The Periodic Table
Terminology
Group: All elements in a group share the same number of valence electrons
Period: All elements in a period share the same number of shells
History of the Periodic Table
Lavioser: Discovered the role oxygen plays in combustion, developed a method for naming compounds
Dobereiner: Discovered that the relative atomic mass of the middle element in a group is close to the average relative atomic mass of the other two (there were only three elements placed per group at the time).
Newlands: Discovered that the element eight elements after another element is similar when arranging elements based on relative atomic mass.
Mendeleev: Arranged them similarly to Newlands but left spaces for undiscovered elements as they were not discovered yet but were theorized to have similar properties to others in the group.
Moseley: Ordered the periodic table based on atomic number, not atomic weight.

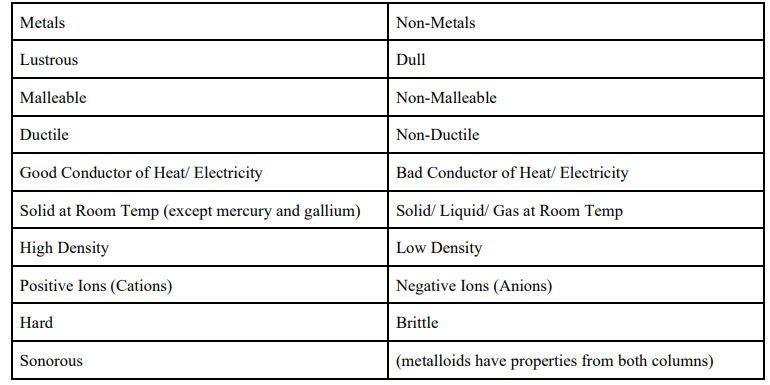
Metals & Non-Metals: Properties
Metal Extraction
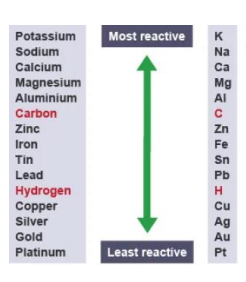
- Metals are listed on what’s known as the reactivity series, a list that describes which metals are more reactive than others.
- Metals that are less reactive than carbon can be extracted by having carbon replace them in whatever compound they are currently in.
- Metals that are less reactive hydrogen are considered ‘native,’ and do not need to be extracted.
- Metals above carbon need to be extracted through electrolysis, through the use of special bacteria, which then release leachate solution, which contains the extracted metal. Electrolysis drives chemical reactions through the use of currents.
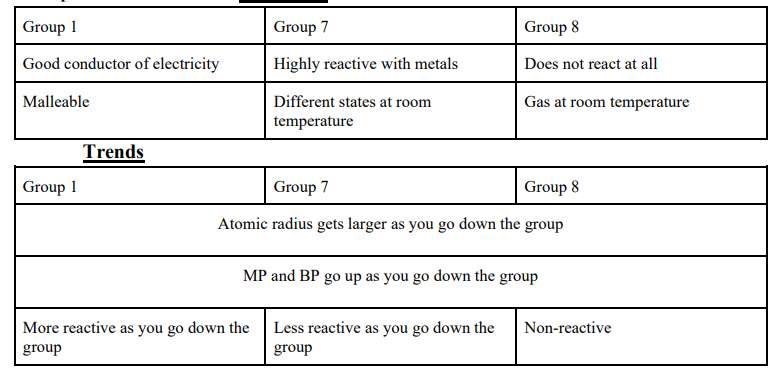
Groups in the Periodic Table: Properties
Ions and Valence
Groups 1,2,3
Group 1: Forms +1 ions
Group 2: Forms +2 ions
Group 3: Forms +3 ions
Groups 5.6.7
Group 5: Forms -3 ions
Group 6: Forms -2 ions
Group 7: Forms -1 ions
Compounds
All compounds have a charge of 0
Transition Metals
Transition metals can sometimes have different charges
For example, iron can have a +2 or +3 charge, shown as iron (II) or iron (III)
Polyatomic Ions
Ions made of 2 or more atoms
Common Polyatomic Ions:
