WAVES
- Waves are mediums of transferring energy without particles. In layman’s terms, they are disturbances propagating through space.
Two types of waves:
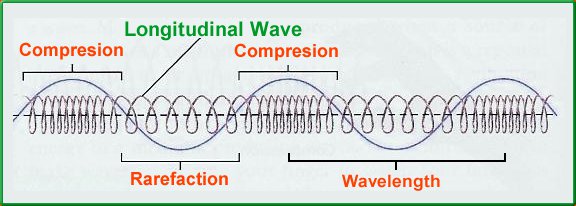
- Longitudinal (coils move horizontally)
- Transverse (coils move vertically)
Longitudinal Wave:
Transverse wave:
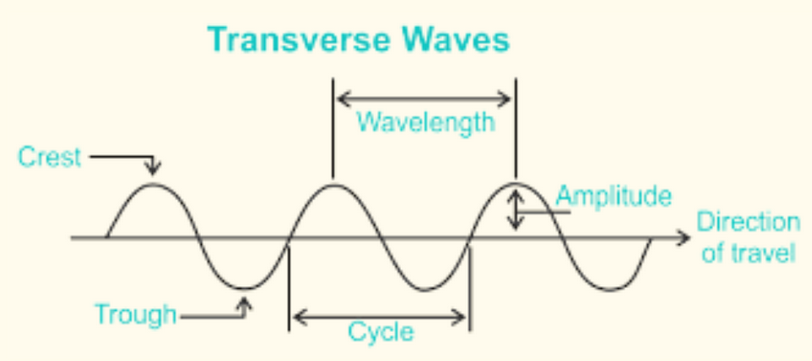
- The wavelength is the distance from one point to the same in the next oscillation. (length of an oscillation) $-\lambda$
- The amplitude is the distance from the maximum minimum point to the mean line.
- The time period of a wave is the time taken for an oscillation. The frequency $\left(\mathrm{H}_2\right)$ is the number of oscillations in one second. They are inversely proportional.
$T=\frac{1}{f}, \quad f=\frac{1}{T}$
- There are 4 main phenomena of waves. These are as follows:
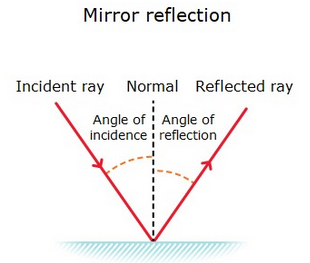
- Reflection is the bouncing of of a wave off a mirror-like substance. Specular reflection takes place when the mirror surface is smooth. Here, the angle of incidence = angle of refraction.
- Refraction is the bending of light due to varying speeds of Hight across different mediums.
- If the speed is faster, the ray will move away from the normal line.
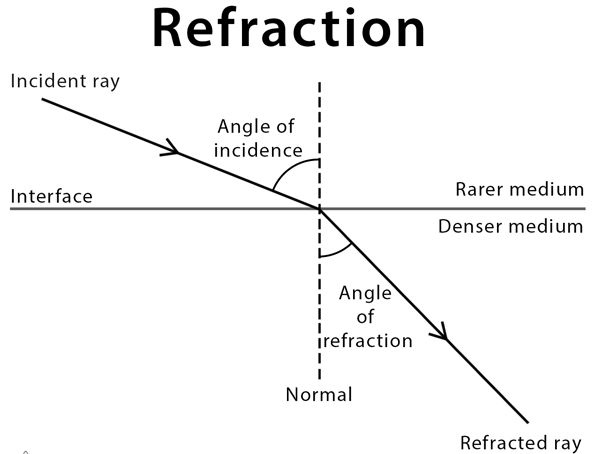
- To find the refractive index, use:
$n=\frac{c}{V}$ or $n=\frac{\sin \theta_1}{\sin \theta_2}$
c= speed of light in medium
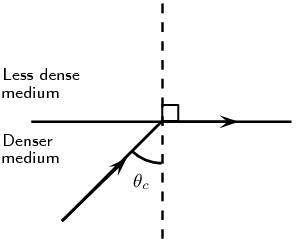
- The critical angle is the angle at which, if light refracts, it becomes straight.
- The third phenomenon is interference. There are two types of interference (waves interacting with other wavers):
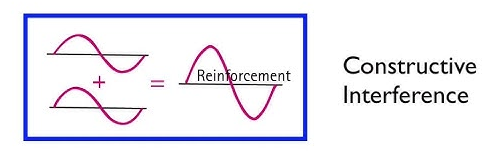
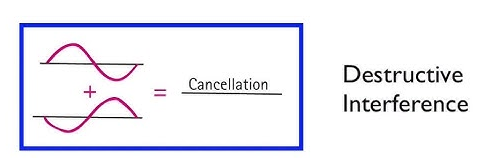
- Constructive interference is crest on crest and trough an trough. This causes a bigger wave to be produced as a result. Destructive interference is crest on trough and vice versa. This causes a smaller wave or no wave at all as the net result.
(1)- constructive interference
(2) – Destructive interference
The last phenomenon is Diffraction, which is the bending of waves as they move through a shit.
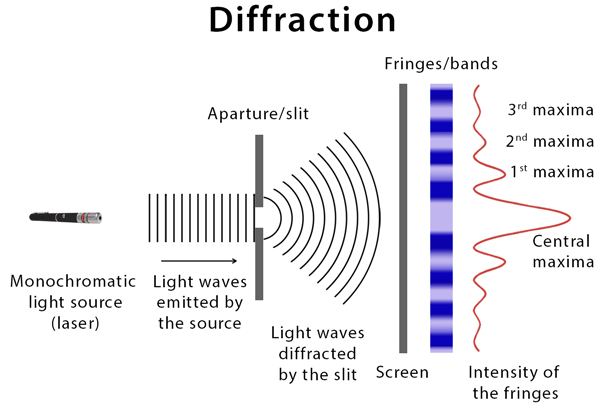
- The optimum level of diffraction takes place when the slit’s length is equal to the wavelength of the wave.
- A wave with longer wavelength has lesser energy.
- About the speed/velocty of a wave:
$
V=f \lambda \quad \text { wavelength }
$
frequency
or
$
V=\frac{\lambda}{T \rightarrow \text { Time period }}
$
- There are several characteristics of sound. These are as follows.
- Pitch is the quality of sounds that distinguishes between grave and shrill sound. pitch is directly proportional to the frequency.
- Quality in a sound is when two sounds have the same amplitude and frequency, but different wave patterns (such as flutes and pianos).
- Intensity is the sound energy transmitted per unit area, which is held perpendicular.
- Amplitude is directly proportional to energy, whereas wavelength is inversely proportional to energy
- How loud a sound depends on 5 factors:
- Intensity
- Amplitude
- Surface Area of vibrating body.
- Sensation of your ear
- Distance from vibrating body.
- For the intensity of a wave:
$
\text { Intensity }=\frac{\text { Power }}{\text { Area }}
$
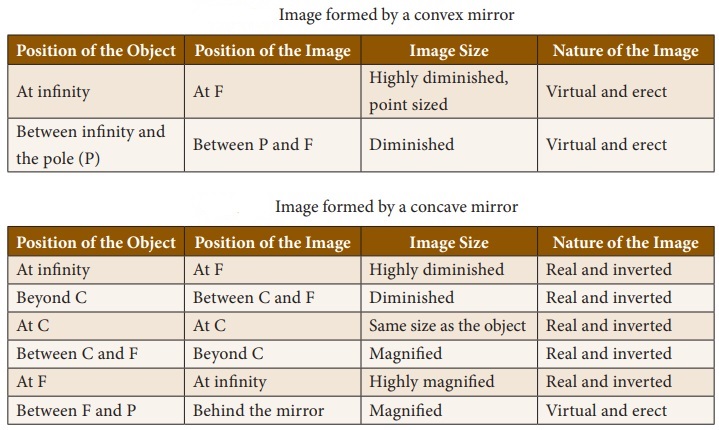
- Waves can help in imaging as well. There are 2 types of mirrors:
- Concave converges
- Convex Diverges
REMEMBER : CAPTAIN COLD VALUED DIAMONDS
Example of Concave Mirror
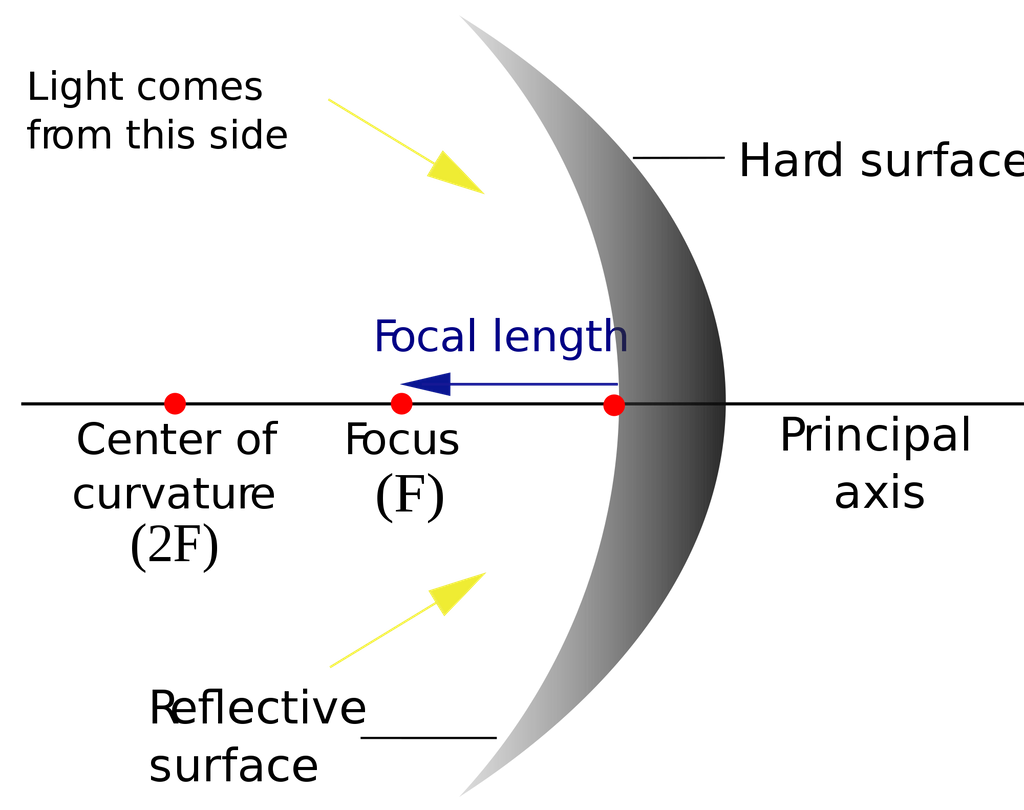
Types of rays + Appearances
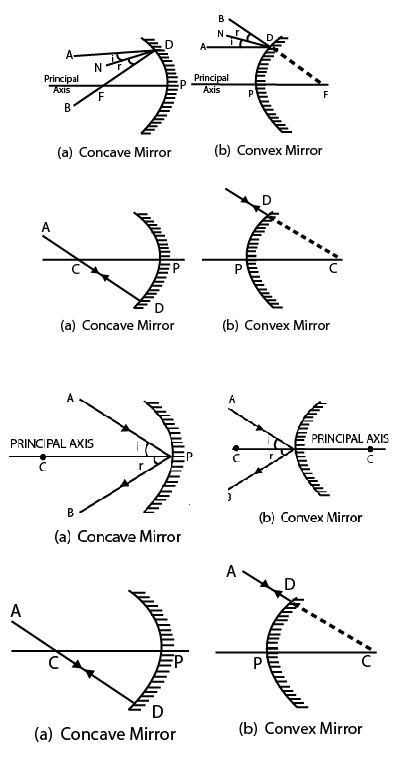
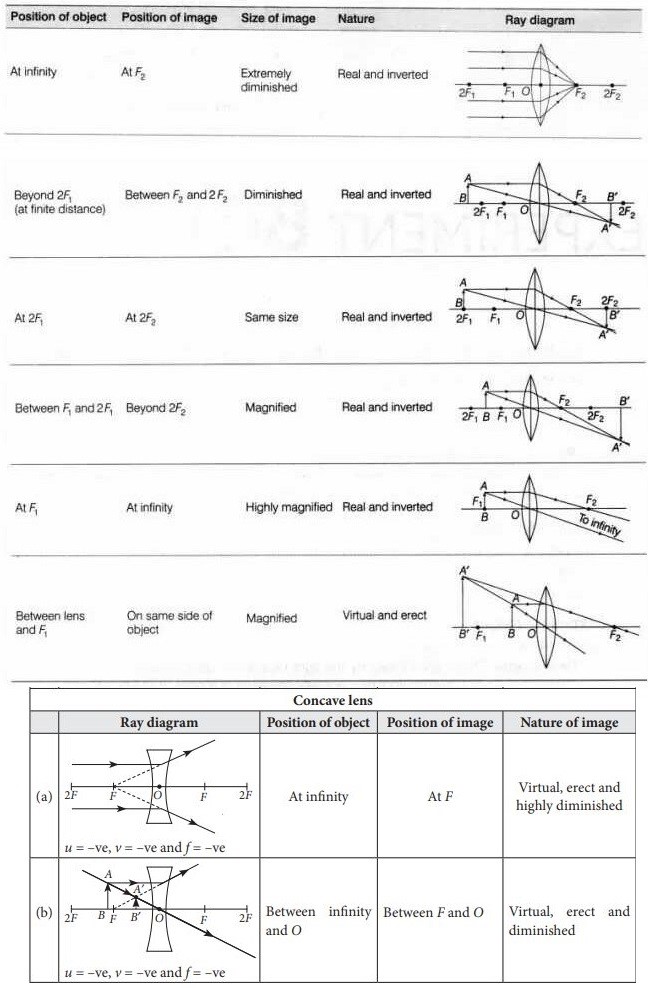
- For ray diagrams:
- $p$ is the object distance
- $q$ is the image distance.
- $f$ is the focal length
- $\frac{1}{p}+\frac{1}{q}=\frac{1}{f}=$ Power of lens
- $\cdot \frac{q}{p}=\frac{H_i}{H_0}=$ Magnification