Atmospheric Composition
- The current composition of air by volume: \(78.09 \%\) Nitrogen, \(20.95 \%\) Oxygen, \(0.93 \%\) Argon, carbon dioxide and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around \(1 \%\) at Sea and \(0.4 \%\) over the entire atmosphere
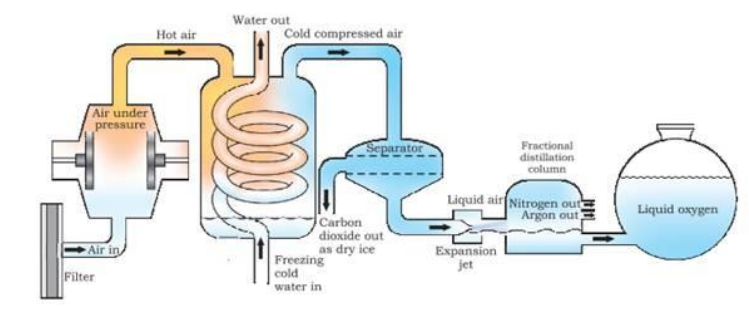
- Fractional Distillation is most commonly used to separate different gases from the general air. This is done due to a property of liquids that they all have different boiling \& melting point. Basically it works through a system in which the gas is first cooled and turned into liquid. Sublimation of few gases convert into solid directly, hence they are easy to separate. Subsequently it is heated. Oxygen flows out while liquid nitrogen becomes a gas due to the different boiling points.
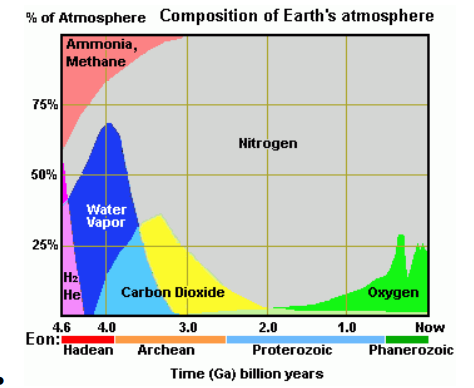
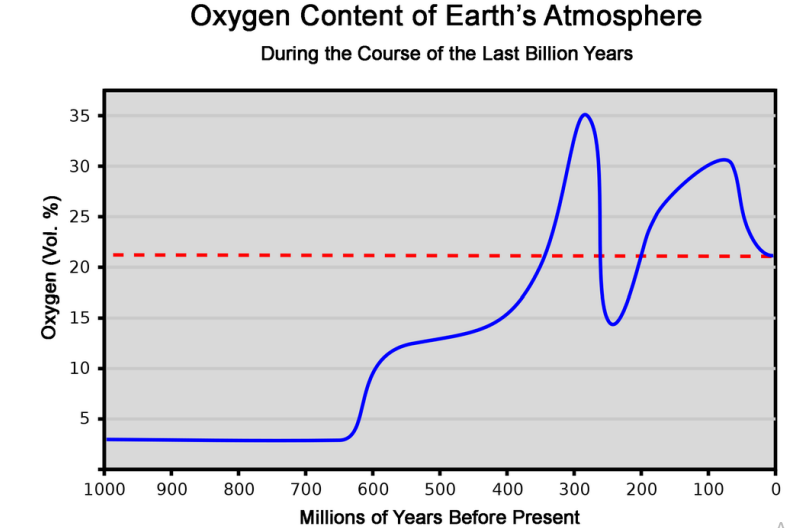
● Over time the composition of earth’s atmosphere has changed. Multiple different factors can account for this
○ Industrial Revolution
○ Ice Age
○ Extinction
○ Plant Growth
● Characteristics of the different atmospheric gases
○ Oxygen
■ Reactive and form oxides with nearly all elements
■ Colorless
■ Odorless
■ Tasteless
○ Carbon Dioxide
■ Colorless
■ Odorless at small amount otherwise smells acidic.
○ Nitrogen
■ Colorless
■ Tasteless
■ Diatomic
■ Does not react much
● Test for different gases
○ Hydrogen
■ The Lit splint test. You collect the hydrogen gas in a test tube and take a
Lit splint. Place the lint splint in the test tube a pop sound should come.
○ Oxygen
■ Take a glowing splint and place it in the test tube where oxygen is meant to be. The glowing splint should ignite.
○ Carbon Dioxide
■ Take the Carbon Dioxide and pass it through lime water. The lime water should turn milky.
Greenhouse Effect
● The greenhouse effect is a process by which radiation from the planet’s atmosphere warms the planet’s surface to a point above what it would be without this atmosphere or additional particles.
○ When looking from physics preservative: As light enter the atmosphere it heats up earth and then bounces back. Although particles such as Water vapor and Carbon Dioxide absorb some of it, and later disperse it, some
of the energy redistributes back to earth.
● The production and creation of the ozone can be described as a two-step process. The first step invo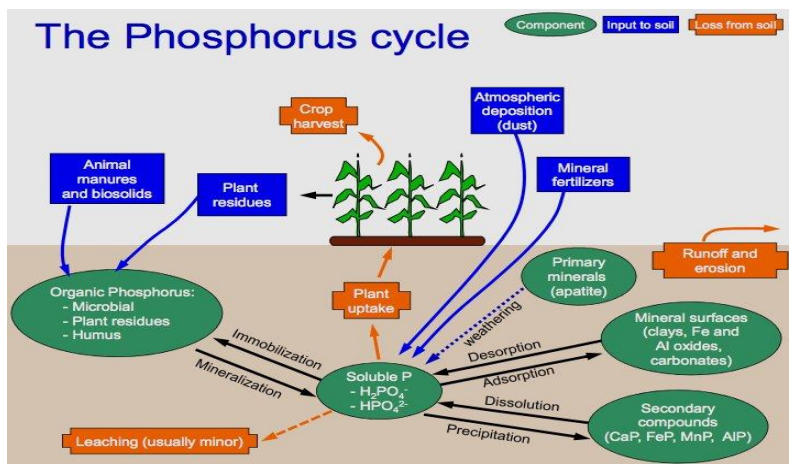 lves the ionization of oxygen. In the same step the ultraviolet light/radiation breaks apart O2 into 2O. In the second step the reactive 2O combine and soon form O3
lves the ionization of oxygen. In the same step the ultraviolet light/radiation breaks apart O2 into 2O. In the second step the reactive 2O combine and soon form O3
● Main Greenhouse Gases
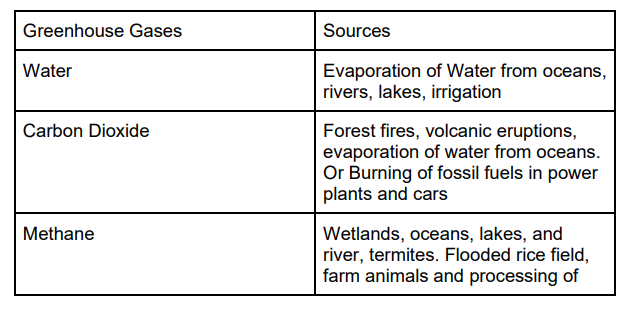
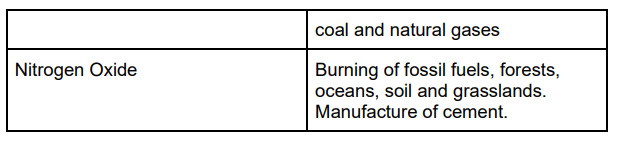
When ultraviolet light hit CFC, the molecules in the upper atmosphere break the carbon chlorine bonds. This leads to the production of chlorine (CL) and the CL then reacts with an ozone molecule and breaks apart the ozone layer.
Nutrient Cycling
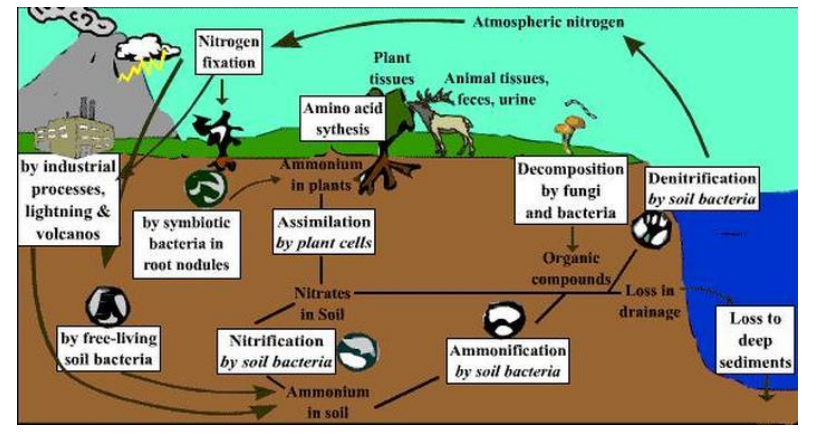
● Main source of nitrogen is from anaerobic, denitrifying bacteria

● Phosphorus is need for all living things. It shows the amount of mater in the food chain.
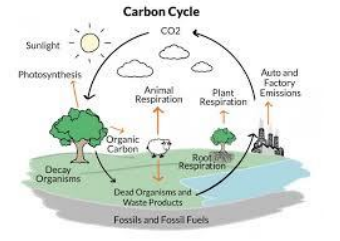
● Carbon Cycle
Air & Water Pollution
● The atmosphere helps in the transportation of water after evaporation takes place.
● Cause of different form of pollution
○ Air pollution
■ Fumes from car exhausts
■ Ammonia
■ Livestock
○ Water Pollution
■ Run off from the environment
○ Land & Soil Pollution
■ Landfills
■ Plastic
○ Noise and Light Pollution
■ Parties
■ Camps
■ Highways
■ Speakers