Substance L takes the shape of the container that holds it.
What could be the state of matter of substance L?
A) liquid or gas
B) gas or solid
C) solid or liquid
D) solid only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Both liquids and gases take the shape of their container. Liquids take the shape but have a fixed volume, while gases take both the shape and volume of their container. Solids maintain their own shape regardless of the container. Therefore, substance L could be either a liquid or a gas.
The melting points and boiling points of pure substances M, N and O are shown.
| M | N | O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| melting point / °C | -114 | 115 | -101 |
| boiling point / °C | 78 | 445 | -34 |
The substances are chlorine, ethanol and sulfur.
Which row identifies M, N and O?
| M | N | O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | chlorine | ethanol | sulfur |
| B | ethanol | sulfur | chlorine |
| C | sulfur | chlorine | ethanol |
| D | sulfur | ethanol | chlorine |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze the data:
1. Ethanol (alcohol) has a melting point of -114°C and boiling point of 78°C, matching M.
2. Sulfur has a high melting point (115°C) and very high boiling point (445°C), matching N.
3. Chlorine is a gas at room temperature with melting point -101°C and boiling point -34°C, matching O.
Therefore, the correct identification is M = ethanol, N = sulfur, O = chlorine, which corresponds to option B.
Which statement explains why the noble gases are unreactive?
A) They are in the same group of the Periodic Table.
B) They are gases at room temperature.
C) They each have a full outer electron shell.
D) They are found in air.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The noble gases are unreactive because they have a complete outer electron shell, which makes them very stable. This full outer shell means they don’t need to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve stability, unlike other elements. While options A, B, and D are true statements about noble gases, they don’t explain their unreactivity – only option C explains the fundamental reason for their lack of chemical reactivity.
What is the electronic configuration of a P3- ion?
A) 2,8,2
B) 2,8,5
C) 2,8,6
D) 2,8,8
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
First, let’s determine the electronic configuration of a neutral phosphorus atom (P):
Phosphorus has atomic number 15, so its electron configuration is 2,8,5 (2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second, and 5 in the third).
The P3- ion means the atom has gained 3 electrons. Adding these to the outer shell: 5 + 3 = 8 electrons in the third shell.
Therefore, the electronic configuration becomes 2,8,8, which matches option D. This gives the ion a stable noble gas configuration similar to argon.
Some information about four metal atoms or ions is shown.
| atom or ion | charge | proton number | number of electrons | nucleon number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | +3 | 10 | 27 | |
| R | +2 | 12 | 24 | |
| S | +2 | 10 | 26 | |
| T | 16 | 16 |
Which two atoms or ions are from isotopes of the same element?
A) Q and R
B) Q and T
C) R and S
D) S and T
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (and therefore different nucleon numbers). Let’s analyze each option:
1. For Q: Charge +3 with 10 electrons means it has 13 protons (10 + 3). Nucleon number is 27.
2. For R: Proton number is 12. Charge +2 means it has 10 electrons (12 – 2). Nucleon number is 24.
3. For S: Charge +2 with 10 electrons means it has 12 protons (10 + 2). Nucleon number is 26.
4. For T: Neutral atom with 16 protons and 16 electrons.
R and S both have 12 protons (same element, magnesium) but different nucleon numbers (24 and 26), making them isotopes. Therefore, the correct answer is C.
Which row describes the changes to the atoms when a metal and a non-metal react together?
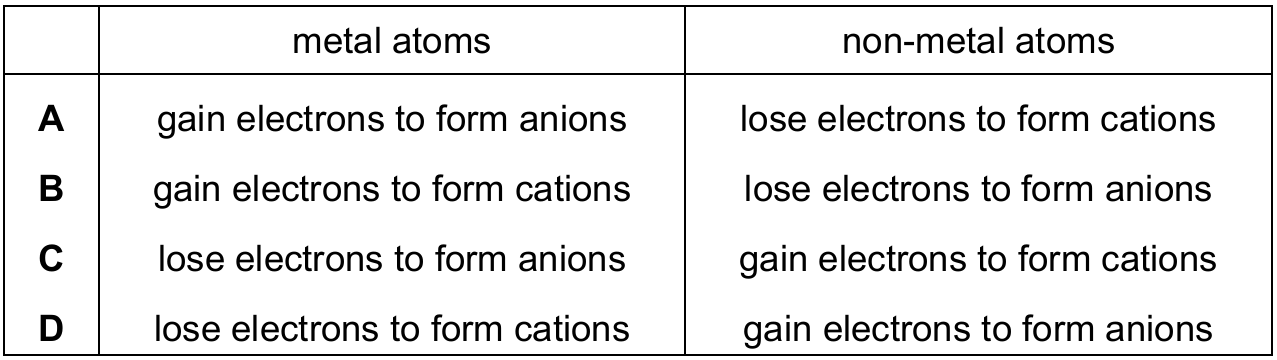
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
When metals and non-metals react, metals tend to lose electrons to form positive ions (cations) because they have few electrons in their outer shell. Non-metals tend to gain electrons to form negative ions (anions) because they have more electrons in their outer shell and need fewer to complete their octet.
Option D correctly describes this behavior: metal atoms lose electrons to form cations, while non-metal atoms gain electrons to form anions. This is the fundamental principle behind ionic bonding.
In the following diagrams, X and Y are atoms of different elements.
Which diagram correctly shows the arrangement of outer shell electrons in a molecule of methane?
A) 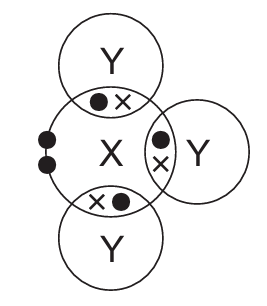
B) 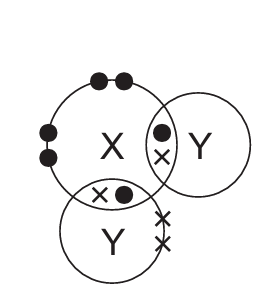
C) 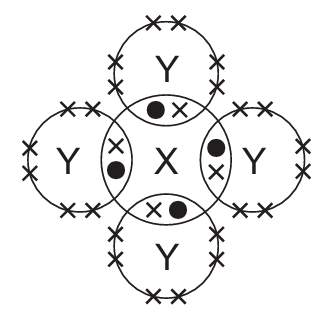
D) 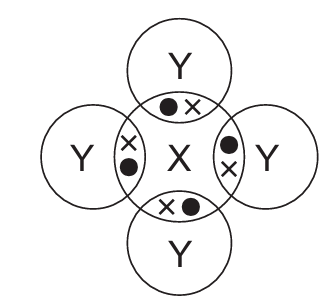
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Methane (CH₄) has a tetrahedral structure with carbon at the center and four hydrogen atoms arranged symmetrically around it. Each hydrogen shares one electron with carbon, forming four single covalent bonds.
The correct diagram should show:
- One central atom (carbon) with four outer electrons (represented as dots or crosses)
- Four surrounding atoms (hydrogen) each sharing one electron with the central atom
- No lone pairs on the central carbon atom
- All bond angles approximately 109.5° (though exact angles may not be shown in the diagram)
Option D correctly represents this arrangement with four shared electron pairs between the central atom and four surrounding atoms.
Which pathway describes the properties of graphite?
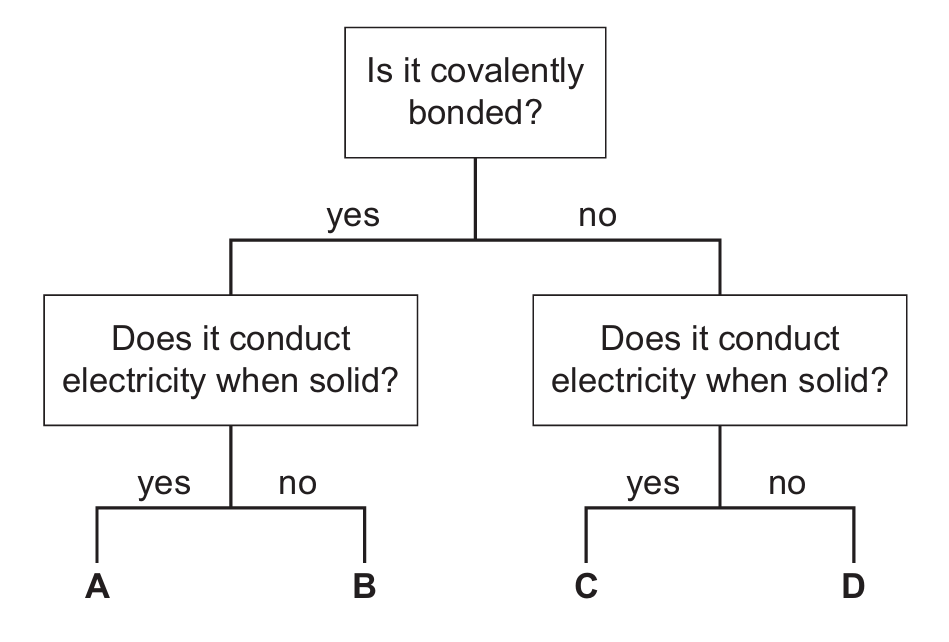
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Graphite is indeed covalently bonded, as it consists of layers of carbon atoms with each carbon atom bonded to three others in a hexagonal arrangement. The fourth electron from each carbon atom is delocalized, which allows graphite to conduct electricity when solid.
The correct pathway is:
- Is it covalently bonded? → yes
- Does it conduct electricity when solid? → yes
- This leads to option A
Graphite’s unique properties come from its layered structure: – Strong covalent bonds within layers – Weak van der Waals forces between layers – Delocalized electrons that can move and carry current
Which row identifies the formula of the named substance?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze each option:
- Option A: Cobalt(II) chloride should be CoCl₂ (not CuCl₂, which is copper(II) chloride)
- Option B: Ethane is correctly given as C₂H₆ (a simple alkane with 2 carbon atoms)
- Option C: Helium is a noble gas and exists as single atoms (He), not as He₂ molecules
- Option D: Iron(III) oxide should be Fe₂O₃ (not Fe₃O₂, which doesn’t follow the typical oxidation states)
Therefore, only option B correctly matches the substance with its formula. Ethane (C₂H₆) is a hydrocarbon with single bonds between all atoms, following the general formula for alkanes (CₙH₂ₙ₊₂).
Antifreeze contains a mixture of water and ethylene glycol.
The diagram shows their displayed formulae.
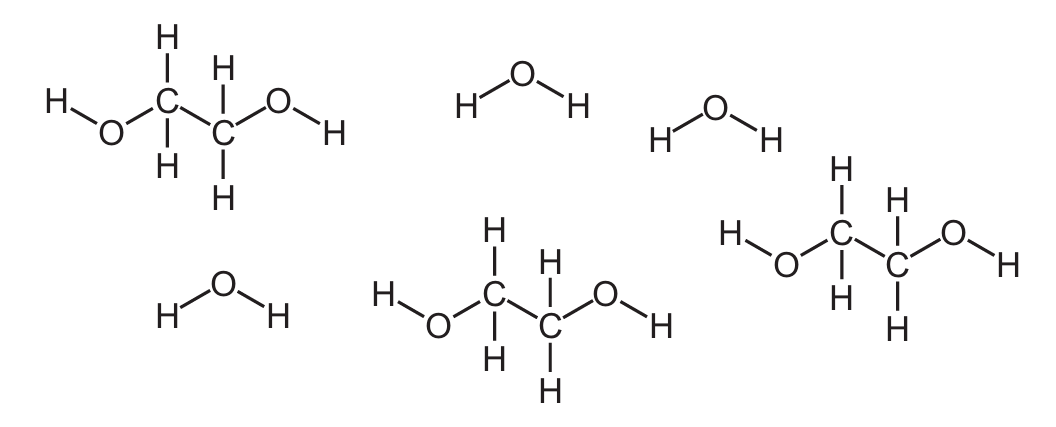
What is the molecular formula of ethylene glycol?
A) CHO
B) C₂H₆O₂
C) C₂H₆O₃
D) C₆H₁₈O₆
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Ethylene glycol has the structural formula HO-CH₂-CH₂-OH, which means:
- 2 carbon atoms (C₂)
- 6 hydrogen atoms (H₆) – 2 on each CH₂ group plus 2 on the OH groups
- 2 oxygen atoms (O₂) – one in each hydroxyl group
Therefore, the molecular formula is C₂H₆O₂.
Key points about ethylene glycol: – It’s a diol (contains two hydroxyl groups) – Used as antifreeze because it lowers the freezing point of water – Has a sweet taste but is highly toxic – The structure shows two carbon atoms single-bonded to each other, each bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one hydroxyl group
The equation for the reaction of magnesium with oxygen is shown.
\[ 2\text{Mg} + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{MgO} \]
In an experiment, 6.0 g of magnesium is reacted with excess oxygen.
Which mass of magnesium oxide, MgO, is produced?
A) 10 g
B) 20 g
C) 40 g
D) 80 g
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
1. Calculate moles of Mg: 6.0 g / 24 g/mol (molar mass of Mg) = 0.25 mol
2. From the balanced equation, 2 moles of Mg produce 2 moles of MgO, so 0.25 mol Mg will produce 0.25 mol MgO
3. Calculate mass of MgO: 0.25 mol × (24 + 16) g/mol = 0.25 × 40 = 10 g
The correct answer is A) 10 g.
Which products are formed when dilute sulfuric acid undergoes electrolysis?
| product formed at the anode | product formed at the cathode | |
|---|---|---|
| A | oxygen | hydrogen |
| B | hydrogen | oxygen |
| C | sulfur dioxide | hydrogen |
| D | oxygen | sulfur dioxide |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
When dilute sulfuric acid is electrolyzed:
1. At the cathode (negative electrode): Hydrogen ions (H⁺) are reduced to form hydrogen gas (H₂)
2. At the anode (positive electrode): Hydroxide ions (OH⁻) are oxidized to form oxygen gas (O₂) and water
The sulfate ions (SO₄²⁻) remain in solution as they are harder to oxidize than water molecules.
Therefore, the correct products are oxygen at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode (Option A).
The diagram shows an experiment to electroplate a nickel spoon with silver.
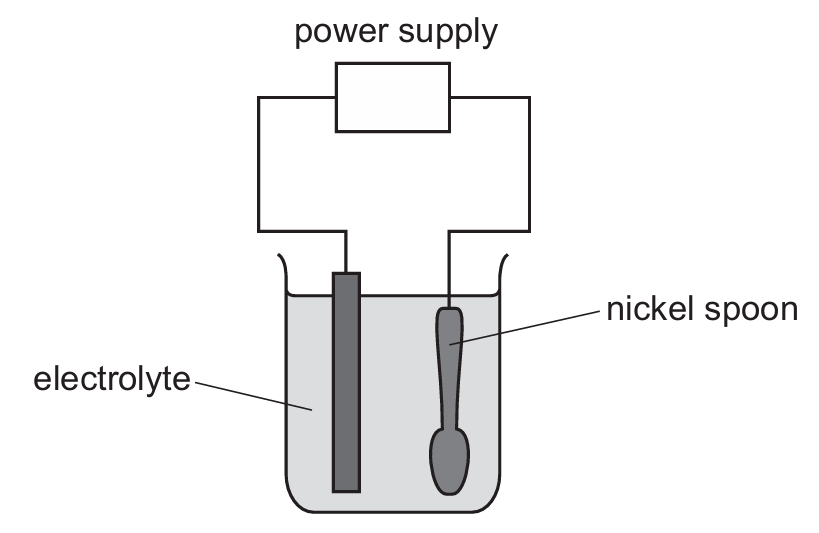
Which row correctly describes the positive electrode, the negative electrode and the electrolyte?
| positive electrode | negative electrode | electrolyte | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | nickel spoon | pure nickel | silver nitrate solution |
| B | nickel spoon | pure silver | nickel nitrate solution |
| C | pure nickel | nickel spoon | silver nitrate solution |
| D | pure silver | nickel spoon | silver nitrate solution |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
For electroplating:
1. The object to be plated (nickel spoon) must be the negative electrode (cathode) where silver ions will be reduced to form a silver coating
2. The positive electrode (anode) should be made of the plating metal (pure silver) which will oxidize to provide silver ions to the solution
3. The electrolyte must contain ions of the plating metal (silver nitrate solution provides Ag⁺ ions)
Therefore, the correct combination is: positive electrode – pure silver, negative electrode – nickel spoon, electrolyte – silver nitrate solution (Option D).
When dilute sulfuric acid reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide, the temperature of the solution increases.
Which words describe this reaction?
A) endothermic and neutralisation
B) endothermic and redox
C) exothermic and neutralisation
D) exothermic and redox
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
1. The reaction between an acid (sulfuric acid) and a base (sodium hydroxide) is a neutralization reaction, forming salt (sodium sulfate) and water
2. Since the temperature increases, the reaction is exothermic (releases heat)
3. This is not a redox reaction as no oxidation states change (H remains +1, O remains -2, S remains +6, Na remains +1)
Therefore, the correct description is exothermic and neutralisation (Option C).
Which statement is correct for both physical and chemical changes?
A) Covalent bonds are broken and formed during the changes.
B) The total mass of substance is the same before and after the changes.
C) The changes are usually reversible.
D) The temperature always rises or falls during the changes.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze each option:
1. A: Only chemical changes involve breaking/forming covalent bonds (physical changes don’t)
2. B: Correct – Law of Conservation of Mass applies to both physical and chemical changes
3. C: While physical changes are often reversible, many chemical changes are not
4. D: Temperature changes may or may not occur in either type of change
Therefore, the only statement true for both types of changes is that the total mass remains the same (Option B).
A sample of calcium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce a final volume of 60 cm3 of gas.
The reaction finishes after 120 seconds.
The experiment is repeated at a lower temperature. All other conditions stay the same.
Which row shows the results of the second experiment?
| final volume of gas produced/cm3 | time for reaction to finish/s | |
| A | 40 | 120 |
| B | 40 | 160 |
| C | 60 | 120 |
| D | 60 | 160 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
1. The reaction between calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid produces carbon dioxide gas: \[ \text{CaCO}_3 + 2\text{HCl} \rightarrow \text{CaCl}_2 + \text{H}_2\text{O} + \text{CO}_2 \]
2. At a lower temperature, the reaction rate decreases because particles have less kinetic energy, so collisions are less frequent and less energetic.
3. However, the final volume of gas produced (60 cm3) remains the same because the amount of reactants hasn’t changed – we’re just using the same amounts at a different temperature.
4. The reaction will take longer to complete (160 seconds instead of 120) because the rate is slower at lower temperatures.
5. Therefore, the correct row is D: same final volume (60 cm3) but longer time (160 s).
In which equation is the iron oxidised?
A) \( \text{C} + \text{FeO} \rightarrow \text{CO} + \text{Fe} \)
B) \( 3\text{CO} + \text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3 \rightarrow 3\text{CO}_2 + 2\text{Fe} \)
C) \( \text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3 + \text{H}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{FeO} + \text{H}_2\text{O} \)
D) \( \text{PbO} + \text{Fe} \rightarrow \text{Pb} + \text{FeO} \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
1. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or gain of oxygen.
2. In option D, iron (Fe) changes from elemental state (oxidation number 0) to FeO (oxidation number +2), meaning it has lost electrons and been oxidized.
3. In the other options:
- A: Fe goes from +2 to 0 (reduction)
- B: Fe goes from +3 to 0 (reduction)
- C: Fe goes from +3 to +2 (reduction)
4. Therefore, only in option D is iron being oxidized (increasing its oxidation state).
HOCI is an acid.
NH4OH is an alkali.
Which row shows the ions present in aqueous solutions that identify the acid and the alkali?
| HOCI(aq) | NH4OH(aq) | |
| A | H+ | H+ |
| B | H+ | OH– |
| C | OH– | H+ |
| D | OH– | OH– |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Acids are substances that produce H+ ions in aqueous solution.
2. Alkalis are bases that dissolve in water to produce OH– ions.
3. HOCI (hypochlorous acid) is an acid, so in aqueous solution it will produce H+ ions.
4. NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide) is an alkali, so in aqueous solution it will produce OH– ions.
5. Therefore, the correct row is B: H+ for the acid and OH– for the alkali.
Which elements form an oxide that reacts with water to produce a blue solution with thymolphthalein?
- calcium
- carbon
- sulfur
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 only
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Thymolphthalein turns blue in alkaline solutions (pH > 9.3).
2. Calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), which is alkaline and would turn thymolphthalein blue: \[ \text{CaO} + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightarrow \text{Ca(OH)}_2 \]
3. Carbon dioxide (CO2) forms carbonic acid (H2CO3) with water, which is acidic and wouldn’t change thymolphthalein’s color.
4. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3) with water, which is also acidic.
5. Therefore, only calcium (option 1) forms an oxide that produces a blue solution with thymolphthalein.
A sample of fertiliser is tested by warming it with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
A colourless gas is produced which turns damp red litmus paper blue.
Which element, essential for plant growth, must be present?
A) nitrogen
B) phosphorus
C) potassium
D) sulfur
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
1. The test described is the standard test for ammonium ions (NH4+), which are common in nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
2. When warmed with NaOH, ammonium compounds release ammonia gas (NH3): \[ \text{NH}_4^+ + \text{OH}^- \rightarrow \text{NH}_3 + \text{H}_2\text{O} \]
3. Ammonia gas is colorless and turns damp red litmus paper blue because it’s alkaline.
4. While phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur are also essential for plant growth, they don’t produce ammonia gas in this test.
5. Therefore, the element that must be present is nitrogen (option A).
Insoluble solid magnesium carbonate reacts with dilute sulfuric acid.
The equation is shown.
magnesium carbonate + sulfuric acid → magnesium sulfate + water + carbon dioxide
The steps used to make crystals of magnesium sulfate are listed.
step 1 – Add excess magnesium carbonate to dilute sulfuric acid and stir the mixture.
step 2 – Filter the mixture.
step 3 – Heat the filtrate to the point of crystallisation.
step 4 – Leave the filtrate to cool.
What is the residue removed from the mixture in step 2?
A) magnesium carbonate
B) sulfuric acid
C) magnesium sulfate
D) water
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
In this process, we’re adding excess magnesium carbonate to ensure all the sulfuric acid reacts. The magnesium carbonate is insoluble, so any unreacted excess will remain as a solid. When we filter the mixture in step 2, the solid residue left on the filter paper must be the unreacted magnesium carbonate. The magnesium sulfate product is soluble in water and will pass through the filter as part of the filtrate, along with water. Therefore, the correct answer is A – magnesium carbonate.
Which trend occurs across the period from sodium to argon?
A) a change from metal to non-metal
B) an increase in melting point
C) a more violent reaction with water
D) an increase in electrical conductivity
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
As we move across Period 3 from sodium to argon, we observe a clear trend from metallic elements (sodium, magnesium, aluminum) through metalloids (silicon) to non-metals (phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine) and finally the noble gas argon. This is the most consistent trend across the period. Option B is incorrect because while there’s an initial increase in melting point up to silicon, it then decreases. Option C is wrong as sodium reacts most violently with water, becoming less reactive as we move right. Option D is incorrect because electrical conductivity decreases as we move from metals to non-metals.
Which statement about the element bromine is correct?
A) It displaces chlorine from aqueous potassium chloride.
B) It has a higher density than chlorine.
C) It is a diatomic metal.
D) It is a green gas at room temperature.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Bromine is a halogen below chlorine in Group VII, and as we go down the group, density increases. Option A is incorrect because chlorine is more reactive than bromine (reactivity decreases down Group VII), so bromine cannot displace chlorine. Option C is wrong because while bromine is diatomic (Br2), it’s a non-metal, not a metal. Option D is incorrect because bromine is actually a red-brown liquid at room temperature, not a green gas (that’s chlorine’s description). Therefore, the only correct statement is B – bromine does have a higher density than chlorine.
Metallic element X has a high density.
Which part of the Periodic Table is X in?
A) Group I
B) halogens
C) transition elements
D) Group VIII
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The question states that element X is metallic and has high density. Among the options: Group I metals (like sodium, potassium) are relatively low density; halogens (Group VII) are non-metals; Group VIII contains noble gases which are non-metals with low densities. The transition elements (option C), however, are well-known for being dense metals – examples include iron, copper, gold, and platinum. These metals are typically hard, have high melting points, and high densities, making them suitable for many structural and decorative applications.
Which statement about the uses of metals is correct?
A) Aluminium has a low density and good electrical conductivity which make it suitable for overhead electrical cables.
B) Aluminium food containers can only be used for a short time because chemicals in the food react with the aluminium.
C) Electrical wiring made from copper is covered with plastic because copper corrodes easily.
D) Copper is used in the manufacture of aircraft because it has a low density and is not malleable.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Option A is correct because aluminium’s combination of low density (lightweight) and good conductivity makes it ideal for overhead cables where weight is a concern. Option B is incorrect – aluminium forms a protective oxide layer that prevents reaction with food, which is why it’s widely used for food containers and foil. Option C is wrong because copper wiring is covered with plastic for insulation and safety, not because copper corrodes easily (it’s actually quite resistant to corrosion). Option D is incorrect because while copper is malleable, it’s not used in aircraft manufacture due to its relatively high density compared to aluminium alloys.
Steel bridges are painted to help stop rust from forming on their surfaces.
What causes steel to rust?
A) water, oxygen and sunlight
B) water and oxygen only
C) water and sunlight only
D) oxygen and sunlight only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Rusting is an electrochemical process that requires both water (to act as an electrolyte) and oxygen (for the oxidation reaction). The chemical equation for rusting is:
\[ 4Fe + 3O_2 + 6H_2O \rightarrow 4Fe(OH)_3 \]
While sunlight can accelerate the process by providing energy, it is not essential for rust formation. The essential components are water and oxygen, which is why option B is correct. Painting steel bridges creates a barrier that prevents these two elements from reaching the iron in the steel.
Which two metals are mixed together to make brass?
- tin
- zinc
- nickel
- copper
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Brass is an alloy primarily composed of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn). The typical composition is about 60-70% copper and 30-40% zinc, though this can vary for different types of brass. The combination of these two metals gives brass its characteristic gold-like appearance and properties such as malleability and acoustic qualities.
While other metals like tin or nickel can be added to create special types of alloys (bronze contains copper and tin, for example), the basic composition of brass is always copper and zinc, making option D (2 and 4) the correct answer.
Metal M is between zinc and iron in the reactivity series.
Which statements about metal M are correct?
- It reacts with cold water to produce hydrogen gas.
- It does not react with cold water but will react with dilute hydrochloric acid.
- The metal can be obtained from its oxide by heating it strongly with carbon.
- The metal oxide cannot be reduced using carbon.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
In the reactivity series, metals between zinc and iron include metals like iron itself, lead, and tin. These metals:
– Do not react with cold water (statement 1 is incorrect)
– Do react with acids to produce hydrogen (statement 2 is correct)
– Can be reduced from their oxides using carbon (statement 3 is correct)
– Their oxides can be reduced by carbon (statement 4 is incorrect)
The correct statements are therefore 2 and 3, making option C the right answer. The key here is understanding the position in the reactivity series: metals below magnesium but above copper generally don’t react with water but do react with acids, and their oxides can be reduced by carbon.
What is the colour change when water is added to anhydrous copper(II) sulfate?
A) blue to white
B) blue to pink
C) pink to blue
D) white to blue
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate is a white powder. When water is added, it forms the hydrated copper(II) sulfate (CuSO₄·5H₂O), which is blue. This is a classic test for the presence of water and is reversible by heating. The reaction can be represented as:
\[ CuSO_4 (white) + 5H_2O \rightarrow CuSO_4·5H_2O (blue) \]
The colour change is therefore from white to blue, making option D correct. This is an important practical test in chemistry for detecting water, and the dramatic colour change makes it very useful for demonstration purposes.
Which statement about the composition of clean, dry air is correct?
A) It contains 78% oxygen.
B) It contains 21% nitrogen.
C) It contains less than 1% argon.
D) It contains 4% carbon dioxide.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The composition of clean, dry air is approximately:
– 78% nitrogen (not oxygen, so A is wrong)
– 21% oxygen (not nitrogen, so B is wrong)
– 0.93% argon (less than 1%, so C is correct)
– 0.04% carbon dioxide (not 4%, so D is wrong)
Option C is the only completely accurate statement. The percentages are often confused, especially between nitrogen and oxygen. Argon, while being the third most abundant gas in air, makes up less than 1% of the total composition. The very small amount of carbon dioxide (about 0.04%) is crucial for plant life but is often overestimated in people’s minds.
Which row identifies a source and an adverse effect of methane?
| source | adverse effect | |
|---|---|---|
| A | car engines | acid rain |
| B | car engines | climate change |
| C | decomposition of vegetation | acid rain |
| D | decomposition of vegetation | climate change |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Methane is primarily produced by natural processes like the decomposition of vegetation (option D) rather than car engines (options A and B). While car engines do produce some methane, it’s not their primary emission.
Regarding adverse effects, methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes significantly to climate change (options B and D), not acid rain (options A and C). Acid rain is mainly caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, not methane.
Therefore, the correct combination is methane coming from decomposition of vegetation and causing climate change, which is option D.
Which statements about alkenes are correct?
- Propene is a saturated hydrocarbon.
- Ethene is made by heating long-chain alkanes to a high temperature in the presence of a catalyst.
- Hexene reacts with aqueous bromine, changing its colour from colourless to orange.
- Ethene, propene and butene have the same general formula.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s analyze each statement:
1. False – Propene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon (it has a double bond), not saturated.
2. True – Ethene is indeed produced by cracking long-chain alkanes at high temperatures with a catalyst.
3. False – Hexene reacts with bromine, but the color change is from orange (bromine’s color) to colorless, not the other way around.
4. True – All alkenes have the same general formula CnH2n, so ethene (C2H4), propene (C3H6), and butene (C4H8) share this formula.
Therefore, the correct combination is statements 2 and 4, which is option D.
The table shows the formulae and names of some organic compounds.
| formula | name | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CH3Cl | chloroethane |
| 2 | CH3COOH | ethanoic acid |
| 3 | BrCH2CH2Br | 1,2-dibromoethane |
| 4 | (CH3COO)2Ca | calcium methanoate |
Which rows give the correct name for the formula shown?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s evaluate each compound:
1. CH3Cl – This is chloromethane (methyl chloride), not chloroethane. Ethane would have 2 carbons (C2H5Cl).
2. CH3COOH – Correctly named ethanoic acid (common name: acetic acid).
3. BrCH2CH2Br – Correctly named 1,2-dibromoethane (the bromines are on carbons 1 and 2 of the 2-carbon chain).
4. (CH3COO)2Ca – This is calcium ethanoate (acetate), not methanoate. Methanoate would have only 1 carbon (HCOO).
Therefore, only rows 2 and 3 are correct, which corresponds to option C.
Which gas is the main constituent of natural gas?
A) hydrogen
B) nitrogen
C) methane
D) oxygen
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Natural gas is primarily composed of methane (CH4), typically making up 70-90% of its composition. While natural gas does contain small amounts of other gases like ethane, propane, and butane, as well as traces of nitrogen and carbon dioxide, methane is by far the main component.
Hydrogen (A) is not a significant component of natural gas. Nitrogen (B) may be present in small amounts, but isn’t the main constituent. Oxygen (D) is generally not present in natural gas as it’s extracted from underground reserves where oxygen isn’t present.
Therefore, the correct answer is C, methane.
A sample of petroleum is separated into three fractions, X, Y and Z, using fractional distillation. Some properties of X, Y and Z are listed.
- X is more viscous than Z.
- Y has a higher boiling point than X.
Which fraction has the longest carbon chain and which fraction is the most volatile?
| longest carbon chain | most volatile | |
|---|---|---|
| A | Y | X |
| B | Y | Z |
| C | Z | X |
| D | Z | Y |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
In fractional distillation of petroleum:
1. Longer carbon chains have higher boiling points and are more viscous.
2. Shorter carbon chains are more volatile (evaporate more easily) and less viscous.
From the information given:
– X is more viscous than Z, suggesting X has longer chains than Z.
– Y has a higher boiling point than X, suggesting Y has longer chains than X.
Therefore, the order from longest to shortest chains is: Y > X > Z.
Thus, Y has the longest carbon chains, and Z (with the shortest chains) is the most volatile.
This matches option B: Y for longest carbon chain and Z for most volatile.
Two salt solutions, P and Q, are tested.
The table shows the results.
| test | P | Q |
|---|---|---|
| a few drops of aqueous sodium hydroxide are added | green precipitate forms | red-brown precipitate forms |
| a few drops of dilute nitric acid and a few drops of barium nitrate are added | no change seen | white precipitate forms |
| a few drops of dilute nitric acid and a few drops of silver nitrate are added | white precipitate forms | no change seen |
What are P and Q?
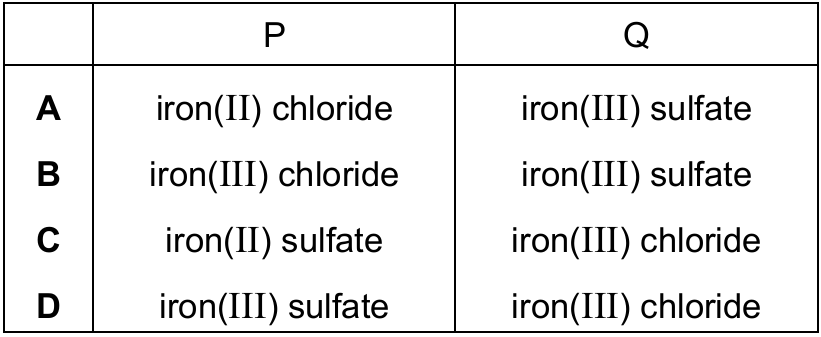
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze each test result:
1. Sodium hydroxide test:
- P forms green precipitate → indicates iron(II) hydroxide (Fe(OH)2)
- Q forms red-brown precipitate → indicates iron(III) hydroxide (Fe(OH)3)
2. Barium nitrate test (for sulfate ions):
- P shows no change → no sulfate present
- Q forms white precipitate → sulfate present (BaSO4)
3. Silver nitrate test (for chloride ions):
- P forms white precipitate → chloride present (AgCl)
- Q shows no change → no chloride present
Putting it all together:
- P must be iron(II) chloride (FeCl2) because it shows Fe2+ and Cl– characteristics
- Q must be iron(III) sulfate (Fe2(SO4)3) because it shows Fe3+ and SO42- characteristics
Therefore, the correct answer is A.
A small quantity of a solid, E, is added to a large excess of aqueous ethanoic acid.
No bubbles of gas are seen and the solid dissolves to give a colourless solution.
What is solid E?
A) calcium hydroxide
B) copper(II) oxide
C) magnesium
D) sodium carbonate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze each option:
A) Calcium hydroxide: This is a base that would react with ethanoic acid to form calcium ethanoate and water. The reaction would not produce gas bubbles, and calcium ethanoate solution is colourless.
B) Copper(II) oxide: While it would react with ethanoic acid, it would form a blue solution of copper(II) ethanoate, not colourless.
C) Magnesium: This would react vigorously with ethanoic acid, producing hydrogen gas bubbles (which we don’t see in this case).
D) Sodium carbonate: This would react with ethanoic acid to produce carbon dioxide gas bubbles (which we don’t see in this case).
The only option that fits all the given observations (no gas bubbles, colourless solution) is A) calcium hydroxide.
Ethanol is manufactured by two different processes.
Which raw materials are used by the two processes to make ethanol?
- glucose
- ethane
- ethene
- steam
A) 1, 2 and 4
B) 1, 3 and 4
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 4 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The two main industrial processes for ethanol production are:
1. Fermentation: Uses glucose (from crops like sugarcane or corn) as the raw material. The glucose is converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast.
2. Hydration of ethene: Uses ethene (from crude oil) and steam (water) as raw materials. The reaction is: C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
Ethane (option 2) is not used in either process, so we can eliminate options A and D.
Between options B and C, option B is correct because it includes all necessary raw materials (glucose for fermentation, and ethene + steam for hydration).
What is used to test for chlorine?
A) a glowing splint
B) damp litmus paper
C) limewater
D) aqueous potassium manganate(VII)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Chlorine gas has distinctive test properties:
A) Glowing splint: Used to test for oxygen (relights the splint), not chlorine.
B) Damp litmus paper: Chlorine bleaches damp litmus paper (turns it white). This is the standard test for chlorine.
C) Limewater: Used to test for carbon dioxide (turns milky), not chlorine.
D) Potassium manganate(VII): Used as an oxidizing agent, not specifically for chlorine testing.
The correct answer is B) damp litmus paper, as chlorine’s bleaching action on moist litmus paper is a characteristic test.
Which statement about paper chromatography is correct?
A) It can show if a substance is pure.
B) It can separate a mixture of insoluble substances.
C) It can separate a compound into its elements.
D) It provides a way of combining substances to make new coloured compounds.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze each statement:
A) Correct: Paper chromatography can indicate purity. A pure substance will show only one spot, while a mixture will show multiple spots.
B) Incorrect: Chromatography separates soluble substances, not insoluble ones (which wouldn’t move up the paper).
C) Incorrect: Chromatography separates mixtures of compounds, not compounds into elements (which would require chemical decomposition).
D) Incorrect: Chromatography is an analytical technique for separation, not for combining substances to make new compounds.
The correct statement is A), as chromatography is commonly used to check the purity of substances by seeing if they separate into multiple components.
