Question
(a) A list of formulae is shown.
$\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{AlCl}_3 \\ & \mathrm{CaCO}_3 \\ & \mathrm{CO} \\ & \mathrm{CO}_2 \\ & \mathrm{CoCl}_2 \\ & \mathrm{CuSO}_4 \\ & \mathrm{MgCl}_2 \\ & \mathrm{~N}_2 \\ & \mathrm{NaCl}_2 \\ & \mathrm{NH}_3 \\ & \mathrm{O}_2 \\ & \mathrm{SO}_2\end{aligned}$
Answer the following questions using these formulae.
Each formula may be used once, more than once or not at all.
State which formula represents:
(i) a compound that changes colour from white to blue when water is added
(ii) a compound that is used to make cement
(iii) an element that forms 78% of clean, dry air
(iv) a compound that contains an ion with a single positive charge
(v) a compound that dissolves in water to form an alkaline solution.
(b) Complete the dot-and-cross diagram to show the electron arrangement in a molecule of ammonia.
(c) State whether magnesium oxide is a basic oxide or an acidic oxide. Give a reason for your answer.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) \(CuSO_4\)
(ii) \(CaSO_3\)
(iii) \(N_2\)
(iv) NaCl
(v) \(NH_3\)
(b) bonding pair of electrons between the N atom and each of the H atoms with no other electrons on the H atom (1)
2 non-bonding electrons on N atom (1)
(c) basic oxide AND magnesium is a metal / metal oxides are basic (1)
Question
The table shows the masses of some of the ions in 1000\(cm^3\) of rainwater.
(a) Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) State which of the positive ions has the highest concentration.
(ii) Name the compound containing \(NH_4^+\) and (SO_4^{2–}\) ions.
(iii) Calculate the mass of magnesium ions in 400\(cm^3\) of rainwater.
mass = ………………………… mg
(b) Describe a test for chloride ions.
test ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
observations ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Small amounts of carboxylic acids are also present in rainwater.
The structure of tartaric acid is shown.
(i) On the structure draw a circle around one alcohol functional group.
(ii) Deduce the formula of tartaric acid to show the number of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
(d) Tartaric acid can be converted into compound A.
The formula of compound A is \(C_3H_4O_3\).
Complete the table to calculate the relative molecular mass of compound A.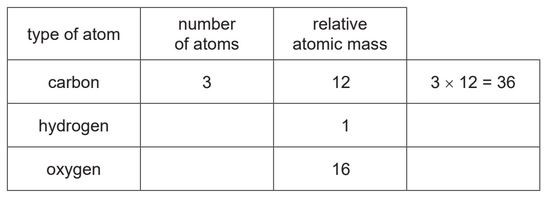
relative molecular mass = …………………………
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) \(Na^+\)
(ii) ammonium sulfate
(iii) 0.032 (mg)
(b) (acidified aqueous) silver nitrate (1)
white precipitate (1)
(c) (i) OH group attached to 2nd or 3rd C atoms circled (1)
(ii) \(C_4H_6O_6\)(d)
88 (2)
if two marks nor scored, 1 mark for 4 × 1 = 4 OR 3 × 16 = 48
Question
The diagram shows a blast furnace used in the extraction of iron.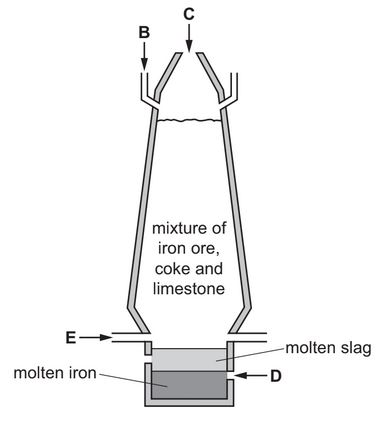
(a) Air is blown into the furnace.
State which letter on the diagram, B, C, D or E, shows where air is blown into the furnace.
(b) (i) Complete the chemical equation for the reduction of iron(III) oxide in the blast furnace.
\(Fe_2O_3 + 3C → ……Fe + ……CO\)
(ii) Explain how this equation shows that iron(III) oxide is reduced.
(c) Calcium carbonate (limestone) is added to the blast furnace.
The calcium carbonate undergoes thermal decomposition.
(i) Complete the word equation for this reaction.
(ii) One of the products of this reaction reacts with impurities in the iron to form slag.
Use the information in the diagram to suggest how you know that molten slag is less dense than molten iron.
(d) (i) Use words from the list to complete these sentences about how steel is made from iron.
acidic basic chlorides methane neutral
nitrogen oxides oxygen sulfates
A gas is blown through the molten iron. The name of this gas is …………………… .
Acidic gases are formed. These acidic gases react with …………………… ……………………
(ii) State one use of mild steel.
(iii) Metals such as chromium are added to iron to make stainless steel.
The symbol for an isotope of chromium is shown.
\(_{24}^{53}Cr\)
Deduce the number of electrons, neutrons and protons in one atom of this isotope of
chromium.
number of electrons ………………………………………………………………………………………………
number of neutrons ………………………………………………………………………………………………
number of protons ………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(e) Chromium conducts electricity and is shiny.
Give two other physical properties of chromium that are characteristic of all metals.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) E
(b) (i) 2 (Fe) (1)
3 (CO) (1)
(ii) iron oxide loses oxygen / it loses oxygen
(c) (i) calcium oxide (1)
carbon dioxide (1)
(ii) slag floats above the iron
(d) (i) oxygen (1)
basic (1) oxides (1)
(ii) car bodies / machinery
(iii) electrons: 24 (1)
neutrons: 29 (1)
protons: 24 (1)
(e) 1 mark each for any two of:
• conducts heat
• malleable
• ductile
Question
The table shows some properties of the Group I elements.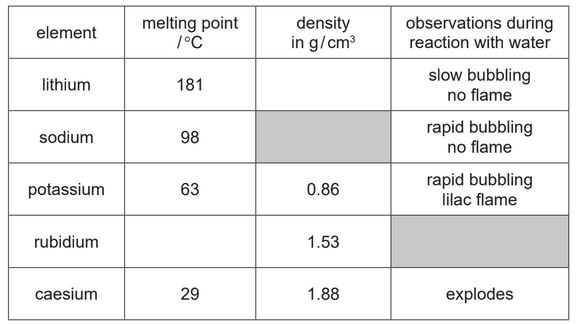
(a) (i) Complete the table by predicting:
● the melting point of rubidium
● the density of lithium.
(ii) Predict the observations when rubidium reacts with water.
(b) Deduce the electronic structure of potassium.
Use the Periodic Table to help you.
(c) Lithium reacts with water to produce aqueous lithium hydroxide and a gas which ‘pops’ with a
lighted splint.
(i) Name the gas which ‘pops’ with a lighted splint.
(ii) Choose one pH value from the list that best describes the pH of aqueous lithium hydroxide.
Draw a circle around the correct answer.
pH 2 pH 5 pH 7 pH 13
(iii) Lithium reacts with nitrogen.
Complete the chemical equation for this reaction.
\(……Li + N_2 → ……Li_3N\)
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) melting point of Rb: values from 31 to 61 °C (inclusive of these values) (1)
density of Li: values from 0.2 to 0.84 (inclusive of these values) (1)
(ii) very rapid bubbling and flame / more rapid bubbling
(b) 2.8.8.1
(c) (i) hydrogen
(ii) pH 13
(iii) 6 (Li) (1)
2 (\(Li_3N\)) (1)
Question
The table shows the structures of some organic compounds.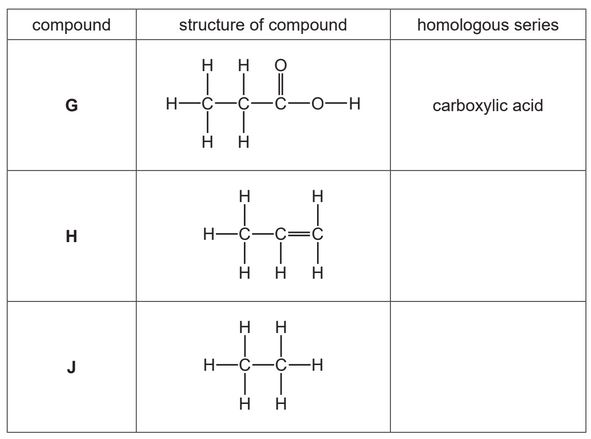
(a) Complete the table by naming the homologous series.
The first one has been done for you.
(b) Draw the structure of a compound containing two carbon atoms which belongs to the same homologous series as compound H.
Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(c) State which compound in the table is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Explain your answer.
(d) State which compound in the table reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Explain your answer.
(e) State the names of the two compounds formed during the complete combustion of compound J.
…………………………………………………………. and ………………………………………………………….
(f) Compound H can be polymerised.
(i) State the general name given to the small units which join together to form a polymer.
(ii) Terylene is also a polymer.
Give one use of Terylene.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) H: alkene (1)
J: alkane (1)
(b) ![]()
(c) H AND has a C=C double bond
(d) G AND acids react with alkalis / G AND acids react with bases / carboxylic acids react with alkalis / carboxylic acids react
with bases (1)
(e) carbon dioxide (1)
water (1)
(f) (i) monomer(s)
(ii) clothing
Question
The diagram shows part of the structures of sodium bromide and graphite at room temperature andpressure.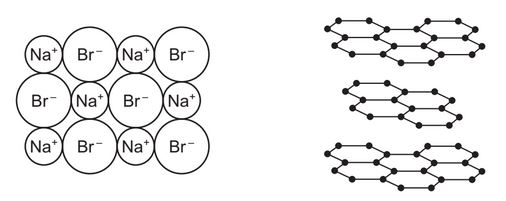
(a) Describe the physical properties of these substances in terms of:
● volatility
sodium bromide ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
graphite ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
● solubility in water
sodium bromide ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
graphite ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
● electrical conductivity when solid.
sodium bromide ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
graphite ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) When dilute sulfuric acid is electrolysed using inert electrodes, oxygen gas is produced at the positive electrode.
Name the gas produced at the negative electrode.
(c) Aqueous sodium bromide reacts with aqueous chlorine.
(i) Complete the word equation for this reaction.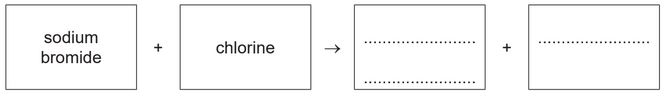
(ii) Explain in terms of the reactivity of the halogens why aqueous sodium chloride does not
react with aqueous bromine.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) 5 of any of:
volatility:
• sodium bromide (very) low / does not evaporate (at room temperature)
• graphite low / does not evaporate (at room temperature)
solubility:
• sodium bromide soluble / dissolves
• graphite insoluble / does not dissolve
electrical conductivity:
• sodium bromide does not conduct
• graphite conducts
(b) hydrogen
(c) (i) sodium chloride (1)
bromine (1)
(ii) chlorine is more reactive than bromine / chlorine higher than bromine in reactivity series
Question
This question is about nitrogen and compounds of nitrogen.
(a) When nitrogen is cooled to below –196°C it changes state from gas to liquid.
(i) Name the change of state from gas to liquid.
(ii) Use the kinetic particle theory to describe the differences between nitrogen gas and liquid
nitrogen in terms of:
● the separation of the particles
● the motion of the particles.
(b) Oxides of nitrogen are pollutants in the air.
(i) State one source of oxides of nitrogen in the air.
(ii) Oxides of nitrogen contribute to acid rain.
Give one adverse effect of acid rain on buildings.
(c) Nitric acid contains the nitrate ion.
(i) Use words from the list to complete the sentences to describe the test for nitrate ions.
aluminium ammonia chloride copper
hydroxide iron oxygen sulfate
Put the sample in a test-tube then add aqueous sodium ……………………. .
Then add ……………………. .
Warm gently. A gas is produced. The name of this gas is …………………….
(ii) Nitric acid reacts with calcium carbonate.
Complete the word equation for this reaction.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) condensation
(ii)
separation:
liquid: particles close together (1)
gas: far apart (1)
motion:
liquid: sliding over each other / limited motion / restricted motion (1)
gas: particles have rapid motion / particles have random motion (1)
(b) (i) car engines
(ii) chemical weathering / chemical erosion
(c) (i) hydroxide (1)
aluminium (1)
ammonia (1)
(ii) calcium nitrate (1)
carbon dioxide (1)
water (1)
Question
The rate of decomposition of aqueous hydrogen peroxide, \(H_2O_2\), is increased by an enzyme.
\(2H_2O_2 → 2H_2O + O_2\)
The rate of reaction is found by measuring the volume of oxygen gas given off as the reaction
proceeds.
The results are shown on the graph.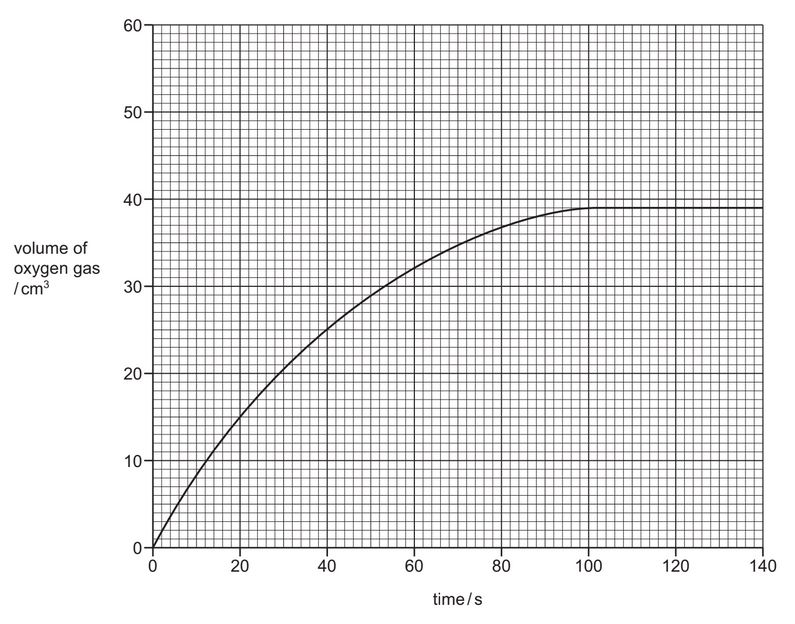 |
|
(a) (i) Deduce the volume of oxygen gas released when the reaction is complete.
volume = ……………………….. \(cm^3\)
(ii) Deduce the volume of oxygen gas produced 50 seconds from the start of the reaction.
volume = ……………………….. \(cm^3\)
(b) The experiment was repeated using hydrogen peroxide of a higher concentration.
All other conditions stayed the same.
Draw a line on the grid to show how the volume of oxygen changes with time when
hydrogen peroxide of a higher concentration is used.
(c) Describe the effect each of the following has on the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
● The reaction is carried out at a lower temperature.
All other conditions stay the same.
● The reaction is carried out without an enzyme.
All other conditions stay the same.
(d) Some metal oxides catalyse the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
The table shows the time taken to produce 20\(cm^3\) of oxygen gas using three different metal oxide powders as catalysts.
All other conditions stay the same.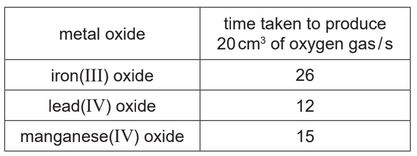
(i) Put the three oxides in order of their ability to catalyse the reaction.
Put the best catalyst first.
(ii) The experiments with the metal oxide catalysts used powdered oxide.
Describe the effect on the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide when large pieces
of catalyst are used instead of powdered catalyst.
All other conditions stay the same.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) 39 (\(cm^3\))
(ii) 29 (\(cm^3\))
(b) steeper initial gradient starting at 0-0 point (1)
final volume of oxygen higher than 39 \(cm^3\) (1)
(c) (rate) decreases / slower (1)
(rate) decreases / slower (1)
(d) (i) lead(IV) oxide > manganese(IV) oxide > iron(III) oxide
(ii) decreased / slower (rate with larger pieces)
