Question
A list of symbols and formulae is shown.
$
\begin{gathered}
\mathrm{Br}_2 \\
\mathrm{CH}_4 \\
\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_4 \\
\mathrm{Cl}^{-} \\
\mathrm{CO}_2 \\
\mathrm{Cr}^{3+} \\
\mathrm{Cu}^{2+} \\
\mathrm{H}_2 \\
\mathrm{~K}^{+} \\
\mathrm{N}_2 \\
\mathrm{~N}^{3-} \\
\mathrm{O}_2 \\
\mathrm{SO}_4{ }^{2-}
\end{gathered}
$
Answer the following questions about these symbols and formulae.
Each symbol or formula may be used once, more than once or not at all.
State which symbol or formula represents:
(a) a molecule containing only five atoms[1]
(b) a diatomic molecule of an element in Group VII of the Periodic Table
(b) a diatomic molecule of an element in Group VII of the Periodic Table……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(c) an ion formed when an atom gains one electron……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(d) an ion which forms a green precipitate when a few drops of aqueous sodium hydroxide are added to it……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(e) a compound produced by the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(f) a product of photosynthesis…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1] [Total: 6]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) \begin{tabular}{l}
(b)\(\mathrm{CH}_4\) \\
(c)\(\mathrm{Br}_2\) \\
(d)\(\mathrm{Cl}^{-}\) \\
(e)\(\mathrm{Cr}^{3+}\) \\
(f)\(\mathrm{CO}_2\) \\
\(\mathrm{O}_2\)
\end{tabular}
Question
(a) A sample of soil is shaken with distilled water.
Draw a diagram to show the filtration apparatus used to separate the soil from the solution
obtained by shaking the soil with distilled water.
On your diagram, label:
● the filtrate
● the residue.[3]
(b) Table 2.1 shows the masses of some of the ions in \(1000 \mathrm{~cm}^3\) of the solution obtained by filtering a sample of soil with distilled water.
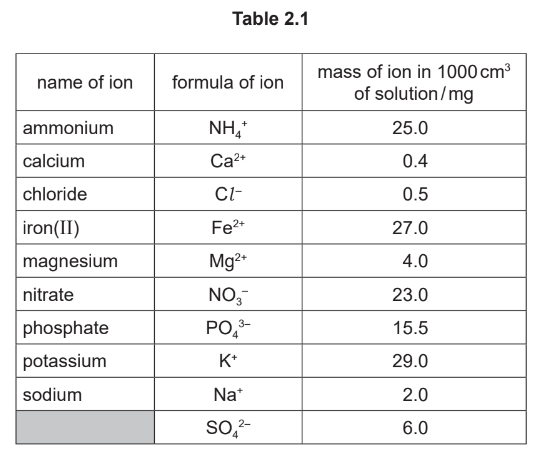
Answer these questions using the information in Table 2.1.
(i) Name the negative ion that has the lowest concentration.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) State the name of the \(\mathrm{SO}_4{ }^{2-}\) ion.
[1]
(iii) Calculate the mass of phosphate ions in \(200 \mathrm{~cm}^3\) of the solution.
mass \(=\) \(\mathrm{mg}[1]\)
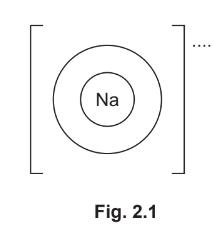
(c) Complete Fig. 2.1 to show:
- the electronic configuration of a sodium ion
- the charge on the ion.
(d) Water from natural sources contains dissolved gases.
Choose from the list the gas which is essential for aquatic life.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.
argon hydrogen nitrogen oxygen [1]
(e) Polluted water may contain sewage or nitrates.
State one harmful effect of each of these water pollutants.
sewage ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
nitrates ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2] [Total: 11]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) filter paper in filter funnel (1)
filtrate labelled (1)
residue labelled (1)
2(b)(i)chloride \(/ \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\)
(ii) sulfate
(iii)\(3.1(\mathrm{mg})\)
(c)electronic configuration 2,8 with no other shells added (1)
+/1+ outside brackets (1)
(d) oxygen 1
(e) sewage: contains harmful bacteria / causes disease (1)
nitrates: deoxygenate water / remove oxygen from water (1)
Question
This question is about compounds of nitrogen.
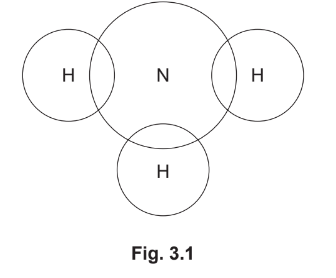
(a) Complete the dot-and-cross diagram in Fig. 3.1 of a molecule of ammonia.
Show outer shell electrons only.
(b) Oxides of nitrogen are air pollutants.
(i) State one source of oxides of nitrogen in the air………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) State one adverse effect of oxides of nitrogen………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(c) State whether nitrogen dioxide is an acidic or basic oxide.
Give a reason for your answer………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1] [Total: 5]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) pair of electrons between each H and N and no other electrons on H atoms (1)
two non-bonding electrons on N atom (1)
(b)(i) car engines / car exhausts / vehicle exhausts
(b)(ii) acid rain / (photochemical) smog / respiratory problems
(c) acidic because nitrogen is a non-metal
Question
This question is about metals and compounds of metals.
(a) Table 4.1 shows some properties of five metals, A, B, C, D and E.
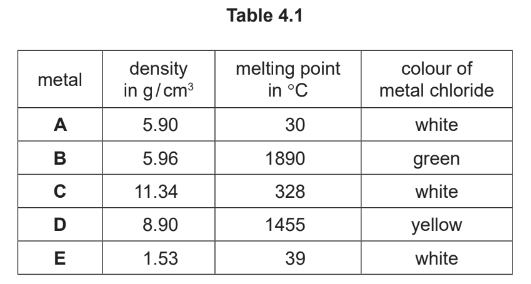
State which two of these metals, A, B, C, D and E, are transition elements.
Give two reasons for your answer using only the information in Table 4.1.
metals …………………………….. and ……………………………..
reason 1 …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
reason 2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [3]
(b) Choose the metal chloride that is insoluble in water.

(c) Magnesium chloride is produced when magnesium burns in chlorine.
$
\mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_2
$
Fig. 4.1 shows an incomplete reaction pathway diagram for this reaction.
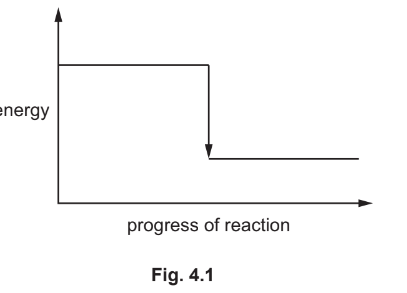
(i) Complete Fig. 4.1 by writing these formulae on the diagram:
- \(\mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{Cl}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{MgCl}_2\).[1]
(ii) Explain how Fig. 4.1 shows that the reaction is exothermic.\([1]\)
(d) Table 4.2 shows the reactions of four different metals with steam.
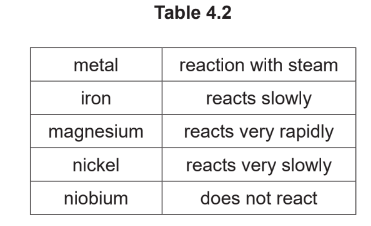
Put the four metals in order of their reactivity.
Put the least reactive metal first.
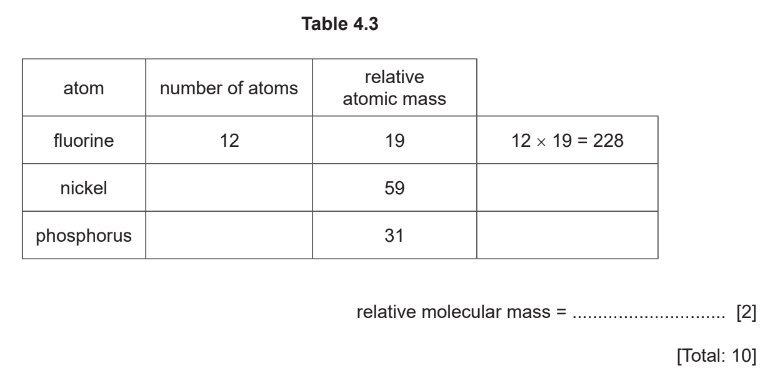
(e) A compound of nickel has the molecular formula \(\mathrm{NiP}_4 \mathrm{~F}_{12}\).
Complete Table 4.3 to calculate the relative molecular mass of \(\mathrm{NiP}_4 \mathrm{~F}_{12}\).
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)\(B\) and \(D(1)\)
have coloured chlorides / have coloured compounds (1)
have high melting points (1)
(b)\(3^{\text {rd }}\) box down ticked (silver chloride)
(c)(i)\(\mathrm{Mg}+\mathrm{Cl}_2\) on line on left AND \(\mathrm{MgCl}_2\) on line on right
(c)(ii)the energy of the reactants is greater than the energy of the products / the energy of the products is less than the energy of the reactants
(d)niobium < nickel < iron < magnesium (2)
1 mark if one pair reversed
(e)\(411(2)\)
if 2 marks not scored 1 mark for \(P=(4 \times 31)=124\)
Question
Potassium iodide is an ionic compound.
(a) State two properties of an ionic compound.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
(b) Molten potassium iodide is electrolysed using graphite electrodes.
(i) Name the products formed at the positive and negative electrodes.
positive electrode ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
negative electrode ………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
(ii) State the name of the positive electrode in an electrolysis experiment………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(c) Deduce the number of protons and neutrons in the iodide ion shown.
$
{ }_{53}^{127} \mathrm{I}^{-}
$
number of protons
number of neutrons[2]
(d) Aqueous chlorine reacts with aqueous potassium iodide.
(i) Complete the symbol equation for this reaction.
$
\mathrm{Cl}_2+2 \mathrm{KI} \rightarrow \ldots \ldots . .+\ldots \mathrm{KCl}
$
(ii) Choose from the list the name of this type of reaction.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.
addition combustion displacement neutralisation\([1]\)
(iii) State the colour of chlorine gas at room temperature and pressure.[1] [Total: 11]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) high melting point (1)
conducts electricity when molten / conducts electricity in aqueous solution (1)
(b)(i) positive electrode: iodine (1)
negative electrode: potassium (1)
(b)(ii) anode 1
5(c) protons: 53 (1)
neutrons: 74 (1)
d(i) \(I_2(1)\)
\(2(\mathrm{KCl})(1)\)
(d)(ii) displacement
(d)(iii) (pale) yellow-green
Question
(a) Fig. 6.1 shows the displayed formula of a molecule of crotyl alcohol.
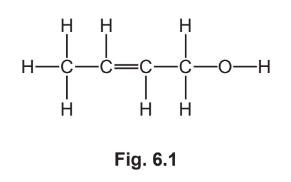
(i) On Fig. 6.1 draw a circle around the alcohol functional group.
(ii) Describe the feature of crotyl alcohol that shows it is an unsaturated compound.[1]
(iii) Deduce the molecular formula of crotyl alcohol.\([1]\)
(iv) Crotyl alcohol is soluble in water.
The boiling point of crotyl alcohol is \(121^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
The boiling point of water is \(100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
Suggest how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture of crotyl alcohol and water\([2]\)
(b) Ethanol is also an alcohol.
Describe two conditions for the manufacture of ethanol by the fermentation of aqueous glucose.
1
2[2]
(c) Ethanol can be converted to ethene.
Choose from the list the general formula for the homologous series to which ethene belongs.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.
$
\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_n \quad \mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 \mathrm{n}} \quad \mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 \mathrm{n}+2} \quad \mathrm{C}_{2 \mathrm{n}} \mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{n}}
$
(d) Ethene can be converted to ethane.
(i) Ethane is an alkane.
Name the type of bonding in alkanes.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
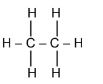
(ii) Draw the displayed formula of a molecule of ethane.[1]
(iii) Complete this sentence.
Alkanes are unreactive except in terms of combustion and substitution by………………………. . [1]
(iv) Complete the symbol equation for the complete combustion of methane.
$
\mathrm{CH}_4+\ldots . \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots .+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
$ [Total: 13]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) circle around the OH group
(a)(ii)C=C bond
(a)(iii) \(\quad \mathrm{C}_4 \mathrm{H}_8 \mathrm{O}\)
(a)(iv) 1 mark each for any two of:
• (when mixture is heated) water boils off first / water boils off before crotyl alcohol
• (because) water has a lower boiling point / crotyl alcohol has a higher boiling point
• water reaches the condenser first / water condenses first
(b) 1 mark each for any two of:
- \(25-35^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) (inclusive of these values)
- anaerobic/absence of oxygen
- yeast
c )$
\mathrm{C}_n \mathrm{H}_{2 n}
$
(d)(i)covalent
(ii)
(d)(iii) chlorine
d(iv) \(\begin{aligned} & 2\left(\mathrm{O}_2\right)(1) \\ & \mathrm{CO}_2(1)\end{aligned}\)
Question
This question is about iron.
(a) Iron is extracted from iron ore in a blast furnace.
(i) Name the main ore of iron………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) The main ore of iron contains iron(III) oxide.
Describe the extraction of iron from iron ore in the blast furnace.
In your answer, describe:
● the production of carbon monoxide
● the role of carbon monoxide
● the role of calcium carbonate, added to the blast furnace.[4]
(iii) Iron collects at the base of the blast furnace as a liquid.
Describe the arrangement and motion of the particles in a liquid.
arrangement ………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
motion ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….[2]
(b) The equation for the reaction of iron with steam is shown.
$
3 \mathrm{Fe}+4 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}_3 \mathrm{O}_4+4 \mathrm{H}_2
$
Describe how this equation shows that iron is oxidised.\([1]\)
(c) Rust is hydrated iron(III) oxide.
(i) Define the term hydrated.
[1]
(ii) Name the two substances needed for iron to rust. and[2]
(d) Crystals of iron(II) chloride can be prepared by adding excess iron to dilute hydrochloric acid.
(i) Suggest how the unreacted iron is removed from the reaction mixture.[1]
(ii) Describe how dry crystals of iron(II) chloride are made from a dilute solution of iron(II) chloride.[2][Total: 14]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) hematite
(a)(ii) 1 mark each for any four of:
the production of carbon monoxide
• carbon burns in oxygen / air
• to form carbon dioxide
• carbon dioxide reduced by carbon / reacts with carbon to form carbon monoxide
the role of carbon monoxide
• iron(III) oxide reduced by carbon monoxide
the role of calcium carbonate, added to the blast furnace
• calcium carbonate decomposes to calcium oxide
• calcium oxide reacts with impurities / silicon(IV) oxide (in iron ore)
• slag formed / calcium silicate formed
(a)(iii) arrangement: irregular / no (particular) arrangement (1)
motion: sliding over each other
(b) iron gains oxygen
(c)(i) (substance) chemically combined with water
(c)(ii) air / oxygen (1)
water (1)
(d)(i) filtration / filter
(d)(ii) 1 mark each for any 2 of:
• evaporate to point of crystallisation / evaporate until saturated solution formed
• leave to crystalise
• filter off crystals / pick out crystals
• dry with filter paper
Question
A student investigates the reaction of iron powder with dilute hydrochloric acid at \(20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The hydrochloric acid is in excess.
(a) Fig. 8.1 shows the volume of hydrogen gas released as the reaction proceeds.
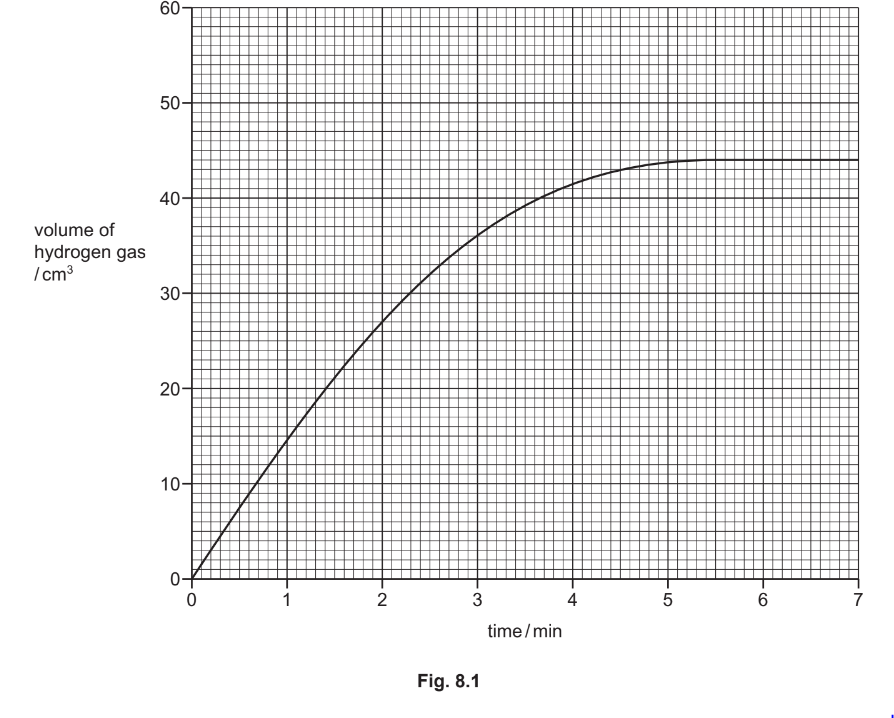
(i) Deduce the volume of hydrogen gas released after 2 minutes.
volume of hydrogen gas \(=\) \(\mathrm{cm}^3[1]\)[1]
(ii) The student repeats the experiment using dilute hydrochloric acid of a higher concentration.
All other conditions stay the same.
Draw a line on the grid in Fig. 8.1 to predict how the volume of hydrogen gas changes
when dilute hydrochloric acid of a higher concentration is used. [2]
(b) (i) The student repeats the experiment with large pieces of iron.
All other conditions stay the same.
Describe how the rate of reaction differs when large pieces of iron are used.\([1]\)
(ii) The student repeats the experiment with iron powder at a temperature of \(15^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\).
All other conditions stay the same.
Describe how the rate of reaction differs when a temperature of \(15^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) is used.\([1]\)
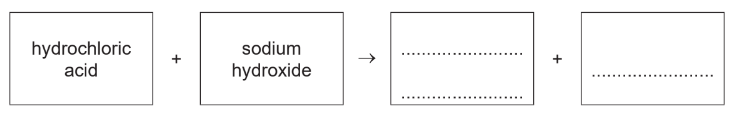
(c) Hydrochloric acid also reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
(i) Complete the word equation for this reaction.
(ii) Write the formula of the ion present in all acids.[1]
(iii) Choose from the list a possible \(\mathrm{pH}\) value of aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.
$
\begin{array}{llll}
\text { pH } 2 & \mathrm{pH} 4 & \mathrm{pH} 7 & \mathrm{pH} 13
\end{array}
$
(iv) State the colour of methyl orange in aqueous sodium hydroxide.[1] [Total: 10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
\begin{tabular}{ll}
(a)(i) & \(27\left(\mathrm{~cm}^3\right)\)
\end{tabular}
(a)(ii) steeper initial gradient starting at \(0-0\) (1) line levels off at \(44 \mathrm{~cm}^3\) (1)
(b)(i) (rate) decreases / reaction slows down
(b)(ii) (rate) decreases / reaction slows down
(c)(i) sodium chloride (1)
water (1)
\begin{tabular}{ll}
\(8(c)(\mathrm{ii})\) & \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\)
\end{tabular}
(c)(iii) pH 13 1
(c)(iv) yellow
