Question
Body fluids have different $\mathrm{pH}$ values.
a. Identify the compound responsible for the acidity of gastric juice, and state whether it is a strong or weak acid.
b. An antacid contains calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate.
Write the equation for the reaction of magnesium carbonate with excess stomach acid.
c. Outline how ranitidine reduces stomach acidity.
d. Calculate the $\mathrm{pH}$ of a buffer solution which contains $0.20 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}^{-3}$ ethanoic acid and $0.50 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{dm}^{-3}$ sodium ethanoate. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
$\mathrm{p} K_{\mathrm{a}}($ ethanoic acid $)=4.76$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. hydrochloric acid/ $\mathrm{HCl}$ «(aq)» AND strong «acid»
b. $\mathrm{MgCO}_3(\mathrm{~s})+2 \mathrm{HCl}(\mathrm{aq}) \rightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_2(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
(I)
NOTE: Accept ionic equation.
c. blocks/binds to H2-histamine receptors «in cells of stomach lining»
OR
prevents histamine molecules binding to $\mathrm{H} 2$-histamine receptors «and triggering acid secretion»
OR
prevents parietal cells from releasing/producing acid
NOTE: Do not accept “antihistamine” by itself.
Accept “H2-receptor antagonist/H2RA” OR “blocks/inhibits action of histamine”.
Accept “blocks receptors in parietal cells “from releasing/producing acid»”.
Do not accept “proton pump/ATPase inhibitor”.
d. $« p K_a=4.76 »$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { «pH }=\mathrm{p} K_{\mathrm{a}}+\log \left(\frac{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH}\right]}\right) » \\
& « \mathrm{pH}=4.76+0.40=» 5.16
\end{aligned}
$$
Question
Question
Enzymes are biological catalysts.
a. The graph shows the relationship between the temperature and the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
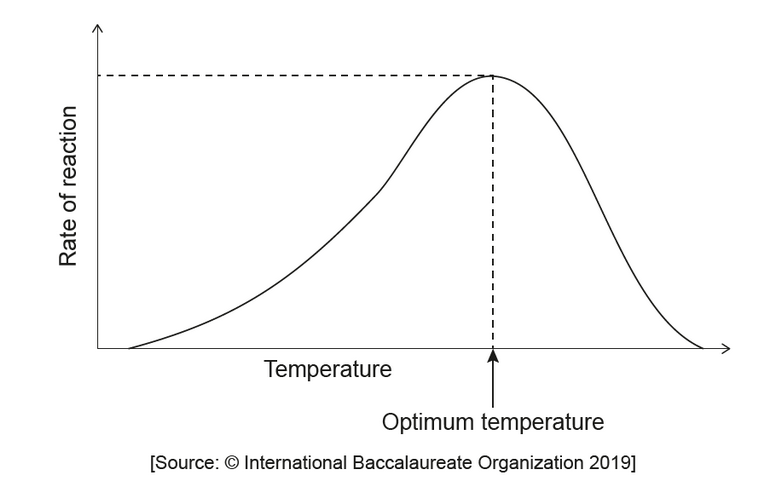
State one reason for the decrease in rate above the optimum temperature.
b. Explain why a change in $\mathrm{pH}$ affects the tertiary structure of an enzyme in solution.
c. State one use of enzymes in reducing environmental problems.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. enzyme denatures
OR
change of conformation/shape of active site
OR
substrate cannot bind to active site/binds less efficiently
NOTE: Accept “change in structure” or “substrate doesn’t fitfits poorly into active site”
b. Any two of:
acidic/basic/ionizable/ $\mathrm{COOH} /$ carboxyl/ $\mathrm{NH}_2$ /amino groups in the $\mathrm{R}$ groups/side chains «react»
exchange/lose/gain protons/ $\mathrm{H}^{+}$
change in H-bonds/ionic interactions/intermolecular forces/London dispersion forces
NOTE: Do not accept “enzyme denatures” OR “change of conformation/tertiary structure” OR “substrate cannot bind to active site/binds less efficiently” as this was the answer to 8(a).
c. breakdown of oil spills/industrial/sewage waste/plastics
OR
production of alternate sources of energy «such as bio diesel»
OR
involve less toxic chemical pathway «in industry»
NOTE: Accept “«enzymes in» biological detergents can improve energy efficiency”.
