Question
(a) A list of symbols and formulae is shown.
$
\begin{gathered}
\mathrm{Al}^{3+} \\
\mathrm{CH}_4 \\
\mathrm{CO}_2 \\
\mathrm{Fe}^{3+} \\
\mathrm{N}_2 \\
\mathrm{NO}_2 \\
\mathrm{O}_2 \\
\mathrm{O}^{2-} \\
\mathrm{Zn}^{2+}
\end{gathered}
$
Answer the following questions about these symbols and formulae. Each symbol or formula may be used once, more than once or not at all.
Which symbol or formula represents:
(i) a compound which contributes to acid rain……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) a compound which is a product of respiration……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(iii) a gas which forms 21% of clean dry air……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(iv) an ion which forms a red-brown precipitate when added to aqueous sodium hydroxide……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(v) an ion formed when an atom gains electrons?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(b) Complete the table to show the relative charge and approximate relative mass of a proton, a neutron and an electron.
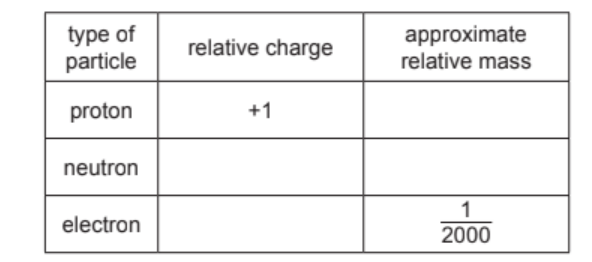
(c) Deduce the number of electrons and neutrons in an atom of the isotope of iron shown.
${ }_{26}^{58} \mathrm{Fe}$
number of electrons …………………………………………………………………………………………………….
number of neutrons ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2] [Total: 10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
$\begin{array}{ll}1 \text { (a)(i) } & \mathrm{NO}_2 / \text { nitrogen dioxide / nitrogen oxide(s) } \\ 1 \text { (a)(ii) } & \mathrm{CO}_2 / \text { carbon dioxide } \\ 1(\mathrm{a})(\text { (iii) } & \mathrm{O}_2 / \text { oxygen } \\ 1(\mathrm{a})(\text { (iv) } & \mathrm{Fe}^{3+} / \text { iron(III) (ions) } \\ 1(\mathrm{a})(\mathrm{v}) & \mathrm{O}^{2-} / \text { oxide }\end{array}$
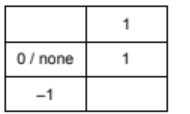
all 4 correct = 3 marks
three correct = 2 marks
one or two correct = 1 mark
Question
A solution is obtained by filtering a mixture of soil and water. The table shows the mass of some of the ions in $1000 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of this solution.
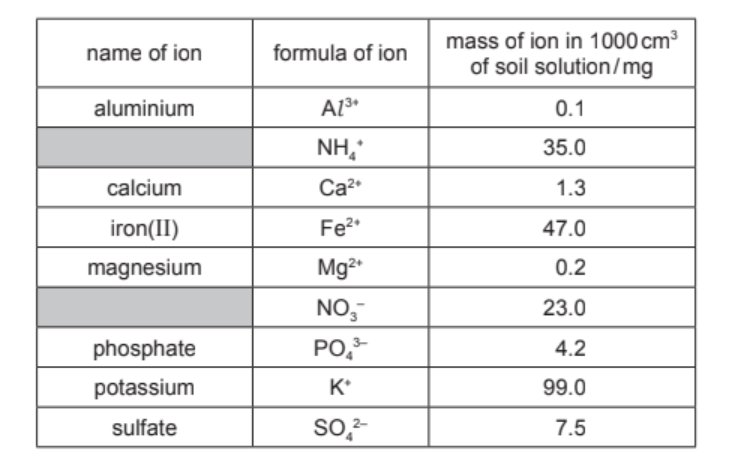
(a) Answer these questions using the information in the table.
(i) Which negative ion has the lowest concentration?
(ii) State the name of the $\mathrm{NO}_3^{-}$ion.[1]
(iii) Calculate the mass of phosphate ions in $250 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of this solution.
$
\text { mass }=
$
$\mathrm{mg}$ [1]
(iv) Name the compound that contains $\mathrm{NH}_4{ }^*$ ions and $\mathrm{PO}_4{ }^{3-}$ ions.[1]
(b) Describe a test for potassium ions.
test……………………………………
observations………………………[2]
(c) The names and formulae for some compounds are shown.
aluminium phosphate, $\mathrm{AlPO}_4$
calcium phosphate, $\mathrm{Ca}_3\left(\mathrm{PO}_4\right)_2$
potassium phosphate, $\mathrm{K}_3 \mathrm{PO}_4$
Deduce the formula for magnesium phosphate. [1] [Total: 7]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
$(\mathrm{a})(\mathrm{i}) \quad \mathrm{PO}_4^{3-} /$ phosphate
(a)(ii) nitrate
(a)(iii) 1.05 (mg)
(a)(iv) ammonium phosphate
(b) flame test / description of flame test
lilac flame
(c) $\quad \mathrm{Mg}_3\left(\mathrm{PO}_4\right)_2$
Question
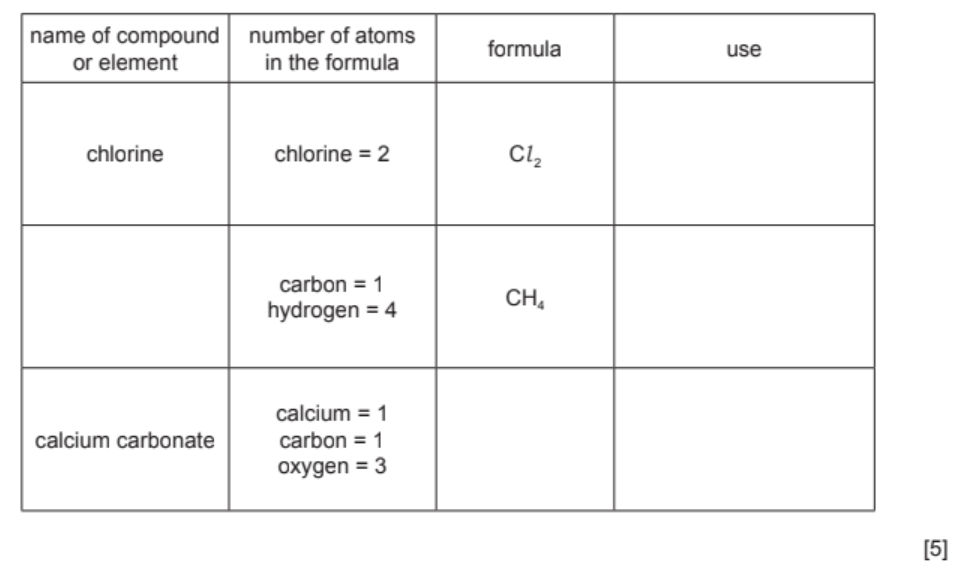
Many compounds and elements have important uses.
(a) Complete the table to show the name, formula and use of each compound and element.
(b) The table shows the minimum temperature for the reduction of four metal oxides by carbon.
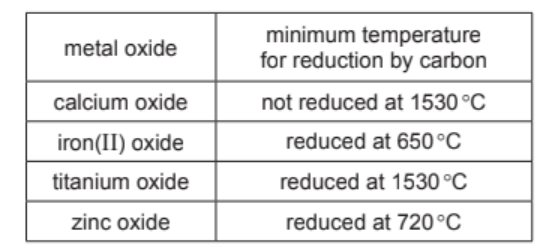
Put the four metals in order of their reactivity.
Put the least reactive metal first.
(c) Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate, $\mathrm{CuSO}_4$, is used to test for water.
(i) Describe the change in colour when water is added to anhydrous copper(II) sulfate.
from………………………. to……………………………………………….. [2]
(ii) This reaction is reversible.
Describe how this reaction can be reversed. [1]
(iii) State one use of water in industry. [1] [Total: 11]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)
(b) iron < zinc < titanium < calcium
IF two marks not scored, one mark for one consecutive pair reversed / all reversed
(c)(i) (from) white
(to) blue
(c)(ii) heat / warm 1
(c)(iii) cooling / coolant / as a solvent
Question
The properties of five alkenes at room temperature are shown in the table.
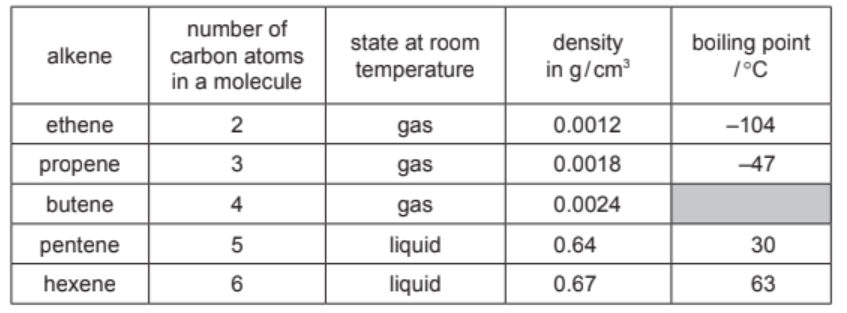
(a) Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) Predict the boiling point of butene.
${ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}[1]$
(ii) Describe the general trend in the density of the alkenes.[1]
(iii) Suggest why the densities of the first three alkenes are much lower than the density of pentene and hexene.[1]
(b) (i) Complete the chemical equation for the complete combustion of propene.
$
2 \mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6+\ldots . . \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 6 \mathrm{CO}_2+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
$
(ii) Describe a test for carbon dioxide.
test…………………………………………..
observations……………………………….[2]
(iii) Universal indicator is added to an aqueous solution of carbon dioxide.
- What colour change is observed?
from green to…………………………………….
- Give a reason for your answer.
(c) When propene undergoes incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide is formed.
(i) What condition is needed for incomplete combustion?
(ii) Give one adverse effect of carbon monoxide on health.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1] [Total: 10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) values between – 46°C and 29°C (inclusive)
(a)(ii) increases as the number of carbon atoms increases / increases as the alkenes get bigger (or longer)
(a)(iii) they are gases (at room temperature and pressure)
(b)(i) $9\left(O_2\right)$
(b)(ii) limewater / aqueous calcium hydroxide
turns milky / turns cloudy / white precipitate
(b)(iii) (green to) yellow
carbon dioxide is an acidic oxide
(c)(i) (combustion in) limited oxygen
(c)(ii) poisonous / toxic
Question
When concentrated hydrochloric acid is electrolysed, gases are produced at the electrodes.
The incomplete apparatus is shown.
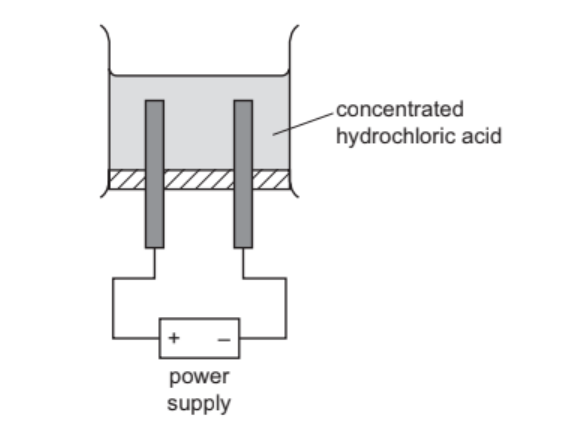
(a) (i) Complete the diagram by:
● labelling the anode and cathode
● showing how the gases are collected. [2]
(ii) Predict the products of this electrolysis at the:
positive electrode ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
negative electrode. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….[2]
(iii) Graphite (carbon) electrodes are used in this electrolysis.
Suggest one other element that can be used as an electrode and give a reason, other
than that it can conduct electricity.
element ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
reason …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
(b) Hydrogen chloride is produced when chlorine reacts with hydrogen.
Complete the chemical equation for this reaction.
$\mathrm{Cl}_2+\ldots \ldots \ldots \rightarrow \ldots . . \mathrm{HCl}$
(c) Aqueous chlorine reacts with aqueous sodium iodide.
$
\mathrm{Cl}_2+2 \mathrm{NaI} \rightarrow \mathrm{I}_2+2 \mathrm{NaCl}
$
(i) How does this reaction show that chlorine is more reactive than iodine?[1]
(ii) What colour is iodine in aqueous solution?[1] [Total: 10]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)(i) anode (on left) and cathode (on right) correctly labelled
test tubes / measuring cylinders over each electrode with open ends dipping into the electrolyte
(a)(ii) positive electrode: chlorine $/ \mathrm{Cl}_2$
negative electrode: hydrogen $/ \mathrm{H}_2$
(a)(iii) platinum
inert / unreactive
(b) $\mathrm{H}_2$ (on left)
$2(\mathrm{HCl})$ (on right)
(c)(i) chlorine has displaced iodine in sodium iodide
/ chlorine has taken the place of iodine in sodium iodide
(c)(ii) brown
Question
Acids have characteristic properties.
(a) Hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium.
Name the products of this reaction and give the observations…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [4]
(b) The rate of reaction of iron(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid can be determined by measuring the time taken to produce $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of carbon dioxide.
A student measured the time taken to produce $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of carbon dioxide at three different temperatures.
In each experiment the student used:
- $1 \mathrm{~g}$ of large pieces of iron(II) carbonate
- dilute hydrochloric acid of the same concentration and volume.
The results are shown in the table.
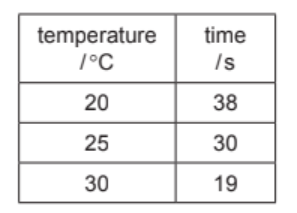
(i) Use the information in the table to describe how the rate of reaction changes with temperature. [1]
(ii) Describe the effect of each of the following on the rate of this reaction at constant
temperature.
● Smaller pieces of iron(II) carbonate are used.
All other conditions stay the same.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
● The concentration of hydrochloric acid is decreased.
All other conditions stay the same.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2]
(c) The reaction of iron(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid is exothermic.
What is meant by the term exothermic?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(d) Rust contains compounds of iron.
State two conditions needed for iron to rust…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
(e) Iron and magnesium are both used in alloys.
Which one of these diagrams, A, B, C or D, best represents an alloy?
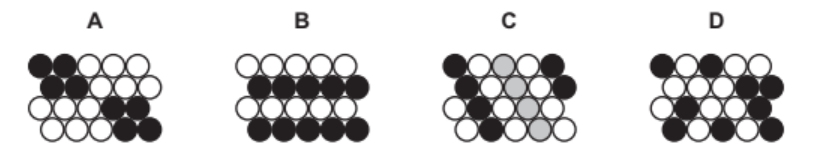 [1] [Total: 11]
[1] [Total: 11]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) forms magnesium chloride (1)
forms hydrogen (1)
one mark each for any two of:
• reaction is exothermic / (reaction mixture) gets warm
• bubbles / effervesces / fizzes
• magnesium disappears (or gets smaller)
(b)(i) increase in temperature increases rate 1
(b)(ii) (smaller pieces of carbonate) increases the rate
(decreasing concentration) decreases the rate
(c) (reaction) gives out heat / reaction mixture gets warmer 1
(d) water
oxygen / air
6(e) D
Question
The structure of myrcene is shown.

(a) Deduce the formula of myrcene to show the number of atoms of carbon and hydrogen. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(b) Myrcene is found in some plants.
The coloured compounds in plant leaves can be separated by chromatography.
Complete the diagram by putting the correct labels in the boxes.

(c) Myrcene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Describe a chemical test to distinguish between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
test ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
observations with saturated hydrocarbon ……………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
observations with unsaturated hydrocarbon…………………[3]
(d) Butane is a saturated hydrocarbon.
To which homologous series does butane belong?
Draw a circle around the correct answer.
alcohol alkane alkene carboxylic acid [1]
(e) Large hydrocarbons can be cracked to form smaller hydrocarbons.
Complete the chemical equation for cracking tridecane, $\mathrm{C}_{13} \mathrm{H}_{28}$, to form an alkene and one other hydrocarbon.
$
\mathrm{C}_{13} \mathrm{H}_{28} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_3 \mathrm{H}_6+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots
$
(f) Ethene is an alkene.
Draw the structure of ethene showing all of the atoms and all of the bonds. [1]
(g) Complete the sentences about the separation of hydrocarbons from petroleum using words from the list.
bitumen combustion condense crystallisation distillation
evaporate gasoline kerosene melt
Hydrocarbons are separated in a fractionating column by fractional ……………………… .
Hydrocarbons with lower boiling points move further up the column. When the temperature
in the column falls below the boiling points of the hydrocarbons they ……………………… . The
fraction at the bottom of the column which is used for making roads is called ……………………… . [3] [Total: 12]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) $\mathrm{C}_{10} \mathrm{H}_{16}$
(b) top box: chromatography paper / filter paper
bottom box: solvent / named solvent e.g. alcohol
(c) bromine / bromine water / aqueous bromine
with saturated hydrocarbon: no colour change / stays orange
with unsaturated hydrocarbon: decolourised / (goes) colourless
(d) alkane
(e) $\mathrm{C}_{10} \mathrm{H}_{22}$
(f)

g) distillation
condense
bitumen
Question
The diagram shows part of the structures of sodium bromide and sulfur.

(a) Describe both sodium bromide and sulfur in terms of:
- bonding………………………………………………….
- electrical conductivity……………………………..
- solubility in water…………………………………….[5]
(b) Sulfur is an element. What is meant by the term element? [1]
(c) Sodium can be extracted from sodium bromide by electrolysis. Sodium is a metal in Group I of the Periodic Table.
(i) Describe one chemical property of sodium.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(ii) Which two of these statements about the physical properties of sodium are correct?
Tick two boxes.
 [2] [Total: 9]
[2] [Total: 9]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) for bonding (maximum three marks)
one mark each for any three of:
• sodium bromide – bonding is ionic
• sodium bromide – strong bonding (between ions)
• sulfur – weak forces between molecules
• sulfur – covalent bonds within molecules
(a) for electrical conductivity (maximum two marks)
one mark each for any three of:
• sodium bromide – conducts when molten / conducts in aqueous solution
• sodium bromide – does not conduct when solid
• sulfur – does not conduct
For solubility in water (maximum two marks)
• sodium bromide – soluble in water
• sulfur– insoluble in water
(b) substance containing only one type of atom / substance which cannot be broken down to simpler substances by
chemical means
(c)(i) reacts with water / reacts with chlorine
(c)(ii) third box ticked (sodium conducts electricity)
fourth box ticked (sodium is malleable)
