IB myp 4-5 Chemistry – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Bonding–states and properties of matter
Topic :Bonding- Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic :structure and bonding,properties,chemical formulas,chemical reactions and the conservation of mass; balancing,equations, the mole concept and chemical calculations;
reaction kinetics [rates, and factors affecting rates/collision theory],equilibria/reversible reactions,energy changes in reactions, endo- and exothermicity; combustion of fuels)
Question:
Find out each compound’s chemical formula and classify it as ionic or covalent. Are the results with respect to conductivity what you predicted given your knowledge of the properties of these compounds?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 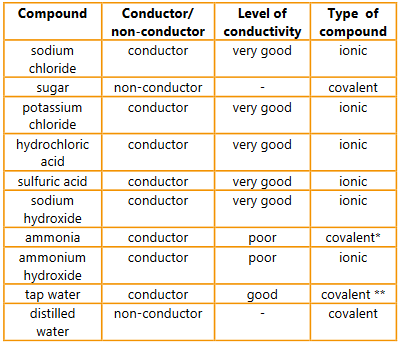
* NH3 + H2O ↔ NH4+ + OH–
** The presence of a wide range of dissolved ions makes tap water a conductor
Summative assessment
Chemical bonding and its effect on the properties of materials
Question:
Ions formed by metals and non-metals are held together by an electrostatic attraction of unlike charges.
a) Determine the number of valence electrons and the charge formed on each of these elements:
sodium (group 1) calcium (group 2) aluminium (group 13)
nitrogen (group 15) oxygen (group 16) bromine (group 17).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 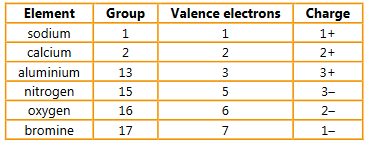
b) Explain how the metallic and non-metallic ions from these groups can combine to form ionic compounds.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Metals like to lose electrons (oxidation) and form positively charged cations; non–metals like to gain electrons (reduction) and form negatively charged anions; the electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions results in the formation of an ionic bond.
c) Using the elements given in part a) construct formula and give the name of the ions and the resulting ionic compound from the following combinations:
i) group 1 and group 17
ii) group 1 and group 16
iii) group 2 and group 16
iv) group 2 and group 15
v) group 13 and group 16
vi) group 13 and group 17.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 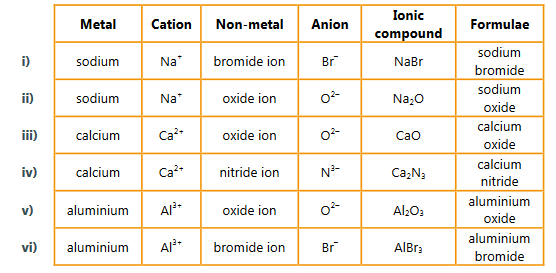
Question:
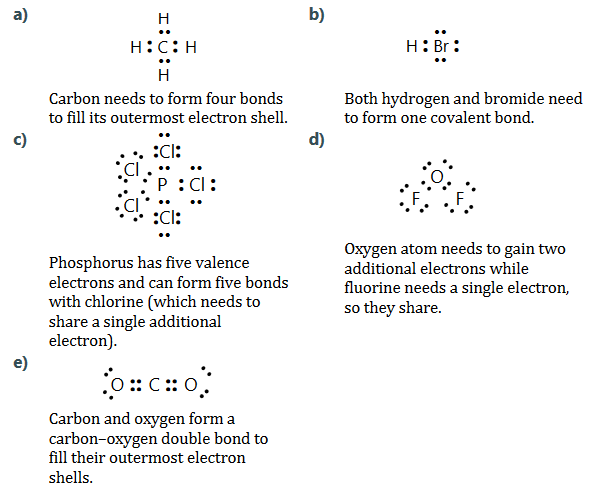
Use Lewis symbols and structures to explain the formation of the following covalently bonded compounds.
a) Methane
b) Hydrogen bromide
c) Phosphorus pentachloride
d) Oxygen difluoride
e) Carbon dioxide
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: