IB myp 4-5 Chemistry – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic :Periodic Table-Periodic trend group and periods
Topic :Periodic Table- Weightage : 21 %
All Questions for Topic : Metals and Non metals,Transition metals,Noble gases,Periodic trend groups and periods
Question:
Complete the following table to determine the number of valence electrons and electron configuration for the following elements. The first one has been done for you.
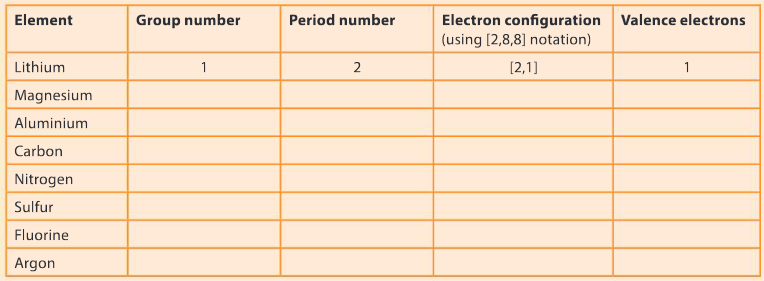
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: 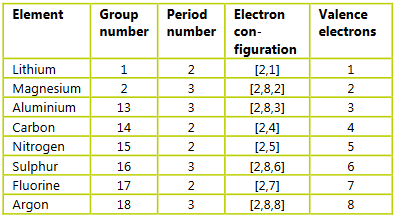
The following chart shows the melting and boiling points of the first 20 elements of the periodic table.
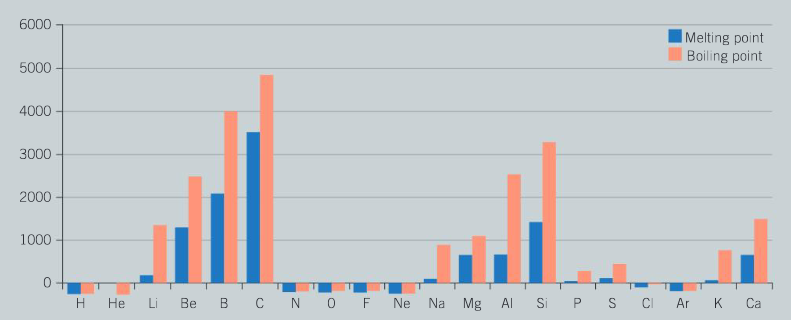
Question:
Examine the graph and describe the pattern in melting points as you move from left to right across period 3 (from sodium to argon).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: There is an increase in melting point of the first three metals (Na, Mg, Al) as the strength of metallic bonding increases; the sudden increase in melting point for silicon is due to the fact that this is a giant covalent structure with very high melting points and boiling points due to the strong covalent bonding; the large decrease in melting points of the final elements of period 3 is due to the fact that these elements (P, S, Cl, Ar) are simple molecular substances which are held together by weak intermolecular forces between the molecules.
Question:
Which group of the periodic table has the maximum values for their melting points? Identify the type of bonding present in these elements and explain why the melting points are so high.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: Group 14 has the maximum values for melting points; the elements carbon (diamond and graphite) and silicon exist as giant covalent lattice structures; the very high melting points are a consequence of the large number of strong covalent bonds within the structure.
Question:
How can we use the value of the ionization energy of an atom as an indicator of the level of reactivity of an element?
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: The lower the ionization energy of an element, the more able it is to share electrons, which indicates higher reactivity.
