IB myp 4-5 physics – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Astrophysics-The Big Bang Theory
Topic :Astrophysics– Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic :Classifications of stellar bodies, stellar composition, astronomers, life cycle of a star
Question (2 marks)
In the 1950 s, cosmologists proposed the “steady-state” theory to explain certain aspects of the universe after it was observed to be expanding. This theory states that:
- the universe has no beginning or end
- the temperature of the universe has always been constant and will not change in the future
- as the universe expands, new matter is created and the density of the universe remains constant.
Outline two ways in which this theory is different to the “big-bang” theory.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
The steady-state theory and the Big Bang theory are two contrasting explanations for the origin and evolution of the universe. Here are two ways in which the steady-state theory differs from the Big Bang theory:
1. Universe’s Origin and Expansion: The steady-state theory proposes that the universe has no beginning or end, implying that it has existed infinitely. In contrast, the Big Bang theory suggests that the universe originated from a singular, incredibly dense and hot state approximately 13.8 billion years ago. According to the Big Bang theory, the universe has been expanding and evolving since its initial explosion.
2. Conservation of Matter and Density: The steady-state theory postulates that as the universe expands, new matter is continuously created to maintain a constant density. This theory rejects the notion that the density of matter decreases over time due to the expansion. Conversely, the Big Bang theory posits that matter and energy were created during the initial singularity and have been gradually spreading out and becoming less dense as the universe expands. It does not require the continuous creation of matter.
Overall, the key differences lie in the concepts of the universe’s origin and the conservation of matter and density. The steady-state theory suggests a constant, eternal universe with continuous matter creation, while the Big Bang theory proposes a singular origin, expansion, and a decrease in matter density over time.
Another solar system
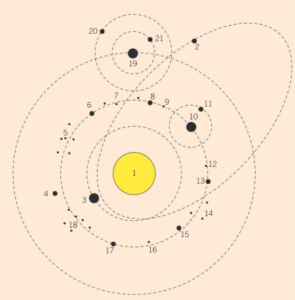
Question:
Planets that orbit other stars are being discovered frequently. Suppose you were to discover another solar system. A drawing of it is shown to the right. Identify which of these objects is most likely to be:
● a star
● a planet
● a dwarf planet
● a moon
● an asteroid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Star: 1
Planet: 3, 19
Dwarf planet: 10 (and maybe others – we cannot see if it
is round or not)
Moon: 11, 20, 21
Asteroid: 2, 4–9, 12–18
Question:
If the Sun (M = 2 × 1030 kg) were to be compressed into a black hole, what would the radius of the event horizon be?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: \(\frac{2\times 6.67\times 10^{-11}\times 2\times 10^{30}}{(3\times 10^{8})^{2}}=3\times 10^{3}m\)