Question
(a) A cell of negligible internal resistance and electromotive force (emf) \(6.0 \mathrm{~V}\) is connected to three resistors \(\mathrm{R}, \mathrm{P}\) and \(\mathrm{Q}\).

R is an ohmic resistor. The I-V characteristics of P and Q are shown in the graph.

The current in \(\mathrm{P}\) is \(0.40 \mathrm{~A}\).
(i) Show that the current in \(Q\) is \(0.45 \mathrm{~A}\).[3]
(ii) Calculate the resistance of \(\mathrm{R}\).[2]
(iii) Calculate the total power dissipated in the circuit.[1]
(b) Resistor \(\mathrm{P}\) is removed. Suggest, without any calculations, the effect of this on the resistance of \(\mathrm{Q}\).[2]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Voltage across \(P\) is 1.4 «V» Voltage across \(Q\) is \(4.6 \propto V m\) And \(6-1.4=4.6 \propto V_n \checkmark\)
ii Current in \(\mathrm{R}\) is \(\propto(0.45-0.4)=00.05 \mathrm{~A}\)
So resistance is \(* \frac{1.4}{0.05} \|=28 * \Omega » v\)
iii \(« 0.45 \times 6.0 »=2.7 \approx W » \checkmark\)
b Q will have a smaller resistance \(\checkmark\)
«Because total resistance in the circuit is now larger so” the current athrough the circuit/Qn is smaller / OWTTE \(\checkmark\)
Question
An electrically heated pad is designed to keep a pet warm.
The pad is heated using a resistor that is placed inside the pad. The dimensions of the resistor are shown on the diagram. The resistor has a resistance of \(4.2 \Omega\) and a total length of \(1.25 \mathrm{~m}\).

When there is a current in the resistor, the temperature in the pad changes from a room temperature of \(20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) to its operating temperature at \(35^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
(a) The designers state that the energy transferred by the resistor every second is \(15 \mathrm{~J}\).
Calculate the current in the resistor. [1]
(b) The designers wish to make the resistor from carbon fibre.
The graph shows the variation with temperature, in Kelvin, of the resistivity of carbon fibre.

(i) The resistor has a cross-sectional area of \(9.6 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~m}^2\).
Show that a resistor made from carbon fibre will be suitable for the pad. [3]
(ii) The power supply to the pad has a negligible internal resistance.
State and explain the variation in current in the resistor as the temperature of the pad increases.[2]
(c) When there is a current in the resistor, magnetic forces act between the resistor strips. For the part of the resistor labelled RS,
(i) outline the magnetic force acting on it due to the current in PQ.[1]
(ii) state and explain the net magnetic force acting on it due to the currents in \(P Q\) and \(T U\).[2]
(d) The design of the pad encloses the resistor in a material that traps air. The design also places the resistor close to the top surface of the pad.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a.\(I=\alpha \sqrt{\frac{P}{R}}=1.9 \alpha \mathrm{A} w\)
b(i) ALTERNATIVE 1 (Calculation of length)
Read off from graph [ \(\left.2.8-3.2 \times 10^{-5} \Omega \mathrm{m}\right] \checkmark\)
Use of \(I=\frac{R A}{\rho}\)
$
I=1.3-1.4 \ll \mathrm{m} * \checkmark
$
ALTERNATIVE 2 (Calculation of area)
Read off from graph [ \(\left.2.8-3.2 \times 10^{-5} \Omega \mathrm{m}\right] \checkmark\)
Use of \(A=\rho \frac{1}{R} \checkmark\)
$
A=8.3-9.5 \times 10^{-6} \ll \mathrm{m}^2{ }^2 \checkmark
$
ALTERNATIVE 3 (Calculation of resistance)
Read off from graph [ \(\left.2.8-3.2 \times 10^{-5} \Omega \mathrm{m}\right] \checkmark\)
Use of \(R=\rho \frac{1}{A} \checkmark\)
$
R=3.6-4.2 * \Omega \approx \checkmark
$
ALTERNATIVE 4 (Calculation of resistivity)
Use of \(\rho=\frac{R A}{I} \checkmark\)
$
\rho=3.2 \times 10^{-5} \kappa \Omega \mathrm{m} \otimes \checkmark
$
Read off from graph \(260-280 \mathrm{~K} \checkmark\)
b(ii) «Resistivity and hence» resistance will decrease
«Pd across pad will not change because internal resistance is negligible» Current will increase \(\checkmark\)
c i.\&The force is» away from \(\mathrm{PQ} /\) repulsive/to the right
c ii The magnetic fields «due to currents in PQ and TU» are in opposite directions OR
There are two «repulsiven forces in opposite directions \(\checkmark\)
Net force is zero \(r\)
d. Air is a poor «thermal» conductor
Lack of convection due to air not being able to move in material
Appropriate statement about energy transfer between the pet, the resistor and surroundings
The rate of thermal energy transfer to the top surface is greater than the bottom adue to thinner material» \(\checkmark\)
Question
The diagram shows a potential divider circuit used to measure the emf E of a cell X. Both cells have negligible internal resistance.
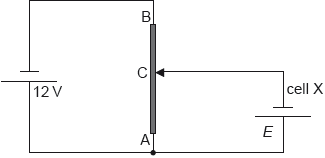
AB is a wire of uniform cross-section and length 1.0 m. The resistance of wire AB is 80 Ω. When the length of AC is 0.35 m the current in cell X is zero.
a.
State what is meant by the emf of a cell.
Show that the resistance of the wire AC is 28 Ω.
Determine E.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.
the work done per unit charge
in moving charge from one terminal of a cell to the other / all the way round the circuit
Award [1] for “energy per unit charge provided by the cell”/“power per unit current”
Award [1] for “potential difference across the terminals of the cell when no current is flowing”
Do not accept “potential difference across terminals of cell”
[2 marks]
the resistance is proportional to length / see 0.35 AND 1«.00»
so it equals 0.35 × 80
«= 28 Ω»
[2 marks]
current leaving 12 V cell is \(\frac{{12}}{{80}}\) = 0.15 «A»
OR
E = \(\frac{{12}}{{80}}\) × 28
E = «0.15 × 28 =» 4.2 «V»
Award [2] for a bald correct answer
Allow a 1sf answer of 4 if it comes from a calculation.
Do not allow a bald answer of 4 «V»
Allow ECF from incorrect current