Question
(a) Photosynthesis enables green plants to store energy from sunlight as glucose.
(i) Write the equation for photosynthesis.
(ii) Identify the structural feature that allows chlorophyll to absorb light. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
(iii) Explain how photosynthesis is being employed to control global warming.
(b) Photovoltaic cells also convert sunlight into energy.
(i) State the form of energy produced by photosynthesis and photovoltaic cells.
Photosynthesis:
Photovoltaic:
(ii) Explain how a silicon-based photovoltaic cell brings about this conversion.
(c) Glucose can be converted to ethanol through fermentation:
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 (aq) → 2C_2H_5OH(aq) + 2CO_2 (g)\)
(i) Determine the energy efficiency of this conversion in terms of the enthalpies of combustion of the reactants and products. Use section 13 of the data booklet.
(ii) Suggest one reason, other than energy density and specific energy, why ethanol may be considered a more useful fuel than glucose.
(d) Both ethanol and glucose can be used to generate energy through fuel cells.
(i) Outline one way fuel cells differ from primary cells.
(ii) State one way to increase the maximum current of a voltaic cell.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) \(6CO_2(g) + 6H_2O(l) → C_6H_{12}O_6(aq) + 6O_2(g)\)
(ii) conjugated «electronic» structure/delocalized «pi» electrons/alternate «single and» double bonds
(iii) reduces/sequesters \(CO_2\)/carbon dioxide «concentration from atmosphere»
«planting» more plants/trees
(b) (i) Photosynthesis: chemical
AND
Photovoltaic: electrical
(ii) Any three of:
n-type AND p-type «silicon layers»
OR
n-type doped with Gp 15 element/P AND p-type doped with Gp 13 element/B
potential difference/charge separation created between layers of silicon
«sunlight produces» free electrons that flow between layers «from p-type to n-
type»
OR
«sunlight produces» positive holes that flow between layers «from n-type to p-
type»
«excess» electrons move “from n-type to p-type” through an external circuit
(c) (i) «(2x-1367 / -2803) x 100 =» 97.54%
OR
2.46% loss «in energy efficiency»
(ii) liquid
OR
easier ignition
OR
more volatile
(d) (i) material provides energy in fuel cells
OR
fuel continually added in fuel cells
(ii) reduce «internal» resistance
Question
\text { Gasoline (petrol), biodiesel and ethanol are fuels. }
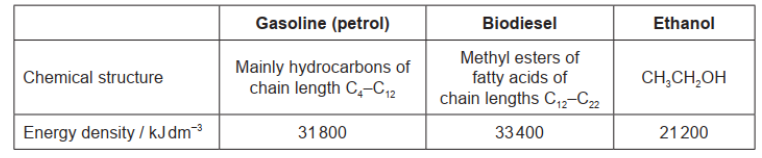
a. Calculate the energy released, in $\mathrm{kJ}$, from the complete combustion of $5.00 \mathrm{dm}^3$ of ethanol.
b. State a class of organic compounds found in gasoline.
c. Outline the advantages and disadvantages of using biodiesel instead of gasoline as fuel for a car. Exclude any discussion of cost.

d. A mixture of gasoline and ethanol is often used as a fuel. Suggest an advantage of such a mixture over the use of pure gasoline. Exclude any discussion of cost.
e(i)When combusted, all three fuels can release carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, as well as particulates. Contrast how carbon dioxide and particulates interact with sunlight.
e(ii) Methane is another greenhouse gas. Contrast the reasons why methane and carbon dioxide are considered significant greenhouse gases.
e(iiisuggest a wavenumber absorbed by methane gas.
e(inDetermine the relative rate of effusion of methane $\left(M_{\mathrm{r}}=16.05\right)$ to carbon dioxide $\left(M_{\mathrm{r}}=44.01\right)$, under the same conditions of temperature and pressure. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. $« 21200 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{dm}^{-3} \times 5.00 \mathrm{dm}^3=» 106000 / 1.06 \times 10^5\langle\mathrm{~kJ} 》\rangle$
b. alkane
$O R$
cycloalkane
OR
arene
Accept “alkene”.
Do not accept just “hydrocarbon”, since given in stem.
Do not accept “benzene/aromatic” for “arene”.
c. Advantages: [2 max]
renewable
uses up waste «such as used cooking oil»
lower carbon footprint/carbon neutral
higher flashpoint
produces less $\mathrm{SO}_{\mathrm{x}} / \mathrm{SO}_2$
OR
less polluting emissions
has lubricating properties
OR
preserves/increases lifespan of engine
increases the life of the catalytic converter
eliminates dependence on foreign suppliers
does not require pipelines/infrastructure «to produce»
relatively less destruction of habitat compared to obtaining petrochemicals
Accept “higher energy density” OR “biodegradable” for advantage.
Disadvantages: [2 max]
needs conversion/transesterification
takes time to produce/grow plants
takes up land
OR
deforestation
fertilizers/pesticides/phosphates/nitrates «used in production of crops» have negative environmental effects
biodiversity affected
OR
loss of habitats «due to energy crop plantations»
cannot be used at low temperatures
variable quality «in production»
high viscosity/can clog/damage engines
Accept “lower specific energy” as disadvantage.
Do not accept “lower octane number” as disadvantage”.
d. Any one:
uses up fossil fuels more slowly
lower carbon footprint/CO2 emissions
undergoes more complete combustion
produces fewer particulates
higher octane number/rating
OR
less knocking
prevents fuel injection system build up
OR
helps keep engine clean
Accept an example of a suitable advantage even if repeated from 11c.
e(i)carbon dioxide allows sunlight/short wavelength radiation to pass through AND particulates reflect/scatter/absorb sunlight
Accept “particulates reflect/scatter/absorb sunlight AND carbon dioxide does not”.
Accept ” $\mathrm{CO}_2$ absorbs IR “radiation” AND particulates reflect/scatter/absorb sunlight”.
Do not accept “traps” for “absorbs”.
e(iicarbon dioxide is highly/more abundant «in the atmosphere»
methane is more effective/potent «as a greenhouse gas» OR
methane/better/more effective at absorbing IR «radiation» OR
methane has greater greenhouse factor OR methane has greater global warming potential/GWP
Accept “carbon dioxide contributes more to global warming” for M1.
$\mathrm{e}$ (iiiąny value or range within $\left.2850-3090 \ll \mathrm{cm}^{-1}\right)$
$\mathrm{e}\left(\mathrm{iv}\right.$ ) rate of effusion of $\frac{\mathrm{CH}_4}{\mathrm{CO}_2}=\sqrt{\frac{44.01}{16.05}}=» 1.656$