Topic – 1.1
The table shows the melting and boiling points of four elements.
Which element is a gas at room temperature and pressure?
| melting point/°C | boiling point/°C | |
|---|---|---|
| A | −101 | −35 |
| B | −7 | 59 |
| C | 10 | 100 |
| D | 113 | 445 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Room temperature is typically around 20-25°C. For an element to be a gas at room temperature, its boiling point must be below this range.
Option A has a boiling point of -35°C, which is below room temperature, so it would be a gas. The melting point (-101°C) tells us it’s not a solid at room temperature.
Option B boils at 59°C (liquid at room temp), C at 100°C (liquid), and D at 445°C (solid at room temp).
Topic – 1.1
Four statements about the arrangement or movement of particles are given.
- Particles are packed in a regular arrangement.
- Particles are randomly arranged.
- Particles move over each other.
- Particles vibrate about fixed points.
Which statements describe the particles in a pure solid?
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
In a pure solid:
- Particles are packed in a regular, fixed arrangement (statement 1 is correct, 2 is incorrect as that describes liquids/gases)
- Particles vibrate about fixed positions but don’t move freely (statement 4 is correct, 3 is incorrect as that describes liquid behavior)
Therefore, the correct combination is 1 and 4.
Topic – 2.2
One atom of an element contains 12 electrons, 12 protons and 13 neutrons.
How many nucleons does this atom contain?
A) 12
B) 13
C) 24
D) 25
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Nucleons are the particles in the nucleus – protons and neutrons.
Number of nucleons = number of protons + number of neutrons
Given: 12 protons + 13 neutrons = 25 nucleons
Note: Electrons are not nucleons as they’re outside the nucleus.
This atom is magnesium-25 (atomic number 12, mass number 25).
Topic – 2.1
A diagram representing a mixture of four particles is shown.

Which statement describes the mixture of particles?
A) It is a mixture of two different compounds.
B) It is a mixture of two different elements.
C) It is a mixture of four different compounds.
D) It is a mixture of four different elements.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
While the diagram isn’t shown, we can deduce from the answer choices and the correct answer (A) that:
The mixture must contain two types of compounds (molecules made of different elements bonded together).
For example, it might show H₂O molecules and CO₂ molecules mixed together – two different compounds, each made of multiple atoms.
Option B would describe a mixture like O₂ and H₂ (two elements), which isn’t the case here.
Topic – 2.5
Chlorine reacts with sodium to form sodium chloride.
What happens to the sodium atoms during this reaction?
A) They gain electrons to form anions.
B) They lose electrons to form anions.
C) They gain electrons to form cations.
D) They lose electrons to form cations.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Sodium is a Group 1 metal that readily loses its single valence electron to achieve a stable noble gas configuration.
In the reaction:
- Sodium atoms lose 1 electron each (oxidation) to become Na⁺ cations
- Chlorine atoms gain 1 electron each (reduction) to become Cl⁻ anions
Key points:
- Metals lose electrons to form positive ions (cations)
- Anions are negative ions formed by gaining electrons
- Sodium would never gain electrons as it’s already electron-deficient being a metal
Topic – 2.5
Nitrogen monoxide, NO, is a simple molecular compound.
Which row shows the properties of nitrogen monoxide?
| boiling point | electrical conductivity | |
|---|---|---|
| A | high | good |
| B | high | poor |
| C | low | good |
| D | low | poor |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Nitrogen monoxide (NO) is a simple molecular compound, which means:
- It has low boiling point because the intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces) between molecules are weak.
- It has poor electrical conductivity because it doesn’t contain free electrons or ions to carry charge.
Simple molecular compounds typically have these characteristics because they consist of small, discrete molecules with covalent bonds within the molecules but only weak forces between them.
Topic – 8.2
Metal X is in Group II of the Periodic Table.
X is reacted separately with dilute sulfuric acid and with oxygen.
Which row identifies the products of each reaction?
| products with dilute sulfuric acid | product with oxygen | |
|---|---|---|
| A | XSO4 and H2 | XO |
| B | XSO4 and H2 | XO2 |
| C | X2SO4 and H2 | XO |
| D | X2SO4 and H2 | XO2 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
For Group II metals:
- With dilute sulfuric acid:
- The general reaction is: X + H2SO4 → XSO4 + H2
- This produces a sulfate salt (XSO4) and hydrogen gas (H2)
- The formula X2SO4 would be incorrect as Group II metals have a +2 charge
- With oxygen:
- Group II metals form oxides (XO) when reacting with oxygen, not peroxides (XO2)
- The reaction is: 2X + O2 → 2XO
Therefore, option A correctly shows both reactions for a Group II metal.
Topic – 3.2
What is the relative molecular mass, Mr, of sulfuric acid, H2SO4?
A) 81
B) 82
C) 97
D) 98
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To calculate the relative molecular mass (Mr) of sulfuric acid (H2SO4):
- Hydrogen (H): 2 atoms × 1 = 2
- Sulfur (S): 1 atom × 32 = 32
- Oxygen (O): 4 atoms × 16 = 64
Total Mr = 2 + 32 + 64 = 98
Remember to use the relative atomic masses from the periodic table:
- H = 1
- S = 32
- O = 16
The correct answer is therefore D) 98.
Topic – 3.3
The equation for the production of ammonia, NH3, is shown.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Which mass of nitrogen is required to make 51 tonnes of ammonia?
A) 21 tonnes
B) 25.5 tonnes
C) 42 tonnes
D) 84 tonnes
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
To solve this stoichiometry problem:
- Calculate the molar masses:
- N2: 2 × 14 = 28 g/mol
- NH3: 14 + (3 × 1) = 17 g/mol
- From the balanced equation: 1 mole N2 produces 2 moles NH3
- Calculate moles of NH3 in 51 tonnes:
- 51 tonnes = 51,000,000 g
- Moles = mass/Mr = 51,000,000/17 = 3,000,000 moles NH3
- Moles of N2 needed = ½ × moles NH3 = 1,500,000 moles
- Mass of N2 = moles × Mr = 1,500,000 × 28 = 42,000,000 g = 42 tonnes
Therefore, 42 tonnes of nitrogen are required to make 51 tonnes of ammonia.
Topic – 4.1
The diagram shows the apparatus used to electroplate a nickel shape with silver.
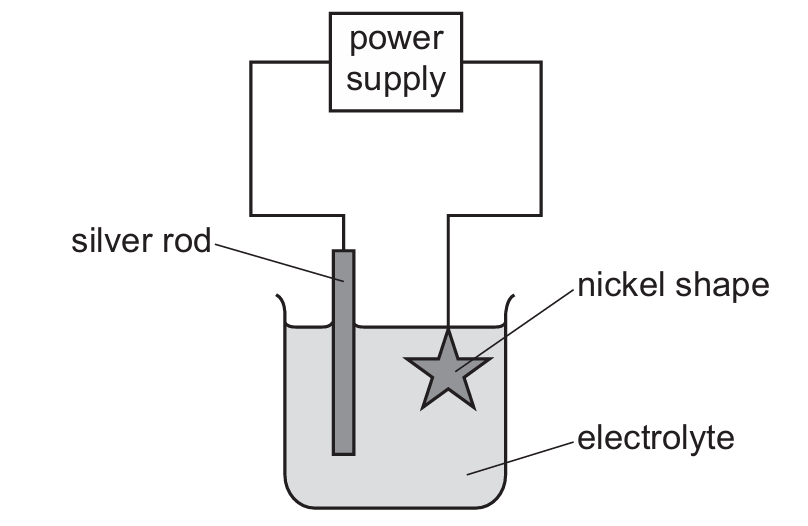
Which row identifies the negative electrode, the positive electrode and the electrolyte?
| negative electrode | positive electrode | electrolyte | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | silver rod | nickel shape | aqueous nickel nitrate |
| B | nickel shape | silver rod | aqueous silver nitrate |
| C | nickel shape | silver rod | aqueous nickel nitrate |
| D | silver rod | nickel shape | aqueous silver nitrate |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
For silver plating:
- The negative electrode (cathode) is the object to be plated (nickel shape), where silver ions gain electrons to form silver atoms.
- The positive electrode (anode) is the silver rod, which dissolves to replenish silver ions in solution.
- The electrolyte must contain silver ions (aqueous silver nitrate), not nickel ions, as we want to deposit silver, not nickel.
The reactions are:
- At cathode (nickel shape): Ag+ + e– → Ag
- At anode (silver rod): Ag → Ag+ + e–
Therefore, option B correctly identifies all components for silver plating.
Topic – 4.1
Concentrated aqueous sodium chloride and dilute sulfuric acid are each electrolysed separately using inert electrodes.
Three statements about the electrolysis of these electrolytes are listed.
- A gas is produced at each electrode for both electrolytes.
- Oxygen is produced at the cathode for both electrolytes.
- Hydrogen is produced at the cathode for both electrolytes.
Which statements are correct?
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 only
C) 2 only
D) 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze each statement:
1. Correct: For concentrated NaCl, chlorine gas forms at the anode and hydrogen gas at the cathode. For dilute H2SO4, oxygen forms at the anode and hydrogen at the cathode.
2. Incorrect: Oxygen is produced at the anode in both cases, not the cathode.
3. Correct: Hydrogen is indeed produced at the cathode in both electrolysis processes.
Therefore, statements 1 and 3 are correct, making option A the right answer.
Topic – 5.1
Which reaction pathway diagram represents an endothermic reaction?
A) 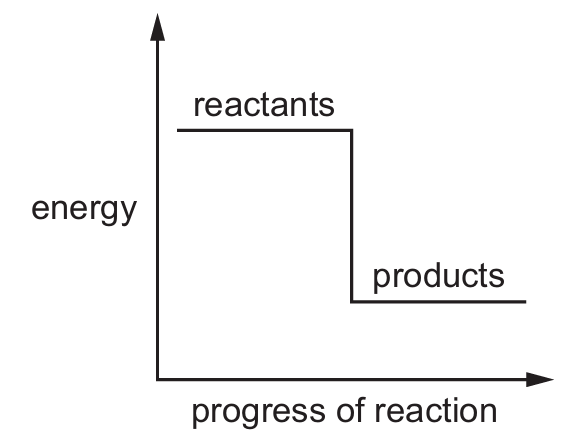
B) 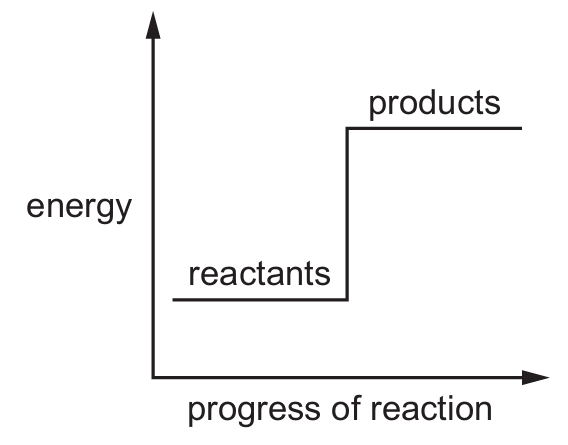
C) 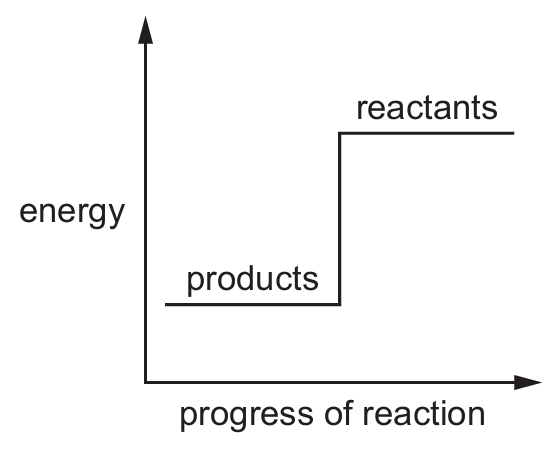
D) 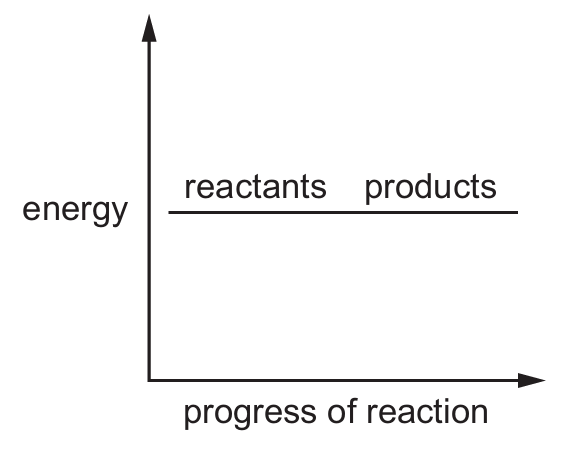
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
An endothermic reaction is one that absorbs energy from its surroundings. In terms of reaction pathway diagrams:
– The products will be at a higher energy level than the reactants
– There will be an upward slope from reactants to products
– The difference in energy represents the energy absorbed
Option B shows this characteristic pattern where the products have higher energy than the reactants, indicating energy was absorbed during the reaction.
Topic – 5.1
The diagram shows a match.
By striking the match, a chemical reaction takes place.
Which row describes the chemical reaction?
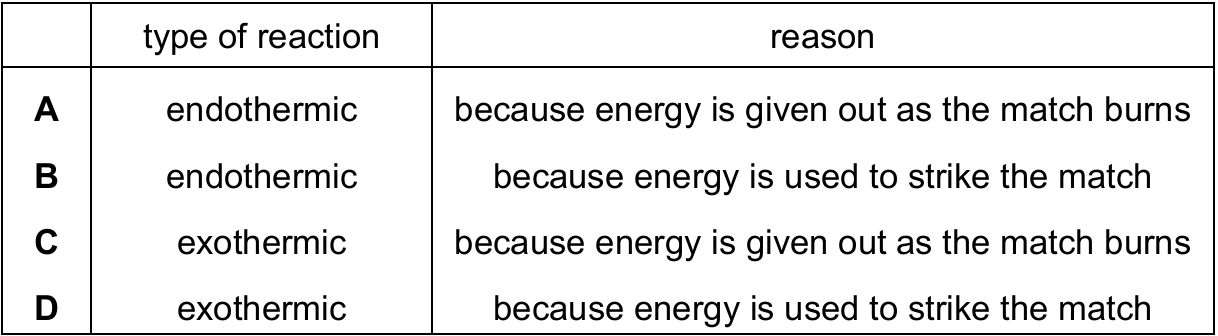
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The burning of a match is a classic example of an exothermic reaction because:
1. Heat and light energy are released during the combustion process
2. The energy required to initiate the reaction (striking the match) is different from the energy change of the reaction itself
3. The correct reason is that energy is given out as the match burns, not that energy is used to strike it
Therefore, option C correctly identifies the reaction as exothermic with the proper explanation.
Topic – 6.2
Hydrogen peroxide decomposes to form water and oxygen. The equation is shown.
\[ 2H_2O_2(l) \rightarrow 2H_2O(l) + O_2(g) \]
Manganese(IV) oxide catalyses this reaction.
Which statements about manganese(IV) oxide are correct?
- It increases the rate of the reaction.
- It increases the total volume of oxygen gas produced at the end of the reaction.
- It will have the same mass at the end of the reaction as it does at the start of the reaction.
A) 1, 2 and 3
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s evaluate each statement about the catalyst manganese(IV) oxide:
1. Correct: Catalysts by definition increase the rate of reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
2. Incorrect: A catalyst doesn’t affect the total amount of product formed, only how quickly it’s formed. The volume of oxygen depends only on the amount of hydrogen peroxide decomposed.
3. Correct: Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain chemically unchanged, so their mass stays constant.
Therefore, statements 1 and 3 are correct, making option C the right answer.
Topic – 6.2
Four students collect the gas produced from the reaction of calcium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid. Each student records the time taken to collect a volume of gas.
Which results show the highest average rate of reaction?
A) 15 cm3 of gas collected in 20 seconds
B) 50 cm3 of gas collected in 40 seconds
C) 75 cm3 of gas collected in 80 seconds
D) 90 cm3 of gas collected in 100 seconds
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To determine the highest average rate of reaction, we calculate the rate of gas production (volume/time) for each option:
A) 15 cm3/20 s = 0.75 cm3/s
B) 50 cm3/40 s = 1.25 cm3/s
C) 75 cm3/80 s ≈ 0.94 cm3/s
D) 90 cm3/100 s = 0.90 cm3/s
Option B has the highest rate at 1.25 cm3/s. Even though option D produces more total gas, it takes proportionally longer, resulting in a lower average rate.
This shows that the highest rate isn’t necessarily the one with the most product, but rather the one that produces gas fastest relative to the time taken.
Topic – 6.4
The equation for the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen is shown.
\[ 2H_2(g) + O_2(g) \rightarrow 2H_2O(g) \]
Which statement explains why this is a redox reaction?
A) Both oxidation and reduction take place.
B) Heat energy is released to the surroundings.
C) Hydrogen is a reactant.
D) The reaction can be reversed.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
A redox reaction involves both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously:
1. Oxidation: Hydrogen is oxidized as its oxidation state increases from 0 in H2 to +1 in H2O (loss of electrons).
2. Reduction: Oxygen is reduced as its oxidation state decreases from 0 in O2 to -2 in H2O (gain of electrons).
Option B describes an exothermic reaction (which this is, but doesn’t define it as redox). Option C is true but irrelevant to redox. Option D describes reversibility, not redox nature. Therefore, option A is correct as it identifies the simultaneous oxidation and reduction.
Topic – 11.7
Which statements about dilute ethanoic acid are correct?
- It has a pH of 8.
- It is an organic compound.
- It turns universal indicator orange-yellow.
- It reacts with magnesium to produce carbon dioxide.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Evaluating each statement about ethanoic acid (CH3COOH):
1. False: Acids have pH < 7. pH 8 would be alkaline.
2. True: Ethanoic acid contains carbon and is an organic compound.
3. True: As a weak acid, it turns universal indicator orange-yellow (pH ~3-6).
4. False: It reacts with magnesium to produce hydrogen gas, not CO2.
Therefore, only statements 2 and 3 are correct, making option C the right answer.
Topic – 7.1
An aqueous solution of Z turns universal indicator paper purple.
Which row identifies the colour of methyl orange and of thymolphthalein when they are added separately to an aqueous solution of Z?
| methyl orange | thymolphthalein | |
|---|---|---|
| A | yellow | blue |
| B | yellow | colourless |
| C | red | blue |
| D | red | colourless |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Universal indicator turning purple indicates Z is alkaline (pH > 7).
Indicator color changes:
1. Methyl orange:
– Red in acid (pH < 3.1)
– Yellow in neutral/alkaline (pH ≥ 4.4)
→ In alkali: yellow
2. Thymolphthalein:
– Colorless in acid/neutral (pH < 9.3)
– Blue in alkali (pH ≥ 10.5)
→ In strong alkali: blue
Therefore, for an alkaline solution Z: methyl orange = yellow, thymolphthalein = blue (option A).
Topic – 7.3
Which row describes the solubility of lead(II) chloride and lead(II) sulfate in water?
| lead(II) chloride | lead(II) sulfate | |
|---|---|---|
| A | soluble | soluble |
| B | soluble | insoluble |
| C | insoluble | soluble |
| D | insoluble | insoluble |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Solubility rules for lead compounds:
1. Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2):
– Most chlorides are soluble, except those of Ag+, Pb2+, and Hg22+
– Therefore, PbCl2 is insoluble
2. Lead(II) sulfate (PbSO4):
– Most sulfates are soluble, except those of Ba2+, Sr2+, Pb2+, and Ca2+
– Therefore, PbSO4 is insoluble
Thus, both lead(II) chloride and lead(II) sulfate are insoluble in water (option D).
Topic – 7.2
Four different groups of oxides are shown.
- MgO FeO CuO
- CaO SO2 TiO2
- PbO CaO Cl2O
- NO2 Br2O P2O5
Which statement about these groups of oxides is correct?
A) 1, 2 and 3 contain basic oxides only.
B) 2, 3 and 4 contain basic oxides only.
C) 1 contains basic oxides only, and 4 contains acidic oxides only.
D) 1 contains acidic oxides only, and 4 contains basic oxides only.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Analyzing each group’s oxide types:
1. MgO, FeO, CuO: All metal oxides → basic oxides (correct in option C)
2. CaO (basic), SO2 (acidic), TiO2 (amphoteric): Mixed properties
3. PbO (amphoteric), CaO (basic), Cl2O (acidic): Mixed properties
4. NO2, Br2O, P2O5: All non-metal oxides → acidic oxides (correct in option C)
Therefore, only statement C is completely correct: Group 1 contains only basic oxides (metal oxides) and Group 4 contains only acidic oxides (non-metal oxides). The other groups contain mixtures of oxide types.
Topic – 7.3
Four steps in the preparation of a soluble salt from a dilute acid and a solid metal oxide are listed.
- Warm the dilute acid.
- Evaporate the solution to half of its volume and allow to cool.
- Add excess metal oxide.
- Filter to remove any unreacted solid.
What is the correct order for these steps?
A) 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
B) 1 → 3 → 4 → 2
C) 3 → 1 → 2 → 4
D) 3 → 4 → 1 → 2
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The correct order for preparing a soluble salt from a dilute acid and solid metal oxide is:
1. First warm the dilute acid to speed up the reaction.
2. Then add excess metal oxide to ensure all the acid reacts.
3. Filter to remove any unreacted solid metal oxide.
4. Finally evaporate the solution to concentrate it and allow crystals to form.
This matches option B: 1 → 3 → 4 → 2.
Topic – 8.3
Which pair of elements react together most violently?
A) chlorine and lithium
B) chlorine and potassium
C) iodine and lithium
D) iodine and potassium
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The most violent reaction would occur between:
1. The most reactive alkali metal (potassium is more reactive than lithium in Group I)
2. The most reactive halogen (chlorine is more reactive than iodine in Group VII)
Potassium reacts more vigorously than lithium with halogens, and chlorine is more reactive than iodine. Therefore, chlorine and potassium (option B) would react most violently.
Topic – 8.2
Rubidium is an element in Group I of the Periodic Table.
Which row describes a physical property and a chemical property of rubidium?
| physical property | chemical property | |
|---|---|---|
| A | hard | reacts with water |
| B | hard | does not react with water |
| C | soft | reacts with water |
| D | soft | does not react with water |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Rubidium is an alkali metal in Group I with these properties:
Physical property: Like all Group I metals, rubidium is soft (can be cut with a knife).
Chemical property: All Group I metals react vigorously with water, producing hydrogen gas and an alkaline solution.
Therefore, the correct description is option C: soft (physical) and reacts with water (chemical).
Topic – 8.3
Which row describes the state and colour of bromine at room temperature and pressure?
| state | colour | |
|---|---|---|
| A | liquid | red-brown |
| B | liquid | grey-black |
| C | solid | red-brown |
| D | solid | grey-black |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Bromine is unique among the halogens because:
State: At room temperature and pressure, bromine is a liquid (the only non-metal that’s liquid at room temperature).
Color: It has a distinctive red-brown color in both its liquid and vapor states.
Therefore, the correct description is option A: liquid and red-brown.
Topic – 8.1
Part of the Periodic Table is shown.
Which element is a metal?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
From the periodic table shown in the question (not visible in text), we can deduce:
1. Metals are typically found on the left side and middle of the periodic table.
2. Non-metals are found on the right side.
3. The question indicates that element A is a metal, which would be positioned in the metal region of the periodic table.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Topic – 8.1
Which compound is made from elements that are all in the same period?
A) Al2(SO4)3
B) C2H5OH
C) LiNO3
D) Na3AlF6
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
To solve this, we need to check which compound contains elements all from the same period (row) in the Periodic Table.
Option A: Al (Period 3), S (Period 3), O (Period 2) – different periods
Option B: C (Period 2), H (Period 1), O (Period 2) – different periods
Option C: Li (Period 2), N (Period 2), O (Period 2) – all same period
Option D: Na (Period 3), Al (Period 3), F (Period 2) – different periods
Only LiNO3 contains elements that are all in Period 2.
Topic – 9.4
Silver metal is separately tested with cold water, with steam and with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Which row identifies the tests that show the chemical reactivity of silver?
| cold water | steam | dilute hydrochloric acid | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| B | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| C | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| D | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| key: ✓ = reaction, ✗ = no reaction | |||
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Silver is a relatively unreactive metal in the reactivity series. It doesn’t react with:
1. Cold water – silver is below hydrogen in the reactivity series
2. Steam – same reason as cold water
3. Dilute hydrochloric acid – silver is below hydrogen so can’t displace it from acids
Therefore, silver shows no reaction in all three tests, which corresponds to option D.
Topic – 9.6
Which statement about the extraction of iron from hematite is correct?
A) Air is blown into the blast furnace to oxidise the molten iron.
B) Carbon dioxide is reduced by coke to carbon monoxide.
C) Hematite is oxidised by carbon to molten iron.
D) The slag produced is denser than molten iron.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze each option:
Option A: Incorrect – Air is blown in to burn coke (carbon) to produce heat and carbon monoxide, not to oxidize iron.
Option B: Correct – CO2 reacts with more coke (C) to form CO: CO2 + C → 2CO
Option C: Incorrect – Hematite (Fe2O3) is reduced by CO, not oxidized.
Option D: Incorrect – Slag (calcium silicate) is less dense than molten iron and floats on top.
The key reaction in the blast furnace is the reduction of CO2 to CO by coke, making option B correct.
Topic – 9.3
What is an alloy?
A) a compound of two metallic elements
B) a compound of metallic and non-metallic elements
C) a mixture of a metal and at least one other element
D) a pure metallic element
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
An alloy is defined as:
– A mixture (not compound) of a metal with one or more other elements
– The other elements can be metals or non-metals
– The components are not chemically bonded but mixed at the atomic level
Option A: Incorrect – alloys are mixtures, not compounds
Option B: Incorrect – describes compounds like metal oxides, not alloys
Option C: Correct – accurate definition of an alloy
Option D: Incorrect – pure metals are not alloys
Examples include brass (copper + zinc) and steel (iron + carbon).
Topic – 9.5
The diagram shows an experiment to investigate how paint affects the rusting of iron.
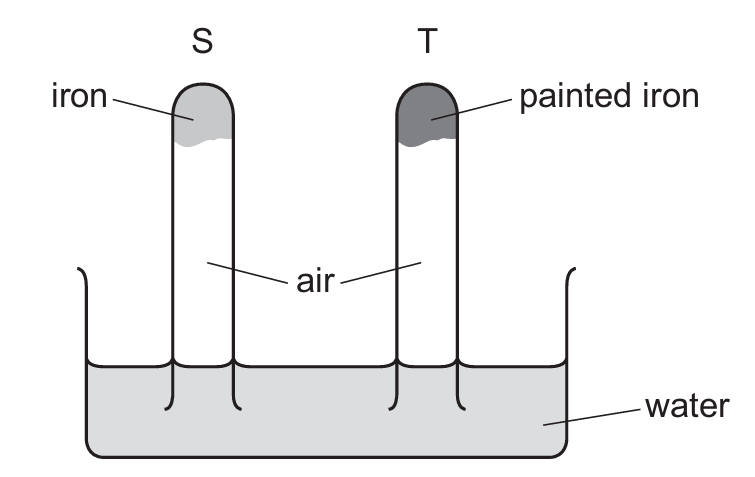
What happens to the water level in tubes S and T?
| tube S | tube T | |
|---|---|---|
| A | falls | rises |
| B | no change | rises |
| C | rises | falls |
| D | rises | no change |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
This experiment demonstrates rusting which requires both oxygen and water:
1. Tube S (unpainted iron): Rusting occurs, consuming oxygen from the air inside the tube. This creates a partial vacuum, causing the water level to rise as atmospheric pressure pushes water up the tube.
2. Tube T (painted iron): The paint prevents oxygen and water from reaching the iron, so no rusting occurs. The water level remains unchanged.
Therefore, the correct observation is that the water level rises in tube S and shows no change in tube T, corresponding to option D.
Topic – 10.3
Which statement describes clean, dry air?
A) It is a compound containing about 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen only.
B) It is a mixture of about 21% nitrogen and 78% oxygen only.
C) It is a mixture of several gases, including nitrogen and oxygen.
D) It is a compound containing nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other gases.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Clean, dry air is a mixture (not a compound) of several gases including nitrogen (~78%), oxygen (~21%), and small amounts of other gases like argon and carbon dioxide. The percentages in options A and B are reversed (nitrogen is actually ~78%, not 21%), and option D incorrectly describes air as a compound. Only option C correctly states that air is a mixture of several gases including nitrogen and oxygen.
Topic – 10.1
Which word equation describes photosynthesis?
A) carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
B) glucose + water → carbon dioxide + oxygen
C) carbon dioxide + oxygen → glucose + water
D) glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The correct word equation is: carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen. Option B describes respiration, while options C and D are incorrect combinations. Remember that photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide and water, and produces glucose and oxygen as byproducts.
Topic – 10.3
Some adverse effects caused by air pollutants are listed.
- acid rain
- photochemical smog
- respiratory problems
Which air pollutant contributes to all three of these adverse effects?
A) carbon monoxide
B) oxides of nitrogen
C) methane
D) particulates
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) contribute to all three effects: (1) They dissolve in rainwater to form nitric acid, causing acid rain. (2) They react with hydrocarbons in sunlight to form photochemical smog. (3) They irritate the respiratory system, causing breathing problems. Carbon monoxide (A) mainly causes health issues, methane (C) is a greenhouse gas, and particulates (D) don’t contribute to photochemical smog formation.
Topic – 11.3
Petroleum is an important raw material that is separated into useful products.
Which terms describe petroleum and the method used to separate it?
| description | separation method | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | compound | cracking |
| B) | compound | fractional distillation |
| C) | mixture | cracking |
| D) | mixture | fractional distillation |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Petroleum is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, not a single compound (eliminating A and B). The initial separation is done by fractional distillation, where petroleum is heated and different fractions condense at different temperatures in the fractionating column. Cracking (options A and C) is a later process that breaks down larger molecules into smaller, more useful ones, but it’s not the initial separation method.
Topic – 11.1
Which statements about homologous series are correct?
- All carboxylic acids have similar chemical properties.
- All alcohols have the same molecular mass.
- Ethane and ethene are members of the same homologous series.
- Ethane and propane are members of the same homologous series.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
1. Correct – Members of a homologous series (like carboxylic acids) have similar chemical properties due to the same functional group.
2. Incorrect – Alcohols have different molecular masses (e.g., methanol CH3OH = 32, ethanol C2H5OH = 46).
3. Incorrect – Ethane (alkane) and ethene (alkene) are in different homologous series with different functional groups.
4. Correct – Ethane (C2H6) and propane (C3H8) are both alkanes in the same homologous series, differing by CH2.
Therefore, only statements 1 and 4 are correct.
Topic – 11.5
The formulae of two organic compounds, P and Q, are shown.

Which type of organic compounds are P and Q?
| P | Q | |
| A | alcohol | alkane |
| B | alcohol | alkene |
| C | carboxylic acid | alkane |
| D | carboxylic acid | alkene |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze both compounds:
For P (CH3CH2CH2OH):
This compound has an -OH functional group attached to a carbon chain, which is the characteristic feature of an alcohol. It’s specifically propan-1-ol.
For Q (CH3CH=CHCH3):
This compound contains a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C), which is the defining feature of an alkene. It’s specifically but-2-ene.
Looking at the options:
Option B correctly identifies P as an alcohol and Q as an alkene, which matches our analysis.
Topic – 11.6
Which fuel is manufactured by fermentation?
A) diesel
B) ethanol
C) hydrogen
D) kerosene
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze each option:
A) Diesel: Produced from fractional distillation of crude oil, not by fermentation.
B) Ethanol: Can be produced by fermentation of sugars by yeast. This is a well-known biological process where sugars are converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide.
C) Hydrogen: Typically produced through electrolysis of water or from natural gas, not by fermentation.
D) Kerosene: Like diesel, it’s obtained from fractional distillation of crude oil.
Therefore, ethanol is the correct answer as it’s the only fuel listed that’s commonly produced through fermentation.
Topic – 11.8
Which statement about the disposal of waste plastics is correct?
A) They are put in landfill sites, where they quickly decompose.
B) They are burned to produce non-toxic products.
C) They accumulate in oceans, where they are harmful to aquatic life.
D) They are dissolved in water and pumped into the sea.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s evaluate each statement:
A) Incorrect – Plastics decompose very slowly in landfills, often taking hundreds of years.
B) Incorrect – Burning plastics typically produces toxic gases and pollutants, unless done under very controlled conditions.
C) Correct – Plastic waste does accumulate in oceans, forming things like the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, and harms marine life through ingestion and entanglement.
D) Incorrect – Most plastics are not water-soluble and this is not a standard disposal method.
Option C is the only completely accurate statement about plastic disposal issues.
Topic – 12.3
Dyes are coloured substances.
The chromatogram of substance X and four different dyes, 1, 2, 3 and 4, is shown.
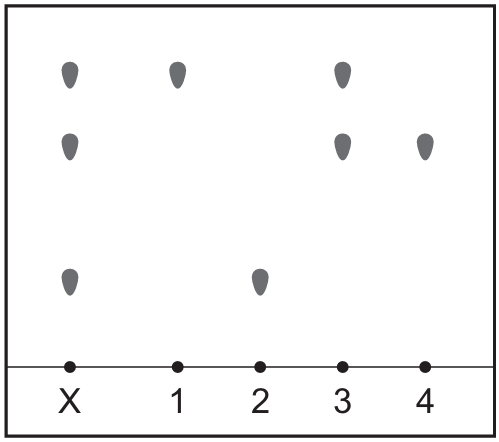
Substance X contains only two of the dyes 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Which two dyes are present in substance X?
A) 1 and 2 B) 1 and 4 C) 2 and 3 D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
In chromatography, a substance that contains other dyes will show spots that align with the dyes it contains.
From the description (though we can’t see the actual chromatogram), we can deduce that substance X has spots that match the positions of dyes 2 and 3.
Key points about chromatography interpretation:
- Each component in a mixture will travel up the chromatography paper to the same extent as it would if it were pure
- The number of spots in the mixture’s chromatogram indicates how many different dyes it contains
- A spot in the mixture that aligns with a spot from a known dye indicates that dye is present in the mixture
Therefore, since substance X contains only two dyes and they match dyes 2 and 3, option C is correct.
Topic – 12.5
The results of two tests on substance G are listed.
- A flame test produces a yellow flame.
- Substance G is added to aqueous sodium hydroxide and powdered aluminium and warmed carefully. A gas is given off which turns damp red litmus paper blue.
What is G?
A) potassium chloride
B) potassium nitrate
C) sodium chloride
D) sodium nitrate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s analyze the test results:
1. Flame test (yellow flame):
– Sodium compounds give a persistent yellow flame
– Potassium gives a lilac flame
This suggests the substance contains sodium, eliminating options A and B.
2. NaOH + Al test:
This is the test for nitrates. The gas produced is ammonia (NH3), which turns damp red litmus blue (ammonia is alkaline).
The reaction is: NO3– + Al + OH– + H2O → NH3 + AlO2–
Between the remaining options (C and D):
– Sodium chloride (C) would not give this nitrate test result
– Sodium nitrate (D) fits both the flame test and the nitrate test
Therefore, G must be sodium nitrate (option D).
