Question
Foods such as rice, bread and potatoes are rich in carbohydrates. There are three main types of carbohydrate – monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Glucose, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}\), is a monosaccharide. When 0.85 g of glucose was completely combusted in a calorimeter, the temperature of 200.10 g of water increased from 20.20 °C to 27.55 °C. Calculate the energy value of glucose in \({\text{J}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}\).
(i) Draw the straight chain structure of glucose.
(ii) Draw the structural formula of \(\alpha \)-glucose.
(iii) Distinguish between the structures of \(\alpha \)- and \(\beta \)-glucose.
(iv) Two \(\alpha \)-glucose molecules condense to form the disaccharide maltose. Deduce the structure of maltose.
One of the major functions of carbohydrates in the human body is as an energy source. State one other function of a carbohydrate.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\Delta T = 7.35\) (K/°C);
\(q( = mc\Delta T = {\text{200.10 g}} \times {\text{4.18 J}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}{{\text{K}}^{ – 1}} \times {\text{7.35 K}}) = 6.15 \times {10^3}{\text{ J}}\) (per 0.85 g of glucose heated);
energy value \( = 7.2 \times {10^3}{\text{ (J}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}{\text{)}}\);
Award [3] for correct final answer.
(i) 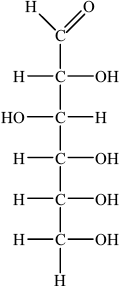
Accept CHO, CH2OH and OH groups on either side of the carbon chain provided OH on C3 is on the opposite side to OHs on C2, C4 and C5.
(ii) 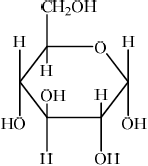 ;
;
Accept CH2OH and OH groups on either face, as long as OH on C3 is on the opposite face to the OH’s on C1, C2 and C4.
No mark awarded if HOCH2 is written, with H bonded to C or if HO is written for hydroxyl groups, with H bonded to C. Penalize this once only in (i), (ii) and (iv).
(iii) the OH on carbon-1/C-1 is inverted / difference in position of OH on carbon-1/C-1;
(iv) 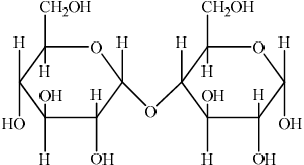 ;
;
energy reserve / can act as precursors in large number of metabolic reactions/for other biologically important molecules;
Examiners report
In (a) SD’s proved the major issue. Most candidates scored the mark for \(\Delta T\). The candidates who struggled made the following errors: incorrect mass (0.85 g) of water was used in \(q = mc\Delta T\), and failure to convert to J per g by dividing \(q\) by 0.85.
In (b)(i) many candidates struggled to draw the straight chain structure of glucose. In many instances the –OH groups were positioned incorrectly and some candidates were careless with bonding writing ‘-C–HO’ rather than ‘-C–OH’.
In (ii) a significant number of candidates mixed up the positions of the substituents on the two faces. In (iii) C1 was commonly omitted. It was surprising to see that quite a few candidates could not draw the structure of maltose in (iv). The most common mistake involved an incorrect linkage
Part (c) was answered well by the vast majority.
Question
A potato chip (crisp) was ignited and the flame was used to heat a test tube containing water.

(i) Calculate the heat required, in kJ, to raise the temperature of the water, using data in the table above and from Table 2 of the Data Booklet.
(ii) Determine the enthalpy of combustion of the potato chip, in \({\text{kJ}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}\).
This energy comes mainly from the combustion of triglycerides. State the name of one other type of lipid found in the body and one role, other than energy storage, of this type of lipid.
Name:
Role:
Explain why lipids have a higher energy content than carbohydrates.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) \({\text{heat}} = \frac{{4.18 \times 20.0 \times (51.3 – 17.8)}}{{1000}}\);
\( = 2.80{\text{ (kJ)}}\);
(ii) \({\text{enthalpy of combustion}} = \left( {\frac{{2.80}}{{0.421}} = } \right){\text{ }} – 6.65{\text{ (kJ}}\,{{\text{g}}^{ – 1}}{\text{)}}\);
Name:
steroids;
Role:
(sex) hormones;
OR
Name:
phospholipids;
Role:
membranes;
lipids less oxidized/contain less oxygen / carbohydrates partially/more oxidized/contain more oxygen / OWTTE;
Examiners report
This part was generally well answered but there were some cases where 33.5 °C was converted into Kelvin. Many candidates had serious problems with unit conversions and gave the answer as 2800 J or 2800 kJ. Some candidates had correct value for (ii) but lost the mark because of the omission of the negative sign.
Part (b) was well answered.
Very few candidates linked the fact that lipids have higher energy content due to being less oxidized.
Question
Polymers are made up of repeating monomer units which can be manipulated in various ways to give structures with desired properties.
(i) Draw the structure of 2-methylpropene.
(ii) Deduce the repeating unit of poly(2-methylpropene).
Deduce the percentage atom economy for polymerization of 2-methylpropene.
(i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
i
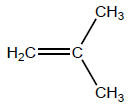
OR
H2C=C(CH3)2
ii
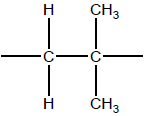
OR
−CH2C(CH3)2−
Continuation bonds needed for mark.
No penalty if square brackets present or “n” appears after the bracket/formula.
«same mass of product as reactant, thus» 100«%»
Accept “less than 100%” only if a reason is given (eg, the catalyst is not converted into the product, or other reasonable answer).
i
due to stability of plastics/strong covalent bonds
OR
low volatility preventing good mixing with oxygen «gas»
OR
lack of/insufficient oxygen
OR
plastics are often parts of devices with non-combustible components «which mechanically prevent the combustion of plastic components»
OR
PVC already partly oxidised «because some C–H bonds are replaced with C–Cl bonds», so it cannot produce enough heat for complete combustion
OR
many industrial/household materials contain additives that reduce their flammability/act as flame retardants
ii
weakly bound to the PVC/no covalent bonds to PVC/only London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces between DEHP and PVC AND leach/evaporate «from PVC» to atmosphere/food chain
OR
has low polarity/contains non-polar hydrocarbon chains AND fat-soluble/deposits in the fatty tissues
OR
has unusual structural fragments/is a xenobiotic/difficult to metabolise AND stays in the body for a long time

