IB myp 4-5 physics – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Waves-Electromagnetic Spectrum,Imaging and Application
Topic :Waves– Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic :Reflection, refraction, diffusion, longitudinal \& transverse waves
Question (5 marks)
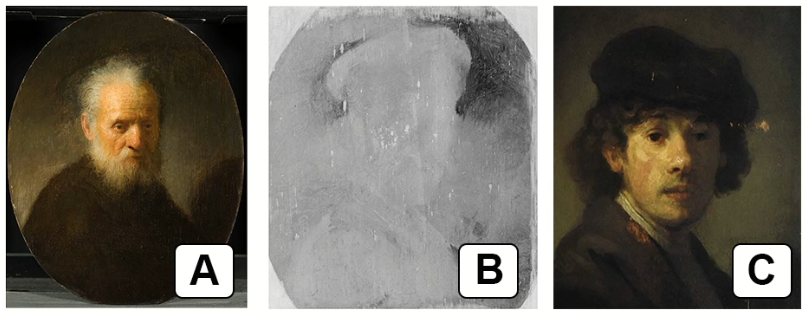
Compare image C to images A and B.
Some art historians suggest that Rembrandt reused the canvas shown in image B.
Question a (2 mark)
Outline the evidence in these three images that supports the suggestion that the canvas was reused.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Evidence supporting the suggestion that the canvas was reused in Image B can be outlined by comparing it to Images A and C. Here are two marks of evidence:
1. Visible ghosting or underlying image: In Image B (x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy), there is a faint but discernible outline of a different painting visible beneath the surface layer. This indicates that the canvas had previously been used for another artwork before being painted over with the Old Man With A Beard. The presence of this underlying image suggests that the canvas was indeed reused by Rembrandt.
2. Differences in subject matter: Comparing the subject matter of the two paintings depicted in Images B and C, we can see that they are distinct. Image B shows the Old Man With A Beard, while Image C portrays a self-portrait of Rembrandt as a young man. The variation in subject matter further supports the idea that the canvas used for Image B was repurposed by Rembrandt for a new painting.
By considering these two pieces of evidence, the visible ghosting of a previous image and the difference in subject matter between the paintings, art historians can make a case for the reuse of the canvas in Image B.
Question b (2 mark)
Suggest two benefits of using XRFS to examine paintings rather than removing areas of paint.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRFS) to examine paintings instead of removing areas of paint offers several benefits. Here are two key advantages:
1. Non-destructive analysis: XRFS is a non-destructive technique that allows art historians and conservators to analyze the composition of a painting without physically removing any paint layers. Traditional methods, such as taking samples from the artwork, can be invasive and potentially damage or alter the artwork. By using XRFS, the integrity and original state of the painting can be preserved, minimizing the risk of irreversible damage.
2. Revealing hidden information: XRFS can provide valuable insights into the materials and techniques used by artists, as well as uncover hidden information about the history of a painting. The technique can detect and map the distribution of various elements within the layers of paint, allowing researchers to identify pigments, analyze layer structures, and even detect hidden or underdrawn sketches or compositions. This non-invasive approach enables art historians to gather information about an artwork’s creation process, artistic choices, and possible alterations without physically altering the painting.
Overall, the use of XRFS in examining paintings offers the benefits of non-destructive analysis and the potential for uncovering hidden information, allowing for a deeper understanding of the artwork while preserving its original condition.
Question:
Red light has a wavelength around 650nm, the wavelength of yellow is about 570nm and blue is about 475nm. A certain color of light has a frequency of 5.66 × 1014Hz. What color is this light?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: \(\lambda =\frac{3\times 10^{8}}{5.66\times 10^{14}}=530 nm\)
This is between yellow and blue so the light is green.