tertiary) amine”.
carbon−carbon double bond/C=C;
Accept “alkene” or “alkenyl”.
ether/C−O−C;
Accept “both have the same ring structure / OWTTE”.
Difference:
ester/CH3COO in diamorphine/heroin and hydroxyl/OH in morphine;
Accept “ethanoate” for ester.
Accept “alcohol” or “hydroxy” for hydroxyl but not hydroxide.
Examiners report
Most candidates matched the analgesics to the properties successfully.
Most candidates identified two similarities and one difference between diamorphine and morphine. For the difference, it was necessary to mention both the hydroxyl groups in morphine and the ester groups in diamorphine.
Question
Diseases may be caused by bacteria or viruses.
Explain how penicillins work as antibacterials.
The R group in the general structure of penicillin shown below represents a side-chain which is regularly modified.
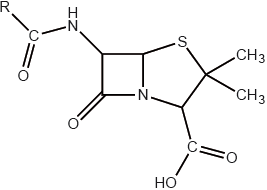
Explain why this modification is necessary.
Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
prevent the formation of bacterial cell walls / interfere with chemicals/enzyme/transpeptidase needed by bacteria to form normal cell walls / inhibits cross-links developing in bacterial cell walls;
(osmosis) causes water to enter bacterial cell and cell bursts / cell wall weakens (making it more permeable to water) and bacterium bursts (and dies);
makes penicillin more effective / makes penicillin resistant to penicillinase (enzyme) / allows different methods of administration / penicillins can be made which are resistant to acid in the stomach;
change cell membrane to prevent viruses entering/attaching to cell;
alter cell’s genetic material so virus cannot use it to multiply;
inhibit enzymes involved in replication/reverse transcriptase / stop enzyme activity inside the cell (and prevent the viruses from multiplying);
prevent replicated virus leaving the cell;
initiates apoptosis/death of cells infected by viruses;
mimic guanosine/base-sugar monomer in DNA/RNA formation inhibiting enzymes involved in replication;
Examiners report
Many students were able to explain how penicillins work as antibacterial agents although sometimes the answers lacked clarity. The reason for the modification of the side-chain of penicillin was often linked to bacterial resistance but did not specifically address how it actually affects the action of penicillin. Candidates were often unclear on the different ways that anti-viral drugs can work and although they usually managed to achieve one of the two marks, many explanations lacked the precision in terms of their mode of action.
Question
Penicillin was one of the first antibiotics to be isolated and identified for its ability to treat bacterial infections.
Explain the importance of the beta-lactam ring in the antibiotic activity of penicillin.
Identify two dangers of the overuse of antibiotics.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ring is «sterically» strained
OR
angles of 90° instead of 109.5/109/120° angles
OR
angles smaller than 109.5/109/120°/tetrahedral/trigonal planar/triangular planar angle
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amide/amido group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
binds to/reacts with/interferes with/inactivates transpeptidase/enzyme
responsible for bacterial cell wall formation/cross-linking
Do not accept “cell membrane” for “cell wall”.
Accept “bonds to” for “binds to” in M3
Any two for [1 max] from:
leads to «bacterial» resistance «of antiobiotics»
OR
makes antibiotics less effective
OR
increased side effects due to larger dosages
proportion of resistant bacteria increases
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
OR
destroyed bacteria replaced by more harmful bacteria
resistant bacteria pass on their resistance/mutation to next generation
damage to ecosystems
Accept “superbugs such as MRSA develop” but superbug must be identified.
Question
Penicillin is an antibiotic which contains a beta-lactam ring. Its general structure is shown below.
(i) Outline what is meant by the term “ring strain”.
(ii) On the diagram above, label with asterisk/s (*) the carbon atom/s that experience ring strain.
(i) Some antibiotic-resistant bacteria produce a beta-lactamase enzyme which destroys penicillin activity. Suggest how adding clavulanic acid to penicillin enables the antibiotic to retain its activity.
(ii) Populations of antibiotic-resistant bacteria have increased significantly over the last 60 years. Outline why antibiotics such as penicillin should not be prescribed to people suffering from a viral infection.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
i
bond angles smaller/distorted
OR
instability resulting from abnormal bond angles
OR
bond angles «approximately» 90° instead of 109.5°/120°
Accept “109/110°” for “109.5°”
ii
asterisks (*) on all 3 lactam ring carbon atoms
Must mark all 3 carbon atoms.
Ignore asterisks on the RHS carbon atoms of the five-membered ring.
i
beta-lactam/four-membered ring «in clavulanic acid» reacts with enzyme/beta lactamase
Accept “acts as enzyme inhibitor/suicide substrate/preferentially binds to enzyme”.
ii
antibiotics not effective against viruses
OR
viruses have no cell wall/cell structure/target structures to attack
increasing exposure of bacteria «to antibiotic» increases resistance
Accept “antibiotics kill beneficial bacteria” for M2.
Question
The mild analgesic aspirin can be prepared in the laboratory from salicylic acid.
(CH3CO)2O + HOC6H4COOH → CH3CO2C6H4COOH + CH3COOH
Salicylic acid Aspirin
After the reaction is complete, the product is isolated, recrystallized, tested for purity and the experimental yield is measured. A student’s results in a single trial are as follows.
Literature melting point data: aspirin = 138–140 °C
Determine the percentage experimental yield of the product after recrystallization. The molar masses are as follows: M(salicylic acid) = 138.13 g mol−1, M(aspirin) = 180.17 g mol−1. (You do not need to process the uncertainties in the calculation.)
Suggest why isolation of the crude product involved the addition of ice-cold water.
Justify the conclusion that recrystallization increased the purity of the product, by reference to two differences between the melting point data of the crude and recrystallized products.
State why aspirin is described as a mild analgesic with reference to its site of action.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ALTERNATIVE 1:
«theoretical yield = \(\frac{{1.552\,{\text{g}}}}{{138.13\,{\text{g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\) × 180.17 g mol−1 =» 2.024 «g»
«experimental yield = \(\frac{{1.124{\rm{g}}}}{{2.024{\rm{g}}}}\) × 100 =» 55.53 «%»
ALTERNATIVE 2:
«\(\frac{{1.552\,{\text{g}}}}{{138.13\,{\text{g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\)»= 0.01124 «mol salicylic acid/aspirin theoretical» AND
«\(\frac{{1.124\,{\text{g}}}}{{180.17\,{\text{g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\)»= 0.006239 «mol aspirin experimental»
«experimental yield = \(\frac{{0.006239{\rm{mol}}}}{{0.01124{\rm{mol}}}}\) x 100 =» 55.51 «%»
Accept answers in the range 55.4 % to 55.7 %.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
low temperature gives greater difference between solubility of aspirin and impurities
OR
«product» crystallizes out from cold solution/«ice-cold water/lower temperature» speeds up crystallization process
OR
aspirin/product has low solubility «in water» at low temperatures
[N/A]
intercepts pain stimulus at source/acts at site of pain
OR
interferes with production of pain sensitizing substances/prostaglandins «at site of pain»
Examiners report
[N/A]
[N/A]
recrystallized melting point is higher
OR
recrystallized melting point is closer to pure substance/literature value
smaller range of values
[N/A]
Question
Solubility plays an important role in the bioavailability of drugs in the body.
Suggest why aspirin is slightly soluble in water. Refer to section 37 of the data booklet.
Formulate an equation for the conversion of aspirin to a more water soluble derivative.
A student prepares aspirin from salicylic acid in the laboratory, extracts it from the reaction mixture, ensures the sample is dry and determines its melting point.
Suggest why the melting point of the student’s sample is lower and not sharp compared to that of pure aspirin.
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the largest producers of waste solvents.
State a green solution to the problem of organic solvent waste.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
presence of «large» benzene/arene ring AND non-polar/hydrophobic
OR
presence of «large» benzene/arene ring AND cannot form H-bond with water
contain COOH/carboxyl/–OH/hydroxyl «and ester group» AND polar/hydrophilic
OR
contain COOH/carboxyl/–OH/hydroxyl «and ester group» AND can form H-bonds with water
Accept “phenyl” for “benzene ring”.
Accept “carboxylic acid” for “carboxyl”.
Do not accept “alcohol” for “hydroxyl”.
[2 marks]
OR
C6H4(OCOCH3)COOH + NaOH → C6H4(OCOCH3)COONa + H2O
Charges (O– and Na+) not necessary to score the mark.
Accept net ionic equation.
Accept any strong base in place of NaOH.
[1 mark]
«student’s» sample impure
lattice disrupted/not uniform «due to presence of impurities»
OR
fewer interparticle/intermolecular forces «due to presence of impurities»
Accept converse arguments.
[2 marks]
One similarity:
peak at 2500–3000 «cm–1»/peak due to O–H/hydroxyl in carboxylic acids
OR
peak at 1700–1750 «cm–1»/peak due to C=O/carbonyl
OR
peak at 2850–3090 «cm–1»/peak due to C–H of arene
One difference:
peak at 3200–3600 «cm–1» in salicylic acid/ peak due to O–H in phenol in salicylic acid
OR
«two» peaks at 1700–1750 «cm–1» in aspirin AND one peak «in the same area» in salicylic acid
Accept “peak at 1600 cm–1 for arene/benzene ring” – not in the data booklet.
Accept “2500–3600 cm–1 «overlapping absorptions of two O–H» in salicylic acid”.
Accept “stronger/broader/split peak at 1700–1750 cm–1 in aspirin”.
[2 marks]
«use of» alternative solvents such as supercritical/liquid CO2
OR
use of water «as solvent»
OR
solvent-free reactions «for example, polymerization of propene»
OR
solid-state chemistry
OR
recycle «waste» solvents
OR
catalysis that leads to better/higher yield
OR
reducing number of steps
Do not accept political/regulatory solutions.
“catalysis” not sufficient for mark.
[1 mark]
Question
Aspirin is one of the most widely used drugs in the world.
Aspirin was synthesized from 2.65 g of salicylic acid (2-hydroxybenzoic acid) (Mr = 138.13) and 2.51 g of ethanoic anhydride (Mr = 102.10).
Calculate the amounts, in mol, of each reactant.
Calculate, in g, the theoretical yield of aspirin.
State two techniques which could be used to confirm the identity of aspirin.
State how aspirin can be converted to water-soluble aspirin.
Compare, giving a reason, the bioavailability of soluble aspirin with aspirin.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
n(salicylic acid) = «\(\frac{{2.65{\text{ g}}}}{{138.13{\text{ g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\)» 0.0192 «mol»
AND
n(ethanoic anhydride) = «\(\frac{{2.51{\text{ g}}}}{{102.10{\text{ g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\)» 0.0246 «mol»
[1 mark]
«mass = 0.0192 mol x 180.17 g\(\,\)mol–1 =» 3.46 «g»
Award ECF mark only if limiting reagent determined in (i) has been used.
[1 mark]
Any two of:
melting point
mass spectrometry/MS
high-performance liquid chromatography/HPLC
NMR/nuclear magnetic resonance
X-ray crystallography
elemental analysis «for elemental percent composition»
Accept “spectroscopy” instead of “spectrometry” where mentioned but not “spectrum”.
Accept “infra-red spectroscopy/IR” OR “ultraviolet «-visible» spectroscopy/UV/UV-Vis”.
Do not accept “gas chromatography/GC”.
Accept “thin-layer chromatography/TLC” as an alternative to “HPLC”.
[2 marks]
react with NaOH
Accept “NaHCO3” or “Na2CO3” instead of “NaOH”.
Accept chemical equation OR name for reagent used.
[1 mark]
«marginally» higher AND increase rate of dispersion
OR
«marginally» higher AND increase absorption in mouth/stomach «mucosa»
OR
«approximately the» same AND ionic salt reacts with HCl/acid in stomach to produce aspirin again
Do not accept “«marginally» higher AND greater solubility in blood”.
[1 mark]
Question
Some analgesics are derived from compounds found in plants.
Aspirin is a mild analgesic derived from salicylic acid found in willow bark.
Describe how mild analgesics function.
The strong analgesics morphine and codeine are opiates. Outline how codeine can be synthesized from morphine. The structures of morphine and codeine are in section 37 of the data booklet.
Explain why opiates are addictive.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
prevents/interferes with the production of prostaglandins
OR
prevents/interferes with the production of substances responsible for
inflammation/pain/fever
at the site of injury/source of pain
react with CH3I/methyl iodide «in alkaline solution»
Accept “react with CH3Cl/methyl chloride” OR “react with methyl halide”.
Accept name or formula of a suitable specific methylating reagent (eg trimethylphenylammonium chloride etc.).
Accept “hydroxy/alcohol” but not “hydroxide” for “hydroxyl”.
Any two of:
interact with opioid receptors in the brain
alter the structure of brain cells
OR
alter the way the brain works «so that it only works normally when the opiates are present»
OR
prevents transmission of pain impulses inside the brain
release dopamine «that the person craves»
OR
give a feeling of pleasure/euphoria «that the person craves»
withdrawal symptoms «prevent patient from terminating drug use»
Accept specific withdrawal symptoms.
[Max 2 Marks]
Question
Molecules of antibiotics often contain a beta-lactam ring. Explain the importance of the betalactam ring in the action of penicillin, using section 37 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ring is «sterically» strained
OR
angles of 90° instead of 109.5/109/120° angles
OR
angles smaller than 109.5/109/120°/tetrahedral/trigonal planar/triangular planar angle
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amido/amine group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
binds to/reacts with/interferes with/inactivates transpeptidase
OR
binds to/reacts with/interferes with/inactivates enzyme responsible for bacterial cell wall formation/cross-linking
Examiners report
Question
Many drugs, including aspirin, penicillin, codeine and taxol, have been modified from compounds that occur naturally.
Aspirin is often taken to reduce pain, swelling or fever. State one other use of aspirin.
State what is meant by the bioavailability of a drug.
Outline how the bioavailability of aspirin may be increased.
Compare and contrast the IR spectrum of aspirin with that of salicylic acid, using section 26 of the data booklet.
Describe how penicillin combats bacterial infections.
Outline two consequences of prescribing antibiotics such as penicillin unnecessarily.
State how penicillins may be modified to increase their effectiveness.
Morphine and codeine are strong analgesics. Outline how strong analgesics function.
Suggest one reason why codeine is more widely used than morphine as an analgesic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any one of:
anticoagulant
lower risk of heart attack/strokes
prevent recurrence of heart attack/stroke
prevents cancer of colon/oesophagus/stomach
Accept “prevents/reduces blood clots” OR “blood thinner”.
[1 mark]
fraction/proportion/percentage «of administered dosage» that reaches target «part of human body»
OR
fraction/ proportion/percentage «of administered dosage» that reaches blood «plasma»/systemic circulation
Accept “the ability of the drug to be absorbed by the body” OR “the extent to which the drug is absorbed by the body”.
Do not accept “the amount/quantity of the drug absorbed”.
[1 mark]
«intravenous» injection/IV
Accept “parenterally”.
Accept “react with alkali/NaOH” OR “convert to ionic form/salt”.
[1 mark]
One absorption found in both spectra:
Any one of:
1050–1410 cm–1 «C–O in alcohols, esters, ethers»
1700–1750 cm–1 «C=O in carboxylic acids, esters»
2500–3000 cm–1 «O–H in carboxylic acids»
2850–3090 cm–1 «C–H in alkanes, alkenes, arenes»
One absorption found in only one of the spectra:
3200–3600 cm–1 «O–H in alcohols, phenols»
Award [1 max] if candidate states bonds (C=O in both, O–H in salicylic acid only) but doesn’t quote wavelength ranges.
Accept a second/additional absorption at 1700–1750 cm–1 from the C=O in ester.
[2 marks]
Any two of:
ring is «sterically» strained
OR
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amide/amido group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
«irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of bacterial cell walls
cells absorb water AND burst
OR
cells cannot reproduce
Award [1 max] for “interferes with cell wall production”.
Do not accept “cell membrane” instead of “cell wall”.
[2 marks]
Any two of:
leads to «bacterial» resistance/proportion of resistant bacteria increases
OR
leads to penicillinase-producing bacteria
damage to/contamination of bodies of water/ecosystems
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
destroyed bacteria replaced by more harmful bacteria
Accept “endocrine disruptor”.
Do not accept “increased cost of developing antibiotics”.
[2 marks]
modify side chain
[1 mark]
temporarily bind to/block/interfere with receptor sites in brain
OR
prevent transmission of pain impulses within CNS/central nervous system
[1 mark]
codeine has a wider therapeutic window
Accept “codeine has lower activity” OR “codeine has lower risk of overdose” OR “codeine is less potent” OR “codeine has less side-effects”.
Do not accept “lower abuse potential for codeine” OR “less addictive «than morphine»” OR “codeine has a lower bioavailability” OR “available without prescription” OR “cheaper”.
[1 mark]
Question
Penicillins and aspirin are important medicines.
Describe how penicillin combats bacterial infections.
State how penicillins may be modified to increase their effectiveness.
State the type of reaction used to synthesize aspirin from salicylic acid.
Explain why aspirin is not stored in a hot, humid location.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of bacterial cell walls
cells absorb water AND burst
OR
cells cannot reproduce
[2 marks]
modify side chain
[1 mark]
condensation
OR
esterification
OR
nucleophilic substitution/nucleophilic displacement/SN2
Do not accept just “substitution/displacement”.
[1 mark]
water causes hydrolysis
OR
aspirin reacts with water
heat increases the rate of hydrolysis
OR
heat increases the rate of the reaction with water
Accept “aspirin will convert into salicylic/ethanoic acid”.
Do not accept “aspirin dissolves in water” OR “aspirin absorbs water/is hygroscopic”.
[2 marks]

