Question
Which gives the equation and cell potential of the spontaneous reaction?
| E Θ / V |
| –1.18 |
A | +0.80 |
|
| E Θ / V |
A | Mn2+ (aq) + 2Ag (s) → Mn (s) + 2Ag+ (aq) | –1.98 |
B |
| +0.38 |
C | Mn (s) + 2A | –0.38 |
D | Mn (s) + 2A | +1.98 |
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The silver half-cell will undergo reduction because its standard reduction potential is higher. The Mn half-cell will undergo oxidation.
Now, to balance electrons in the two equations, Multiply the second equation by 2 and subtract first equation from it.
We obtain, Mn (s) + 2A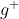 (aq) →
(aq) → 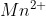 (aq) + 2Ag (s).
(aq) + 2Ag (s).
Eocell = Eored – Eooxid
Cell potential of the resulting equation would be : (+0.8)-(-1.18)=1.98.
Question
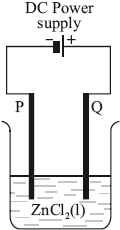
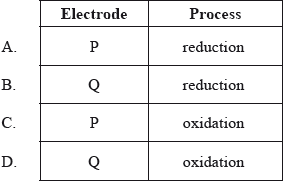
In the electrolytic cell shown, at which electrode will chlorine form, and what is the process taking place there?
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Chloride ions loose electrons (oxidation) to form chlorine gas at the positive anode Q.
Zinc ions gain electrons (reduction) to form Zn metal at the negative cathode P.
Question
Which are correct statements about a voltaic cell?
I. A spontaneous redox reaction occurs which converts chemical energy to electrical energy.
II. Oxidation occurs at the negative electrode (anode).
III. Electricity is conducted by the movement of electrons through the salt bridge.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Anode is negatively charged electrode in a voltaic cell and oxidation occurs at this electrode.
Galvanic cells, also called voltaic cells, are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction. This means that electrons will flow spontaneously from one side of the electrochemical cell to the other. This produces an electric current through an outside circuit.
A voltaic cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Question
Which species are produced at each electrode during the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide, \({\text{PbB}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(l)}}\)?
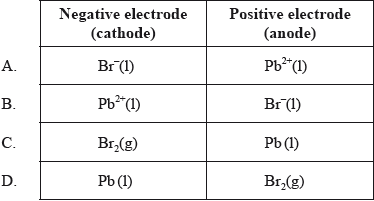
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Bromide ions loose electrons (oxidation) to form bromine gas at the positive anode.
Lead ions gain electrons (reduction) to form Pb metal at the negative cathode.
Question
Which statement is correct for an electrolytic cell but not for a voltaic cell?
B. The anode is where oxidation occurs.
C. Ions move in the electrolyte.
D. Electrons flow from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. It contain positively charged anode and negatively charged cathode. Reduction occurs at cathode and oxidation occurs at anode.
In voltaic cells, Electrons always flow from the anode to the cathode i.e. from the negative electrode to the positive electrode.
