IB myp 4-5 Biology – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Evolution-Inheritance and Variation
Topic :Evolution– Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic : Life Cycles,Natural Selection,Cell division,Mitosis,Meiosis,Reproduction,Biodiversity,Inheritance and variation,DNA and genetics
Question
1(d.) A gene carries information for a trait which can be passed on from a parent to a child. Having dimples is one example of a trait. Dimples are a result of a dominant allele (D) whereas not having dimples is a result of a recessive allele (d). (1 mark)

The father of a child has dimples (Dd) and the mother does not have dimples. State the genotype of the mother
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: According to the information, father has the genotype “Dd” which means he has one dominant allele (D) for dimples and one recessive allele (d) for not having dimples. Since the mother does not have dimples, it means she does not have the dominant allele (D) and must have two recessive alleles (dd). Therefore, the genotype of the mother would be “dd”.
Question
e .Use the symbols \(\mathrm{D}\) and \(\mathrm{d}\) to complete the table and determine the possibility that the child has dimples.(2 marks)
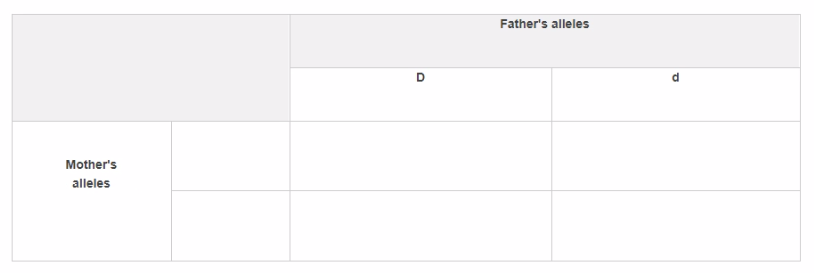
▶️Answer/Explanation
>Ans: According to the information, father has the genotype “Dd” which means he has one dominant allele (D) for dimples and one recessive allele (d) for not having dimples. Since the mother does not have dimples, it means she does not have the dominant allele (D) and must have two recessive alleles (dd). Therefore, the genotype of the mother would be “dd”. Now child have genotype as “Dd, dd, Dd & dd”. By the genotype of child we can easly determine that student has 50% possibility of having pimple.
Question
f .Variation is the difference between individuals of a species. Explain why variation is important for the survival of a species.(5 marks)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Variation is important for survival of any species. It brings diversity and allows individuals to have different traits. This means that some individuals may be better suited to their environment, like having traits that help them find food or avoid predators. When the environment changes, individuals with different traits might have an advantage and be more likely to survive and reproduce. So, variation helps ensure that a species can adapt and survive in different conditions.
Two pea plants having different alleles are bred as shown. Find the missing combinations and complete the table
Parent plants | T(tall) | t (short) |
T(tall) | TT(tall) | Tt(tall) |
T(tall) |
Q For the same plants, the F1 progeny are bred with each other. Find the missing combinations and complete the table.
F1 Generation | T(tall) | t (short) |
T(tall) | ||
t (short) |
▶️Answer/Explanation
Punnett square for the F2 generation of a pea plant cross where the parents are heterozygous for both tall and short alleles:
Fill in the gametes for each parent. Since the F1 generation plants are Tt, they can produce T and t gametes. Fill in the “T” and “t” in the top row and leftmost column of the Punnett square.
Combine the gametes to get the genotypes of the offspring. Each square in the Punnett square represents the combination of one gamete from each parent. For example, the top left square should be filled with TT, which represents the offspring that inherits a T allele from both parents.
Determine the phenotypes of the offspring. Based on the genotypes, you can determine the phenotypes. In this case, T is dominant to t, so any offspring with at least one T allele will be tall (T_). Only offspring with tt will be short.
Fill in the remaining squares and count the phenotypes. Once you have filled in all the squares, you can count the number of offspring with each phenotype. This will give you the phenotypic ratio for the F2 generation.
Here is the completed Punnett square for the F2 generation of the pea plant cross:
| T | t | |
|---|---|---|
| T | TT (tall) | Tt (tall) |
| t | Tt (tall) | tt (Short) |
Phenotypic ratio:
- Tall: 3 ( 1 TT and 2 Tt)
- Short: 1 (tt)
Therefore, the missing combinations are Tt in the bottom left square and Tt in the top right square. The phenotypic ratio for the F2 generation is 3:1 (tall:short).