IB myp 4-5 Chemistry – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Bonding–energy changes in reactions
Topic :Bonding- Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic :structure and bonding,properties,chemical formulas,chemical reactions and the conservation of mass; balancing,equations, the mole concept and chemical calculations;
reaction kinetics [rates, and factors affecting rates/collision theory],equilibria/reversible reactions,energy changes in reactions, endo- and exothermicity; combustion of fuels)
Question:
How might you prevent the formation of carbon monoxide during the combustion of alkanes?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Ensure that the combustion reaction has a constant supply of oxygen.
Question:
Draw the structural formula for each alcohol in your table.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 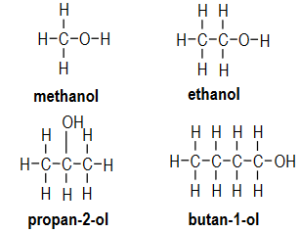
Question:
Analyze the qualitative data collected and then explain with reasons why each reaction is either complete or incomplete combustion.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Qualitative data collected should reveal differences in the colour of the flame. A yellow flame that gives off dark coloured smoke is evidence of incomplete combustion. A clean blue flame is evidence of complete combustion.
