Question
Carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) is a useful composite. Epoxy is a thermoset polymer that is used as a binding polymer when making CFRP.
a. Outline the two distinct phases of this composite.
b(i)Thermoplastic composites are increasingly replacing thermosets.
Suggest one advantage of thermoplastic polymers over thermosets.
b(ii )Explain how thermoplastics, such as polyvinylchloride, PVC, can be made more flexible by the addition of phthalate ester plasticizers.
b(ii)Explain why phthalates are replaced by other plasticizers in the production of plastics.
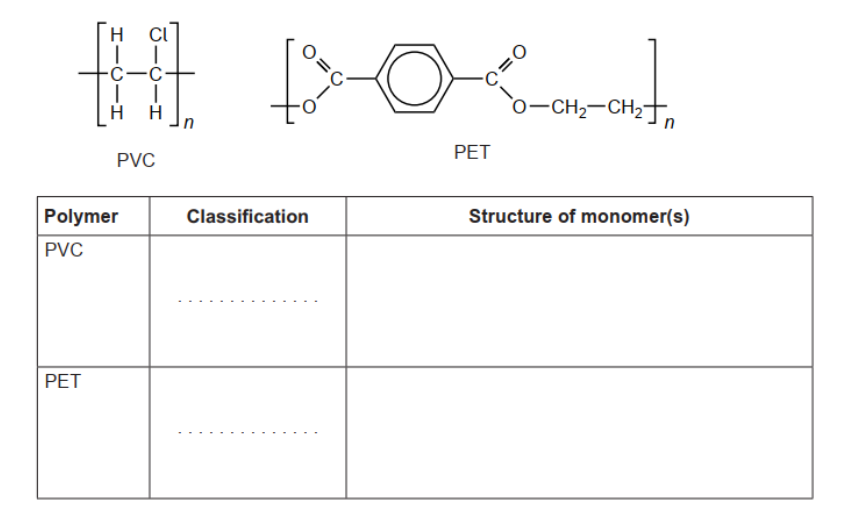
c. Classify PVC and polyethene terephthalate, PET, as addition or condensation polymers and deduce the structural formulas.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. carbon fibre reinforcing phase
«in a» matrix phase of epoxy
Award [1 max] for “reinforcing phase “embedded» in a matrix”.
b(i)can be recycled
OR
can be reformed when hot
OR
high impact/chemical/abrasion resistance
b(ii)Any three of:
plasticizers embed/fit between «polymer» chains
keep polymer strands/chains/molecules separated/apart
weaken intermolecular/London/dispersion/attractive/forces/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole/forces «between chains» prevent chains from packing closely/forming regular packing/structure
Accept “van der Waals/vdW” for “London”.
b(iii)Any two of:
readily released into environment
OR
have weak intermolecular forces «rather than covalent bonds between chains»
get into biological systems by ingestion/inhalation
interrupt endocrine systems
OR
affect release of hormones
OR
effect development of male reproductive system
considered carcinogenic
OR
can cause cellular damage
can cause early puberty in females
can cause thyroid effects
can cause asthma
Do not accept just “are a health concern”.
c.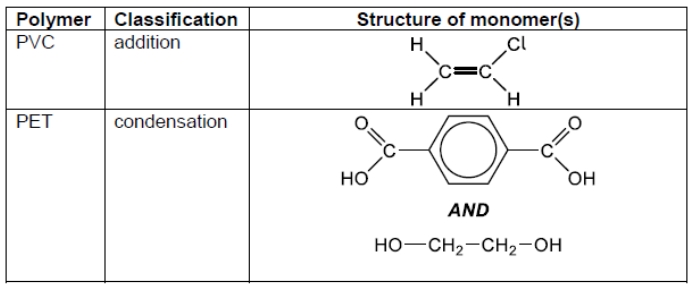
PVC: addition AND PET: condensation $\boldsymbol{V}$
structure of PVC monomer
structure of PET monomers
Accept full OR condensed structural formulas.
Question
Lithium has many uses.
\text { The emission spectra obtained by ICP-OES for a mixture containing the isotope }{ }^6 \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{Li}-6) \text { and naturally occurring lithium (Li (N)) is shown. }
a(i)ldentify the type of bonding in lithium hydride, using sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
a(iiExplain why lithium is paramagnetic while lithium hydride is diamagnetic by referring to electron configurations.
b(i)Suggest why ICP-OES does not give good quantitative results for distinguishing ${ }^6$ Li from naturally occurring lithium.
b(iißSuggest a better method.
c. Lithium is obtained by electrolysis of molten lithium chloride. Calculate the time, in seconds, taken to deposit $0.694 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{Li}$ using a current of $2.00 \mathrm{~A}$.
$$
Q(\text { charge })=I(\text { current }) \times t(\text { time })
$$
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a(i)ionic [ $\boldsymbol{N}$ ]
a(ii)ithium has an unpaired electron $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
all electrons in lithium hydride are paired $[\boldsymbol{}]$
Note: Award [1 max] for correct electron configurations of $\mathrm{Li}_{\mathrm{AND}} \mathrm{Li}^{+}$AND $\mathrm{H}$ without discussion of pairing.
OR
they have same electron transitions/same nuclear charge $[\boldsymbol{U}]$
Note: Accept “the spectra are almost identical”.
b(ii)CP-MS [ $\boldsymbol{V}$ ]
Note: Accept “MS/mass spectrometry”.
c.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{n} «=\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}_{\mathrm{r}}}=\frac{0.694}{6.94} »=0.100 \text { «mol»[ }[\mathbf{J}] \\
& « t=\frac{0.100 \mathrm{~mol} \times 96500 \mathrm{C} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}}{2.00 \mathrm{C} \mathrm{s}^{-1}}=» \\
& 4830 « \mathrm{~S} »[\boldsymbol{V}]
\end{aligned}
$$
Note: Accept “4820” OR “4825 “S»”.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Question
Metals are extracted from their ores by several methods, including electrolysis and reduction with carbon.
a. Determine the mass of aluminium, in g, that could be extracted from an appropriate solution by a charge of $48250 \mathrm{C}$. Use sections 2 and 6 of the data booklet.
b. Once extracted, the purity of the metal can be assessed using ICP-MS. Suggest two advantages of using plasma technology rather than regular mass spectrometry.
c. Explain the action of metals as heterogeneous catalysts.
d. Outline how alloys conduct electricity and why they are often harder than pure metals.
Conduct electricity:
Harder than pure metals:
e. Carbon nanotubes are added to metals to increase tensile strength.
Write an equation for the formation of carbon nanotubes from carbon monoxide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. moles of electrons $«=\frac{48250 \mathrm{C}}{96500 \mathrm{C} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}} »=0.5000$ «mol»[ $[\boldsymbol{]}$ moles of aluminium «= $\frac{0.5000 \mathrm{~mol}}{3} »=0.1667$ «mol» [ $\left.\checkmark\right]$ mass of aluminium «= $26.98 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \times 0.1667 \mathrm{~mol} »=4.50$ «” [ $\left.\mathcal{C}\right]$
Note: Award [3] for correct final answer.
b. Any two of:
larger linear calibration [ $/]$
«accurate» detection of multiple elements/metals $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$ «accurate» detection of elements in low concentration [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}]$ temperature around $10000 \mathrm{~K}$ atomises/ionises every material [ $\boldsymbol{\nu}$ ]
c. Any two of:
reactant(s) adsorb onto active sites/surface [
bonds weakened/broken/stretched «in adsorbed reactants» OR
activation energy lowered [ $\boldsymbol{C}]$
products desorbed [ $/$
Note: Accept “products released” for M3.
d. Conduct electricity:
«delocalized/valence» electrons free to move «under potential difference» [ $[$ ]
Harder than pure metals:
atoms/ions of different sizes prevent layers «of atoms/ions» from sliding over one another [ $\boldsymbol{V}]$
e. $2 \mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{C}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Question
Metals are extracted from their ores by various means.
Aluminium is produced by the electrolysis of alumina (aluminium oxide) dissolved in cryolite.
a. Discuss why different methods of reduction are needed to extract metals.
$b(i)$ Determine the percentage of ionic bonding in alumina using sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
b(ii)Write half-equations for the electrolysis of molten alumina using graphite electrodes, deducing the state symbols of the products.
Anode (positive electrode):
Cathode (negative electrode):
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. ions of more reactive metals are harder to reduce
OR
more reactive metals have more negative electrode potentials
electrolysis is needed/used for most reactive metals
OR
carbon is used to reduce metal oxides of intermediate reactivity/less reactive than carbon OR
heating ore is sufficient for less reactive metals
NOTE: Award [1 max] for ” “eease of reduction/extraction” depends on reactivity”.
$b(i)$ electronegativity difference $=1.8$ «and average electronegativity $=2.5$ »
57 «\%
NOTE: Accept any value in the range $52-65 \%$.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
b(ii)Anode (positive electrode):
$$
2 \mathrm{O}^{2-} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{e}^{-}+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})
$$
OR
$$
2 \mathrm{O}^{2-}+\mathrm{C} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{e}^{-}+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})
$$
NOTE: Award [1 max] for M1 and M2 if correct half-equations are given at the wrong electrodes OR if incorrect reversed half-equations are given at the correct electrodes.
Cathode (negative electrode):
$\mathrm{Al}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Al}(\mathrm{I})$
$\mathrm{O}_2$ gas $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ Al liquid
NOTE: Only state symbols of products required, which might be written as ( $g$ ) and (I) in half-equations. Ignore any incorrect or missing state symbols for reactants.
Question
Lanthanum, La, and antimony, $\mathrm{Sb}$, form compounds with bromine that have similar formulas, $\mathrm{LaBr}_3$ and $\mathrm{SbBr}_3$.
a. Determine the type of bond present in $\mathrm{SbBr}_3$, showing your method. Use sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
b. Lanthanum has a similar electronegativity to group 2 metals. Explain, in terms of bonding and structure, why crystalline lanthanum bromide is brittle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. polar covalent
average electronegativity $«=\frac{1}{2}(3.0+2.0) »=2.5$ AND electronegativity difference $«=3.0-2.0 »=1.0$
[2 marks]
b. ionic bonding
OR
electrostatic forces between ions
«slight» movement brings ions of same charge adjacent to each other «causing the crystal to break»
OR
“Slight» movement results in repulsion between layers «causing the crystal to break»
[2 marks]
Question
Polymer nanocomposites often have better structural performance than conventional materials. Lithographic etching and metal coordination are two methods of assembling these nanocomposites.
Nanoparticles anchor plasticizers in PVC so that they cannot escape from the polymer as easily.
a. State the two distinct phases of a composite.
b. Identify the methods of assembling nanocomposites by completing the table.
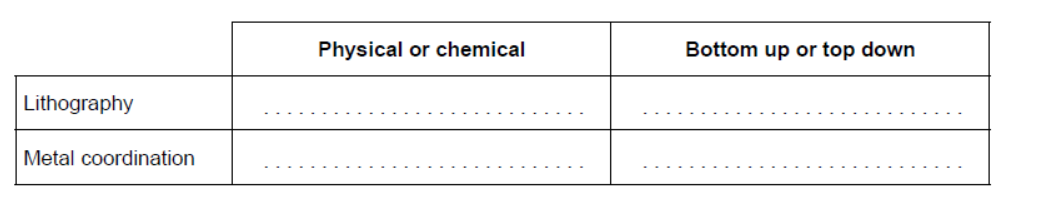
c.i. Explain how the structure of plasticizers enables them to soften PVC.
c.ii.Suggest a reason why nanoparticles can better anchor plasticizers in the polymer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. reinforcing «phase»
«embedded in» matrix «phase»
[2 marks]
b.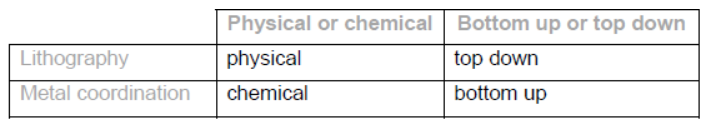
Award [2] for all 4, [1] for 2 or 3 correct.
[2 marks]
c.i. Any three of:
contain a polar group «which locks into the polymer»
a non-polar group «which weakens the forces between chains»
embedded between chains of polymers
«plasticizer molecules» fit between chains
«plasticizer molecules» prevent chains from forming crystalline regions
«plasticizer molecules» keeps strands/chains/molecules separated
«plasticizer molecules» increase space/volume between chains
weakens intermolecular/dipole-dipole/London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole/van der Waals/vdW forces
Do not accept “«plasticizer molecules» “lower density” or “softer”.
[3 marks]
c.ii.more places «for plasticizers» to bond
OR
increased surface area
[1 mark]
Question
Materials science involves understanding the properties of materials and applying those properties to desired structures.
a. Magnesium oxide, $\mathrm{MgO}$, and silicon carbide, $\mathrm{SiC}$, are examples of ceramic materials. State the name of the predominant type of bonding in each material.
b. Predict the predominant type of bonding for a binary compound AB in which the electronegativity of both atoms is low. Use section 29 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. MgO: ionic AND SiC: covalent
Accept “covalent network/network covalent” for “covalent” but not just “network”.
b. metallic «bonding»
Question
One way of classifying materials is based on the type of bonding present.
Caprolactam reacts with water to form compound $\mathbf{X}$, a monomer.
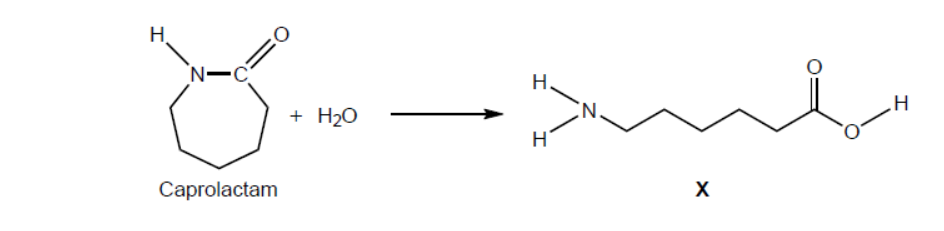
One way of classifying materials is based on the type of bonding present.
One reaction to convert cyclohexanone to caprolactam using concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst is shown.
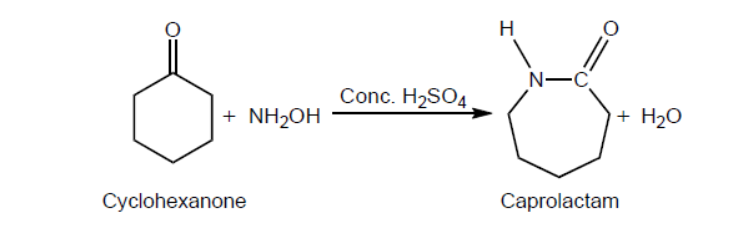
a. Outline why this type of classification is not entirely satisfactory by using magnesium diboride, $\mathrm{MgB}_2$, as an example. Refer to sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
b. Structures of poly(methyl acrylate), PMA, and Bakelite ${ }^{\circledR}$ are shown.
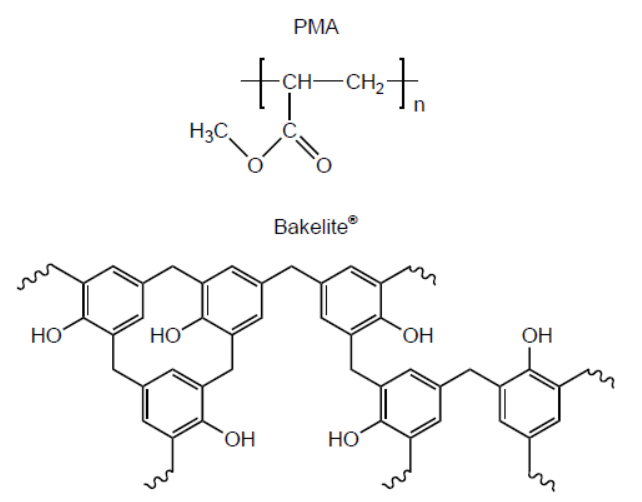
Suggest, giving reasons, which is the thermoplastic polymer and which is the thermosetting polymer.

c. A zeolite is an alternative catalyst for this reaction.
Explain how zeolites act as selective catalysts.
d.i. State the names of the two terminal functional groups in $\mathbf{X}$.
d.ii.Deduce the repeating unit of the polymer of $\mathbf{X}$.
d.iiiRepeating units of several polymers are listed.
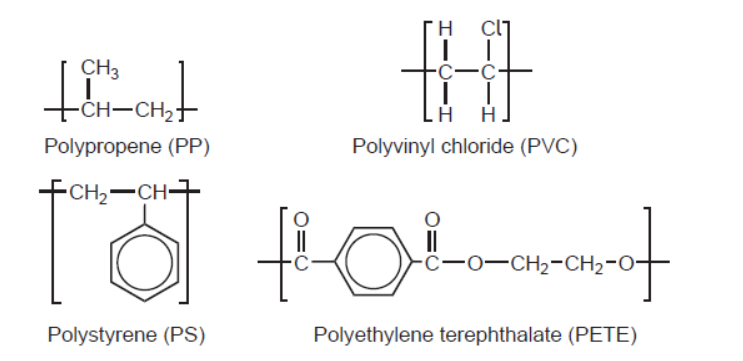
The infrared (IR) spectrum of one of these polymers is shown.
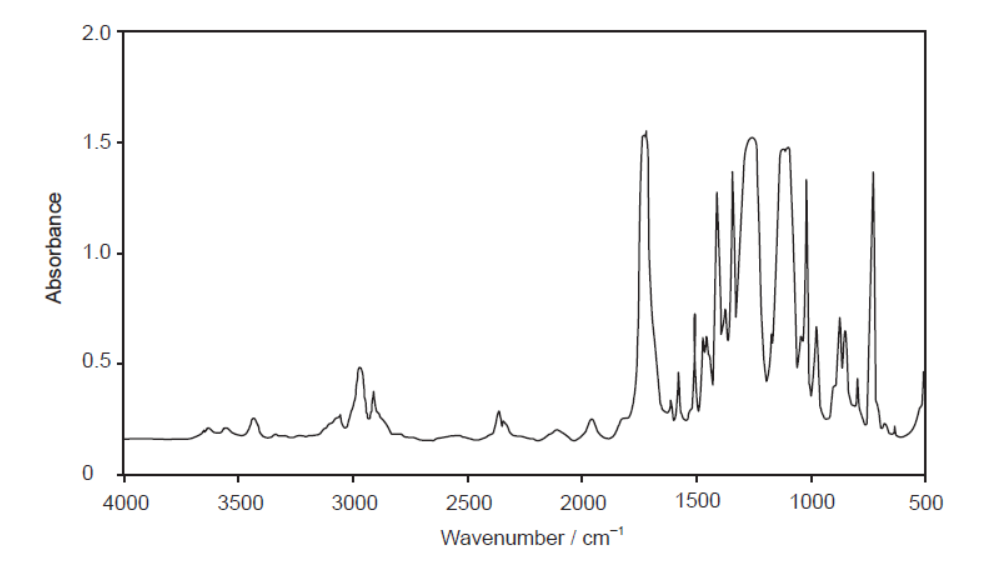
Deduce, giving a reason, the name of this polymer and its Resin Identification Code (RIC), using sections 26 and 30 in the data booklet.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. $\Delta \chi=0.7$ AND average $\Delta \chi=1.7$
bonding between metallic and ionic
OR
more than one type of bonding present
OR
bond type difficult to determine as close to several regions/several types/named bonding types «eg ionic and covalent etc.»
OR
bond is mostly covalent «based on \% covalent scale on diagram»
OR
bond has « $\frac{0.7}{3.2} \times 100=» 22 \%$ ionic character
Accept “EN” for ” $\chi$ “.
Accept “bond is ionic but close to several regions/several types/other named bonding type(s) (eg covalent, metallic and covalent etc.)”.
Do not accept just “bond is ionic”.
Accept any value for \% ionic character in range $15-24 \%$ or $\%$ covalent character in range $76-85 \%$.
b. Thermoplastic polymer:
PMA AND «weak» intermolecular/IMFs/London/dispersion/van der Walls/vdW/dipole-dipole forces «between layers/chains»
OR
PMA AND no/few cross-links «between layers/chains»
Thermosetting polymer:
Bakelite ${ }^{\circledR}$ AND «strong» covalent bonds «between layers/chains»
OR
Bakelite ${ }^{\circledR}$ AND extensive cross-links «between layers/chains»
Do not accept “hydrogen bonding” for M1.
Award [1 max] for correct reasons for both polymer classes even if named polymers are incorrectly classified.
c. pores/cavities/channels/holes/cage-like structures «in zeolites» have specific shape/size
only reactants «with appropriate size/geometry» fit inside/go through/are activated/can react
d.i. amino $A N D$ carboxyl
Do not accept “carbonyl”, “hydroxyl”.
d.ii.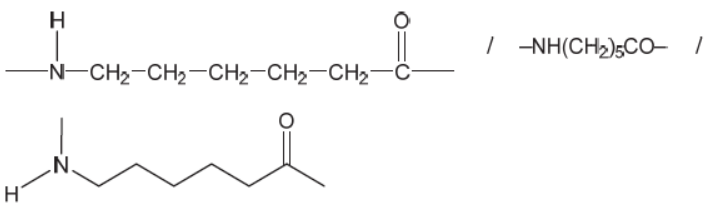
Continuation bonds at NH and $\mathrm{CO}$ are required for mark.
Ignore any brackets and $n$.
d.iiiName and reason:
PET/PETE AND peak for $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ «at $1700-1750 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}$ »
RIC:
1
Accept “PETIPETE AND peak for C-O «at 1050-1410 cm”-1»” for M1.
Accept “PETIPETE AND peak(s) for COO” for M1.
Accept name or abbreviation for polymer.
No ECF for M2.
Question
Propene can polymerize to form polypropene.
Propene monomer: 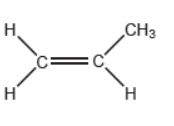
a.Sketch four repeating units of the polymer to show atactic and isotactic polypropene.

b.i. State the chemical reason why plastics do not degrade easily.
b.ii.Compare two ways in which recycling differs from reusing plastics.
c. Civilizations are often characterized by the materials they use.
Suggest an advantage polymers have over materials from the iron age.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.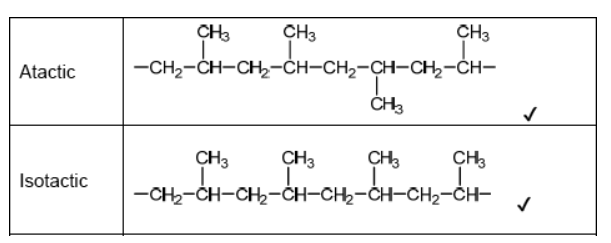
\text { Do not accept syndiotactic (alternating orientation of the } \mathrm{CH}_3 \text { groups), eg, }
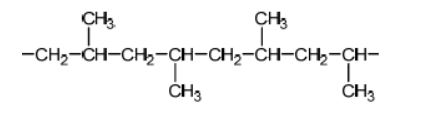
for M1 or M2.
Accept any correct atactic ordering of $\mathrm{CH}_3$ groups.
Penalize missing hydrogens or incorrect bond connectivities once only.
Accept skeletal structures.
Ignore continuation bonds, brackets and ” $n$ ” indices in structures.
[2 marks]
b.i.strong covalent bonds
Accept “moisture cannot get inside the plastic matrix, and bacteria cannot live without moisture, so they cannot attack the polymer chains”.
Accept “bacteria lack the enzymes required to break down the hydrocarbon chains”.
[1 mark]
b.ii Any two of:
Recycling: shredded/melted/reformed AND Reuse: used in its current form
recycling is more energy intensive «than reusing»
recycling degrades the quality of plastic but reusing «typically» does not
recycling breaks down original product to form a new product whereas reuse extends product life
[2 marks]
c. more pliable/flexible materials
OR more durable/non-corrosive/longer-lasting materials OR greater variety of materials OR
lower density
OR
can be clear/translucent
Accept “more adaptable”.
Do not accept just “more useful”.
[1 mark]
Question
It is wise to fill dental cavities before irreversible tooth decay sets in. An amalgam (alloy of mercury, silver, and other metals) is often used although many prefer a white composite material.
a. Outline the composition of an alloy and a composite.

b.i. Outline why an alloy is usually harder than its components by referring to its structure.
b.iiAt present, composite fillings are more expensive than amalgam fillings.
Suggest why a patient might choose a composite filling.
c. Explain how Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) Spectroscopy could be used to determine the concentration of mercury in a sample of dental filling.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Alloy:
mixture of metal with other metals/non-metals
OR
mixture of elements that retains the properties of a metal
Composite:
reinforcing phase embedded in matrix phase
Award [1 max] for implying “composites only have heterogeneous/nonhomogeneous compositions”.
[Max 2 Marks]
b.i. difference in ionic/atomic radius prevents layers sliding over each other
Accept “difference in diameter/packing of cations prevents layers sliding over each other”.
b.ii.concern about $\mathrm{Hg}$ poisoning
OR
«composite» is white «so looks more like tooth»
OR
galvanic response potential exists
OR
local allergic potential
OR
less damage/destruction of healthy tooth tissue
OR
long term corrosion requires replacement
OR
gradual darkening of tooth
Accept other correct responses.
c. Any three of:
sample injected into argon «plasma»
atoms «of sample» are excited/ionised
OR
electrons are promoted
electrons drop back/recombine with ions AND emit photons of characteristic energies/wavelengths/frequencies
total number of photons is proportional to concentration of element
actual concentration found from calibration/standard curve
Accept “graph/plot” for “curve”.
[Max 3 Marks]
Question
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) used with Mass Spectrometry (MS) or Optical Emission Spectrometry (OES) can be used to identify and quantify elements in a sample.
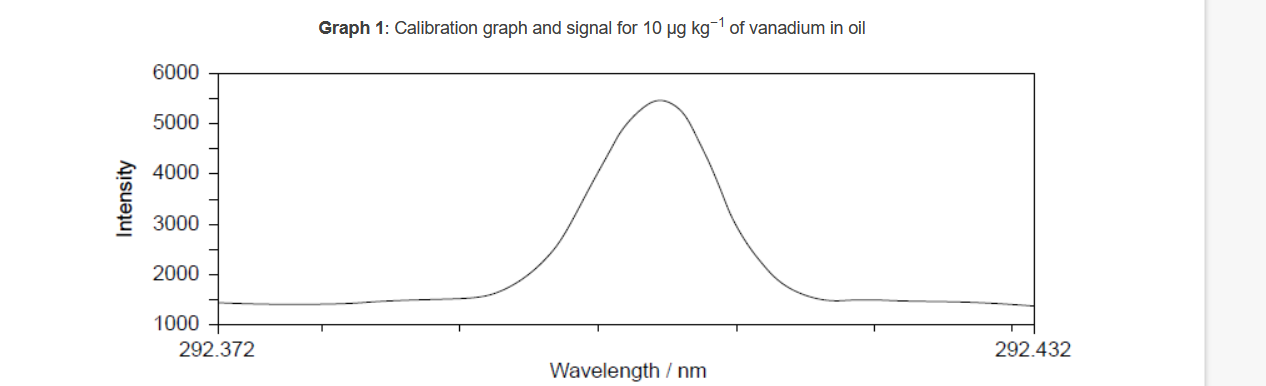
The following graphs represent data collected by ICP-OES on trace amounts of vanadium in oil.
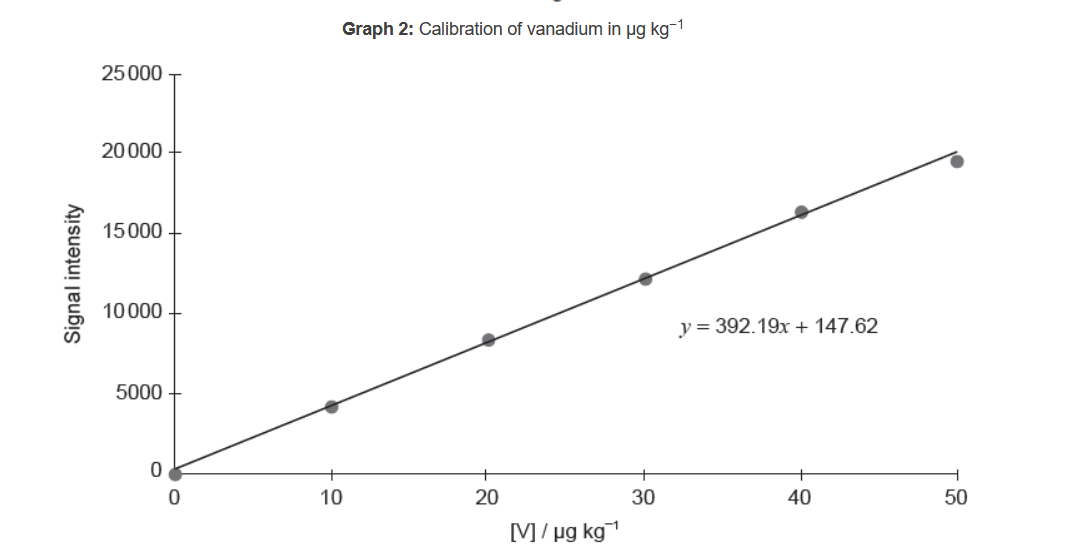
a. ICP-OES/MS can be used to analyse alloys and composites. Distinguish between alloys and composites.
b. ICP-MS is a reference mode for analysis. The following correlation graphs between ICP-OES and ICP-MS were produced for yttrium and nickel.
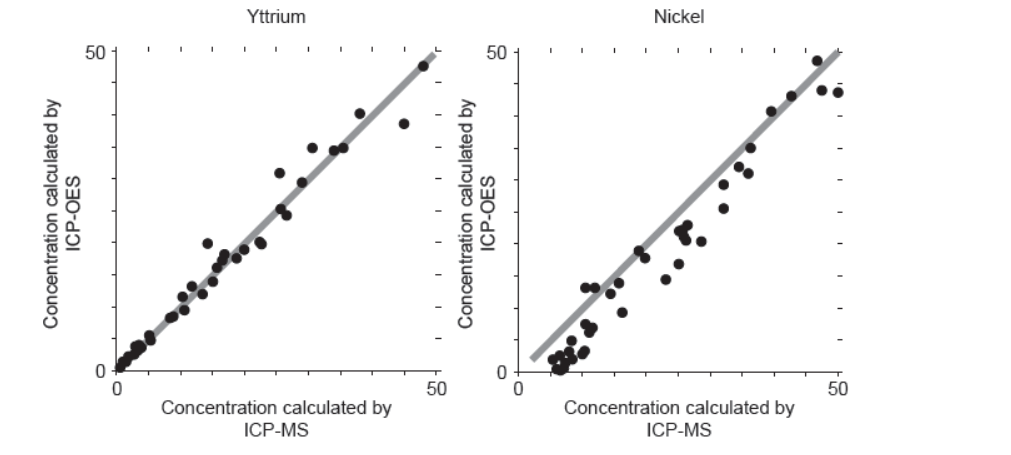
Each $y$-axis shows concentrations calculated by ICP-OES; each $x$-axis shows concentrations for the same sample as found by ICP-MS.
The line in each graph is $y=x$.
Discuss the effectiveness of ICP-OES for yttrium and nickel.
c.i. Identify the purpose of each graph.

c.ii.Calculate, to four significant figures, the concentration, in $\mu \mathrm{g} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$, of vanadium in oil giving a signal intensity of 14950 .
c.iiiVanadium $(V)$ oxide is used as the catalyst in the conversion of sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{SO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{V}_2 \mathrm{O}_5(\mathrm{~s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{SO}_3(\mathrm{~g})+2 \mathrm{VO}_2(\mathrm{~s}) \\
& \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})+2 \mathrm{VO}_2(\mathrm{~s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{V}_2 \mathrm{O}_5(\mathrm{~s})
\end{aligned}
$$
Outline how vanadium( $\mathrm{V})$ oxide acts as a catalyst.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Alloy:
mixture of metal with other metals/non-metals
OR
mixture of elements that retains the properties of a metal
Composite:
reinforcing phase embedded in matrix phase
Award [1 max] for implying “composites only have heterogeneous/nonhomogeneous compositions”.
[2 marks]
b. effective for yttrium «but less/not for nickel»
points on nickel graph do not lie on «y $=x »$ line
OR
cannot be used for low concentrations of nickel
OR
concentration of nickel is lower than recorded value
Accept “ICP-OES is more accurate for lower yttrium concentrations than higher concentrations” for M1.
Accept [Ni] and [Y] for concentrations of nickel and yttrium.
Accept “detection limit for yttrium is lower than for nickel” for M2.
Award [1 max] for “more accurate for yttrium at lower concentrations AND nickel at higher concentrations”.
[2 marks]
c.i. Graph 1: determines wavelength of maximum absorption/maximum intensity «for vanadium»
Graph 2: determines absorption of known concentrations «at that wavelength»
OR
estimates $[\mathrm{V}]$ /concentration in a sample using «the signal» intensity
Do not accept just “determines maximum wavelength/ $\Lambda_{\max }$ ” for $M 1$.
Do not accept “calibration curve” for M2.
[2 marks]
c.ii.« $14950=392.19 x+147.62 »$
$$
x=37.74 \ll \mu \mathrm{kg}^{-1} »
$$
Answer must be given to four significant figures.
Do not accept values obtained directly from the graph.
[1 mark]
c.iiiyanadium reduced in first reaction $A N D$ oxidized in second reaction
OR
$\mathrm{V}_2 \mathrm{O}_5$ oxidizes $\mathrm{SO}_2$ in first reaction $A N D \mathrm{VO}_2$ reduces $\mathrm{O}_2$ in second reaction
OR
vanadium returns to original oxidation state «after reaction»
provides an alternative reaction pathway/mechanism «with a lower activation energy»
Do not accept “reactants adsorb onto surface AND products desorb”.
Accept “oxidation number” for “oxidation state”.
[2 marks]
Question
Both HDPE (high density polyethene) and LDPE (low density polyethene) are produced by the polymerization of ethene.
a. Both of these are thermoplastic polymers. Outline what this term means.
b.i. Compare and contrast the structures of HDPE and LDPE.
b.ii.State one way in which a physical property of HDPE, other than density, differs from that of LDPE as a result of this structural difference.
c.i. The production of HDPE involves the use of homogeneous catalysts. Outline how homogeneous catalysts reduce the activation energy of reactions.
c.ii.Trace amounts of metal from the catalysts used in the production of HDPE sometimes remain in the product. State a technique that could be used to measure the concentration of the metal.
d. Suggest two of the major obstacles, other than collection and economic factors, which have to be overcome in plastic recycling.
e. Suggest why there are so many different ways in which plastics can be classified. HDPE can, for example, be categorized thermoplastic, an addition polymer, having Resin Identification Code (RIC) 2, etc.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. soften/melt when heated
OR
can be melted and moulded
Accept “low melting point” OR “can be moulded when heated”.
[1 mark]
b.i. both have «long» hydrocarbon chains
OR
both have chains comprising $\mathrm{CH}_2$ units
HDPE has little/no branching AND LDPE has «more» branching
Accept ” $\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2$ units”.
Accept “HDPE more crystalline”.
[2 marks]
b.ii.HDPE is more rigid/less flexible
OR
HDPE has a higher melting point
OR
HDPE has greater «tensile» strength
Accept “HDPE has lower ductility”.
[1 mark]
c.i. form «temporary» activated complexes/reaction intermediates
Accept “consumed in one reaction/step AND regenerated in a later reaction/step”.
Accept “provides alternative mechanism”.
[1 mark]
c.ii.inductively coupled plasma/ICP spectroscopy using mass spectroscopy/mass spectrometry/MS/ICP-MS
OR
inductively coupled plasma/ICP spectroscopy using optical emission spectroscopy/OES/ICP-OES
Accept “atomic absorption/aa spectroscopy” or “MS/massspectroscopy/mass spectrometry”.
[1 mark]
d. Any two of:
many types «of plastics» exist
OR
«plastics» require sorting «by type»
«plastics» need to be separated from non-plastic materials
OR
«often» composites/moulded on/bound to non-plastic/other components
Accept other valid factors such as thermal decomposition of some plastics, production of toxic fumes, etc.
[2 marks]
e. «different classifications are appropriate for» different properties/applications/purposes
[1 mark]
Question
Aluminium and high density polyethene (HDPE) are both materials readily found in the kitchen, for example as saucepans and mixing bowls respectively. In these applications it is important that they are impermeable to water.
Both materials are also used in other applications that are more demanding of their physical properties. Carbon nanotubes are often incorporated into their structures to improve certain properties.
a. Discuss, in terms of its structure, why an aluminium saucepan is impermeable to water.
b.i. State the name given to a material composed of two distinct solid phases.
b.ii.State one physical property of HDPE that will be affected by the incorporation of carbon nanotubes.
b.iiiDescribe how carbon nanotubes are produced by chemical vapour deposition (CVD).
b.ivState the property of carbon nanotubes that enables them to form a nematic liquid crystal phase.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. «close packed» lattice of metal atoms/ions
no spaces for water molecules to pass though the structure
[2 marks]
b.i.composite
[1 mark]
b.iimelting point
OR
permeability
OR
density
OR
conductivity
OR
elasticity/stiffness
OR
brittleness/flexibility
OR
«tensile» strength
Accept “colour/transparency”.
[1 mark]
b.iiiAny three of:
hydrocarbon/carbon-containing gas/compound
mixed with inert gas
heat/high temperature
«transition» metal catalyst
hydrocarbon/carbon compound decomposes to form carbon «nanotubes»
nanotubes form on catalyst surface
Accept “ethanol” or specific hydrocarbons.
Accept ” $\mathrm{N}_2$ “, ” $\mathrm{H}_2$ “, ” $\mathrm{NH}_3$ ” or specific inert gases.
Accept temperature or range within $600-800^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$.
Accept specific metals such as $\mathrm{Ni}$, Co or $\mathrm{Fe}$.
[3 marks]
b.ivod shaped molecules
[1 mark]
Question
Polymer nanocomposites often have better structural performance than conventional materials. Lithographic etching and metal coordination are two methods of assembling these nanocomposites.
Nanoparticles anchor plasticizers in PVC so that they cannot escape from the polymer as easily.
a. State the two distinct phases of a composite.
b. Identify the methods of assembling nanocomposites by completing the table.

c.i. Explain how the structure of plasticizers enables them to soften PVC.
c.ii.Suggest a reason why nanoparticles can better anchor plasticizers in the polymer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. reinforcing «phase»
«embedded in» matrix «phase»
[2 marks]
b.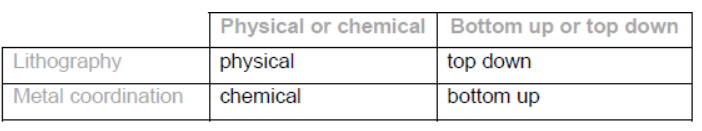
Award [2] for all 4, [1] for 2 or 3 correct.
[2 marks]
c.i. Any three of:
contain a polar group «which locks into the polymer»
a non-polar group «which weakens the forces between chains»
embedded between chains of polymers
«plasticizer molecules» fit between chains
«plasticizer molecules» prevent chains from forming crystalline regions
«plasticizer molecules» keeps strands/chains/molecules separated
«plasticizer molecules» increase space/volume between chains
weakens intermolecular/dipole-dipole/London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole/van der Waals/vdW forces
Do not accept “«plasticizer molecules» “lower density” or “softer”.
[3 marks]
c.ii.more places «for plasticizers» to bond
OR
increased surface area
[1 mark]
