Question
Bromine, \(Br_2\) (l), and methanoic acid, HCOOH(aq), react in the presence of sulfuric acid.
\(Br_2 (l) + HCOOH(aq) → 2HBr(aq) + CO_2 (g)\)
(a) Suggest an experimental method that could be used to determine the rate of reaction.
(b) The sulfuric acid is a catalyst in this reaction. Explain how a catalyst increases the reaction rate.
(c) Methanoic acid can react with ethanol to produce an ester. Draw the full structural formula of the organic product and state its name.
Structural formula:
Name:
(d) (i) Write the equation for the complete combustion of ethanol.
(ii) Determine the enthalpy change for the combustion of ethanol, in kJ \(mol^{−1}\), using section 11 of the data booklet.
(e) Bromine also reacts with but-2-ene.
(i) Identify the type of reaction.
(ii) Predict the structural formula of the reaction product.
(iii) Draw the structure of a section of a polymer formed from three monomers of but-2-ene.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) «measure change in»
mass
OR
pressure
OR
volume of gas/\(CO_2\) produced
OR
«intensity of» colour
OR
«electrical» conductivity
OR
pH
with time
(b) provides an alternative reaction pathway AND lower activation energy/\(E_a\)
larger fraction/number of molecules with E ≥ \(E_a\)/enough energy «for a successful
collision»
(c) Structural formula:
Name:
ethyl methanoate
(d) (i) \(CH_3CH_2OH(l) + 3O_2(g) → 2CO_2(g) + 3H_2O(g)\)
(ii) «bond breaking»
1 C-C + 5 C-H + 1 C-O + 1 O-H + 3 O=O / 346 + 5(414) + 358 + 463 +3(498) /
4731 «kJ»
«bond forming»
4 C=O + 6 O-H / 4(804) + 6(463) / 5994 «kJ»
∆H «= 4731– 5994» = −1263 «kJ \(mol^{−1}\) »
(e) (i) «electrophilic» addition/\(A_E\)
(ii) \(CH_3CHBrCHBrCH_3\)
(iii) 
Question
Phosgene, COCl2, is usually produced by the reaction between carbon monoxide and chlorine according to the equation:

(i) Deduce the equilibrium constant expression, Kc, for this reaction.
(ii) State the effect of an increase in the total pressure on the equilibrium constant, Kc.
(i) Sketch the potential energy profile for the synthesis of phosgene, using the axes given, indicating both the enthalpy of reaction and activation energy.
(ii) This reaction is normally carried out using a catalyst. Draw a dotted line labelled “Catalysed” on the diagram above to indicate the effect of the catalyst.
(iii) Sketch and label a second Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curve representing the same system but at a higher temperature, Thigher.
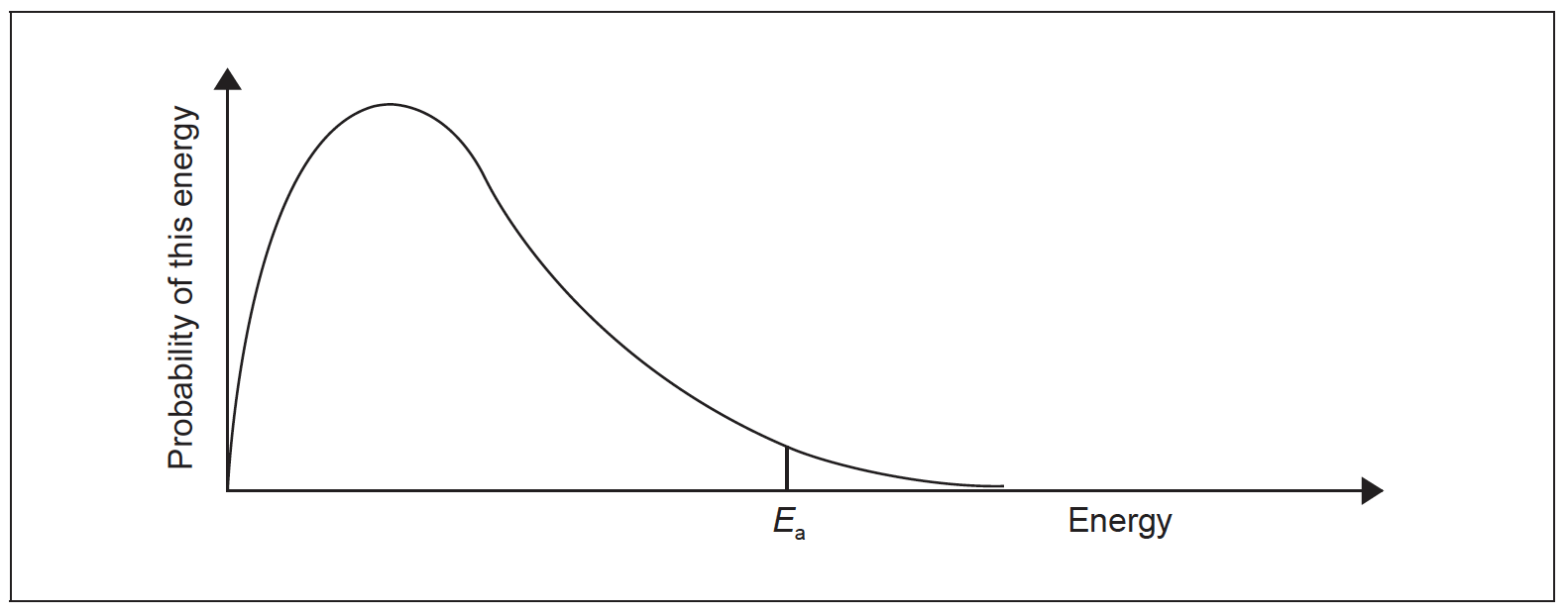
(iv) Explain why an increase in temperature increases the rate of this reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i)
\( \ll {K_{\rm{c}}} = \gg \frac{{\left[ {{\rm{COC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{2}}}} \right]}}{{\left[ {{\rm{CO}}} \right]\left[ {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}_2}} \right]}}\)
(ii)
no effect
(i)
products lower than reactants AND enthalpy of reaction correctly marked and labelled with name or value
activation energy correctly marked and labelled with name or value
Accept other clear ways of indicating energy/ enthalpy changes.
(ii)
lower dotted curve, between same reactants and product levels, labelled “Catalysed”
(iii)
second curve at a higher temperature is correctly drawn (maximum lower and to right of original)
(iv)
greater proportion of molecules have E ≥ Ea or E >Ea
OR
greater area under curve to the right of the Ea
greater frequency of collisions «between molecules»
OR
more collisions per unit time/second
Do not accept just particles have greater kinetic energy.
Do not accept just “more collisions”.