IB myp 4-5 Biology – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Evolution-DNA and Genetics
Topic :Evolution– Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic : Life Cycles,Natural Selection,Cell division,Mitosis,Meiosis,Reproduction,Biodiversity,Inheritance and variation,DNA and genetics
Question
1(c). Label the diagram below.(2 marks)
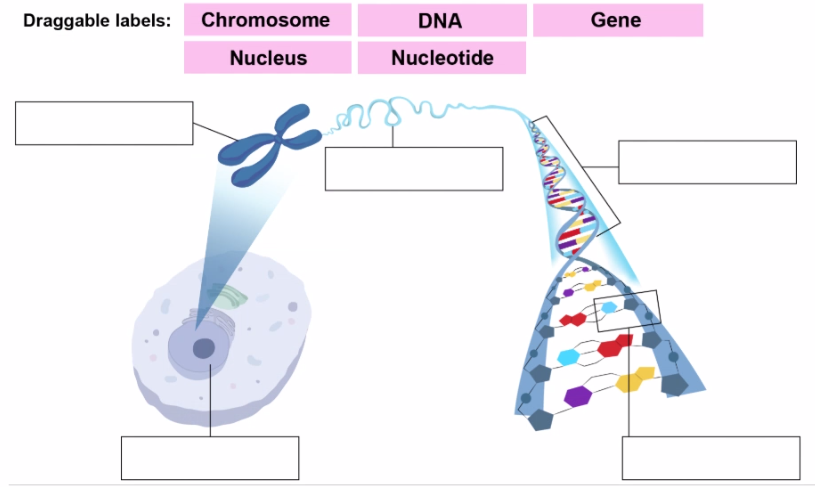
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A) Nucleus, B) Chromosome, C) Gene, D) DNA, E) Nucleotide
Question:
What are the names of each of the differently colored parts of the molecule?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Red = three phosphates, black = sugar/ribose, blue = adenine/base.
Question:
What is removed from ATP to make
a) ADP,
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: One phosphate group.
b) AMP and
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Two phosphate groups.
c) adenosine?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Three phosphate groups.
Q 1.1 Define the term gene.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity that resides within chromosomes. It’s a specific sequence of nucleotides in DNA that carries the coded instructions for producing a functional product, typically a protein. These instructions are responsible for determining many of an organism’s traits.
Here’s a breakdown of the key points:
- Location: Genes are found within chromosomes, which are thread-like structures in the cell nucleus that carry genetic information.
- Composition: Genes are made up of DNA, a molecule that stores genetic information in the form of a code.
- Function: Genes act as instructions for producing functional products, like proteins. These products are responsible for many of an organism’s traits, such as eye color, hair type, and susceptibility to certain diseases.
- Specificity: Each gene has a unique sequence of nucleotides that determines the specific product it codes for.
- Inheritance: Genes are passed from parents to offspring, contributing to the offspring’s characteristics.
Q 1.2 Define homologous chromosomes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that share similar characteristics, like size, gene location, and staining patterns. They are inherited, one from each parent, during sexual reproduction. Here’s a breakdown of their key features:
- Matching pairs: Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes, with one chromosome in each pair inherited from each parent. Homologous chromosomes are the two members of each pair.
- Similar structure: Homologous chromosomes have roughly the same size and shape, although they may not be identical. They also share similar gene locations, although the specific gene versions (alleles) might differ.
- Genetic exchange: During meiosis, a special type of cell division for sexual reproduction, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. This shuffling of genes contributes to genetic diversity in offspring.