Question
a. Describe the proper disposal of low-level radioactive waste in hospitals.
b. Outline a green chemistry solution for problems generated by the use of organic solvents.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. store until material becomes inactive/radiation levels drop
dispose with other waste
OR
dispose in landfills
Only award M2 if M1 correct.
Accept “dispose by incineration” for M2.
b. “use of» alternative solvents such as supercritical/liquid $\mathrm{CO}_2$
Do not accept political or regulatory solutions.
OR
use of water «as solvent»
$O R$
solvent-free reactions «for example, polymerization of propene»
$O R$
solid-state chemistry
$O R$
recycle «waste» solvents
OR
catalysis that leads to better/higher yield
“catalysis” alone not sufficient for mark.
OR
reducing number of steps $\boldsymbol{V}$
Question
Most of the nuclear waste generated in a hospital is low-level waste (LLW).
a. Outline what is meant by low-level waste.
b. Outline the disposal of LLW.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. small/low amounts of radiation $A N D$ for a short time $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
Note: Accept “weakly ionizing radiation” instead of “small amounts of radiation”.
Accept “short half-lives” instead of “for a short time”.
b. stored in shielded containers until radiation drops «to a safe level» [ $[$ ]
Question
\text { A student synthesized aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, in a school laboratory. }
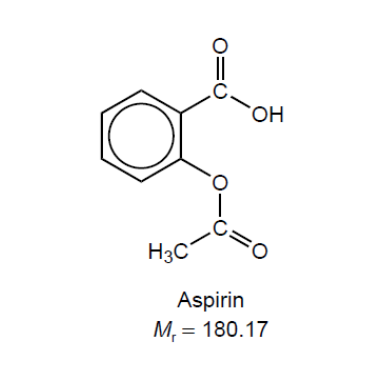
$0.300 \mathrm{~g}$ of crude aspirin was dissolved in ethanol and titrated with sodium hydroxide solution, $\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})$.
$\mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{C}_9 \mathrm{H}_8 \mathrm{O}_4$ (in ethanol) $\rightarrow \mathrm{NaC}_9 \mathrm{H}_7 \mathrm{O}_4(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l})$
a. Predict one absorption band present in an infrared (IR) spectrum of aspirin, using section 26 of the data booklet.
b(i)Determine the mass of aspirin which reacted with $16.25 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of $0.100 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}{ }^{-3} \mathrm{NaOH}$ solution.
$\mathrm{b}$ (ii)etermine the percentage purity of the synthesized aspirin.
c. Outline how aspirin can be chemically modified to increase its solubility in water.
d. State why aspirin should not be taken with alcohol.
e. Outline two factors which must be considered to assess the greenness of any chemical process.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any one of:
1050-1410 «cm ${ }^{-1}$ due to $C-O »[M]$
$1700-1750$ «cm ${ }^{-1}$ due to $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ in acids and esters» [ $\boldsymbol{V}$ ]
$2500-3000$ «cm ${ }^{-1}$ due to $\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{H}$ in acids» [ $[$ ]
$2850-3090$ «cm ${ }^{-1}$ due to $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ in alkanes and arenes» [ $\sim$ ]
$$
\begin{gathered}
\mathrm{b}(\mathrm{i}) \mathrm{n}(\text { aspirin }) «=\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{NaOH})=\frac{16.25 \mathrm{~cm}^3}{1000} \times 0.100 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}^{-3} »=1.625 \times 10^{-3} \text { «mol» }[\boldsymbol{U}] \\
\mathrm{m}\left(\text { aspirin) } «=1.625 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~mol} \times 180.17 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} »=0.293 « \mathrm{~g} »[\boldsymbol{U}]\right.
\end{gathered}
$$
Note: Award [2] for correct final answer.
$$
\text { b(ii)s } \left.\frac{0.293 \mathrm{~g}}{0.300 \mathrm{~g}} \times 100 \% »=97.7 \text { «\% [ } \mathbf{V}\right]
$$
c. convert to a salt
OR
react with sodium hydroxide/NaOH $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept other reactions forming soluble salts.
Accept “to ionize” but not “more polar”.
d. synergistic effect/increased toxicity
OR
increased risk of stomach/intestines bleeding/ulcers/heartburn
$O R$
increased risk of liver toxicity/damage
OR
increased risk of nausea/vomiting $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
e. Any two of:
energy requirements «during production» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
use of toxic materials «during production» $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
use of solvents «that are not recycled» $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
emission of toxic by-products $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
quantity of waste produced
OR
atom economy $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept “E-factor/carbon efficiency/\% of carbon in reactants vs products” for M1.
Accept references to materials being/not being recycled for $M 3$.
Question
Disposal of chemical waste is a growing problem in industry.
a. Outline the impact of antibiotic waste on the environment.
b. Suggest a concern about the disposal of solvents from drug manufacturing.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «leads to bacterial» resistance «to antibiotics»
$O R$
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
OR
useful/beneficial/less harmful bacteria replaced with «more» harmful bacteria
NOTE: Accept “affects/disturbs micro-ecosystems”.
b. Any one of:
«most are» toxic «to living organisms»
$O R$
incomplete combustion/incineration can produce toxic products/dioxins/phosgene
$O R$
carcinogenic/can cause cancer
accumulate in groundwater
OR
have limited biodegradability
cost of disposal
NOTE: Do not accept “harmful to the environment”.
Do not accept just “pollutes water”.
Do not accept “hazard of disposal”.
Accept “ozone depletion” only if there is some reference to chlorinated solvents.
Question
The structure of penicillin is shown in section 37 of the data booklet.
a. State the internal bond angles in the $\beta$-lactam ring and the expected bond angles for the same atoms in an open structure.
b. Explain how the open $\beta$-lactam ring kills bacteria.
c. Outline one effect of over-prescription of penicillin.
d. State how the structure of penicillin can be changed to combat this effect.
e. Suggest why human cells are not affected by penicillin.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.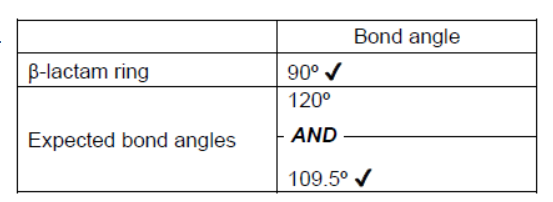
Accept “109”.
b. «irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of bacterial cell walls
cells absorb water $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ burst
OR
cells cannot reproduce
Accept “reacts with” for “bonds to” for M1.
Do not accept “cell membrane” for “cell wall” for M1.
Accept “cells burst due to osmotic pressure” for M2.
Accept “bacteria” for “cells” for M2.
c. Any one of:
leads to «bacterial» resistance «to antibiotics»
OR
makes antibiotics less effective
OR
increased side effects due to larger dosages/over time
increases proportion of resistant bacteria
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
OR
destroyed bacteria replaced by more harmful bacteria
resistant bacteria pass on their mutation to next generation damage to ecosystems
Accept “superbugs such as MRSA develop” but superbug must be identified.
Accept “immune” for resistant but do not accept “tolerance”
d. «modify» side-chain
Accept “«modify» R”.
e. no cell walls
OR
humans do not have transpeptidase
Question
Suggest two reasons why chlorinated solvents should neither be released into the atmosphere nor incinerated (burnt).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
«weak» $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{Cl}$ bonds break/produce radicals
contribute to ozone depletion
contribute to «photochemical» smog $\checkmark$
cause cancers
damage respiratory system
cause organ failure
produce toxic chemicals/phosgene/dioxins
Accept “chlorinated solvents are toxic”.
Question
Drug synthesis often involves solvents.
Identify a common hazardous solvent and a Green solvent that could replace it.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Hazardous solvent:
Any one of:
methanal/formaldehyde
methanol
chlorinated solvent/carbon tetrachloride/methylene chloride/dichloromethane
diethyl ether/ethoxyethane
benzene
OR
methyl benzene/toluene
OR
«1,2/1,3/1,4» dimethylbenzene/«ortho/o-/meta/m-/para/p-» xylene
Green solvent:
Any one of:
water
«supercritical/liquid» carbon dioxide/supercritical fluids
ethanol «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
propan-2-ol/2-propanol/isopropanol «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
propanone/acetone «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
ethyl ethanoate/ethyl acetate «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
organic carbonates/dimethyl carbonate/diethyl carbonate/ethylene
carbonate/propylene carbonate
ionic liquids
fluorous solvents
Accept correct names (either IUPAC or generic) or formulas.
Do not accept inorganic acids such as $\mathrm{HCl}, \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4$, etc.
Accept any specific chlorinated solvent.
Accept other hazardous solvents.
Do not accept any solvent given as both hazardous and green.
Award [2] for combination “Hazardous solvent: dimethylformamide/DMF/N,N-dimethylmethanamide” AND “Green solvent: methanol ronly if replacing \text { a hazardous solvents”. }
Accept other green solvents but not “solvents from biomass/food waste”.
[2 marks]
Question
Many drugs, including aspirin, penicillin, codeine and taxol, have been modified from compounds that occur naturally.
a. Aspirin is often taken to reduce pain, swelling or fever. State one other use of aspirin.
b.i. State what is meant by the bioavailability of a drug.
b.ii.Outline how the bioavailability of aspirin may be increased.
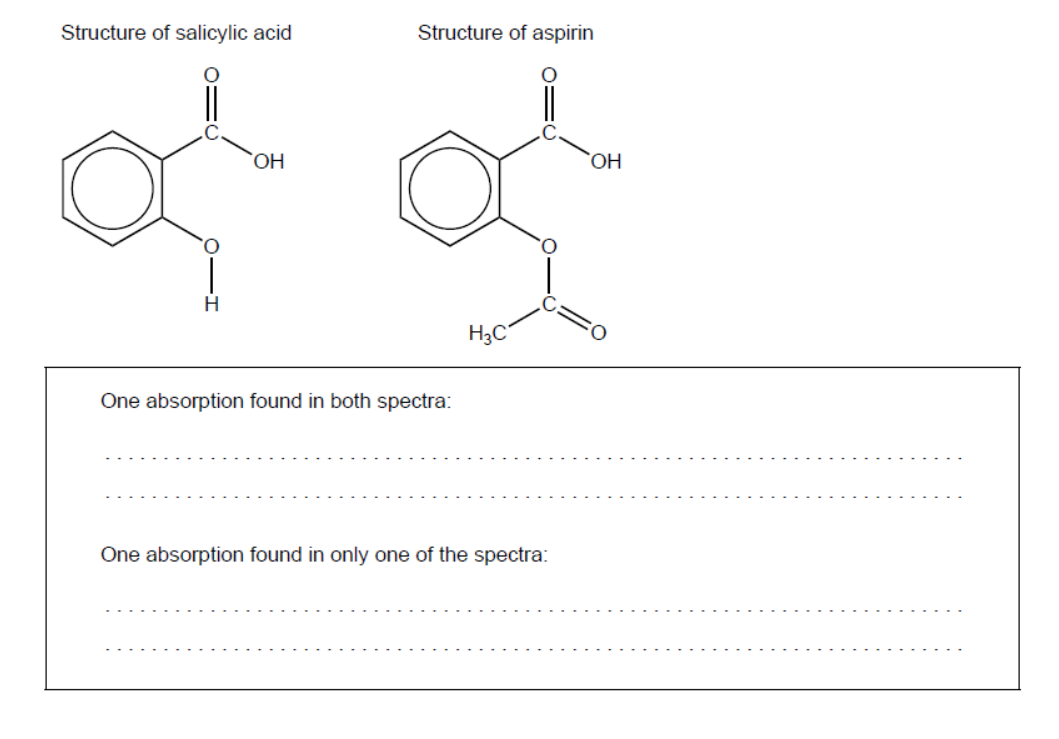
c.i. Compare and contrast the IR spectrum of aspirin with that of salicylic acid, using section 26 of the data booklet.
c.ii.Describe how penicillin combats bacterial infections.
c.iiiOutline two consequences of prescribing antibiotics such as penicillin unnecessarily.
c.ivState how penicillins may be modified to increase their effectiveness.
d.i. Morphine and codeine are strong analgesics. Outline how strong analgesics function.
d.ii.Suggest one reason why codeine is more widely used than morphine as an analgesic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Any one of:
anticoagulant
lower risk of heart attack/strokes
prevent recurrence of heart attack/stroke
prevents cancer of colon/oesophagus/stomach
Accept “prevents/reduces blood clots” OR “blood thinner”.
[1 mark]
b.i. fraction/proportion/percentage «of administered dosage» that reaches target «part of human body»
OR
fraction/ proportion/percentage «of administered dosage» that reaches blood «plasma»/systemic circulation
Accept “the ability of the drug to be absorbed by the body” OR “the extent to which the drug is absorbed by the body”.
Do not accept “the amount/quantity of the drug absorbed”.
[1 mark]
b.ii.«intravenous» injection/IV
Accept “parenterally”.
Accept “react with alkali/NaOH” OR “convert to ionic form/salt”.
[1 mark]
c.i. One absorption found in both spectra:
Any one of:
1050-1410 cm ${ }^{-1}$ “C-O in alcohols, esters, ethers”
$1700-1750 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}$ “C=O in carboxylic acids, esters»
$2500-3000 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}$ «O-H in carboxylic acids»
$2850-3090 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}$ «C-H in alkanes, alkenes, arenes»
One absorption found in only one of the spectra:
$3200-3600 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}$ «O-H in alcohols, phenols»
Award [1 max] if candidate states bonds ( $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ in both, $\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{H}$ in salicylic acid only) but doesn’t quote wavelength ranges.
Accept a second/additional absorption at $1700-1750 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}$ from the $C=0$ in ester.
[2 marks]
c.ii Any two of:
ring is «sterically» strained
OR
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amide/amido group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
«irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of bacterial cell walls
cells absorb water $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ burst
OR
cells cannot reproduce
Award [1 max] for “interferes with cell wall production”.
Do not accept “cell membrane” instead of “cell wall”.
[2 marks]
c.iiiAny two of:
leads to «bacterial» resistance/proportion of resistant bacteria increases
OR
leads to penicillinase-producing bacteria
damage to/contamination of bodies of water/ecosystems
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
destroyed bacteria replaced by more harmful bacteria
Accept “endocrine disruptor”.
Do not accept “increased cost of developing antibiotics”.
[2 marks]
c.ivmodify side chain
[1 mark]
d.i. temporarily bind to/block/interfere with receptor sites in brain
OR
prevent transmission of pain impulses within CNS/central nervous system
[1 mark]
d.ii.codeine has a wider therapeutic window
Accept “codeine has lower activity” OR “codeine has lower risk of overdose” OR “codeine is less potent” OR “codeine has less side-effects”.
Do not accept “lower abuse potential for codeine” OR “less addictive “than morphine” OR “codeine has a lower bioavailability” OR “available without prescription” OR “cheaper”.
[1 mark]
Question
Antiviral drugs are a major research focus.
a. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) are used against flu viruses. Explain how these drugs function.
b. Shikimic acid, the precursor for oseltamivir (Tamiflu), was originally extracted from star anise, and is now produced using genetically modified $E$. coli bacteria.
Suggest one difficulty associated with synthesizing oseltamivir (Tamiflu) from star anise.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. blocks/inhibits neuraminidase/NA/«viral» enzyme which allows viruses to pass through cell membrane prevent virus from leaving/escaping host cell «thus it cannot infect other cells»
[2 marks]
b. Any one of:
limited supply of star anise/plant
«star anise» takes time to grow
time-consuming/multi-step extraction
low concentration in plan
Accept “low yield for extraction/conversion” OR “requires environmentally damaging solvents”.
[1 mark]
Question
Penicillin was one of the first antibiotics to be isolated and identified for its ability to treat bacterial infections.
Explain the importance of the beta-lactam ring in the antibiotic activity of penicillin.
Identify two dangers of the overuse of antibiotics.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ring is «sterically» strained
OR
angles of 90° instead of 109.5/109/120° angles
OR
angles smaller than 109.5/109/120°/tetrahedral/trigonal planar/triangular planar angle
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amide/amido group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
binds to/reacts with/interferes with/inactivates transpeptidase/enzyme
responsible for bacterial cell wall formation/cross-linking
Do not accept “cell membrane” for “cell wall”.
Accept “bonds to” for “binds to” in M3
Any two for [1 max] from:
leads to «bacterial» resistance «of antiobiotics»
OR
makes antibiotics less effective
OR
increased side effects due to larger dosages
proportion of resistant bacteria increases
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
OR
destroyed bacteria replaced by more harmful bacteria
resistant bacteria pass on their resistance/mutation to next generation
damage to ecosystems
Accept “superbugs such as MRSA develop” but superbug must be identified.
Question
Radioactive isotopes are used in a variety of medical procedures including medical imaging and radiotherapy.
Identify examples of two types of medical radioactive waste and how each must be treated for proper disposal.
Outline an ethical implication of using nuclear treatments in medicine.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Award [1] for example AND corresponding treatment.
Award [1 max] for the two examples.
risk vs benefit «patient and environment»
OR
providing adequate information to patients about risks
OR
security concerns if nuclear radioactive material ended up with terrorists
OR
cultural resistance/superstition/lack of education
OR
«potential» exposure of health workers «to radioactivity»
OR
proper training «in radioactive hazards» not always given to workers
OR
proper disposal of radioactive materials
Accept other valid ethical implications (note that risk of cancer to the patient is not an ethical issue, while risk of cancer to the health worker is).
Do not accept “security concerns” alone – there must be some reference to an ethical implication.
Question
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) are both used as antivirals to help prevent the spread of the flu virus, but are administered by different methods.
Zanamivir must be taken by inhalation, not orally. Deduce what this suggests about the bioavailability of zanamivir if taken orally.
Oseltamivir does not possess the carboxyl group needed for activity until it is chemically changed in the body. Deduce the name of the functional group in oseltamivir which changes into a carboxyl group in the body. Use section 37 of the data booklet.
The synthesis of oseltamivir is dependent on a supply of the precursor shikimic acid, which is available only in low yield from certain plants, notably Chinese star anise. State one alternative green chemistry source of shikimic acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«oral bioavailability is» low
OR
drug is broken down/pH too low/unable to be absorbed from gut
OR
only a small proportion of the drug «taken by mouth» reaches the target organ
ethoxycarbonyl/carbonyl attached to oxygen
Accept “ester”.
Any one of:
fermentation
OR
microbial production
genetically engineered bacteria/E.coli
sweetgum «seeds/leaves/bark»
OR
pine/fir/spruce tree «needles»
OR
Ginkgo biloba
Accept other specific examples of more plentiful plant sources.
Question
Solubility plays an important role in the bioavailability of drugs in the body.
Suggest why aspirin is slightly soluble in water. Refer to section 37 of the data booklet.
Formulate an equation for the conversion of aspirin to a more water soluble derivative.
A student prepares aspirin from salicylic acid in the laboratory, extracts it from the reaction mixture, ensures the sample is dry and determines its melting point.
Suggest why the melting point of the student’s sample is lower and not sharp compared to that of pure aspirin.
Organic molecules can be characterized using infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
Compare and contrast the infrared peaks above 1500 cm−1 in pure samples of aspirin and salicylic acid using section 26 of the data booklet.
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the largest producers of waste solvents.
State a green solution to the problem of organic solvent waste.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
presence of «large» benzene/arene ring AND non-polar/hydrophobic
OR
presence of «large» benzene/arene ring AND cannot form H-bond with water
contain COOH/carboxyl/–OH/hydroxyl «and ester group» AND polar/hydrophilic
OR
contain COOH/carboxyl/–OH/hydroxyl «and ester group» AND can form H-bonds with water
Accept “phenyl” for “benzene ring”.
Accept “carboxylic acid” for “carboxyl”.
Do not accept “alcohol” for “hydroxyl”.
[2 marks]
OR
C6H4(OCOCH3)COOH + NaOH → C6H4(OCOCH3)COONa + H2O
Charges (O– and Na+) not necessary to score the mark.
Accept net ionic equation.
Accept any strong base in place of NaOH.
[1 mark]
«student’s» sample impure
lattice disrupted/not uniform «due to presence of impurities»
OR
fewer interparticle/intermolecular forces «due to presence of impurities»
Accept converse arguments.
[2 marks]
One similarity:
peak at 2500–3000 «cm–1»/peak due to O–H/hydroxyl in carboxylic acids
OR
peak at 1700–1750 «cm–1»/peak due to C=O/carbonyl
OR
peak at 2850–3090 «cm–1»/peak due to C–H of arene
One difference:
peak at 3200–3600 «cm–1» in salicylic acid/ peak due to O–H in phenol in salicylic acid
OR
«two» peaks at 1700–1750 «cm–1» in aspirin AND one peak «in the same area» in salicylic acid
Accept “peak at 1600 cm–1 for arene/benzene ring” – not in the data booklet.
Accept “2500–3600 cm–1 «overlapping absorptions of two O–H» in salicylic acid”.
Accept “stronger/broader/split peak at 1700–1750 cm–1 in aspirin”.
[2 marks]
«use of» alternative solvents such as supercritical/liquid CO2
OR
use of water «as solvent»
OR
solvent-free reactions «for example, polymerization of propene»
OR
solid-state chemistry
OR
recycle «waste» solvents
OR
catalysis that leads to better/higher yield
OR
reducing number of steps
Do not accept political/regulatory solutions.
“catalysis” not sufficient for mark.
[1 mark]
Question
Antiviral drugs are designed to take different approaches to fighting viruses.
Outline how oseltamivir (Tamiflu®) works.
Oseltamivir was commercially produced from shikimic acid, a precursor which is a metabolite in micro-organisms and plants.
Outline how green chemistry was used to develop the precursor for oseltamivir in order to overcome a shortage of the drug during the flu season.
Suggest why the administration of antibiotics to humans and animals can affect the environment.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«drug» blocks/inhibits «viral» enzyme/neuraminidase/NA «activity»
prevents virus from leaving/escaping host cells «thus cannot infect other cells»
[2 marks]
ALTERNATIVE 1:
«using» genetically modified/GM E. Coli/bacteria/microorganisms
E. Coli/bacteria biosynthesis
OR
E. Coli/bacteria «overfed by glucose» undergo fermentation
OR
cells of the bacteria «are broken down to» form precursor/shikimic acid
ALTERNATIVE 2:
use readily available cyclic ester/lactone
forms «the correct stereoisomer of oseltamivir» in a shorter number of chemical steps
Do not accept “planting more Chinese star anise” or “other plant sources of shikimic acid”.
[2 marks]
«can develop antibiotic» resistance in bacteria/microorganisms
OR
changes in microbial/bacterial population
Accept secondary effects, such as reduced biodiversity of aquatic/soil ecosystems, denitrification of soil (due to decline in nitrogen-fixing bacteria). No mark for just stating “water contamination”.
No mark for just stating “failure of aquatic/marine environment”.
[1 mark]
Question
The production of many pharmaceutical drugs involves the use of solvents.
Suggest one problem associated with chlorinated organic solvents as chemical waste.
Suggest how the principles of green chemistry can be used to solve the environmental problems caused by organic solvents.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any of:
«most are» toxic «to living organisms»
OR
incomplete combustion/incineration can produce toxic products/dioxins/phosgene
OR
carcinogenic
«some can be» greenhouse gases
ozone-depleting
can contribute to formation of «photochemical» smog
accumulate in groundwater
OR
have limited biodegradability
cost/hazards of disposal
Do not accept “harmful to the environment”.
Do not accept just “pollutes water”.
[1 mark]
use organic solvent-free synthetic methods
OR
use water as a solvent
OR
based on atom economy
OR
recover/reuse solvents
[1 mark]
Question
Radioisotopes are used to diagnose and treat various diseases. Explain the low environmental impact of most medical nuclear waste.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
emits weak ionising radiation
OR
low activity/radioactivity
can be stored until material becomes inactive AND then disposed with normal waste
«isotopes» have short lives
OR
exist for a short period of time
Award [1 max] for “low-level waste/LLW”.
[Max 2 Marks]
Examiners report
Question
Many drugs, including aspirin, penicillin, codeine and taxol, have been modified from compounds that occur naturally.
Aspirin is often taken to reduce pain, swelling or fever. State one other use of aspirin.
State what is meant by the bioavailability of a drug.
Outline how the bioavailability of aspirin may be increased.
Compare and contrast the IR spectrum of aspirin with that of salicylic acid, using section 26 of the data booklet.
Describe how penicillin combats bacterial infections.
Outline two consequences of prescribing antibiotics such as penicillin unnecessarily.
State how penicillins may be modified to increase their effectiveness.
Morphine and codeine are strong analgesics. Outline how strong analgesics function.
Suggest one reason why codeine is more widely used than morphine as an analgesic.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any one of:
anticoagulant
lower risk of heart attack/strokes
prevent recurrence of heart attack/stroke
prevents cancer of colon/oesophagus/stomach
Accept “prevents/reduces blood clots” OR “blood thinner”.
[1 mark]
fraction/proportion/percentage «of administered dosage» that reaches target «part of human body»
OR
fraction/ proportion/percentage «of administered dosage» that reaches blood «plasma»/systemic circulation
Accept “the ability of the drug to be absorbed by the body” OR “the extent to which the drug is absorbed by the body”.
Do not accept “the amount/quantity of the drug absorbed”.
[1 mark]
«intravenous» injection/IV
Accept “parenterally”.
Accept “react with alkali/NaOH” OR “convert to ionic form/salt”.
[1 mark]
One absorption found in both spectra:
Any one of:
1050–1410 cm–1 «C–O in alcohols, esters, ethers»
1700–1750 cm–1 «C=O in carboxylic acids, esters»
2500–3000 cm–1 «O–H in carboxylic acids»
2850–3090 cm–1 «C–H in alkanes, alkenes, arenes»
One absorption found in only one of the spectra:
3200–3600 cm–1 «O–H in alcohols, phenols»
Award [1 max] if candidate states bonds (C=O in both, O–H in salicylic acid only) but doesn’t quote wavelength ranges.
Accept a second/additional absorption at 1700–1750 cm–1 from the C=O in ester.
[2 marks]
Any two of:
ring is «sterically» strained
OR
ring breaks up/opens/reacts «easily»
OR
amide/amido group «in ring» is «highly» reactive
«irreversibly» binds/bonds to enzyme/transpeptidase
OR
inhibits enzyme/transpeptidase «in bacteria» that produces cell walls
OR
prevents cross-linking of bacterial cell walls
cells absorb water AND burst
OR
cells cannot reproduce
Award [1 max] for “interferes with cell wall production”.
Do not accept “cell membrane” instead of “cell wall”.
[2 marks]
Any two of:
leads to «bacterial» resistance/proportion of resistant bacteria increases
OR
leads to penicillinase-producing bacteria
damage to/contamination of bodies of water/ecosystems
destroys useful/beneficial bacteria
destroyed bacteria replaced by more harmful bacteria
Accept “endocrine disruptor”.
Do not accept “increased cost of developing antibiotics”.
[2 marks]
modify side chain
[1 mark]
temporarily bind to/block/interfere with receptor sites in brain
OR
prevent transmission of pain impulses within CNS/central nervous system
[1 mark]
codeine has a wider therapeutic window
Accept “codeine has lower activity” OR “codeine has lower risk of overdose” OR “codeine is less potent” OR “codeine has less side-effects”.
Do not accept “lower abuse potential for codeine” OR “less addictive «than morphine»” OR “codeine has a lower bioavailability” OR “available without prescription” OR “cheaper”.
[1 mark]
Question
Antiviral drugs are a major research focus.
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) and zanamivir (Relenza) are used against flu viruses. Explain how these drugs function.
Shikimic acid, the precursor for oseltamivir (Tamiflu), was originally extracted from star anise, and is now produced using genetically modified E. coli bacteria.
Suggest one difficulty associated with synthesizing oseltamivir (Tamiflu) from star anise.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
blocks/inhibits neuraminidase/NA/«viral» enzyme which allows viruses to pass through cell membrane
prevent virus from leaving/escaping host cell «thus it cannot infect other cells»
[2 marks]
Any one of:
limited supply of star anise/plant
«star anise» takes time to grow
time-consuming/multi-step extraction
low concentration in plan
Accept “low yield for extraction/conversion” OR “requires environmentally damaging solvents”.
[1 mark]
Question
Drug synthesis often involves solvents.
Identify a common hazardous solvent and a Green solvent that could replace it.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Hazardous solvent:
Any one of:
methanal/formaldehyde
methanol
chlorinated solvent/carbon tetrachloride/methylene chloride/dichloromethane
diethyl ether/ethoxyethane
benzene
OR
methyl benzene/toluene
OR
«1,2/1,3/1,4» dimethylbenzene/«ortho/o-/meta/m-/para/p-» xylene
Green solvent:
Any one of:
water
«supercritical/liquid» carbon dioxide/supercritical fluids
ethanol «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
propan-2-ol/2-propanol/isopropanol «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
propanone/acetone «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
ethyl ethanoate/ethyl acetate «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»
organic carbonates/dimethyl carbonate/diethyl carbonate/ethylene
carbonate/propylene carbonate
ionic liquids
fluorous solvents
Accept correct names (either IUPAC or generic) or formulas.
Do not accept inorganic acids such as HCl, H2SO4, etc.
Accept any specific chlorinated solvent.
Accept other hazardous solvents.
Do not accept any solvent given as both hazardous and green.
Award [2] for combination “Hazardous solvent: dimethylformamide/DMF/N,N-dimethylmethanamide” AND “Green solvent: methanol «only if replacing a hazardous solvent»”.
Accept other green solvents but not “solvents from biomass/food waste”.
[2 marks]

