Question
The diagram shows part of the Periodic Table.
Answer the following questions using only the symbols of the elements in the diagram.
Each symbol may be used once, more than once or not at all.
Give the symbol of the element that:
(a) is extracted from bauxite
(b) forms 21% of clean, dry air
(c) forms an oxide which contributes to acid rain
(d) forms an aqueous ion that gives a red-brown precipitate on addition of aqueous
sodium hydroxide
(e) has an atom with a complete outer electron shell.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) Al
(b) O
(c) N
(d) Fe
(e) Ar
Question
The table shows the mass of some of the ions in a 1000 \(cm^3\) sample of sea water.
(a) Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) State which negative ion has the lowest mass in 1000 \(cm^3\) of sea water.
(ii) Give the formulae of the ions in potassium sulfate.
………………………………………………………. and ………………………………………………………
(iii) Calculate the mass of calcium ions in 200cm3
of this sample of sea water.
mass = ………………………… mg
(iv) A sample of this sea water is evaporated.
State the name of the compound which is present in the greatest quantity when this sample is evaporated.
(v) Give the name of the ion which reacts with aqueous silver nitrate to give a cream precipitate.
(b) The \(B_3O_6^{3–}\) ion can be converted to boric acid, \(H_3BO_3\).
Boric acid is also produced when boron trichloride, \(BCl_3\), reacts with water.
Complete the equation for this reaction.
\(BCl_3 + …..H_2O → H_3BO_3 + …..HCl\)
(c) The symbol of a strontium ion is shown.
\(^{87}_{38} Sr^{2+}\)
Deduce the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in one atom of this strontium ion.
number of electrons …………………………………………………………………………………………………….
number of protons ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
number of neutrons …………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(d) Some isotopes of strontium are radioactive.
(i) Give one medical use of radioactive isotopes.
(ii) The isotope \(^{235}\)U is also radioactive.
State the major use of this isotope of uranium.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) \(B_3O_6^{3-}\) / metaborate
(ii) \(K^+\) AND \(SO_4^{2-}\)
(iii) 80 (mg)
(iv) sodium chloride
(v) bromide
(b) \(3(H_2O)\)
3(HCl)
(c) number of electrons: 36 (1)
number of protons: 38 (1)
number of neutrons: 49 (1)
(d) (i) cancer treatment / tracer (e.g. for thyroid function)
(ii) source of energy / energy production
Question
The table shows some properties of four halogens.
(a) (i) Complete the table by predicting:
● the boiling point of chlorine
● the density of fluorine at its melting point.
(ii) Describe the trend in the melting points of the halogens down the group.
(iii) Deduce the physical state of iodine at 130°C.
Explain your answer.
(b) (i) Give the electronic structure of a fluorine atom.
(ii) Explain why a fluoride ion has a single negative charge.
(c) Magnesium reacts with excess fluorine to produce magnesium fluoride.
When 2.40g of magnesium is reacted, 6.20g of magnesium fluoride is produced. Calculate the mass of magnesium needed to produce 1.24g of magnesium fluoride.
mass of magnesium = ………………………… g
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) boiling point of chlorine: any values between –100 and 10 (°C) (inclusive of these values) (1)
density of fluorine: any values between 0.20 and 1.55 (g / cm3) (inclusive of these values) (1)
(ii) increases
(iii) liquid (1)
130 (°C) is between the melting and boiling point / the melting point is lower than 130 (°C) AND the boiling point is above
130 (°C) (1)
(b) (i) 2.7
(ii) the number of electrons is one more than the number of protons / it has 9 protons and 10 electrons (1)
(c) 0.48(0) (g)
Question
A student investigates the reaction of magnesium powder with dilute hydrochloric acid. The
magnesium is in excess.
\(Mg + 2HCl → MgCl_2 + H_2\)
The rate of reaction can be found by measuring the increase in volume of hydrogen with time.
The results are shown on the graph.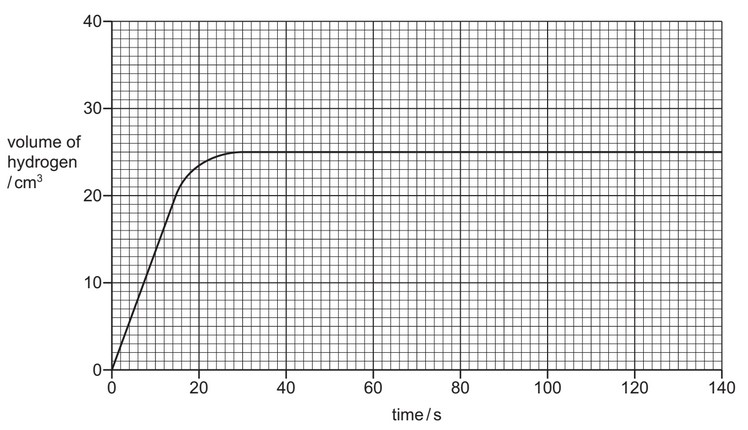
(a) Deduce the time taken for the reaction to finish.
time taken = ………………………… s
(b) The experiment is repeated using dilute hydrochloric acid of a lower concentration.
Draw a line on the grid to show how the volume of hydrogen changes with time using dilute
hydrochloric acid of a lower concentration.
All other conditions stay the same.
(c) Describe the effect each of the following has on the rate of reaction of magnesium with
hydrochloric acid.
● The temperature is increased.
All other conditions stay the same.
● Magnesium ribbon is used instead of magnesium powder.
All other conditions stay the same.
(d) Hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium carbonate.
Name the products of this reaction and give the observations.
products …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
observations ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) values between 28–30 s (inclusive of these values)
(b) initial gradient is shallower and line starts at 0-0 (1)
final volume below 25 cm3 hydrogen AND levelling off (1)
(c) higher temperature: faster / increases (1)
magnesium ribbon: slower / decreases (1)
(d) calcium chloride (1)
carbon dioxide (1)
water (1)
bubbles / fizzing / calcium carbonate becomes smaller / tube gets warm (1)
Question
This question is about sulfur and compounds of sulfur.
(a) Sulfur is a non-metal.
Describe three physical properties which are typical of non-metals.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Name one source of sulfur.
(c) When carbon is heated with sulfur, carbon disulfide, CS2, is produced.
\(C + 2S → CS_2\)
(i) Complete the energy level diagram for the production of carbon disulfide by writing these
formulae on the diagram:
● C + 2S
● \(CS_2\).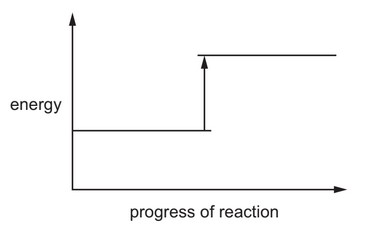
(ii) Explain, using information on the energy level diagram, how you know that this reaction is endothermic.
(d) Carbon disulfide is a liquid at room temperature.
Describe the separation and motion of the particles in carbon disulfide liquid.
separation ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
motion ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) Hydrogen sulfide is a gas which turns filter paper soaked in aqueous lead(II) ethanoate from white to black.
Hydrogen sulfide is slightly soluble in water.
A long glass tube is set up as shown.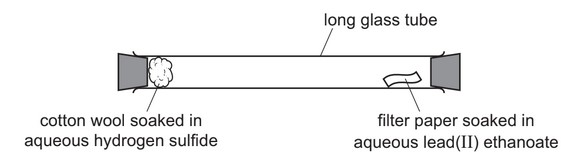
At first, the filter paper soaked in aqueous lead(II) ethanoate does not turn black.
After a short time, the filter paper soaked in aqueous lead(II) ethanoate turns black.
Explain these observations using the kinetic particle model.
(f) Sulfur dioxide is a pollutant in the air.
(i) Give one adverse effect of sulfur dioxide on buildings.
(ii) Sulfur dioxide is used to bleach paper.
Give one other use of sulfur dioxide.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) 1 mark each for any 3 of:
• does not conduct electricity / poor conductor of electricity / insulator
• does not conduct heat / poor conductor of heat
• brittle / not malleable / not ductile
• not sonorous / dull sound when hit
• not lustrous / not shiny
• has (relatively) low melting point / low boiling point
(b) in underground deposits / sulfide ores / volcanoes
(c) (i) C + (2)S on lower line to left AND \(CS_2\) on upper line to right (1)
(ii) the product energy level is above the reactant energy level
(d) separation: particles close together / small spaces between the particles (1)
motion: limited (movement) / restricted (movement) / sliding over each other / random (motion) (1)
(e) 1 mark each for any 3 of:
• evaporation of hydrogen sulfide from the cotton wool / hydrogen sulfide molecules escape from solution
• diffusion
• molecules in (constant) movement / molecules collide / molecules travel
• (movement of) molecules is random / in every direction
• molecules spread out / molecules mix
• molecules hit filter paper
• (molecules spread) from higher concentration to lower concentration
(f) (i) (chemical) weathering / ironwork corrodes
(ii) food preservation / food preservative
Question
6. The structure of compound A is shown.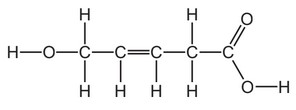
(a) (i) On the structure of compound A, draw a circle around the carboxylic acid functional group.
(ii) State the name of the carboxylic acid that has only two carbon atoms.
(iii) Deduce the molecular formula of compound A to show the number of carbon, hydrogen
and oxygen atoms.
(iv) Explain, by referring to its structure, why compound A is described as unsaturated.
(b) Ethene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Draw the structure of ethene to show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(c) Ethene can be produced by cracking hydrocarbons.
(i) State the meaning of the term cracking.
(ii) Give the conditions required for cracking.
1 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) Ethene can be polymerised.
Complete these sentences about the polymerisation of ethene using words from the list.
addition decomposition neutralisation poly(ethene)
poly(ethane) reduction Terylene
When ethene polymerises, it produces a molecule called …………………………. .
The type of reaction which occurs is ………………………….
(e) Describe one pollution problem caused by non-biodegradable plastics.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) circle around COOH group
(ii) ethanoic acid
(iii) \(C_5H_8O_3\)
(iv) has a C=C double bond
(b) 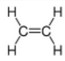
C=C bond and 2 carbon atoms and no other types of atom (1)
rest of molecule correct (1)
(c) (i) idea of breaking down large hydrocarbons to smaller hydrocarbons (using heat)
(ii) heat / high temperature (1)
catalyst (1)
(d) poly(ethene) (1)
(e) filling landfill sites / gets stuck in animals digestive system / animals get stuck in the plastic / blocks drains / floats on surface
of water / stops light getting to organisms in sea (or rivers/ lake)
Question
Sodium is manufactured by electrolysis.
(a) Explain why sodium is manufactured by electrolysis and not by reduction with carbon.
(b) The diagram shows the equipment for the production of sodium.
(i) The anode is inert.
Suggest a suitable substance that can be used for the anode.
(ii) Label the anode on the diagram.
(iii) Describe, by reference to the diagram, how you know that sodium is less dense than
molten sodium chloride.
(c) When concentrated aqueous sodium chloride is electrolysed, gases are produced at each electrode.
State the names of the products and give the observations at each electrode.
product at the negative electrode ………………………………………………………………………………….
observations at the negative electrode …………………………………………………………………………..
product at the positive electrode ……………………………………………………………………………………
observations at the positive electrode ……………………………………………………………………………
(d) Give two ways in which the physical properties of sodium are different from the physical properties of transition elements.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) The symbol equation for the production of sodium hydride is shown.
\(2Na + H_2 → 2NaH\)
(i) Write a word equation for this reaction.
(ii) Suggest why the hydrogen must be dry.
(iii) Sodium hydride reduces iron(III) oxide to iron.
\(Fe2O_3 + 3NaH → 2Fe + 3NaOH\)
Explain how this equation shows that iron(III) oxide is reduced.
(f) State the colour observed in the flame test for sodium.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) sodium is too reactive / sodium is high in the electrochemical series / it takes too high a temperature to extract sodium using
carbon
(b) (i) graphite / platinum
(ii) ‘square’ in middle of diagram labelled anode
(iii) the sodium floats on top of the sodium chloride
(c) negative electrode:
hydrogen (1)
bubbles / fizzing / colourless gas (1)
positive electrode:
chlorine (1)
bubbles / fizzing / green gas / yellow-green gas (1)
(d) 1 mark each for any 2 of:
• sodium is soft / not strong / more malleable / more ductile
• sodium has low density
• sodium has (relatively) low melting point
(e) (i) sodium + hydrogen → sodium hydride
(ii) so that sodium does not react with water / sodium reacts with water
(iii) the iron oxide has lost oxygen
(f) yellow (1)
Question
Aqueous ammonia is an alkali.
(a) Complete the dot-and-cross diagram to show the electron arrangement in a molecule of ammonia.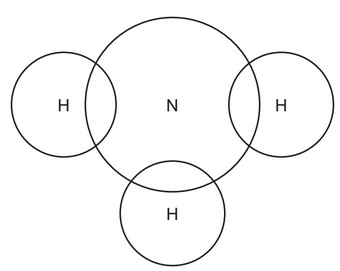
Complete the word equation for the reaction of aqueous ammonia with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(c) Describe the colour change when excess aqueous ammonia is added to an acidified solution of methyl orange.
from ………………………………………………………. to ……………………………………………………….
(d) Aqueous ammonia reacts with aqueous copper(II) ions to produce compound B.
The formula of compound B is \(CuN_4H_{16}O_2\).
Complete the table to calculate the relative molecular mass of compound B.
relative molecular mass = …………………………
(e) Ammonia is used in the production of fertilisers.
State why farmers put fertilisers on the soil where crops are to be grown.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) bonding pair of electrons between each H and N AND no other electrons on H (1)
2 non-bonded electrons on N (1)
(b) ammonium chloride (1)
(c) red / pink to yellow (1)
(d) 168 (2 marks)
if 2 marks not scored, 1 mark for :
(16 × 1) = 16 OR (2 × 16) = 32 (on the appropriate line)
(e) makes plants grow faster / increases yield
