IB myp 4-5 Biology – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Organsims-Inter dependency
Topic :Organisms– Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic : Habitat,Ecosystem,Inter dependency,Unity and diversity in life forms,Energy transfer and cycles,Classification
Question
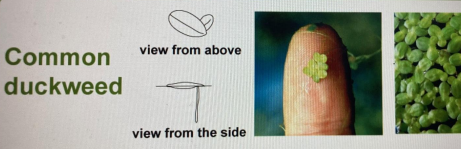
While on the field trip, the students noticed two ponds of approximately the same size that had green plants floating on the surface of the pond. The instructor pointed out that these were duckweed plants, small water plants whose leaves float on the surface of the pond and whose roots hang down below. The image below shows a duckweed plant.
The independent variable is the amount of light, this will be manipulated by changing the voltage of the bulbs in order to adjust the brightness.
The dependent variable is the number of duckweed grown. This will be measured by counting the number of duckweed that are present in the pond.
The two control variables are the number of duckweed plants and the amount of water that the plants are given/grown in. They will have to keep the duckweed plants equal in both containers and also ensure that the amount of water that they are grown in is the same amount.
- Materials and Apparatus:
- Duckweed seeds
- water
- bulb
- lux meter
- large beaker
Fill 5 large beakers with equal amounts of water.
Add an equal number of duckweed seeds to each beaker.
Add a bulb to 4 of the beakers and vary the light levels. Leave the bulbs on for 12 hours and off for the other 12 hours in order to mimic natural conditions.
After one month, count the amount of duckweed and note down your results in an observation table. Note down any other observations you have made in your science journal.
One of the ponds had very few duckweed plants and was surrounded by trees that were shading the pond. The surface of the other pond was mostly covered in duckweed and was in full sun. No trees were shading its surface.
The students wondered if light was a factor in the growth of the plants. They decided to collect duckweed plants to bring back to their school’s science lab and grow them under experimental conditions. The students chose the dependent variable to be the final number of duckweed plants. They then planned to calculate the change in number of duckweed plants.
Design an investigation that would allow them to obtain quantitative data. In your answer, you should:
- identify the independent variable and two control variables
- formulate a testable hypothesis with a scientific explanation
- describe how to manipulate, measure or monitor all of the variables
- describe the method to collect sufficient data
- list any safety considerations.
I predict that as the amount of light increases, the amount of duckweed that will grow will also increase, this is until a certain extent after which it will be too bright and the plants will either cease growing and start dying off, grow very slowly or just stay constant. This is because in order to live plants go through a process known as photosynthesis. In order to undergo this process, the plant needs sunlight. The more sunlight the plant can take in the more it ‘ll be able to grow. Hence, I believe that as the amount of light increases the amount duckweed that grows will also increase.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
0
Question:
Explain how the data could be tested to see whether it fits the mathematical model that is called Yoda’s law.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The equation of the regression line for logW on log ρ can be found by entering the values of log W and log ρ into a calculator in 2–variable statistics mode; the calculator will give the equation of the line in the form y = A + Bx, so logW = A + Blog ρ. If B = –3/2 (within the expected variability) then the equation is of the form W = C ρ–3/2 showing that Yoda’s law fits the data; the value of C can be estimated from the graphs as log W = log C ρ–3/2, so log C = A and therefore C = 10A.
Question:
Suggest examples of:
a) overexploitation of natural resources, apart from overfishing of cod.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Excessive logging of rainforests so few trees of a particular species remain; collection of all or most wild orchids of one species; extraction of so much water from a river for irrigation that the river downstream runs dry; poaching of more elephants for ivory than are added to the population each year by reproduction.
b) adverse effects of humans on ecosystems, apart from overexploitation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Examples of chemical pollution; light pollution; fragmentation; disturbance due to noise; drainage of wetlands; climate change/global warming; introduction of alien species; raising of sea levels; acidification of oceans.