Topic – 1.1
The table shows some information about the three states of matter.
| particle separation | particle arrangement | type of motion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | touching with some particles having spaces between them | random | slide past each other at low speed |
| 2 | particles are far apart | random | rapid motion in straight lines |
| 3 | touching with very little space between the particles | regular | vibration only |
Which row is correct?
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | gas | liquid | solid |
| B | liquid | solid | gas |
| C | liquid | gas | solid |
| D | solid | gas | liquid |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each state:
State 1: Particles touching with some spaces, random arrangement, sliding past each other – these are characteristics of a liquid.
State 2: Particles far apart, random arrangement, rapid motion – these are characteristics of a gas.
State 3: Particles touching with little space, regular arrangement, vibrating only – these are characteristics of a solid.
Therefore, the correct matching is: 1 = liquid, 2 = gas, 3 = solid, which corresponds to option C.
Topic – 1.2
Which arrow represents evaporation?
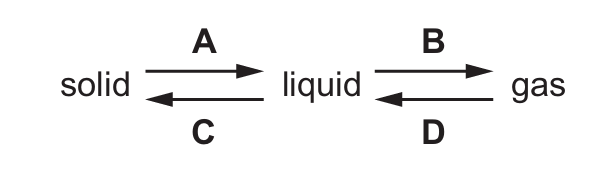
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Evaporation is the process where a liquid changes to a gas. In the given options, we’re looking for the arrow that goes from liquid to gas. Since option B is the only one mentioned between liquid and gas (as we can see from the labels), it must represent evaporation.
Topic – 1.2
In which states of matter does diffusion occur readily?
A) gases and liquids
B) gases only
C) liquids and solids
D) solids only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Diffusion occurs most readily in gases because the particles are far apart and move rapidly. It also occurs in liquids, though more slowly, because liquid particles can move past each other. In solids, diffusion is extremely slow because particles are locked in fixed positions and can only vibrate.
Therefore, the correct answer is A (gases and liquids), as diffusion occurs readily in both these states, though at different rates.
Topic – 2.1
Which statement about the boxes P, Q and R is correct?

A) Box P contains two compounds, and box R contains two elements.
B) Box P contains two elements, and box Q contains a mixture.
C) Box P contains two elements, and box Q contains one compound.
D) Box Q contains two compounds, and box R contains a mixture.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Without the diagram, we can analyze the options based on typical exam patterns:
Option C is correct because it’s common for exam questions to show two elements (like separate atoms of different types) in one box (P), and a compound (molecules made of bonded atoms) in another box (Q).
The other options are less likely because:
A: If P contains two compounds, R would typically show a mixture, not elements.
B: If Q contains a mixture, it would show separate compounds/elements, not just one type.
D: Two compounds in Q would typically be shown as distinct molecules, which would make R a mixture of these, but this is less common in basic questions.
Topic – 2.2
Which information about an element is given by its atomic number?
A) the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element
B) the number of particles in the nucleus of an atom of an element
C) the relative mass of one atom of an element
D) the total number of particles in one atom of an element
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The atomic number of an element specifically refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of its atoms. This is a fundamental definition in chemistry.
The other options are incorrect because:
B: The number of particles in the nucleus would include both protons and neutrons (nucleons), but the atomic number only counts protons.
C: The relative mass is given by the mass number (protons + neutrons), not the atomic number.
D: The total number of particles would include electrons as well, but the atomic number doesn’t account for these.
Remember: Atomic number = number of protons (which also equals number of electrons in a neutral atom).
Topic – 2.3
The symbols represent four atoms. The letters used are not the usual atomic symbols.
\( _{20}^{40}\textrm{W}\) \( _{19}^{40}\textrm{X}\) \( _{20}^{46}\textrm{Y}\) \( _{22}^{46}\textrm{Z}\)
Which atoms are isotopes of the same element?
A) W and X
B) W and Y
C) X and Y
D) Y and Z
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same atomic number) with different mass numbers.
Looking at the given atoms:
- W has atomic number 20 and mass number 40
- Y has atomic number 20 and mass number 46
Both W and Y have the same atomic number (20) but different mass numbers (40 and 46), making them isotopes of the same element.
X has atomic number 19 (different element), and Z isn’t shown in the given data.
Topic – 2.5
Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are ……1…… .
Most covalent compounds have ……2…… electrical conductivity.
Which words correctly complete gaps 1 and 2?
| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| A | shared | high |
| B | shared | low |
| C | transferred | high |
| D | transferred | low |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms, not by transferring electrons (which is characteristic of ionic bonds).
Most covalent compounds have low electrical conductivity because:
- They don’t have free electrons or ions to carry charge
- They are typically molecular compounds that don’t ionize in solution
Exceptions include some covalent network structures like graphite, but the question specifies “most” covalent compounds.
Topic – 2.6
Which row describes the structure and a use of diamond?
| structure | use | |
|---|---|---|
| A | ionic | in cutting tools |
| B | ionic | as a lubricant |
| C | giant covalent | in cutting tools |
| D | giant covalent | as a lubricant |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Diamond has a giant covalent structure where each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
Key properties and uses:
- Extremely hard due to strong covalent bonds – used in cutting tools
- High melting point
- Doesn’t conduct electricity (no free electrons)
Graphite is the form of carbon used as a lubricant, not diamond. Diamond is never ionic (options A and B are incorrect).
Topic – 7.3
Which symbol equation represents the reaction between aqueous sodium hydroxide and dilute sulfuric acid?
A) Na₂OH + H₂SO₄ → 2NaSO₄ + H₂O
B) Na(OH)₂ + H₂SO₄ → Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
C) 2NaOH + H₂SO₄ → 2NaSO₄ + 2H₂O
D) 2NaOH + H₂SO₄ → Na₂SO₄ + 2H₂O
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
This is a neutralization reaction between an acid (H₂SO₄) and a base (NaOH).
The correct balanced equation is:
\[ 2NaOH + H_2SO_4 \rightarrow Na_2SO_4 + 2H_2O \]
Key points:
- Sodium hydroxide formula is NaOH (not Na₂OH or Na(OH)₂)
- The sulfate ion is SO₄²⁻, so sodium sulfate is Na₂SO₄ (not NaSO₄)
- The equation must balance for atoms and charge
Option D is the only one that meets all these requirements.
Topic – 3.2
What is the relative formula mass of magnesium bromide?
A) 47
B) 82
C) 104
D) 184
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
First, we need to know:
- Magnesium (Mg) has atomic mass ≈ 24
- Bromine (Br) has atomic mass ≈ 80
The formula for magnesium bromide is MgBr₂ (magnesium has 2+ charge, bromide has 1- charge).
Calculating relative formula mass:
\[ \text{MgBr}_2 = 24 + (2 \times 80) = 24 + 160 = 184 \]
Therefore, the correct answer is 184.
Common mistake would be forgetting there are two bromine atoms in the formula.
Topic – 4.1
Three substances are listed.
- solid copper
- aqueous sodium bromide
- solid lead(II) bromide
Which substances conduct electricity?
A) 1, 2 and 3
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To determine which substances conduct electricity, we need to consider their physical states and bonding:
1. Solid copper is a metal, so it conducts electricity due to its delocalized electrons.
2. Aqueous sodium bromide conducts electricity because it’s an ionic compound dissolved in water, forming free-moving ions.
3. Solid lead(II) bromide doesn’t conduct electricity in solid state as the ions are fixed in position, though it would conduct when molten or dissolved.
Therefore, only substances 1 and 2 conduct electricity under the given conditions.
Topic – 4.2
Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells can be used to power cars.
Which processes produce the fuel of a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell?
- the cracking of hydrocarbons
- the electrolysis of dilute sulfuric acid
- photosynthesis
- the electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The fuel for hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells is hydrogen gas. Let’s evaluate each process:
1. Cracking of hydrocarbons can produce hydrogen as one of the products.
2. Electrolysis of dilute sulfuric acid produces hydrogen at the cathode.
3. Photosynthesis produces oxygen and glucose, not hydrogen.
4. Electrolysis of molten aluminium oxide produces aluminium and oxygen, not hydrogen.
Therefore, only processes 1 and 2 can produce hydrogen fuel.
Topic – 4.1
Molten sodium sulfide, Na2S, is electrolysed using inert electrodes.
Which row identifies the product at each electrode?
| cathode | anode | |
|---|---|---|
| A | sodium | sulfur |
| B | sulfur | sodium |
| C | hydrogen | sulfur |
| D | sodium | hydrogen |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
When molten Na2S is electrolyzed:
At the cathode (negative electrode): Na+ ions are reduced to sodium metal because sodium ions are more easily reduced than sulfide ions.
At the anode (positive electrode): S2- ions are oxidized to sulfur because there are no other ions present to be oxidized (the electrodes are inert).
Hydrogen isn’t produced because the compound is molten (no water present) and we’re not dealing with aqueous solutions.
Topic – 5.1
The temperature of the water in two beakers, X and Y, is measured as 21.5°C.
5 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in the water in beaker X. The temperature changes to 18.0°C.
5 g of calcium oxide is dissolved in the water in beaker Y. The temperature changes to 29.4°C.
Which types of process are occurring in beakers X and Y?
| X | Y | |
|---|---|---|
| A | endothermic | endothermic |
| B | endothermic | exothermic |
| C | exothermic | endothermic |
| D | exothermic | exothermic |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
To determine whether the processes are endothermic or exothermic:
Beaker X (sodium chloride):
The temperature decreases from 21.5°C to 18.0°C, indicating heat is absorbed from the surroundings. This is characteristic of an endothermic process.
Beaker Y (calcium oxide):
The temperature increases from 21.5°C to 29.4°C, indicating heat is released to the surroundings. This is characteristic of an exothermic process.
This matches option B: X is endothermic and Y is exothermic.
Topic – 6.1
Which process involves a chemical change?
A) adding sodium chloride to water
B) adding magnesium to hydrochloric acid
C) heating solid iodine until it turns into a gas
D) melting lead
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
A chemical change involves the formation of new substances. Let’s analyze each option:
A) Dissolving NaCl in water is a physical change – the NaCl dissociates into ions but can be recovered by evaporation.
B) Magnesium reacting with hydrochloric acid produces magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas – a clear chemical change with new substances formed.
C) Iodine subliming is a physical change of state (solid to gas) with no new substances formed.
D) Melting lead is a physical change (change of state from solid to liquid).
Only option B represents a chemical change where new substances are formed.
Topic – 6.2
Which two pieces of apparatus are most useful to measure the rate of a reaction in which a gas is given off?
A) accurate balance and gas syringe
B) accurate balance and thermometer
C) gas syringe and stop-watch
D) stop-watch and thermometer
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
To measure the rate of a gas-producing reaction, we need to measure either:
- The volume of gas produced over time (using a gas syringe)
- The time taken to produce a certain amount of gas (using a stop-watch)
Option C combines both these essential pieces of apparatus. A gas syringe measures the volume of gas produced, while a stop-watch measures the time taken. The other options either include unnecessary equipment (thermometer) or less direct measurement methods (balance measures mass change, which isn’t as straightforward for gas evolution).
Topic – 6.2
Reaction 1 and reaction 2 both produce a gas. The total volume of gas produced in each reaction is measured every minute for 10 minutes.
A graph of the results is shown.
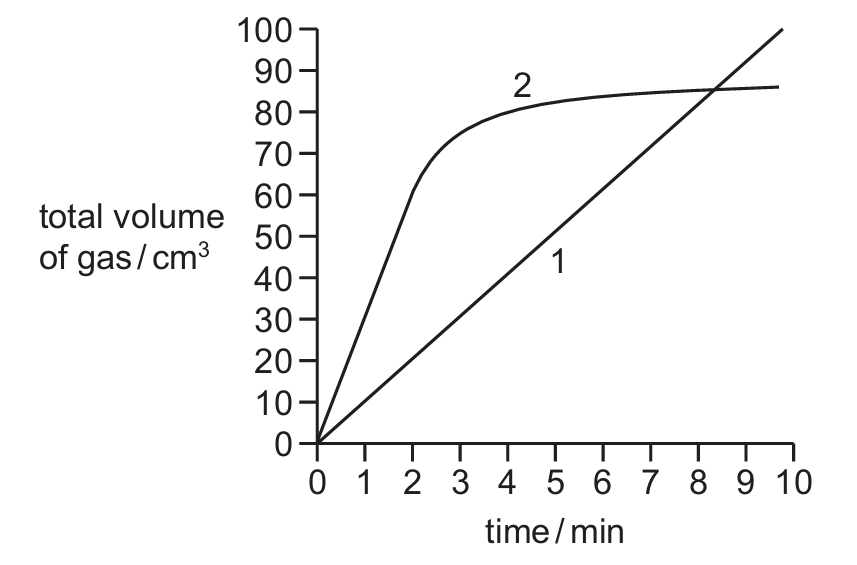
Which row describes how the rate of reaction changes, if at all, during each reaction?
| reaction 1 | reaction 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| A | the rate is constant | the rate decreases after 2 minutes |
| B | the rate increases | the rate increases |
| C | the rate increases | the rate decreases after 2 minutes |
| D | the rate is constant | the rate increases |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
From the graph description:
Reaction 1: The straight line indicates a constant rate of reaction (volume increases steadily with time).
Reaction 2: The steep initial slope followed by leveling off indicates the rate decreases after 2 minutes (likely because reactants are being used up).
Therefore, option A correctly describes both reactions – Reaction 1 has a constant rate while Reaction 2’s rate decreases after 2 minutes.
Topic – 7.1
When a few drops of water are added to a solid, E, the colour changes from blue to pink. What is E?
A) anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride
B) anhydrous copper(II) sulfate
C) hydrated cobalt(II) chloride
D) hydrated copper(II) sulfate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The key observations are:
- The solid changes color when water is added
- The color change is from blue to pink
This is characteristic of anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl₂):
- Anhydrous form: Blue
- Hydrated form: Pink
Copper(II) sulfate changes from white (anhydrous) to blue (hydrated), so it doesn’t match. The hydrated forms wouldn’t show this color change when more water is added. Therefore, the correct answer is anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride.
Topic – 6.4
The equation for the reaction of magnesium with copper(II) oxide is shown.
\[ \text{Mg} + \text{CuO} \rightarrow \text{MgO} + \text{Cu} \]
Which word describes this reaction?
A) combustion
B) decomposition
C) neutralisation
D) redox
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
This is a redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction because:
- Magnesium is oxidized (loses electrons, going from Mg to Mg²⁺ in MgO)
- Copper is reduced (gains electrons, going from Cu²⁺ in CuO to Cu)
It’s not:
- Combustion (no oxygen or burning involved)
- Decomposition (one compound isn’t breaking down into simpler substances)
- Neutralisation (no acid-base reaction occurring)
The transfer of oxygen from copper to magnesium and the change in oxidation states clearly indicate a redox reaction.
Topic – 7.1
Compound M contains calcium. Two reactions of M are listed.
- M reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form a salt and water only.
- M reacts with aqueous ammonium chloride to form a gas that turns damp red litmus paper blue.
What is M?
A) CaOH
B) Ca(OH)₂
C) CaCO₃
D) Ca(CO₃)₂
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze the clues:
First reaction: Forms salt and water only – this is characteristic of a base (hydroxide) reacting with acid. Carbonates would produce CO₂ gas as well.
Second reaction: The gas turns damp red litmus blue – this indicates ammonia (NH₃), which is basic. Calcium hydroxide reacts with ammonium chloride to produce ammonia:
\[ \text{Ca(OH)}_2 + 2\text{NH}_4\text{Cl} \rightarrow \text{CaCl}_2 + 2\text{NH}_3 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \]
CaOH doesn’t exist as a stable compound. The carbonate options would produce CO₂ with acid, not just salt and water. Therefore, M must be calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)₂.
Topic – 7.2
The diagram shows one period of the Periodic Table.
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne |
Which two elements form acidic oxides?
A) beryllium and lithium
B) carbon and neon
C) carbon and nitrogen
D) nitrogen and neon
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Acidic oxides are formed by non-metals. In the given period:
- Lithium (Li) and Beryllium (Be) are metals that form basic oxides.
- Neon (Ne) is a noble gas and doesn’t form oxides.
- Carbon (C) forms CO2 and CO, both acidic oxides.
- Nitrogen (N) forms several oxides like NO2 and N2O5, which are acidic.
Therefore, the correct pair is carbon and nitrogen (Option C).
Topic – 7.1
A student tests four solutions with universal indicator.
Which colour identifies the solution containing the greatest concentration of OH– ions?
A) red
B) yellow
C) green
D) blue
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Universal indicator shows different colors at different pH levels:
- Red (pH 1-3): Strongly acidic (very low OH– concentration)
- Yellow (pH 4-6): Weakly acidic (low OH– concentration)
- Green (pH 7): Neutral (equal H+ and OH– concentrations)
- Blue (pH 8-11): Alkaline (high OH– concentration)
The blue color indicates the highest pH and therefore the greatest concentration of OH– ions among the given options.
Topic – 7.3
The following steps are done to prepare solid magnesium sulfate.
- filtration
- measurement of 20 cm3 of dilute sulfuric acid using a measuring cylinder
- evaporation
- addition of an excess of solid magnesium carbonate to dilute sulfuric acid
What is the correct order for these steps?
A) 2 → 4 → 3 → 1
B) 2 → 4 → 1 → 3
C) 4 → 2 → 1 → 3
D) 4 → 2 → 3 → 1
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The correct sequence is:
- First measure the acid (step 2)
- Then add excess magnesium carbonate to ensure all acid reacts (step 4)
- Filter to remove the unreacted magnesium carbonate (step 1)
- Evaporate the filtrate to obtain solid magnesium sulfate (step 3)
This gives the order: 2 → 4 → 1 → 3 (Option B). The excess magnesium carbonate ensures complete reaction of the acid and is removed by filtration before evaporation.
Topic – 8.1
Which statement about the Periodic Table is correct?
A) All the metals in the Periodic Table are transition elements.
B) The halogens are elements in Group I of the Periodic Table.
C) The elements become more metallic across a period from Group I to Group VII.
D) The Periodic Table can be used to predict the properties of the elements.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s evaluate each option:
- A: Incorrect – There are many metals (like alkali and alkaline earth metals) that aren’t transition elements.
- B: Incorrect – Halogens are in Group VII, not Group I.
- C: Incorrect – Elements become less metallic (more non-metallic) across a period from left to right.
- D: Correct – The Periodic Table organizes elements by atomic number and shows periodic trends in properties, allowing predictions about element behavior.
The Periodic Table’s main purpose is to show periodic trends and allow prediction of element properties based on position.
Topic – 6.4
Zinc is formed when zinc oxide is heated with carbon.
\[ \text{zinc oxide + carbon} \rightarrow \text{zinc + carbon monoxide} \]
Which substance is oxidised in this reaction?
A) carbon
B) carbon monoxide
C) zinc
D) zinc oxide
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Oxidation involves loss of electrons or gain of oxygen. Let’s analyze the reaction:
\[ \text{ZnO + C} \rightarrow \text{Zn + CO} \]
- Zinc oxide (ZnO) is reduced to Zn (loses oxygen)
- Carbon (C) is oxidized to CO (gains oxygen)
The oxidation numbers change as follows:
- Carbon goes from 0 (in C) to +2 (in CO) – oxidation
- Zinc remains +2 throughout (in ZnO and Zn, though elemental Zn is 0)
- Oxygen remains -2 throughout
Therefore, carbon is the substance that is oxidized in this reaction (Option A).
Topic – 9.5
Which word equation represents the rusting of iron?
A) iron + oxygen + water → anhydrous iron(II) hydroxide
B) iron + oxygen → hydrated iron(II) oxide
C) iron + oxygen + water → anhydrous iron(III) hydroxide
D) iron + oxygen + water → hydrated iron(III) oxide
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Rusting of iron is a chemical reaction where iron reacts with oxygen and water to form hydrated iron(III) oxide, commonly known as rust. The key points are:
- Water must be present for rusting to occur (eliminates option B)
- The product is iron(III) oxide, not iron(II) (eliminates options A and B)
- The product is hydrated (contains water molecules in its structure), not anhydrous (eliminates option C)
The correct equation is: iron + oxygen + water → hydrated iron(III) oxide, which matches option D.
Topic – 8.1
Which option describes the electronic configurations of three different elements from the same group of the Periodic Table?
A) 2 2,2 2,8,8,2
B) 2 2,8 2,8,2
C) 2,1 2,8,1 2,8,8,1
D) 2,1 2,2 2,3
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. Let’s analyze each option:
- Option A: Shows configurations with 2, 2, and 2 valence electrons respectively – but the second element (2,2) is in Group 2 while the third (2,8,8,2) is in Group 2 but the first (2) is helium (Group 18).
- Option B: Shows configurations with 2, 8, and 2 valence electrons – different numbers, so not same group.
- Option C: All configurations end with 1 valence electron (2,1; 2,8,1; 2,8,8,1) – these are all Group 1 elements (alkali metals).
- Option D: Shows 1, 2, and 3 valence electrons respectively – different groups.
Only option C shows three elements all with 1 valence electron, meaning they’re in the same group (Group 1).
Topic – 8.4
Which metal forms compounds that can be used to colour glass?
A) aluminium
B) calcium
C) chromium
D) sodium
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Transition metal compounds are commonly used to color glass due to their colorful ions:
- Aluminium (A): Compounds are generally colorless in glass.
- Calcium (B): Used to make glass but doesn’t provide color.
- Chromium (C): Correct answer. Chromium compounds produce different colors:
- Chromium(III) oxide (Cr2O3) – green
- Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) – orange
- Sodium (D): Used in glass manufacturing but doesn’t provide color.
Chromium is a transition metal whose compounds are well-known for their use in coloring glass and ceramics.
Topic – 8.3
Two properties of element R are listed.
- It is a dark solid at room temperature.
- It is a diatomic molecule.
Where on the Periodic Table is R placed?
A) Group I
B) Group VII
C) Group VIII
D) transition elements
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze the clues:
- Dark solid at room temperature:
- Group I elements are all shiny metals (not dark solids)
- Group VII (halogens) include iodine (dark solid) and bromine (dark liquid)
- Group VIII (noble gases) are all colorless gases
- Transition elements are typically metallic and shiny
- Diatomic molecule:
- Group VII elements exist as diatomic molecules (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2)
- Group I metals don’t form diatomic molecules in their elemental state
The best match is Group VII (halogens), where iodine fits both properties perfectly: it’s a dark gray solid and exists as I2 molecules.
Topic – 9.4
Four metals, W, X, Y and Z, are tested with either cold water, steam or both.
The observations are shown.
| metal | observations |
|---|---|
| W | reacts slowly with cold water |
| X | reacts rapidly with cold water |
| Y | does not react with cold water but reacts with steam |
| Z | does not react with cold water or steam |
What is the order of reactivity of the metals from the least reactive to the most reactive?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The reactivity series of metals with water/steam is as follows (from most reactive to least):
- Metals that react rapidly with cold water (e.g., Group 1 metals like sodium)
- Metals that react slowly with cold water (e.g., calcium)
- Metals that react only with steam (e.g., magnesium, aluminum, zinc, iron)
- Metals that don’t react with water or steam (e.g., copper, silver, gold)
From the observations:
- X (reacts rapidly with cold water) is most reactive
- W (reacts slowly with cold water) is next
- Y (reacts only with steam) is less reactive than W
- Z (no reaction) is least reactive
Therefore, the correct order from least to most reactive is: Z → Y → W → X, which matches option D.
Topic – 8.3
Which statement about the displacement reactions of the halogens is correct?
A) Iodine displaces bromine from aqueous sodium bromide.
B) Bromine displaces chlorine from aqueous potassium chloride.
C) Iodine displaces chlorine from aqueous potassium chloride.
D) Chlorine displaces bromine from aqueous sodium bromide.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In halogen displacement reactions, a more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from its compound. The reactivity of halogens decreases down the group: chlorine > bromine > iodine.
Option D is correct because chlorine (more reactive) can displace bromine (less reactive) from sodium bromide. The other options are incorrect because:
- Iodine cannot displace bromine (A is wrong)
- Bromine cannot displace chlorine (B is wrong)
- Iodine cannot displace chlorine (C is wrong)
The correct reaction for option D would be: Cl2 + 2NaBr → 2NaCl + Br2
Topic – 10.1
Which substances in water from natural sources are beneficial to aquatic animals?
- metal compounds
- plastics
- phosphates
- dissolved oxygen
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s analyze each substance:
- Metal compounds: Some metal compounds in trace amounts (like calcium and magnesium) are essential for aquatic life.
- Plastics: Harmful to aquatic animals as they can cause entanglement or be mistaken for food.
- Phosphates: While necessary in small amounts, excess phosphates can lead to eutrophication and harm aquatic ecosystems.
- Dissolved oxygen: Absolutely essential for aquatic animals to breathe.
Therefore, the beneficial substances are metal compounds (1) and dissolved oxygen (4), making option B correct.
Topic – 11.6
What are the products formed when glucose is fermented?
A) ethanol and carbon dioxide
B) ethanol and oxygen
C) ethene and carbon dioxide
D) ethene and oxygen
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The fermentation of glucose is represented by the following equation:
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
This shows that glucose breaks down into ethanol (C2H5OH) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Key points to remember:
- Fermentation is an anaerobic process (doesn’t require oxygen)
- It’s carried out by yeast or certain bacteria
- The bubbles in bread and beer come from the CO2 produced
- Ethene is not a product of fermentation (eliminates options C and D)
Topic – 11.6
Which structure represents a molecule of ethanol?
A) 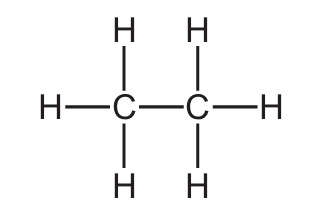
B) 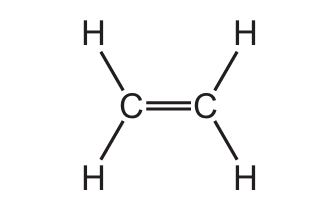
C) 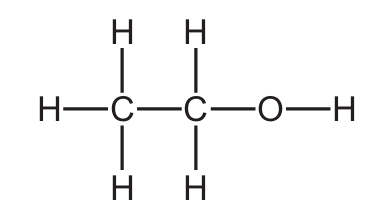
D) 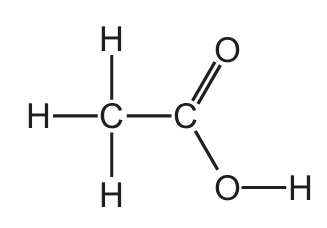
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Ethanol has the molecular formula C2H5OH, which can be represented as CH3-CH2-OH.
Let’s analyze each option:
- A) H-C≡C-H: This is ethyne (acetylene), a triple-bonded hydrocarbon.
- B) H-C=C-H: This is ethene, a double-bonded hydrocarbon.
- C) H-C-C-O-H: This correctly shows ethanol with two carbon atoms, single bonds, and an -OH group.
- D) H-C-O-C-H: This represents an ether (methoxymethane), not ethanol.
The key features of ethanol’s structure are:
- Two carbon atoms with single bonds
- An -OH (hydroxyl) functional group
- No double or triple bonds
Topic – 11.1
Which statement describes a homologous series?
A) a family of elements in the same group of the Periodic Table
B) a family of elements with similar chemical properties
C) a family of compounds with the same functional group
D) a family of compounds with similar physical properties
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
A homologous series is a family of organic compounds that:
- Have the same functional group
- Show a gradual change in physical properties
- Have similar chemical properties
- Differ by a CH2 unit in their molecular formulae
Key points:
- Option A describes groups in the Periodic Table, not homologous series
- Option B is partially correct but too vague – it’s about compounds, not elements
- Option D is partially correct but not the complete definition
- Option C is the most accurate as the functional group defines the series (e.g., alcohols, alkanes)
Examples of homologous series include alkanes (CH4, C2H6, etc.) and alcohols (CH3OH, C2H5OH, etc.).
Topic – 11.7
What are the properties of aqueous ethanoic acid?
| decolourises aqueous bromine | reacts with calcium carbonate to make carbon dioxide | turns damp red litmus paper blue | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| B | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| C | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| D | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each property of aqueous ethanoic acid:
1. Decolourises aqueous bromine: Ethanoic acid does not decolourise bromine water as it doesn’t have any double bonds (unlike unsaturated compounds). So this should be ✗.
2. Reacts with calcium carbonate: Ethanoic acid is a weak acid but will react with calcium carbonate to produce carbon dioxide gas. This is ✓.
3. Turns damp red litmus blue: Acids turn blue litmus red, not the other way around. So this should be ✗.
Only option C matches all these observations (✗, ✓, ✗).
Topic – 12.4
Four different organic compounds are separated by a fractionating column.
The table shows the boiling points of the compounds.
The diagram shows the position in the fractionating column where they are separated.
| compound | boiling point/°C |
|---|---|
| Q | 69 |
| R | 196 |
| S | 90 |
| T | 125 |
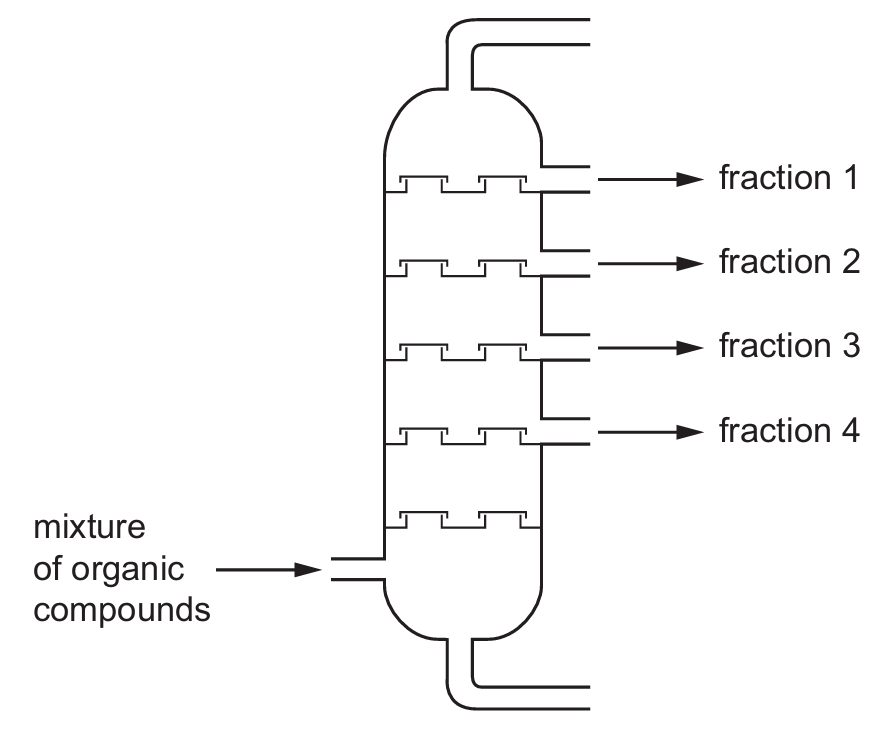
Which row identifies the compound in each fraction?
| fraction 1 | fraction 2 | fraction 3 | fraction 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Q | S | T | R |
| B | Q | T | S | R |
| C | R | T | S | Q |
| D | R | S | T | Q |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
In fractional distillation, compounds with the lowest boiling points come off first (at the top of the column), while those with higher boiling points come off later (at the bottom).
Ordering the compounds by boiling point:
1. Q (69°C) – lowest boiling point, comes first
2. S (90°C)
3. T (125°C)
4. R (196°C) – highest boiling point, comes last
This matches option A where the fractions are ordered Q → S → T → R.
The diagram shows fraction 1 at the top (lowest boiling point) through to fraction 4 at the bottom (highest boiling point).
Topic – 12.1
Which piece of apparatus is used to measure exactly 21.50 cm3 of dilute sulfuric acid?
A) beaker
B) burette
C) measuring cylinder
D) volumetric pipette
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s evaluate each option:
A) Beaker: Not precise, only used for rough measurements.
B) Burette: Can measure variable volumes accurately to ±0.05 cm³, perfect for measuring exactly 21.50 cm³.
C) Measuring cylinder: Less precise than a burette, typically accurate to ±0.5 cm³.
D) Volumetric pipette: Only measures fixed volumes (like 25.00 cm³), can’t measure 21.50 cm³.
The burette is the only apparatus that can measure an exact volume like 21.50 cm³ with high precision.
Topic – 12.2
Which row shows an advantage and a disadvantage for the stated apparatus used in a titration?
| apparatus | advantage | disadvantage | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 25 cm3 volumetric pipette | measures volume accurately | can only be used to measure 25 cm3 of solution |
| B | 50 cm3 burette | measures volume accurately | can only be used to measure 50 cm3 of solution |
| C | 100 cm3 beaker | suitable for filling burette | can only be used to fill a 100 cm3 burette |
| D | 250 cm3 conical flask | allows solutions to be mixed without spilling | not suitable for holding volumes less than 250 cm3 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze each option:
Option A: Correct. A volumetric pipette measures exact volumes (like 25.00 cm³) very accurately, but can only measure its fixed volume.
Option B: Incorrect. A burette can measure variable volumes accurately, not limited to 50 cm³ (it can measure any volume up to 50 cm³).
Option C: Incorrect. Beakers aren’t accurate measuring devices, and their disadvantage isn’t limited to filling 100 cm³ burettes.
Option D: Incorrect. Conical flasks can hold volumes less than 250 cm³ perfectly well.
Only option A correctly states both an accurate advantage and limitation of the volumetric pipette.
Topic – 12.4
Sample M contains calcium carbonate and sodium nitrate.
The result of adding water to M, stirring and filtering is shown.
No chemical reaction occurs.
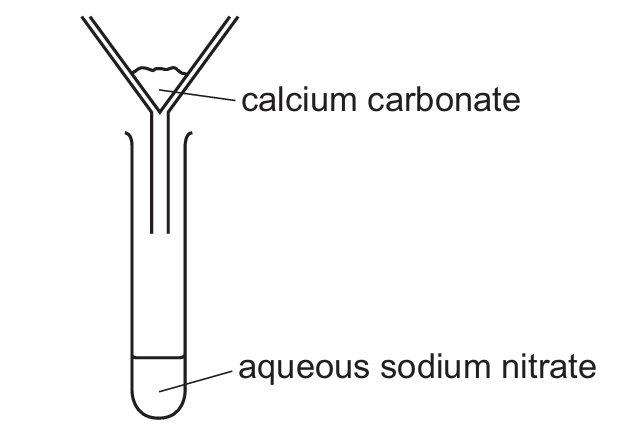
Which terms describe M, calcium carbonate and aqueous sodium nitrate?
| sample M | calcium carbonate | aqueous sodium nitrate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | compound | filtrate | residue |
| B | compound | residue | filtrate |
| C | mixture | filtrate | residue |
| D | mixture | residue | filtrate |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s analyze each component:
1. Sample M: Since it contains two different substances (calcium carbonate and sodium nitrate) physically mixed together, it’s a mixture, not a compound.
2. Calcium carbonate: Insoluble in water, so it remains as the solid residue after filtration.
3. Aqueous sodium nitrate: Soluble in water, so it passes through the filter paper to become the filtrate.
This matches option D where:
– M is a mixture
– Calcium carbonate is the residue
– Aqueous sodium nitrate is the filtrate
The key points are that no chemical reaction occurred (just physical separation) and calcium carbonate is insoluble while sodium nitrate is soluble.
