Question
A gas is released at point P in the apparatus shown.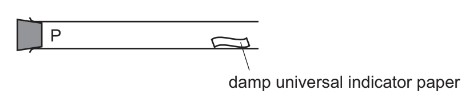
Which gas turns the damp universal indicator paper red most quickly?
A ammonia, \(NH_3\)
B chlorine, \(Cl_2\)
C hydrogen chloride, HCl
D sulfur dioxide, \(SO_2\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
A mixture is separated using the apparatus shown.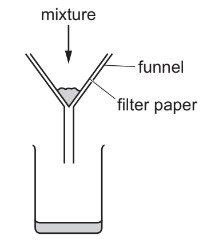
What is the mixture?
A aqueous copper(II) sulfate and aqueous sodium chloride
B aqueous copper(II) sulfate and copper
C copper and sulfur
D ethanol and ethanoic acid
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which statement about paper chromatography is correct?
A A solvent is needed to dissolve the paper.
B Paper chromatography separates mixtures of solvents.
C The solvent should cover the baseline.
D The baseline should be drawn in pencil.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Element X has 7 protons.
Element Y has 8 more protons than X.
Which statement about element Y is correct?
A Y has more electron shells than X.
B Y has more electrons in its outer shell than X.
C Y is in a different group of the Periodic Table from X.
D Y is in the same period of the Periodic Table as X.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A covalent molecule Q contains only six shared electrons.
What is Q?
A ammonia, \(NH_3\)
B chlorine, \(Cl_2\)
C methane, \(CH_4\)
D water, \(H_2O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The arrangement of particles in each of two solids, S and T, are shown.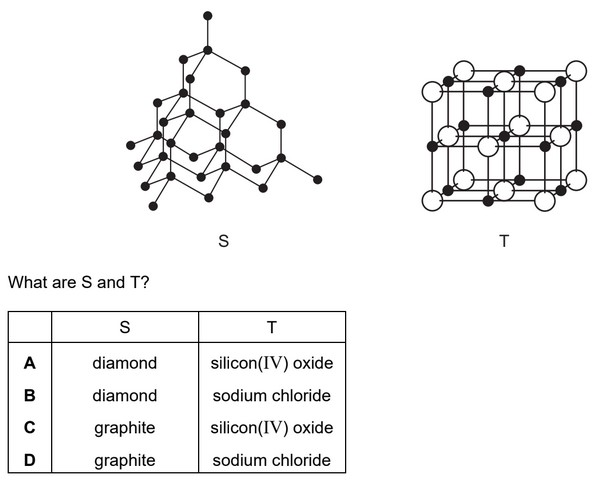
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which statement about metals is correct?
A Metals conduct electricity when molten because negative ions are free to move.
B Metals conduct electricity when solid because positive ions are free to move.
C Metals are malleable because the bonds between the atoms are weak.
D Metals are malleable because the layers of ions can slide over each other.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Two elements, P and Q, are in the same period of the Periodic Table.
P and Q react together to form an ionic compound. Part of the lattice of this compound is shown.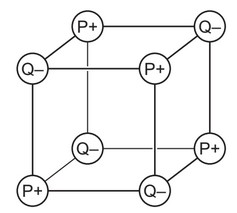
Which statement is correct?
A An ion of P has more electrons than an ion of Q.
B Element P is non-metallic.
C P is to the left of Q in the Periodic Table.
D The formula of the compound is \(P_4Q_4\).
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
2.56 g of a metal oxide, \(MO_2\), is reduced to 1.92 g of the metal, M.
What is the relative atomic mass of M?
A 48 B 96 C 128 D 192
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
In separate experiments, electricity was passed through concentrated aqueous sodium chloride
and molten lead(II) bromide.
What would happen in both experiments?
A A halogen would be formed at the anode.
B A metal would be formed at the cathode.
C Hydrogen would be formed at the anode.
D Hydrogen would be formed at the cathode.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
What is the ionic half-equation for the reaction that occurs at the cathode when molten
lead(II) bromide is electrolysed?
A \(Pb_2+ + 2e^– \rightarrow Pb\)
B \(2Br^– \rightarrow Br_2 + 2e^–\)
C \(Br_2 + 2e^– \rightarrow 2Br^–\)
D \(Pb \rightarrow Pb_2+ + 2e^–\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
The complete combustion of propane is exothermic.
The equation for this reaction is shown.
\(C_3H_8 + 5O_2 \rightarrow 3CO_2 + 4H_2O\)
Which energy level diagram represents the complete combustion of propane?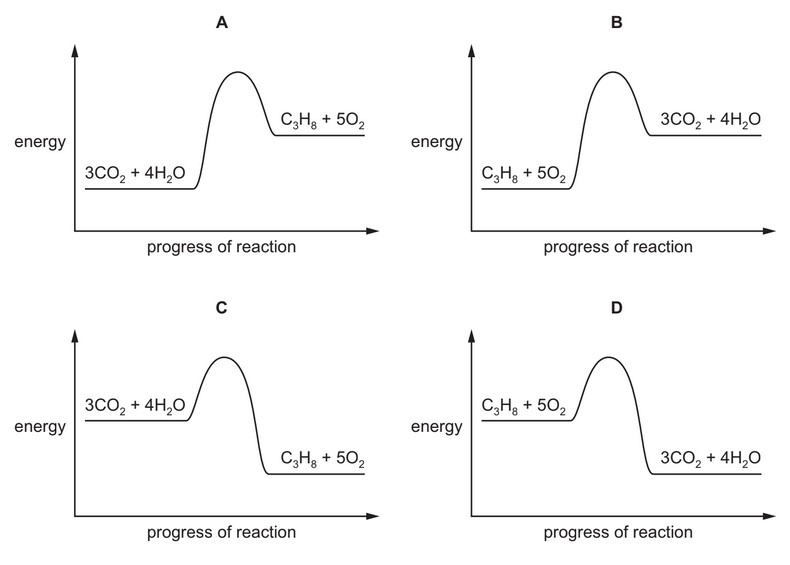
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which equation represents a reaction that takes place in a fuel cell?
A \(C + O_2 \rightarrow CO_2\)
B \(2H_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2H_2O\)
C \(CH_4 + 2O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 + 2H_2O\)
D \(C_3H_8 + 5O_2 \rightarrow 3CO_2 + 4H_2O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
When sulfur is heated it undergoes a ……1…… change as it melts.
Further heating causes the sulfur to undergo a ……2…… change and form sulfur dioxide.
Which words complete gaps 1 and 2?
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Four statements about the effect of increasing temperature on a reaction are shown.
1 The activation energy becomes lower.
2 The particles move faster.
3 There are more collisions between reacting particles per second.
4 There are more collisions which have energy greater than the activation energy.
Which statements are correct?
A 1, 2 and 3 B 1, 3 and 4 C 2, 3 and 4 D 2 and 3 only
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
An example of a redox reaction is shown.
\(Zn + Cu_{2+} \rightarrow Zn_{2+} + Cu\)
Which statement about the reaction is correct?
A Zn is the oxidising agent and it oxidises \(Cu^{2+}\).
B Zn is the oxidising agent and it reduces \(Cu^{2+}\).
C Zn is the reducing agent and it oxidises \(Cu^{2+}\).
D Zn is the reducing agent and it reduces \(Cu^{2+}\).
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which statement about a reaction in equilibrium is correct?
A Both the forward and the backward reactions are proceeding at the same rate.
B Neither the forward nor the backward reaction is proceeding.
C The amount of product present is no longer affected by changes in temperature or pressure.
D The amount of product present is only affected by a change in pressure.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Element X forms an oxide, XO, that neutralises sulfuric acid.
Which row describes X and XO?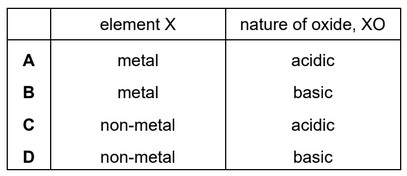
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Copper(II) sulfate is prepared by adding excess copper(II) oxide to warm dilute sulfuric acid.
Which purification methods are used to obtain pure solid copper(II) sulfate from the reaction
mixture?
1 crystallisation
2 filtration
3 chromatography
4 distillation
A 1 and 4 B 1 and 2 C 2 and 3 D 3 and 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Some reactions of element M are shown.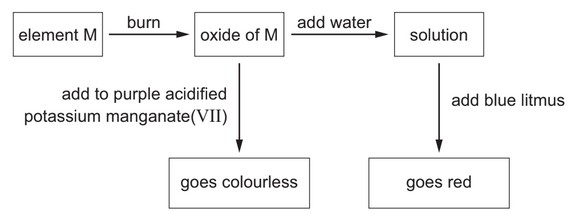
What is element M?
A carbon
B iron
C magnesium
D sulfur
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
In which equation is the underlined reactant acting as a base?
A \(CH_3COO^– + H_3O^+ \rightarrow CH_3COOH + H_2O\)
B \(NH_4^+ + OH^– \rightarrow NH_3 + H_2O\)
C \(CO_2 + 2H_2O \rightarrow H_3O^+ + HCO_3^–\)
D \(H^+ + OH^– \rightarrow H_2O\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Why is helium used to fill balloons?
A Helium is monoatomic.
B Helium is in Group VIII of the Periodic Table.
C Helium has a full outer electron shell.
D Helium is less dense than air.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Which elements in the table are transition elements?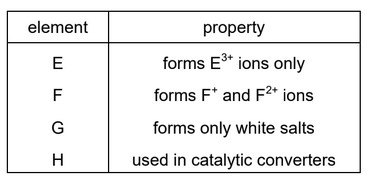
A E and G B E and H C F and G D F and H
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Element R forms a covalent compound R2Si with silicon.
Which row describes R?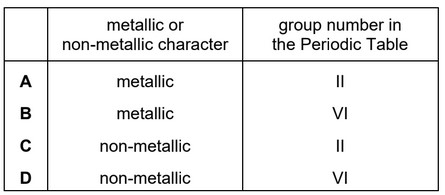
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
Some properties of metal J are listed.
● J does not react with cold water.
● J reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
● No reaction occurs when the oxide of J is heated with carbon.
What is J?
A copper
B iron
C magnesium
D sodium
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Some metal nitrates and carbonates decompose when heated strongly.
Metal Q has a nitrate that decomposes to give a salt and a colourless gas only.
The carbonate of metal Q does not decompose when heated with a Bunsen burner.
What is metal Q?
A calcium
B copper
C sodium
D zinc
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which substances are used in the extraction of aluminium?
A bauxite and cryolite
B bauxite and hematite
C cryolite and zinc blende
D hematite and zinc blende
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Different types of steel alloys are manufactured by changing the percentage of carbon in the alloy.
The properties of four steel alloys are shown.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Ammonia is made by reacting nitrogen with hydrogen in the Haber process.
The equation for the process is shown.
\(N_2 + 3H_2 \leftrightarrow 2NH_3\)
Which changes in reaction conditions would produce a greater yield of ammonia?
1 adding more iron catalyst
2 increasing the reaction pressure
3 increasing the particle size of the iron catalyst
A 1 only B 2 only C 1 and 2 D 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which process removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
A combustion of fossil fuels
B fermentation
C photosynthesis
D respiration
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which catalyst is used in the Contact process?
A calcium oxide
B iron
C manganese(II) oxide
D vanadium(V) oxide
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A white solid Z reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce a gas.
The same gas is produced when compound Z is heated strongly.
What is Z?
A calcium
B calcium carbonate
C calcium hydroxide
D calcium oxide
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
What is the structure of butanoic acid?
A \(CH_3CH_2CO_2H\)
B \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CO_2H\)
C \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CO_2H\)
D \(CH_3CH_2CH_2CO_2CH_3\)
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Compound Z contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Molecules of compound Z have four hydrogen atoms and two carbon atoms.
Compound Z can be made by oxidation of an alcohol.
What is compound Z?
A ethene
B ethanol
C ethanoic acid
D methyl methanoate
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Which statement about homologous series and isomerism is correct?
A Butane and butene are structural isomers.
B Compounds in the same homologous series have the same general formula.
C Compounds in the same homologous series have the same molecular formula.
D Structural isomers have different molecular formulae.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which statement about alkanes is correct?
A They burn in oxygen.
B They contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
C They contain double bonds.
D They contain ionic bonds.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
What is an advantage of manufacturing ethanol by fermentation?
A The process is very fast.
B The ethanol requires no separation.
C The raw materials used are renewable.
D There are no other products formed.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
P, Q, R and S are four organic compounds.
P is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Q burns but otherwise is unreactive.
R contains a C–C single bond and a C=C double bond.
S undergoes addition polymerisation.
Which compounds are alkenes?
A P and R only B P, R and S C P, Q and S D Q, R and S
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
The structure of a synthetic polymer is shown.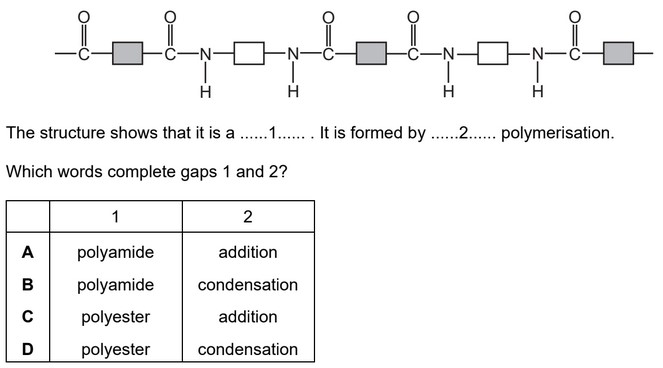
Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question
Which substance is a natural polymer?
A ethene
B Terylene
C nylon
D protein
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
