Unit 2: Thermodynamics
- 2.1 Thermodynamic Systems
- 2.2 Pressure, Thermal Equilibrium, and the Ideal Gas Law
- 2.3 Thermodynamics and Forces
- 2.4 Thermodynamics and Free-Body Diagrams
- 2.5 Thermodynamics and Contact Forces
- 2.6 Heat and Energy Transfer
- 2.7 Internal Energy and Energy Transfer
- 2.8 Thermodynamics and Elastic Collisions: Conservation of Momentum
- 2.9 Thermodynamics and Inelastic Collisions: Conservation of Momentum
- 2.10 Thermal Conductivity
- 2.11 Probability, Thermal Equilibrium, and Entropy
Unit 3: Electric Force, Field, and Potential
- 3.1 Electric Systems
- 3.2 Electric Charge
- 3.3 Conservation of Electric Charge
- 3.4 Charge Distribution—Friction, Conduction, and Induction
- 3.5 Electric Permittivity
- 3.6 Introduction to Electric Forces
- 3.7 Electric Forces and Free-Body Diagrams
- 3.8 Describing Electric Force
- 3.9 Gravitational and Electromagnetic Forces
- 3.10 Vector and Scalar Fields.
- 3.11 Electric Charges and Fields
- 3.12 Isolines and Electric Fields
- 3.13 Conservation of Electric Energy
Course Content
AP Physics 2 is the equivalent of the second semester in the college-level introductory course, covering the topics of fluid mechanics; thermodynamics; electricity and magnetism; optics; and quantum, atomic, and nuclear physics.
Units Exam Weighting
Unit 1: Fluids 10–12%
Unit 2: Thermodynamics 12–18%
Unit 3: Electric Force, Field, and Potential 18–22%
Unit 4: Electric Circuits 10–14%
Unit 5: Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction 10–12%
Unit 6: Geometric and Physical Optics 12–14%
Unit 7: Quantum, Atomic, and Nuclear Physics 10–12%
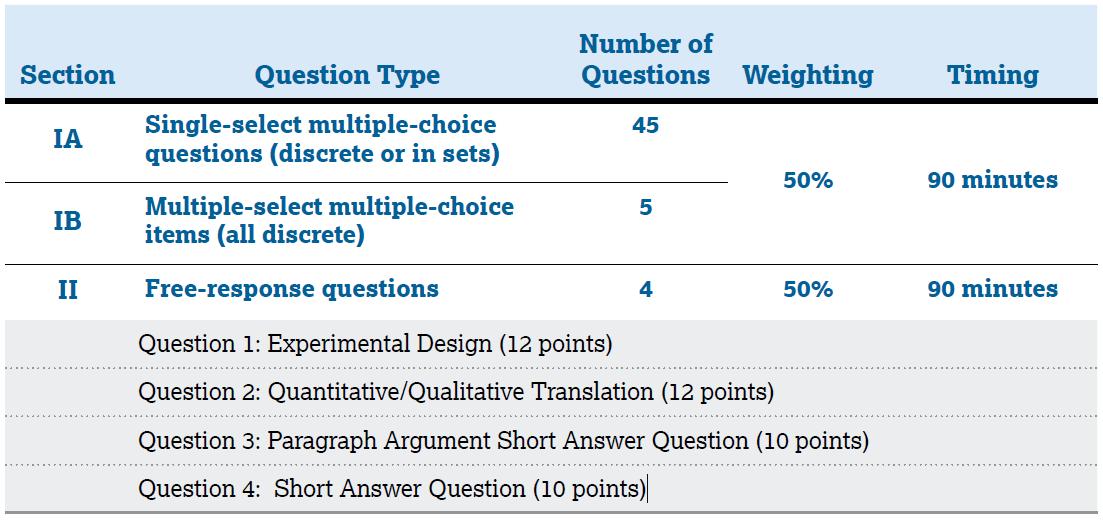
About Advanced Placement(AP) Exams: Conducted annually in May, APs are college-level courses which enable you to earn college credit, advanced placement, or both while you are still in high school
About AP Physics exams
- AP Physics 1
- AP Physics 2
- AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
- AP Physics C: Mechanics