Question
New materials have brought many benefits to society but come with associated risks.
(a) High-pressure carbon monoxide disproportionation (HiPco) produces carbon atoms that react with nano catalysts to produce carbon nanotubes.
(i) Write the equation for the disproportionation of carbon monoxide to produce carbon atoms.
(ii) Calculate the percent atom economy of producing carbon using this method. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
(iii) Outline how a metal functions as a heterogeneous catalyst.
(iv) Explain whether the production of carbon nanotubes using HiPco is a bottom up or top down nanotechnology technique.
(v) Suggest one health risk of using nanoparticles.
(b) Kevlar® is a recyclable polyamide polymer and a liquid crystal. One repeating unit of the polyamide is shown.
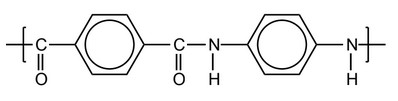
(i) Outline what is meant by a liquid crystal.
(ii) Some liquid crystal displays (LCD) use liquid crystals between two polarizing filters. The display appears black until a small voltage is applied. Outline how the liquid crystals allow polarized light to pass through the filters.
(iii) Identify the resin identification code (RIC) that applies to Kevlar®. Use section 30 of the data booklet.
The IR spectrum of Kevlar® is shown.
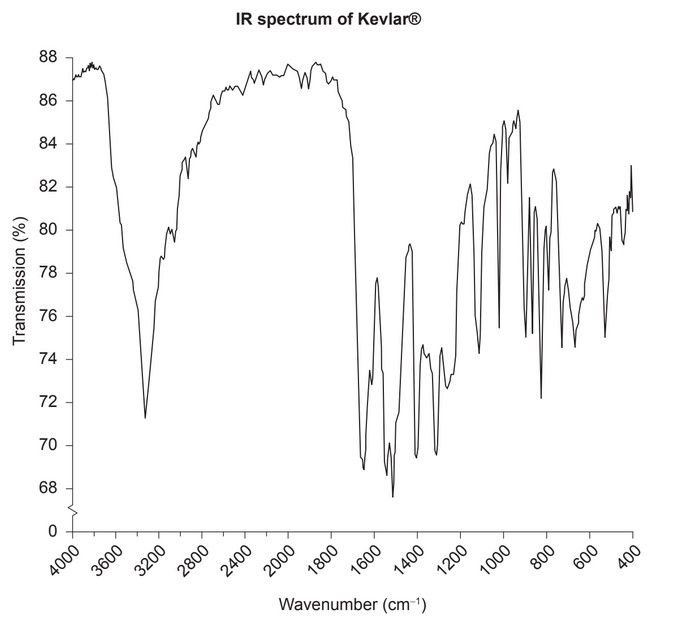
(iv) Deduce the peak in the Kevlar® IR spectrum which would not be found in compounds with any other RIC code. Use Sections 26 and 30 of the data booklet.
(v) Kevlar® is a condensation polymer. Distinguish between addition and condensation polymerization, in terms of monomers and products.
Monomers:
Products:
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) \(2CO(g) \rightarrow C(s) + CO_2(g)\)
(ii) «100 × 12.01 / 2 × (12.01+16.00) = » 21.44%
(iii) «gaseous» reactants adsorb onto «metal» surface
OR
catalyst provides surface for reaction to occur
weakens «reactant» bonds
OR
products desorb
(iv) bottom up AND molecular assembly «rather than decomposition»
(v) Any one of:
more easily airborne/inhaled
have similar dimensions as biological molecules/interfere with biochemical
reactions
easily absorbed into body
may cross cell membranes
large surface area could increase toxicity
human defence system not effective with small size
(b) (i) fluids with «some» properties that are anisotropic/depend on molecular orientation «relative to a fixed axis»
(ii) polar «molecules»
change orientation upon application of electric field
OR
«in some orientations» molecules rotate plane of polarization «of polarized light»
(iii) 7
(iv) 3300 to 3500
(v) Monomers:
addition: unsaturated/containing C=C/C≡C
condensation: monomers have two reactive sites/functional groups
Products:
addition: one product/no by-products AND
condensation: small molecule/HCl eliminated/two products
Question
Metals are extracted from their ores by several methods, including electrolysis and reduction with carbon.
a. Determine the mass of aluminium, in g, that could be extracted from an appropriate solution by a charge of $48250 \mathrm{C}$. Use sections 2 and 6 of the data booklet.
b. Once extracted, the purity of the metal can be assessed using ICP-MS. Suggest two advantages of using plasma technology rather than regular mass spectrometry.
c. Explain the action of metals as heterogeneous catalysts.
d. Outline how alloys conduct electricity and why they are often harder than pure metals.
Conduct electricity:
Harder than pure metals:
e. Carbon nanotubes are added to metals to increase tensile strength.
Write an equation for the formation of carbon nanotubes from carbon monoxide.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. moles of electrons $«=\frac{48250 \mathrm{C}}{96500 \mathrm{C} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}} »=0.5000 \ll \mathrm{mol} »$ [
moles of aluminium «= $\frac{0.5000 \mathrm{~mol}}{3} »=0.1667$ «mol» [ $\left.\checkmark\right]$
Note: Award [3] for correct final answer.
b. Any two of:
larger linear calibration [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
«accurate» detection of multiple elements/metals $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
«accurate» detection of elements in low concentration [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
temperature around $10000 \mathrm{~K}$ atomises/ionises every material [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}$ ]
c. Any two of:
reactant(s) adsorb onto active sites/surface [ $\boldsymbol{M}$
bonds weakened/broken/stretched «in adsorbed reactants»
OR
activation energy lowered $[\boldsymbol{\nu}]$
products desorbed [ $\boldsymbol{\swarrow}]$
Note: Accept “products released” for M3.
d. Conduct electricity:
«delocalized/valence» electrons free to move «under potential difference» $[\boldsymbol{D}$
Harder than pure metals:
atoms/ions of different sizes prevent layers «of atoms/ions» from sliding over one another [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
e. $2 \mathrm{CO}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{C}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$