Question
This question asks you to investigate some properties of the sequence of functions of the form $f_n(x)=\cos (n \arccos x),-1 \leq x \leq 1$ and $n \in Z^{+}$.
Important: When sketching graphs in this question, you are not required to find the coordinates of any axes intercepts or the coordinates of any stationary points unless requested.
For odd values of $n>2$, use your graphic display calculator to systematically vary the value of $n$. Hence suggest an expression for odd values of $n$ describing, in terms of $n$, the number of
For even values of $n>2$, use your graphic display calculator to systematically vary the value of $n$. Hence suggest an expression for even values of $n$ describing, in terms of $n$, the number of
The sequence of functions, $f_n(x)$, defined above can be expressed as a sequence of polynomials of degree $n$.
Consider $f_{n+1}(x)=\cos ((n+1) \arccos x)$.
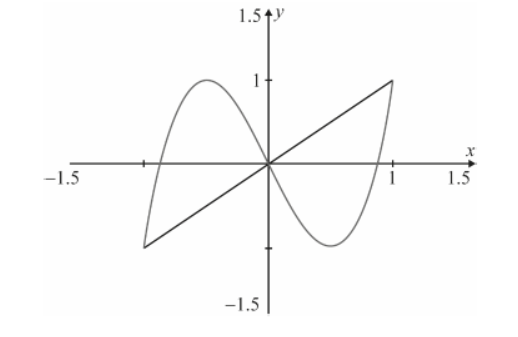
a. On the same set of axes, sketch the graphs of $y=f_1(x)$ and $y=f_3(x)$ for $-1 \leq x \leq 1$.
b.i.local maximum points;
b.iilocal minimum points;
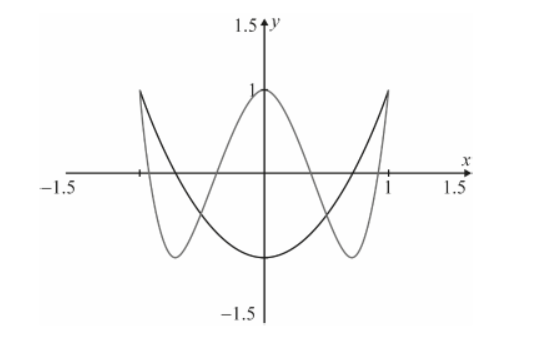
c. On a new set of axes, sketch the graphs of $y=f_2(x)$ and $y=f_4(x)$ for $-1 \leq x \leq 1$.
d.i.local maximum points;
d.iilocal minimum points.
e. Solve the equation $f_n^{\prime}(x)=0$ and hence show that the stationary points on the graph of $y=f_n(x)$ occur at $x=\cos \frac{k \pi}{n}$ where $k \in \mathrm{Z}^{+}$and $0<k<n$.
f. Use an appropriate trigonometric identity to show that $f_2(x)=2 x^2-1$.
g. Use an appropriate trigonometric identity to show that $f_{n+1}(x)=\cos (n \arccos x) \cos (\arccos x)-\sin (n \arccos x) \sin (\arccos x)$.
h.i. Hence show that $f_{n+1}(x)+f_{n-1}(x)=2 x f_n(x), n \in \mathrm{Z}^{+}$.
h.ii.Hence express $f_3(x)$ as a cubic polynomial.
[5]
▶️Answer/Explanation
a. correct graph of $y=f_1(x) \quad \boldsymbol{A 1}$
correct graph of $y=f_3(x) \quad$ A1
b.i.graphical or tabular evidence that $n$ has been systematically varied
M1
eg $n=3,1$ local maximum point and 1 local minimum point
$n=5,2$ local maximum points and 2 local minimum points
$n=7,3$ local maximum points and 3 local minimum points
(A1)
$\frac{n-1}{2}$ local maximum points
$A 1$
[3 marks]
b.ii. $\frac{n-1}{2}$ local minimum points
$A 1$
Note: Allow follow through from an incorrect local maximum formula expression.
[1 mark]
c. correct graph of $y=f_2(x) \quad$ A1
correct graph of $y=f_4(x) \quad$ A1
d.i. graphical or tabular evidence that $n$ has been systematically varied
M1
eg $n=2,0$ local maximum point and 1 local minimum point $n=4,1$ local maximum points and 2 local minimum points $n=6,2$ local maximum points and 3 local minimum points
(A1) $\frac{n-2}{2}$ local maximum points
$A 1$
[3 marks]
d.ii. $\frac{n}{2}$ local minimum points
A1
[1 mark]
e. $f_n(x)=\cos (n \arccos (x))$
$f_n^{\prime}(x)=\frac{n \sin (n \arccos (x))}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} \quad$ M1A1
Note: Award $\boldsymbol{M} 1$ for attempting to use the chain rule.
$f_n^{\prime}(x)=0 \Rightarrow n \sin (n \arccos (x))=0 \quad$ M1
$n \arccos (x)=k \pi\left(k \in \mathrm{Z}^{+}\right) \quad \boldsymbol{A 1}$
leading to
$x=\cos \frac{k \pi}{n}\left(k \in \mathrm{Z}^{+}\right.$and $\left.0<k<n\right) \quad \boldsymbol{A G}$
[4 marks]
f.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& f_2(x)=\cos (2 \arccos x) \\
& =2(\cos (\arccos x))^2-1 \quad M 1
\end{aligned}
$$
stating that $(\cos (\arccos x))=x$
A1
$$
\text { so } f_2(x)=2 x^2-1 \quad \boldsymbol{A G}
$$
[2 marks]
g.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& f_{n+1}(x)=\cos ((n+1) \arccos x) \\
& =\cos (n \arccos x+\arccos x) \quad \text { A1 }
\end{aligned}
$$
use of $\cos (A+B)=\cos A \cos B-\sin A \sin B$ leading to $M 1$
$$
=\cos (n \arccos x) \cos (\arccos x)-\sin (n \arccos x) \sin (\arccos x) \quad \text { AG }
$$
[2 marks]
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { h.i. } f_{n-1}(x)=\cos ((n-1) \arccos x) \quad \text { A1 } \\
& \quad=\cos (n \arccos x) \cos (\arccos x)+\sin (n \arccos x) \sin (\arccos x) \quad \text { M1 } \\
& f_{n+1}(x)+f_{n-1}(x)=2 \cos (n \arccos x) \cos (\arccos x) \quad \text { A1 } \\
& \quad=2 x f_n(x) \quad \text { AG }
\end{aligned}
$$
[3 marks]
$$
\begin{aligned}
\text { h.ii } f_3(x)=2 x f_2(x)-f_1(x) \\
\quad=2 x\left(2 x^2-1\right)-x \\
=4 x^3-3 x \quad \boldsymbol{A 1}
\end{aligned}
$$
(M1)
[2 marks]