Question
Let c be a positive, real constant. Let G be the set \(\{ \left. {x \in \mathbb{R}} \right| – c < x < c\} \) . The binary operation \( * \) is defined on the set G by \(x * y = \frac{{x + y}}{{1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}}}\).
a.Simplify \(\frac{c}{2} * \frac{{3c}}{4}\) .[2]
b.State the identity element for G under \( * \).[1]
c.For \(x \in G\) find an expression for \({x^{ – 1}}\) (the inverse of x under \( * \)).[1]
d.Show that the binary operation \( * \) is commutative on G .[2]
e.Show that the binary operation \( * \) is associative on G .[4]
f.(i) If \(x,{\text{ }}y \in G\) explain why \((c – x)(c – y) > 0\) .
(ii) Hence show that \(x + y < c + \frac{{xy}}{c}\) .[2]
h.Explain why \(\{ G, * \} \) is an Abelian group.[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\frac{c}{2} * \frac{{3c}}{4} = \frac{{\frac{c}{2} + \frac{{3c}}{4}}}{{1 + \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{3}{4}}}\) M1
\( = \frac{{\frac{{5c}}{4}}}{{\frac{{11}}{8}}} = \frac{{10c}}{{11}}\) A1
[2 marks]
identity is 0 A1
[1 mark]
inverse is –x A1
[1 mark]
\(x * y = \frac{{x + y}}{{1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}}},{\text{ }}y * x = \frac{{y + x}}{{1 + \frac{{yx}}{{{c^2}}}}}\) M1
(since ordinary addition and multiplication are commutative)
\(x * y = y * x{\text{ so }} * \) is commutative R1
Note: Accept arguments using symmetry.
[2 marks]
\((x * y) * z = \frac{{x + y}}{{1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}}} * z = \frac{{\left( {\frac{{x + y}}{{1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}}}} \right) + z}}{{1 + \left( {\frac{{x + y}}{{1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}}}} \right)\frac{z}{{{c^2}}}}}\) M1
\( = \frac{{\frac{{\left( {x + y + z + \frac{{xyz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}}}{{\frac{{\left( {1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}} + \frac{{xz}}{{{c^2}}} + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}}} = \frac{{\left( {x + y + z + \frac{{xyz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + \left( {\frac{{xy + xz + yz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)} \right)}}\) A1
\(x * (y * z) = x * \left( {\frac{{y + z}}{{1 + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}}}}} \right) = \frac{{x + \left( {\frac{{y + z}}{{1 + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}}}}} \right)}}{{1 + \frac{x}{{{c^2}}}\left( {\frac{{y + z}}{{1 + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}}}}} \right)}}\)
\( = \frac{{\frac{{\left( {x + \frac{{xyz}}{{{c^2}}} + y + z} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}}}{{\frac{{\left( {1 + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}} + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}} + \frac{{xz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + \frac{{yz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}}} = \frac{{\left( {x + y + z + \frac{{xyz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)}}{{\left( {1 + \left( {\frac{{xy + xz + yz}}{{{c^2}}}} \right)} \right)}}\) A1
since both expressions are the same \( * \) is associative R1
Note: After the initial M1A1, correct arguments using symmetry also gain full marks.
[4 marks]
(i) \(c > x{\text{ and }}c > y \Rightarrow c – x > 0{\text{ and }}c – y > 0 \Rightarrow (c – x)(c – y) > 0\) R1AG
(ii) \({c^2} – cx – cy + xy > 0 \Rightarrow {c^2} + xy > cx + cy \Rightarrow c + \frac{{xy}}{c} > x + y{\text{ (as }}c > 0)\)
so \(x + y < c + \frac{{xy}}{c}\) M1AG
[2 marks]
if \(x,{\text{ }}y \in G{\text{ then }} – c – \frac{{xy}}{c} < x + y < c + \frac{{xy}}{c}\)
thus \( – c\left( {1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}} \right) < x + y < c\left( {1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}} \right){\text{ and }} – c < \frac{{x + y}}{{1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}}}} < c\) M1
\(({\text{as }}1 + \frac{{xy}}{{{c^2}}} > 0){\text{ so }} – c < x * y < c\) A1
proving that G is closed under \( * \) AG
[2 marks]
as \(\{ G, * \} \) is closed, is associative, has an identity and all elements have an inverse R1
it is a group AG
as \( * \) is commutative R1
it is an Abelian group AG
[2 marks]
Examiners report
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Most candidates were able to answer part (a) indicating preparation in such questions. Many students failed to identify the command term “state” in parts (b) and (c) and spent a lot of time – usually unsuccessfully – with algebraic methods. Most students were able to offer satisfactory solutions to part (d) and although most showed that they knew what to do in part (e), few were able to complete the proof of associativity. Surprisingly few managed to answer parts (f) and (g) although many who continued to this stage, were able to pick up at least one of the marks for part (h), regardless of what they had done before. Many candidates interpreted the question as asking to prove that the group was Abelian, rather than proving that it was an Abelian group. Few were able to fully appreciate the significance in part (i) although there were a number of reasonable solutions.
Question
The binary operation \( * \) is defined on \(\mathbb{N}\) by \(a * b = 1 + ab\).
Determine whether or not \( * \)
a.is closed;[2]
b.is commutative;[2]
c.is associative;[3]
d.has an identity element.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\( * \) is closed A1
because \(1 + ab \in \mathbb{N}\) (when \(a,b \in \mathbb{N}\)) R1
[2 marks]
consider
\(a * b = 1 + ab = 1 + ba = b * a\) M1A1
therefore \( * \) is commutative
[2 marks]
EITHER
\(a * (b * c) = a * (1 + bc) = 1 + a(1 + bc){\text{ }}( = 1 + a + abc)\) A1
\((a * b) * c = (1 + ab) * c = 1 + c(1 + ab){\text{ }}( = 1 + c + abc)\) A1
(these two expressions are unequal when \(a \ne c\)) so \( * \) is not associative R1
OR
proof by counter example, for example
\(1 * (2 * 3) = 1 * 7 = 8\) A1
\((1 * 2) * 3 = 3 * 3 = 10\) A1
(these two numbers are unequal) so \( * \) is not associative R1
[3 marks]
let e denote the identity element; so that
\(a * e = 1 + ae = a\) gives \(e = \frac{{a – 1}}{a}\) (where \(a \ne 0\)) M1
then any valid statement such as: \(\frac{{a – 1}}{a} \notin \mathbb{N}\) or e is not unique R1
there is therefore no identity element A1
Note: Award the final A1 only if the previous R1 is awarded.
[3 marks]
Examiners report
For the commutative property some candidates began by setting \(a * b = b * a\) . For the identity element some candidates confused \(e * a\) and \(ea\) stating \(ea = a\) . Others found an expression for an inverse element but then neglected to state that it did not belong to the set of natural numbers or that it was not unique.
For the commutative property some candidates began by setting \(a * b = b * a\) . For the identity element some candidates confused \(e * a\) and \(ea\) stating \(ea = a\) . Others found an expression for an inverse element but then neglected to state that it did not belong to the set of natural numbers or that it was not unique.
For the commutative property some candidates began by setting \(a * b = b * a\) . For the identity element some candidates confused \(e * a\) and \(ea\) stating \(ea = a\) . Others found an expression for an inverse element but then neglected to state that it did not belong to the set of natural numbers or that it was not unique.
For the commutative property some candidates began by setting \(a * b = b * a\) . For the identity element some candidates confused \(e * a\) and \(ea\) stating \(ea = a\) . Others found an expression for an inverse element but then neglected to state that it did not belong to the set of natural numbers or that it was not unique.
Question
The binary operation \(\Delta\) is defined on the set \(S =\) {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} by the following Cayley table.
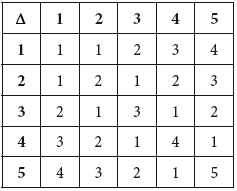
(a) State whether S is closed under the operation Δ and justify your answer.
(b) State whether Δ is commutative and justify your answer.
(c) State whether there is an identity element and justify your answer.
(d) Determine whether Δ is associative and justify your answer.
(e) Find the solutions of the equation \(a\Delta b = 4\Delta b\), for \(a \ne 4\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(a) yes A1
because the Cayley table only contains elements of S R1
[2 marks]
(b) yes A1
because the Cayley table is symmetric R1
[2 marks]
(c) no A1
because there is no row (and column) with 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 R1
[2 marks]
(d) attempt to calculate \((a\Delta b)\Delta c\) and \(a\Delta (b\Delta c)\) for some \(a,{\text{ }}b,{\text{ }}c \in S\) M1
counterexample: for example, \((1\Delta 2)\Delta 3 = 2\)
\(1\Delta (2\Delta 3) = 1\) A1
Δ is not associative A1
Note: Accept a correct evaluation of \((a\Delta b)\Delta c\) and \(a\Delta (b\Delta c)\) for some \(a,{\text{ }}b,{\text{ }}c \in S\) for the M1.
[3 marks]
(e) for example, attempt to enumerate \(4\Delta b\) for b = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and obtain (3, 2, 1, 4, 1) (M1)
find \((a,{\text{ }}b) \in \left\{ {{\text{(2, 2), (2, 3)}}} \right\}\) for \(a \ne 4\) (or equivalent) A1A1
Note: Award M1A1A0 if extra ‘solutions’ are listed.
[3 marks]
Total [12 marks]
Examiners report
Question
The set of all permutations of the elements \(1,{\text{ }}2,{\text{ }} \ldots 10\) is denoted by \(H\) and the binary operation \( \circ \) represents the composition of permutations.
The permutation \(p = (1{\text{ }}2{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}4{\text{ }}5{\text{ }}6)(7{\text{ }}8{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}10)\) generates the subgroup \(\{ G,{\text{ }} \circ \} \) of the group \(\{ H,{\text{ }} \circ \} \).
a.Find the order of \(\{ G,{\text{ }} \circ \} \).[2]
b.State the identity element in \(\{ G,{\text{ }} \circ \} \).[1]
c.Find
(i) \(p \circ p\);
(ii) the inverse of \(p \circ p\).[4]
d.(i) Find the maximum possible order of an element in \(\{ H,{\text{ }} \circ \} \).
(ii) Give an example of an element with this order.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
the order of \((G,{\text{ }} \circ )\) is \({\text{lcm}}(6,{\text{ }}4)\) (M1)
\( = 12\) A1
[2 marks]
\(\left( 1 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 2 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 3 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 4 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 5 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 6 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 7 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 8 \right){\rm{ }}\left( 9 \right){\rm{ }}\left( {10} \right)\) A1
Note: Accept ( ) or a word description.
[1 mark]
(i) \(p \circ p = (1{\text{ }}3{\text{ }}5)(2{\text{ }}4{\text{ }}6)(7{\text{ }}9)(810)\) (M1)A1
(ii) its inverse \( = (1{\text{ }}5{\text{ }}3)(2{\text{ }}6{\text{ }}4)(7{\text{ }}9)(810)\) A1A1
Note: Award A1 for cycles of 2, A1 for cycles of 3.
[4 marks]
(i) considering LCM of length of cycles with length \(2\), \(3\) and \(5\) (M1)
\(30\) A1
(ii) eg\(\;\;\;(1{\text{ }}2)(3{\text{ }}4{\text{ }}5)(6{\text{ }}7{\text{ }}8{\text{ }}9{\text{ }}10)\) A1
Note: allow FT as long as the length of cycles adds to \(10\) and their LCM is consistent with answer to part (i).
Note: Accept alternative notation for each part
[3 marks]
Total [10 marks]
Examiners report
[N/A]
[N/A]
[N/A]
[N/A]
