Question
Consider the structures of medicinal molecules in section 37 of the data booklet.
a. Explain how zanamivir works as a preventative agent against flu viruses.
b(i)Circle the side-chain in penicillin on the structure below.
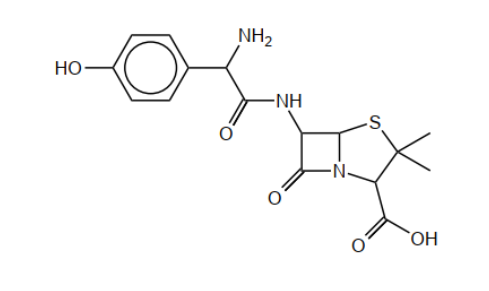
b(iiExplain, with reference to the action of penicillin, why new penicillins with different side-chains need to be produced.
c(i)State and explain the relative solubility of codeine in water compared to morphine and diamorphine.
c(ii)State the natural source from which codeine, morphine and diamorphine are obtained.
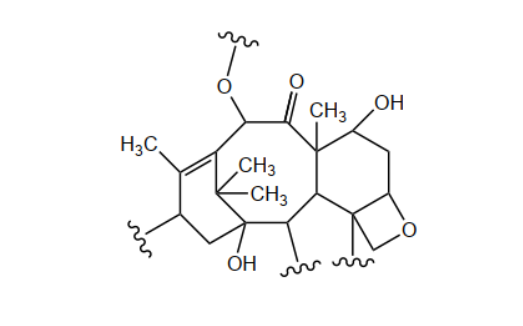
d. Circle two chiral carbons in the section of the Taxol structure below.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «drug» blocks/inhibits «viral» enzyme/neuraminidase/NA «activity» prevents virus from leaving/escaping host cells «thus cannot infect other cells»
Do not accept other anti-viral methods (as question is specific to Zanamivir).
b(i).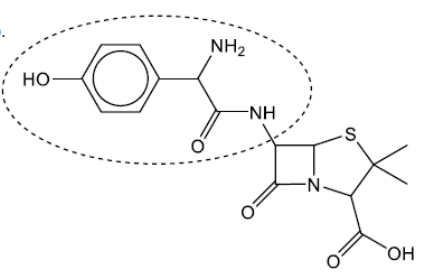
Accept a circle that does not surround the amido group.
Do not accept a circle that only surrounds the phenol group.
b(ii)acterial resistance «to older penicillins/antibiotics»
prevent penicillinase/beta-lactamase/enzyme in bacterium to deactivate/open penicillin/beta-lactam ring
Accept “antibiotic resistant bacteria” but not “antibiotic resistance” for M1.
Accept “reduce allergic reactions from penicillin” for $M 2$.
Award [1 max] for “increased efficiency” OR “increased stability in GIT”.
Do not accept “bacteria develop tolerance”.
c(i)codeine less soluble «in water» than morphine AND more soluble than diamorphine
OR
morphine > codeine > diamorphine «in terms of solubility in water»
more/stronger/greater hydrogen/H bonding «due to more hydroxyl groups leads to greater solubility»
c(ii)pium poppy/plants/seeds
Accept “poppy” OR “opioid”.
d.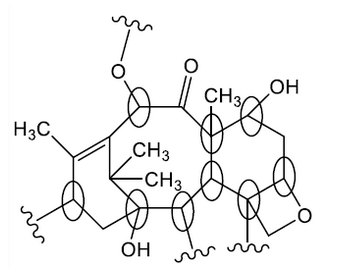
\text { any two chiral carbons identified } \checkmark
Question
This question is about antiviral drugs.
Oseltamivir, used for the treatment of severe flu, is inactive until converted in the liver to its active carboxylate form.
a(i)Draw a circle around the functional group that can be converted to the carboxylate by hydrolysis.
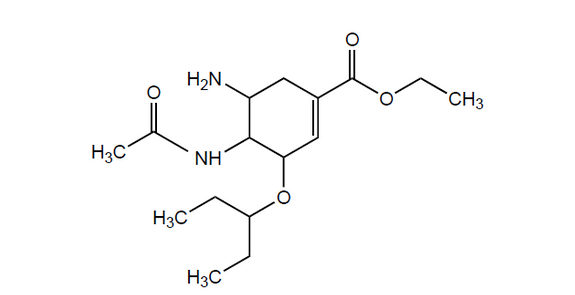
a(ii)Suggest a reason for using a phosphate salt of oseltamivir in oral tablets.
b. Anti-HIV drugs, such as zidovudine, often become less effective over time.
Explain the development of resistant virus strains in the presence of antiviral drugs.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a(i).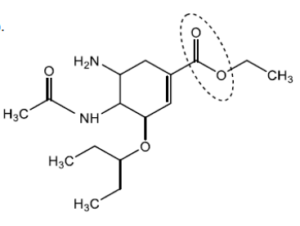
Note: Accept circles that include the alkyl side chain.
a(ii)more soluble «in water» $[\mathfrak{U}]$
b. viruses undergo «rapid» mutation $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
mutation causes a change in viral protein OR
drug to no longer binds to virus [ $]$
Note: Accept “rapid reproduction “allows resistant viruses to multiply»”.
Question
Antiviral medications have recently been developed for some viral infections.
a. Outline one way in which antiviral drugs work.
b. Discuss two difficulties associated with solving the AIDS problem.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any one of:
alter cell’s genetic material «so that virus cannot use it to multiply» [ $\cdot]$
prevent viruses from multiplying by blocking enzyme activity within host cell
OR
inhibit the synthesis of viral components by blocking enzymes inside the cell $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
prevent viruses from entering «host» cell
OR
bind to cellular receptors targeted by viruses
OR
bind to virus-associated proteins/VAPs which target cellular receptors
OR
prevents removal of protein coat/capsid OR prevents injection of viral DNA/RNA into cell $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
prevent/hinder the release of viruses from the cell $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Note: Accept “prevents synthesis of virus by host cell”.
Accept “alters RNA/DNA/genetic material of virus”.
b. Any two of:
viruses lack cell structure «so difficult to target with drugs» [ ]
HIV is a retrovirus
OR
HIV genetic material is in the form of RNA instead of DNA [ $]$
HIV affects/destroys helper/T-cells which are necessary to fight infection $[\mathcal{U}]$
HIV has great genetic diversity so difficult to produce «a» vaccine [ $]$
anti-retroviral agents are expensive so not everyone/country can afford them $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
socio-cultural issues deter people from seeking treatment/prevention/diagnosis
OR
lack of education/conversation/stigma associated with being HIV-positive $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
mutation of virus/HIV $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
virus/HIV metabolism linked to that of host cell $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
drugs harm host cell as well as virus/HIV $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
HIV difficult to detect/remains dormant $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Question
Infectious diseases can be caused by bacteria or viruses.
a. State one difference between bacteria and viruses.
b. Discuss two difficulties, apart from socio-economic factors, associated with finding a cure for AIDS.
c. The discovery of penicillins contributed to the development of antibiotics.
Explain how the beta-lactam ring is responsible for the antibiotic properties of penicillin. Refer to section 37 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any one of:
bacteria perform living functions «on their own and viruses do not without host cell»
OR
bacteria have cell walls «and viruses do not»
OR
bacteria do not have a capsid «and viruses do»
OR
bacteria larger than viruses
OR
bacteria reproduce by fission/budding «and viruses reproduce within a living host cell»
$O R$
bacteria affected by antibiotics «while viruses are not»
NOTE: Accept “bacteria have flagella/cytoplasm/ribosome “and virus can have head/protein tail/double stranded RNA/single stranded DNA»”
Accept “asexual reproduction” for bacteria.
Accept other specific structural differences between bacteria and viruses, and examples of living functions that bacteria perform (such as excretion, reproduction etc.) that viruses do not.
Accept “bacteria are living and viruses are not”
b. Any two of:
HIV difficult to detect/remains dormant
HIV mutates rapidly/quickly
NOTE: Do not accept “AIDS mutates” without mention of the HIV/virus.
HIV replicates rapidly/quickly
HIV destroys «T-» helper cells/white blood cells/lymphocytes
OR
HIV attacks immune system
HIV has several «significantly different» strains/subtypes
NOTE: Accept “virus” for “HIV”.
Penalize the use of “AIDS” for “HIV” once only.
Accept “HIV metabolism linked to that of host cell” OR “drugs harm host cell as well as HIV”.
c. ring is «sterically» strained
OR
angles of $90^{\circ}$ instead of $109.5 / 109 / 120^{\circ}$ angles
OR
angles smaller than $109.5 / 109 / 120^{\circ}$ /tetrahedral/trigonal planar/triangular planar angle
NOTE: Accept arguments using correct descriptions of hybridization for M1.
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amido/amide group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
«irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of «bacterial» cell walls
NOTE: Do not accept “breaks/binds to cell walls” – a reference to the enzyme is needed for alternatives 1 and 2 for M3.
Do not accept “cell membrane” for “cell wall” for M3.
Question
Viruses and bacteria both cause diseases and are frequently confused.
a. State one way in which viruses differ from bacteria.
b. Outline two different ways in which antiviral medications work.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. bacteria perform living functions «on their own and viruses do not without host cell»
OR
bacteria have cell walls «and viruses do not»
OR
bacteria do not have a capsid «and viruses do»
OR
bacteria larger than viruses
OR
bacteria reproduce by fission/budding «and viruses reproduce within a living host cell»
OR
bacteria affected by antibiotics «while viruses are not»
Accept “bacteria have flagella/ cytoplasm/ribosome “and virus can have head/protein tail/double stranded RNA/single stranded DNA»”, “asexual reproduction for bacteria”, other specific structural differences between bacteria and viruses, and examples of living functions that bacteria perform (such as excretion, reproduction etc.) that viruses do not.
b. Any two of:
prevents virus attaching to host cell
alters cell’s genetic material/DNA «so that virus cannot use it to multiply»
blocks enzyme activity in the host cell «so that virus cannot use it to multiply»
prevents removal of protein coat/capsid
prevents injection of viral DNA/RNA into cell
prevents release of «replicated» viruses from host cell
Accept “prevents synthesis of virus by host cell”.
Accept “alters RNAVDNA/genetic material of virus”.
Do not accept just “mimics nucleotides”.
Question
Describe and explain difficulties associated with solving the AIDS problem.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
HIV invades/bind to white blood cells/T4/T cells / OWTTE;
HIV viruses can mutate;
HIV viruses have similar metabolism to (human) cells/uses host cells to replicate;
high price of (antiretroviral) drugs / socioeconomic / cultural issues;
Examiners report
The question was answered surprisingly poorly. Many candidates gave a description of the mechanism of action of anti-viral drugs, but made no reference to socio-economic issues, other gave a detailed description of socio-economic issues, and only obtained one mark.
Question
Bacterial and viral infections require different types of medication.
(a) Outline two differences between bacteria and viruses.
(b) Antiviral drugs are used for the treatment of HIV and other viral infections. Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
(c) Discuss why viral infections are generally harder to treat than bacterial infections.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(a) bacteria are self-reproducing units while viruses are not / viruses need living hosts/cells to multiply / OWTTE;
bacteria are able to grow/metabolise/feed and excrete / viruses lack metabolic functions;
bacteria contain various cell subunits/organelles/cell wall (performing specific functions) / viruses consist only of genetic material and protective coating;
bacteria are (many times) larger than viruses / viruses are smaller than bacteria;
bacteria have more complex DNA / viruses have simpler DNA;
viruses mutate/multiply (much) faster than bacteria / bacteria mutate/multiply slower than viruses;
If comparative term used e.g. smaller what it’s compared to is not required.
(b) alter cells genetic material so that virus cannot use it to multiply;
prevent viruses from multiplying by blocking enzyme activity within host cell / inhibit the synthesis of viral components by blocking enzymes inside the cell;
prevent viruses from entering (human) cell / bind to cellular receptors targeted by viruses / bind to virus-associated proteins/VAPs which target cellular receptors;
prevent/hinder the release of viruses from the cell;
(c) viruses mutate quickly so adapt to drugs/evade immune system response / OWTTE;
bacteria are more complex and thus can be targeted in more ways / viruses lack subunits/functions targeted by antibacterials / OWTTE;
bacteria can be killed/impaired by simple chemical agents / viruses cannot be killed and must be targeted on genetic level / OWTTE;
different types of bacteria employ similar metabolic processes and thus can be targeted by common antibacterials / each kind of virus usually requires special drugs/approaches / OWTTE;
Examiners report
This was probably the question in this option that candidates found most difficult and whilst many could give correct differences between viruses and bacteria they seemed to have little knowledge about the action of antiviral drugs or the reasons why viral infections are more difficult to treat.
Question
AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome) has resulted in millions of deaths worldwide since it was first recorded in 1981. The control and treatment of HIV is made worse by the high price of anti-retroviral agents and sociocultural issues. Discuss one sociocultural difficulty facing society today associated with solving this global problem.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
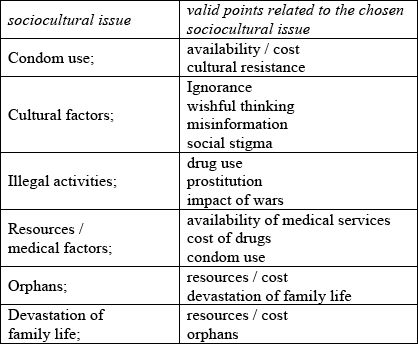
Award [1] for identification of sociocultural issue.
Award [1] each for any two valid points related to the chosen sociocultural issue.
Do not accept contraception for condom use.
Apply OWTTE throughout.
Examiners report
This part of the question proved very challenging to most candidates. Many journalistic responses were given here also. Candidates struggled to provide a sociocultural difficulty associated with AIDS and found it difficult to articulate a coherent response. However, OWTTE allowed candidates to score some marks.
Question
State one difference between viruses and bacteria.
Discuss three methods in which the activities of humans has created an increase in the resistance to penicillin in bacteria populations.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
viruses smaller than bacteria;
viruses do not have a nucleus/cytoplasm/cell membrane/cell wall/ribosomes;
viruses are not cells;
viruses do not feed/excrete/grow;
Allow viruses are not living/alive.
overuse of antibiotics has increased proportion of resistant bacteria;
use of penicillin in animal feedstock has introduced antibiotics into human food chain (increasing proportion of resistant bacteria);
patients not completing course of antibiotics increases proportion/spread of resistant bacteria;
Examiners report
Most candidates scored the mark in (a).
A number of journalistic responses were given in part (b) where candidates did not discuss the activities of humans that have created an increase in resistant bacteria. Some candidates misread the question and discussed how penicillin had been modified to combat resistant bacteria. Overuse and developing resistance was generally the only valid reason given.
Question
State two differences in structure between viruses and bacteria.
Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
Discuss two difficulties associated with the development of drugs for the effective treatment of AIDS.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
viruses do not have cell/cellular structure;
viruses do not have nucleus;
viruses do not have cell wall;
viruses do not have cytoplasm;
Accept opposite statements for bacteria.
stops virus replication;
Accept reproduction / multiplication.
becomes part of DNA of virus / alters virus DNA / blocks polymerase which builds DNA;
changes the cell membrane that inhibits the entry of virus into the cells;
prevents viruses from leaving the cell (after reproducing);
HIV mutates (rapidly);
Accept AIDS mutates
HIV metabolism linked to that of host cell / HIV uses host cell / drugs harm host cell as well as HIV / difficult to target HIV without damaging host cell;
HIV destroys helper cells of the immune system;
Examiners report
Many students failed to note that the first part of the question referred to structural differences between viruses and bacteria, rather than more general differences. The mode of action of antiviral drugs appeared to be poorly understood and answers were often very vaguely expressed, as were answers to why effective AIDS treatment is such a problem.
Question
Many diseases are the result of infection of the body by either bacteria or viruses.
(i) State the name of one disease caused by each.
Bacteria:
Viruses:
(ii) Discuss the differences between bacteria and viruses.
Describe two misuses of antibiotics that have led to some bacteria becoming resistant.
It is much more difficult to produce effective antiviral drugs than drugs that kill bacteria. Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) Bacteria:
tuberculosis/TB / syphilis / cholera / salmonella / bronchitis / botulism / lyme disease / (stomach) ulcers / anthrax / diptheria / meningitis / MRSA / gonorrhea / chlamydia / septicaemia;
Viruses:
influenza / common cold / AIDS / herpes / rabies / small pox / polio / rubella / yellow fever / measles / mumps / encephalitis / chicken pox / shingles / mononucleosis;
Do not accept name of an organism (such as e-coli) rather than a disease.
(ii) bacteria larger than viruses / viruses are smaller than bacteria;
bacteria are cells / viruses comprise DNA in a protein coat;
bacteria have cell wall/nucleus/cytoplasm / viruses do not have cell components;
bacteria can reproduce without a host / viruses require host/cell for replication/reproduction;
bacteria are not always harmful/parasitic / viruses are always parasitic;
patient non-compliance / not completing courses / OWTTE;
overprescription;
use for animals/in animal feedstock;
Accept overuse.
Do not accept overdose.
becomes part of DNA of virus / alters virus DNA/genetic material / blocks enzyme (polymerase) which builds DNA;
changes the cell membrane so that it inhibits the virus entry/bonding to the cell;
prevents virus from leaving the cell (after reproduction);
prevents virus from using cell to multiply/reproduce/replicate;
Examiners report
Many candidates stated the correct name of one bacterial and one viral disease but some had problems stating differences between bacteria and viruses. Candidates must realize that AIDS is a viral disease not HIV.
In part (c), the terms “over dosage” and “over prescription” were often used interchangeably.
In part (d), the method of action of anti-viral was poorly explained. It seemed candidates, at times, learned several key phrases without clearly understanding their meaning and so used them in inappropriate context.
Question
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), a disease caused by the HIV virus, has resulted in millions of deaths worldwide since it was first identified in 1981.
Explain why viral infections, such as AIDS, are generally more difficult to treat than bacterial infections.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
viruses mutate quickly so adapt to drugs/evade immune system response / OWTTE;
bacteria are more complex and thus can be targeted in more ways / viruses lack sub-units/functions targeted by antibacterials / OWTTE;
different types of bacteria employ similar metabolic processes and thus can be targeted by common antibacterials / each kind of virus usually requires special drugs/approaches / OWTTE;
bacteria can be killed by interfering with cell wall production without attacking host cell / difficult to attack the virus without attacking host cell;
Examiners report
Candidates tended to write a lot in this answer – and it was not very well structured. They needed to keep the focus of their answer on the differences between viral and bacterial infections. It may be that the examiners’ intention to help the candidates by setting the question in context turned out to be more of a hindrance. Candidates spent far too long discussing the specifics of HIV rather than answering the question required.
Question
State two ways in which viruses are different from bacteria.
Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
bacteria are a single cell / viruses are not cellular;
bacteria have cell walls/nuclei / viruses have no nucleus/cell wall;
bacteria larger than viruses / viruses smaller than bacteria;
viruses need host cell to reproduce / viruses take over another cell;
bacteria are organisms/living / bacteria metabolise/can grow/feed/excrete /
viruses are not living / viruses do not metabolise/grow/feed/excrete;
Allow “bacteria have both DNA and RNA / viruses have either RNA or DNA only (but not both)”.
alter cell’s genetic material;
block enzyme activity within host cell;
(changes cell membrane so that it) inhibits virus entry/bonding to cell;
prevents virus from leaving cell (after reproduction);
becomes part of DNA of virus / alters virus / blocks enzyme (polymerase) which builds DNA;
prevents virus from using cell to multiply/reproduce/replicate / prevents virus from using cell’s metabolism;
Examiners report
This question proved to be a life-line for candidates with a strong knowledge of biology and in both parts many candidates scored full marks. Many candidates gave overly lengthy answers here and more concise answers could easily have been given such as bacteria are larger than viruses and bacteria have cell walls unlike viruses in part (a).
Question
Many common illnesses are caused by viral infections.
Acyclovir is an antiviral drug used to treat herpes infections. Outline two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
Discuss two difficulties associated with the development of drugs for the effective treatment of AIDS.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
alter cell’s genetic material;
(changes cell membrane so that it) inhibits virus entry/binding to cell;
prevents virus from leaving cell (after reproduction);
becomes part of DNA of virus / alters virus / blocks enzyme (polymerase) which builds DNA;
prevents virus from using cell to multiply/reproduce/replicate;
Do not accept “blocks enzyme activity within host cell / OWTTE”.
HIV mutates (rapidly) / OWTTE;
Do not accept “AIDS mutates” without mention of the virus.
HIV destroys (T-)helper cells/white blood cells/lymphocytes / HIV attacks immune system;
Penalize the use of “AIDS” for “HIV” once only.
Do not accept general answers based on “cost of drugs” or “cost of development”.
Examiners report
More than half of the candidates showed a good understanding of how antiviral drugs work.
Most candidates talked about the rapid mutation of viruses, however, only a few talked about viruses destroying T-helper cells as a difficulty associated with the development of drugs for the treatment of AIDS. A number of candidates discussed the high cost of such drugs that was irrelevant to the question. Some candidates confused AIDS with HIV.
Question
Diseases may be caused by bacteria or viruses.
Explain how penicillins work as antibacterials.
The R group in the general structure of penicillin shown below represents a side-chain which is regularly modified.
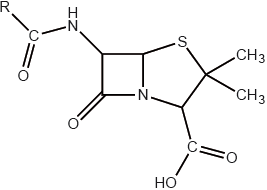
Explain why this modification is necessary.
Describe two ways in which antiviral drugs work.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
prevent the formation of bacterial cell walls / interfere with chemicals/enzyme/transpeptidase needed by bacteria to form normal cell walls / inhibits cross-links developing in bacterial cell walls;
(osmosis) causes water to enter bacterial cell and cell bursts / cell wall weakens (making it more permeable to water) and bacterium bursts (and dies);
makes penicillin more effective / makes penicillin resistant to penicillinase (enzyme) / allows different methods of administration / penicillins can be made which are resistant to acid in the stomach;
change cell membrane to prevent viruses entering/attaching to cell;
alter cell’s genetic material so virus cannot use it to multiply;
inhibit enzymes involved in replication/reverse transcriptase / stop enzyme activity inside the cell (and prevent the viruses from multiplying);
prevent replicated virus leaving the cell;
initiates apoptosis/death of cells infected by viruses;
mimic guanosine/base-sugar monomer in DNA/RNA formation inhibiting enzymes involved in replication;
Examiners report
Many students were able to explain how penicillins work as antibacterial agents although sometimes the answers lacked clarity. The reason for the modification of the side-chain of penicillin was often linked to bacterial resistance but did not specifically address how it actually affects the action of penicillin. Candidates were often unclear on the different ways that anti-viral drugs can work and although they usually managed to achieve one of the two marks, many explanations lacked the precision in terms of their mode of action.
Question
Penicillin is an antibiotic which contains a beta-lactam ring. Its general structure is shown below.
(i) Outline what is meant by the term “ring strain”.
(ii) On the diagram above, label with asterisk/s (*) the carbon atom/s that experience ring strain.
(i) Some antibiotic-resistant bacteria produce a beta-lactamase enzyme which destroys penicillin activity. Suggest how adding clavulanic acid to penicillin enables the antibiotic to retain its activity.
(ii) Populations of antibiotic-resistant bacteria have increased significantly over the last 60 years. Outline why antibiotics such as penicillin should not be prescribed to people suffering from a viral infection.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
i
bond angles smaller/distorted
OR
instability resulting from abnormal bond angles
OR
bond angles «approximately» 90° instead of 109.5°/120°
Accept “109/110°” for “109.5°”
ii
asterisks (*) on all 3 lactam ring carbon atoms
Must mark all 3 carbon atoms.
Ignore asterisks on the RHS carbon atoms of the five-membered ring.
i
beta-lactam/four-membered ring «in clavulanic acid» reacts with enzyme/beta lactamase
Accept “acts as enzyme inhibitor/suicide substrate/preferentially binds to enzyme”.
ii
antibiotics not effective against viruses
OR
viruses have no cell wall/cell structure/target structures to attack
increasing exposure of bacteria «to antibiotic» increases resistance
Accept “antibiotics kill beneficial bacteria” for M2.
Question
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) are both used as antivirals to help prevent the spread of the flu virus, but are administered by different methods.
Zanamivir must be taken by inhalation, not orally. Deduce what this suggests about the bioavailability of zanamivir if taken orally.
Oseltamivir does not possess the carboxyl group needed for activity until it is chemically changed in the body. Deduce the name of the functional group in oseltamivir which changes into a carboxyl group in the body. Use section 37 of the data booklet.
The synthesis of oseltamivir is dependent on a supply of the precursor shikimic acid, which is available only in low yield from certain plants, notably Chinese star anise. State one alternative green chemistry source of shikimic acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«oral bioavailability is» low
OR
drug is broken down/pH too low/unable to be absorbed from gut
OR
only a small proportion of the drug «taken by mouth» reaches the target organ
ethoxycarbonyl/carbonyl attached to oxygen
Accept “ester”.
Any one of:
fermentation
OR
microbial production
genetically engineered bacteria/E.coli
sweetgum «seeds/leaves/bark»
OR
pine/fir/spruce tree «needles»
OR
Ginkgo biloba
Accept other specific examples of more plentiful plant sources.
Question
Antiviral drugs are designed to take different approaches to fighting viruses.
Outline how oseltamivir (Tamiflu®) works.
Oseltamivir was commercially produced from shikimic acid, a precursor which is a metabolite in micro-organisms and plants.
Outline how green chemistry was used to develop the precursor for oseltamivir in order to overcome a shortage of the drug during the flu season.
Suggest why the administration of antibiotics to humans and animals can affect the environment.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«drug» blocks/inhibits «viral» enzyme/neuraminidase/NA «activity»
prevents virus from leaving/escaping host cells «thus cannot infect other cells»
[2 marks]
ALTERNATIVE 1:
«using» genetically modified/GM E. Coli/bacteria/microorganisms
E. Coli/bacteria biosynthesis
OR
E. Coli/bacteria «overfed by glucose» undergo fermentation
OR
cells of the bacteria «are broken down to» form precursor/shikimic acid
ALTERNATIVE 2:
use readily available cyclic ester/lactone
forms «the correct stereoisomer of oseltamivir» in a shorter number of chemical steps
Do not accept “planting more Chinese star anise” or “other plant sources of shikimic acid”.
[2 marks]
«can develop antibiotic» resistance in bacteria/microorganisms
OR
changes in microbial/bacterial population
Accept secondary effects, such as reduced biodiversity of aquatic/soil ecosystems, denitrification of soil (due to decline in nitrogen-fixing bacteria). No mark for just stating “water contamination”.
No mark for just stating “failure of aquatic/marine environment”.
[1 mark]
Question
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) are antiviral drugs used to prevent flu.
State the names of two functional groups that both compounds contain, using section 37 of the data booklet.
Explain how oseltamivir and zanamivir can stop the spread of the flu virus in the body.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
amido
ether
carbonyl
Accept “amide/carboxamide”.
Accept “alkenyl/alkene”.
Accept “amino/amine”.
[Max 2 Marks]
by preventing the virus from leaving the host cell
by inhibiting viral enzymes/neuraminidases «needed to release virus»
Question
Antiviral drugs are a major research focus.
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) are used against flu viruses. Explain how these drugs function.
Shikimic acid, the precursor for oseltamivir (Tamiflu), was originally extracted from star anise, and is now produced using genetically modified E. coli bacteria.
Suggest one difficulty associated with synthesizing oseltamivir (Tamiflu) from star anise.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
blocks/inhibits neuraminidase/NA/«viral» enzyme which allows viruses to pass through cell membrane
prevent virus from leaving/escaping host cell «thus it cannot infect other cells»
[2 marks]
Any one of:
limited supply of star anise/plant
«star anise» takes time to grow
time-consuming/multi-step extraction
low concentration in plan
Accept “low yield for extraction/conversion” OR “requires environmentally damaging solvents”.
[1 mark]
Question
Antiviral medications such as zanamivir (Relenza) are commonly available for consumer use.
Identify the names of two functional groups present in zanamivir using section 37 of the data booklet.
Distinguish between bacteria and viruses.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
hydroxyl
carboxyl/carbonyl
ether
amido/carbonyl
Accept “alcohol/hydroxy” for “hydroxyl”, “carboxylic acid” for “carboxyl” and “amide/carboxamide” for “amido”.
Accept “amino/amine” OR “imine/imino” but these are not correct as they are part of the guanidino group.
Accept “alkenyl/alkene/carbon to carbon double bond” but not “C=C” OR “carbon double bond”.
Accept “carbonyl” only once.
Accept “heterocyclic ring” for “ether”.
[2 marks]
Any two of:
bacteria perform living functions «on their own» AND viruses do not «without host cell»
bacteria have cell walls AND viruses do not
OR
bacteria do not have a capsid AND viruses do
bacteria larger than viruses
bacteria reproduce by fission/budding AND viruses reproduce within a living host cell
Accept examples of living functionsexcretion, reproduction etc for M1.
Accept “bacteria have flagella/cytoplasm/ribosome AND virus can have head/protein tail/double stranded RNA/single stranded DNA”.
Accept other specific structural differences for M2.
Accept “asexual reproduction for bacteria” for M4.
[2 marks]

