Topic – 1.1
Which conditions cause gas particles to move the fastest and the furthest apart?
| temperature | pressure | |
|---|---|---|
| A | high | high |
| B | low | high |
| C | high | low |
| D | low | low |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Gas particles move fastest at high temperatures because temperature is directly related to the kinetic energy of particles. At higher temperatures, particles have more energy and move faster.
Particles move furthest apart at low pressures because there’s more space between them when the pressure is reduced. High pressure forces particles closer together.
Therefore, the combination that causes gas particles to move fastest and furthest apart is high temperature and low pressure.
Topic – 1.1
Which statement describes a liquid at room temperature?
A) A sample of a liquid has a fixed volume and shape.
B) A sample of a liquid does not have a fixed volume or shape.
C) The particles are touching but can move by sliding over each other.
D) The particles spread out and fill all available space.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each option:
A) Incorrect – Liquids have fixed volume but not fixed shape (they take the shape of their container).
B) Incorrect – Liquids do have fixed volume, though they don’t have fixed shape.
C) Correct – This accurately describes the particle arrangement and movement in liquids. The particles are close together (touching) but can move past one another.
D) Incorrect – This describes gas particles, not liquid particles.
Topic – 1.1
A compound, X, has a melting point of 71°C and a boiling point of 375°C.
Which statement about X is correct?
A) It is a liquid at 52°C and a gas at 175°C.
B) It is a liquid at 69°C and a gas at 380°C.
C) It is a liquid at 75°C and a gas at 350°C.
D) It is a liquid at 80°C and a gas at 400°C.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
To determine the state of a substance at different temperatures, we compare the given temperature to its melting and boiling points:
- Below melting point: solid
- Between melting and boiling points: liquid
- Above boiling point: gas
Analyzing each option:
A) 52°C is below melting point (should be solid), 175°C is below boiling point (should be liquid). Incorrect.
B) 69°C is below melting point (should be solid), 380°C is just above boiling point (correct for gas). Partially correct but not fully.
C) 75°C is above melting point (correct for liquid), but 350°C is below boiling point (should be liquid, not gas). Incorrect.
D) 80°C is above melting point (correct for liquid), 400°C is above boiling point (correct for gas). Fully correct.
Topic – 2.2
What is the nucleon number of an atom?
A) the number of neutrons
B) the number of protons
C) the total number of protons and neutrons
D) the total number of protons and electrons
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The nucleon number (also called mass number) of an atom is defined as the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Let’s analyze each option:
A) Incorrect – This describes only the neutron number.
B) Incorrect – This describes the atomic number (proton number).
C) Correct – This is the exact definition of nucleon number.
D) Incorrect – This would include electrons, which are not part of the nucleus (hence not nucleons).
Topic – 2.2
An atom has three electron shells. There are three electrons in the outer shell.
How many protons and how many neutrons are in this atom?
| protons | neutrons | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 13 | 14 |
| B | 13 | 27 |
| C | 14 | 13 |
| D | 21 | 24 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
To solve this, we need to determine the element based on its electron configuration:
- Three electron shells means it’s in period 3 of the periodic table.
- Three electrons in the outer shell means it’s in Group 13 (or III).
- The element with this configuration is aluminum (Al), which has:
- Atomic number (protons) = 13
- Most common isotope has 14 neutrons (mass number 27)
Looking at the options:
A) Correct – Matches aluminum’s proton and neutron numbers.
B) Incorrect – Neutron number can’t be 27 (that would be the mass number).
C) Incorrect – 14 protons would be silicon (Group 14).
D) Incorrect – 21 protons would be scandium (a transition metal).
Topic – 2.5
Which row gives the number of covalent bonds in one molecule of ammonia and in one molecule of hydrogen chloride?
| ammonia | hydrogen chloride | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 3 | 1 |
| B | 3 | 2 |
| C | 4 | 1 |
| D | 4 | 2 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Ammonia (NH₃) has 3 covalent bonds – one between nitrogen and each hydrogen atom. Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons and forms 3 single bonds, leaving one lone pair.
Hydrogen chloride (HCl) has just 1 covalent bond between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms. Hydrogen can only form one bond, and chlorine needs just one more electron to complete its outer shell.
Therefore, the correct combination is 3 bonds in ammonia and 1 bond in hydrogen chloride.
Topic – 2.6
Which statements about the structure and bonding in diamond are correct?
- Each carbon atom in diamond is bonded to three other carbon atoms only.
- Diamond contains many strong covalent bonds.
- Diamond contains layers of carbon atoms, which can slide over each other.
- Diamond has a giant structure.
A) 1, 2 and 3
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 2 and 4
D) 4 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each statement:
1. Incorrect – Each carbon atom in diamond is actually bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
2. Correct – Diamond does contain many strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms, which is why it’s so hard.
3. Incorrect – This describes graphite, not diamond. Diamond has a 3D network structure, not layers.
4. Correct – Diamond does have a giant covalent structure where all atoms are connected by covalent bonds.
Therefore, only statements 2 and 4 are correct.
Topic – 3.3
Magnesium burns in oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
The equation for the reaction is shown.
\[ 2\text{Mg} + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{MgO} \]
Which mass of magnesium oxide is formed when 48 g of magnesium is burned?
A) 20 g
B) 40 g
C) 80 g
D) 160 g
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
First, calculate the moles of magnesium used:
Molar mass of Mg = 24 g/mol
Moles of Mg = 48 g ÷ 24 g/mol = 2 moles
From the equation, 2 moles of Mg produce 2 moles of MgO (1:1 ratio)
Molar mass of MgO = 24 (Mg) + 16 (O) = 40 g/mol
Mass of MgO formed = 2 moles × 40 g/mol = 80 g
Therefore, 80 g of magnesium oxide is formed when 48 g of magnesium is burned.
Topic – 11.3
Propane, \( C_3H_8 \), is burned in a limited amount of oxygen.
Which equation represents this reaction?
A) \( C_3H_8 + 5O_2 \rightarrow 3CO_2 + 4H_2O \)
B) \( C_3H_8 + 4O_2 \rightarrow 3CO + 4H_2O \)
C) \( C_3H_8 + 4O_2 \rightarrow 3CO_2 + 2H_2O + 2H_2 \)
D) \( 2C_3H_8 + 7O_2 \rightarrow 6CO + 8H_2O \)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
When propane burns in limited oxygen, incomplete combustion occurs, producing carbon monoxide (CO) instead of carbon dioxide (CO₂).
Option A shows complete combustion, which doesn’t occur with limited oxygen.
Option B is incorrect because it shows 4O₂ but forms CO₂ (should be CO with limited oxygen).
Option C is incorrect because it shows a mixture of CO₂ and H₂, which doesn’t represent typical incomplete combustion products.
Option D correctly shows the incomplete combustion of propane with limited oxygen, producing carbon monoxide and water.
The equation is balanced with 6 carbon atoms, 16 hydrogen atoms, and 14 oxygen atoms on both sides.
Topic – 2.3
The isotope of which element is used to define the relative atomic mass of other elements?
A) sulfur
B) oxygen
C) nitrogen
D) carbon
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The standard for atomic masses is based on the carbon-12 isotope (¹²C).
Carbon-12 is defined as having an atomic mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu).
All other elements’ atomic masses are measured relative to 1/12th the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
This standard was adopted because:
- Carbon forms many compounds, making it useful for mass spectrometry
- Carbon-12 is abundant and stable
- It provides a convenient reference point for the atomic mass scale
Previously, oxygen was used as the standard, but carbon-12 was adopted in 1961 for greater consistency and precision.
Topic – 4.1
What is the definition of electrolysis?
A) the formation of a positive ion by the removal of electrons using an electric current
B) the decomposition of an ionic compound, when molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of an electric current
C) the substance containing ions through which an electric current can pass
D) the coating of a metal with a different metal by passing an electric current through an aqueous solution of an ionic salt
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Electrolysis is specifically defined as the decomposition of an ionic compound (when molten or in aqueous solution) by passing an electric current through it. This process causes the compound to break down into its constituent elements or simpler compounds. Option A describes ionization, option C describes an electrolyte, and option D describes electroplating, which is an application of electrolysis but not its definition.
Topic – 4.1
Which statement about electroplating a copper spoon with silver is correct?
A) Both the anode and cathode are made of carbon.
B) The copper spoon is the anode.
C) Aqueous copper(II) sulfate is the electrolyte.
D) Silver is formed at the negative electrode.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In electroplating, the object to be plated (copper spoon) must be the cathode (negative electrode), where reduction occurs and silver ions gain electrons to form silver metal. The anode is typically made of the plating metal (silver in this case), not carbon. The electrolyte must contain ions of the plating metal (silver nitrate solution would be used, not copper(II) sulfate). Therefore, the only correct statement is that silver is formed at the negative electrode (cathode).
Topic – 5.1
Which row describes the reaction pathway diagram and energy change in an exothermic reaction?
| reaction pathway diagram | energy is | |
|---|---|---|
| A | reactants higher than products | absorbed |
| B | reactants higher than products | released |
| C | reactants lower than products | absorbed |
| D | reactants lower than products | released |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
In an exothermic reaction, the reactants have more energy than the products, so the reaction pathway diagram shows reactants at a higher energy level than products. Energy is released to the surroundings in an exothermic reaction (often as heat). Therefore, the correct combination is: reactants higher than products and energy is released. Option A describes an endothermic reaction where energy is absorbed, and options C and D have the energy levels reversed.
Topic – 5.1
The table shows the initial and final temperatures for four different reactions.
| reaction | initial temperature/°C | final temperature/°C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19 | 28 |
| 2 | 18 | 16 |
| 3 | 20 | 20 |
| 4 | 18 | 19 |
Which reactions are endothermic?
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 3
C) 2 only
D) 4 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
An endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings, causing the temperature to decrease. Only reaction 2 shows a temperature decrease (from 18°C to 16°C). Reaction 1 shows a temperature increase (exothermic), reaction 3 shows no change (possibly no reaction or perfect insulation), and reaction 4 shows a slight increase (exothermic). Therefore, only reaction 2 is endothermic.
Topic – 6.1
Which process is a chemical change?
A) boiling water
B) cooking an egg
C) dissolving sugar
D) melting ice cubes
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
A chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties. Cooking an egg involves the denaturation of proteins (irreversible change), which is a chemical change. Boiling water (A) and melting ice (D) are both physical changes as they only change the state of matter. Dissolving sugar (C) is also a physical change because the sugar molecules remain unchanged and can be recovered by evaporation.
Topic – 6.2
A student reacts strips of zinc with dilute sulfuric acid and measures the time taken to produce 100 cm3 of hydrogen.
The experiment is repeated using different conditions.
The results are shown in the table.
| experiment | time to produce 100 cm3 of hydrogen/s |
|---|---|
| 1 | 250 |
| 2 | 100 |
Which changes in conditions produce the results shown in experiment 2?
- Add a catalyst.
- Dilute the acid.
- Use zinc powder.
- Heat the acid.
A) 1, 3 and 4
B) 1 and 4 only
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
To understand why option A is correct, let’s analyze each condition:
1. Adding a catalyst increases the reaction rate by providing an alternative pathway with lower activation energy.
2. Diluting the acid would actually slow down the reaction (decrease rate), so this can’t be correct.
3. Using zinc powder increases the surface area, which increases the reaction rate.
4. Heating the acid provides more energy to the particles, increasing their collision frequency and energy.
Since experiment 2 shows a faster reaction (100s vs 250s), we need conditions that increase the rate. Only options 1, 3, and 4 would increase the rate, making A the correct answer.
Topic – 6.3
When blue copper(II) sulfate is heated, a white solid and water are formed.
The white solid turns blue and gives out heat when water is added to it.
Which terms describe the blue copper(II) sulfate and the reactions?
| blue copper(II) sulfate is | reactions | |
|---|---|---|
| A | a mixture | can be reversed |
| B | a mixture | cannot be reversed |
| C | hydrated | can be reversed |
| D | hydrated | cannot be reversed |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The blue copper(II) sulfate is hydrated copper sulfate (CuSO4·5H2O), which contains water molecules in its crystal structure. When heated, it loses water to form anhydrous white copper(II) sulfate (CuSO4).
The reaction is reversible because adding water to the white anhydrous copper(II) sulfate reforms the blue hydrated form. The heat given out when water is added indicates the reverse reaction is exothermic.
This makes option C correct: the original blue substance is hydrated, and the reactions can be reversed by adding or removing water.
Topic – 6.4
Which statements about a redox reaction are correct?
- Oxidation is the gain of oxygen.
- Both oxidation and reduction take place in a redox reaction.
- Reduction is the gain of oxygen.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 only
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s evaluate each statement:
1. Correct – Oxidation can be defined as gain of oxygen (though it’s more accurately loss of electrons).
2. Correct – Redox reactions always involve both oxidation and reduction occurring simultaneously.
3. Incorrect – Reduction is actually the loss of oxygen (or gain of electrons/hydrogen).
Therefore, only statements 1 and 2 are correct, making option A the right answer.
Topic – 7.2
Which row identifies a basic oxide and describes an alkali?
| basic oxide | description of an alkali | |
|---|---|---|
| A | sodium oxide | insoluble base |
| B | sodium oxide | soluble base |
| C | sulfur dioxide | insoluble base |
| D | sulfur dioxide | soluble base |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Sodium oxide (Na2O) is a basic oxide because it reacts with acids to form salts and water. Basic oxides are typically formed by metals.
An alkali is specifically defined as a soluble base. Therefore, the correct description is “soluble base”.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is actually an acidic oxide, not basic, as it forms sulfurous acid when dissolved in water. This eliminates options C and D.
Between A and B, the key difference is the description of alkali. Since alkalis are soluble bases, option B is correct.
Topic – 7.1
Which indicators turn blue when added to aqueous ammonia?
- litmus
- thymolphthalein
- universal indicator
A) 1, 2 and 3
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 2 and 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Aqueous ammonia is a weak alkali (pH about 11). Let’s examine each indicator:
1. Litmus turns blue in alkaline solutions (pH > 7).
2. Thymolphthalein is colorless in acidic and neutral solutions but turns blue in alkaline solutions (pH > 9.3).
3. Universal indicator turns blue/purple in alkaline solutions, depending on the pH.
Since all three indicators turn blue (or bluish colors) in alkaline solutions like aqueous ammonia, the correct answer is A (1, 2, and 3).
Topic – 7.1
Ammonium chloride reacts with solution X to produce alkaline gas Y. The equation is shown.
ammonium chloride + solution X → alkaline gas Y
Which row identifies X and Y?
| X | Y | |
|---|---|---|
| A | hydrochloric acid | ammonia |
| B | hydrochloric acid | chlorine |
| C | sodium hydroxide | ammonia |
| D | sodium hydroxide | chlorine |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Ammonium chloride reacts with sodium hydroxide (a base) to produce ammonia gas (NH₃), which is alkaline. This is a typical test for ammonium ions. The reaction is:
NH₄Cl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O + NH₃
Hydrochloric acid (options A and B) would not produce an alkaline gas, and chlorine (options B and D) is not alkaline. Therefore, the correct combination is sodium hydroxide (X) and ammonia (Y).
Topic – 7.3
The solubility of some salts is shown.
| chloride | nitrate | sulfate | carbonate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| barium | soluble | soluble | insoluble | insoluble |
| lead(II) | insoluble | soluble | insoluble | insoluble |
| potassium | soluble | soluble | soluble | soluble |
| zinc | soluble | soluble | soluble | insoluble |
Which two aqueous solutions produce an insoluble salt when mixed together?
A) barium chloride and zinc nitrate
B) barium nitrate and lead(II) nitrate
C) lead(II) nitrate and potassium carbonate
D) potassium nitrate and zinc sulfate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
To find which pair produces an insoluble salt, we need to check the solubility of the possible products:
Option C: lead(II) nitrate + potassium carbonate → lead(II) carbonate + potassium nitrate
From the table, lead(II) carbonate is insoluble (lead(II) carbonates are generally insoluble). Potassium nitrate is soluble (all potassium salts are soluble). Therefore, this mixture will produce an insoluble salt (lead(II) carbonate).
The other options:
A) All products (barium nitrate and zinc chloride) are soluble
B) Both barium nitrate and lead(II) nitrate are soluble
D) Both potassium nitrate and zinc sulfate are soluble
Topic – 8.3
The table shows some properties of the halogens.
| halogen | melting point /°C | colour at room temperature | state at room temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| chlorine | −101 | yellow-green | gas |
| bromine | −7 | red-brown | liquid |
| iodine | 114 | grey-black | solid |
| astatine |
Which statement describes astatine?
A) It is a yellow gas at room temperature.
B) It is a black liquid at room temperature.
C) Its melting point is higher than the melting point of bromine but lower than that of chlorine.
D) Its melting point is higher than the melting point of both iodine and bromine.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Looking at the trends in the halogen group:
1. As we go down the group (from chlorine to iodine to astatine), melting points increase.
2. The states at room temperature progress from gas (chlorine) to liquid (bromine) to solid (iodine). Astatine, being below iodine, would also be solid.
3. Colors darken down the group (yellow-green → red-brown → grey-black). Astatine would be darker than iodine.
Therefore:
A) Incorrect – astatine is not a gas
B) Incorrect – astatine is a solid, not liquid
C) Incorrect – astatine’s melting point would be higher than iodine’s (114°C), so higher than bromine’s (-7°C)
D) Correct – astatine’s melting point would be higher than both iodine (114°C) and bromine (-7°C)
Topic – 8.2
J, L and M are elements in the Periodic Table.
- J has the highest density.
- L has the highest reactivity with water.
- M has the highest atomic number.
Which row identifies the elements J, L and M?
| J | L | M | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | copper | lithium | bromine |
| B | lithium | copper | bromine |
| C | bromine | copper | lithium |
| D | copper | bromine | lithium |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze each characteristic:
1. Highest density (J): Copper (8.96 g/cm³) has higher density than lithium (0.534 g/cm³) and bromine (3.12 g/cm³).
2. Highest reactivity with water (L): Lithium (Group I metal) is much more reactive with water than copper (which doesn’t react with water) or bromine (a halogen).
3. Highest atomic number (M): Bromine (35) has higher atomic number than copper (29) and lithium (3).
Therefore, the correct identification is:
J = copper, L = lithium, M = bromine → Option A.
Topic – 8.2
Which statement about elements in Group I of the Periodic Table is correct?
A) Rubidium has a greater density than caesium.
B) Lithium has a higher melting point than potassium.
C) Potassium is more reactive than rubidium.
D) Rubidium atoms have more outer shell electrons than sodium atoms.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Let’s evaluate each statement:
A) Incorrect – Density increases down Group I, so caesium has greater density than rubidium.
B) Correct – Melting points decrease down Group I. Lithium (180°C) has higher melting point than potassium (63°C).
C) Incorrect – Reactivity increases down Group I, so rubidium is more reactive than potassium.
D) Incorrect – All Group I elements have 1 outer shell electron, regardless of their position in the group.
Topic – 8.5
Which diagram shows a mixture of noble gases?
A) 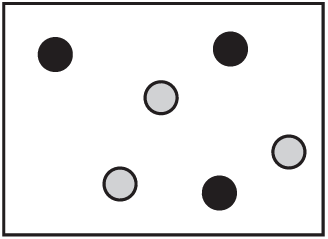
B) 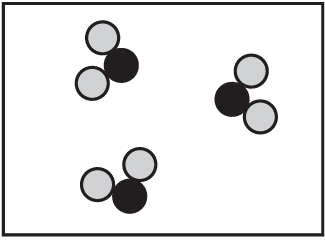
C) 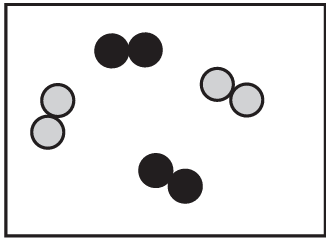
D) 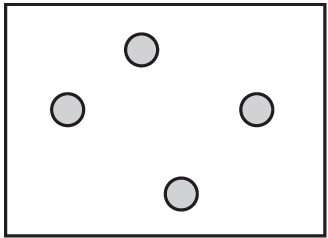
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Noble gases are monatomic elements that don’t form molecules or compounds with each other. A mixture of noble gases would show individual atoms of different noble gas elements (like helium, neon, argon) mixed together without any chemical bonding between them. This is best represented by diagram A.
The other diagrams likely show either compounds (where atoms are bonded together) or pure elements rather than mixtures.
Topic – 9.3
Which statements about the alloy brass are correct?
- It is harder than pure copper.
- It does not conduct electricity.
- It is a mixture of copper and nickel.
- It is stronger than pure copper.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc (not nickel, so statement 3 is incorrect).
Statement 1 is correct – alloys are generally harder than their pure metal components because the different sized atoms disrupt the regular structure, making it more difficult for layers to slide over each other.
Statement 2 is incorrect – brass, like most metals and alloys, conducts electricity well.
Statement 4 is correct – alloys are generally stronger than their pure metal components for the same reason they’re harder.
Therefore, the correct statements are 1 and 4 (option B).
Topic – 9.2
The bodies of aircraft are often made using aluminium.
Which two properties of aluminium make it suitable for this use?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
For aircraft construction, the most important properties are:
1. Low density (lightweight) – to minimize the weight of the aircraft, which is crucial for flight efficiency.
2. Strength – to withstand the stresses of flight and maintain structural integrity.
While aluminum does conduct electricity and heat well, these properties aren’t the primary reasons for its use in aircraft bodies. The combination of strength and low density (option D) makes it ideal for this application.
Topic – 9.4
Four metals, P, Q, R and S, are added separately to water and to dilute hydrochloric acid.
The table shows the results.
| observation with water | observation with dilute hydrochloric acid | |
|---|---|---|
| P | no reaction | fizzes slowly |
| Q | fizzes rapidly | fizzes rapidly |
| R | no reaction | no reaction |
| S | fizzes slowly | fizzes rapidly |
Which conclusion can be made from these observations?
A) P is the least reactive of the four metals.
B) Q is more reactive than S.
C) Q is less reactive than P.
D) R is the most reactive of the four metals.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
From the observations, we can deduce the reactivity order:
1. Q reacts rapidly with both water and acid, indicating it’s the most reactive.
2. S reacts slowly with water but rapidly with acid, making it less reactive than Q but more reactive than P.
3. P only reacts with acid (and slowly), making it less reactive than both Q and S.
4. R doesn’t react with either, making it the least reactive.
Therefore, the correct conclusion is B: Q is more reactive than S. The other options are incorrect because:
A) P isn’t the least reactive (R is)
C) Q is more reactive than P
D) R is actually the least reactive
Topic – 9.6
Iron is extracted from its ore in the blast furnace.
Which statement about one of the reactions in the blast furnace is correct?
A) Carbon monoxide is reduced to carbon dioxide.
B) Iron(III) oxide is reduced by carbon dioxide.
C) Slag is produced when calcium carbonate reacts with carbon dioxide.
D) The reaction that heats the blast furnace produces carbon dioxide.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In the blast furnace:
A) Incorrect – Carbon monoxide is oxidized to carbon dioxide when it reduces iron(III) oxide, not reduced.
B) Incorrect – Iron(III) oxide is reduced by carbon monoxide, not carbon dioxide.
C) Incorrect – Slag is produced when calcium oxide (from the decomposition of calcium carbonate) reacts with silicon dioxide (impurity).
D) Correct – The exothermic reaction of coke (carbon) with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide provides the heat needed for the process.
The key reactions are:
\( \text{C} + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow \text{CO}_2 \) (heat-producing reaction)
\( \text{CO}_2 + \text{C} \rightarrow 2\text{CO} \)
\( \text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3 + 3\text{CO} \rightarrow 2\text{Fe} + 3\text{CO}_2 \) (reduction of iron ore)
Topic – 10.1
Which pollutants found in river water lead to deoxygenation?
- nitrates
- harmful microbes
- metal compounds
- phosphates
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Nitrates (1) and phosphates (4) are nutrients that cause excessive growth of algae in water bodies. When these algae die and decompose, the process consumes oxygen from the water, leading to deoxygenation. This phenomenon is called eutrophication.
Harmful microbes (2) may cause diseases but don’t directly reduce oxygen levels. Metal compounds (3) can be toxic but don’t typically cause deoxygenation. Therefore, the correct combination is 1 and 4, which corresponds to option B.
Topic – 10.3
Three effects of air pollutants are listed.
- photochemical smog
- respiratory problems
- acid rain
Which effects are caused by oxides of nitrogen?
A) 1, 2 and 3
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 1 only
D) 2 and 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) contribute to all three effects:
1. Photochemical smog – NOx reacts with volatile organic compounds in sunlight to form smog.
2. Respiratory problems – NOx irritates lungs and can worsen conditions like asthma.
3. Acid rain – NOx reacts with water vapor to form nitric acid, a component of acid rain.
Therefore, all three effects (1, 2, and 3) are caused by oxides of nitrogen, making option A correct.
Topic – 11.3
Fractional distillation is used to separate petroleum into its fractions.
Which statement about the fractional distillation of petroleum is correct?
A) The kerosene fraction is used as a fuel for ships.
B) The fractions with the highest boiling points are extracted from the top of the fractionating column.
C) The naphtha fraction contains larger hydrocarbon molecules than the lubricating oil fraction.
D) The refinery gas fraction contains hydrocarbon molecules which consist of five atoms.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s analyze each option:
A) Incorrect – The fuel for ships is typically the heavier fuel oil fraction, not kerosene.
B) Incorrect – Fractions with higher boiling points condense at the bottom of the column, not the top.
C) Incorrect – Naphtha contains smaller molecules (C5-C10) than lubricating oil (C20-C50).
D) Correct – Refinery gas contains small molecules like methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10), which have 5 atoms (e.g., C3H8 has 3+8=11 atoms, so this might be misleading. Actually, the smallest molecules in refinery gas have 5 atoms (CH4 has 5). The answer key indicates D is correct, though the statement isn’t entirely accurate for all components.
Topic – 10.2
Fertilisers are mixtures of different compounds used to increase the growth of crops.
Which pair of substances contain the three essential elements for plant growth?
A) ammonium nitrate and calcium phosphate
B) ammonium nitrate and potassium chloride
C) ammonium phosphate and potassium chloride
D) potassium nitrate and calcium carbonate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The three essential elements for plant growth are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Let’s analyze the options:
A) NH4NO3 (N) + Ca3(PO4)2 (P) – Missing K
B) NH4NO3 (N) + KCl (K) – Missing P
C) (NH4)3PO4 (N and P) + KCl (K) – Contains all three
D) KNO3 (N and K) + CaCO3 – Missing P
Only option C provides all three essential elements: nitrogen from ammonium, phosphorus from phosphate, and potassium from potassium chloride.
Topic – 11.4
Which row gives the relative molecular mass, \( M_r \), of the first member of the named homologous series?
| homologous series | \( M_r \) | |
|---|---|---|
| A | alkanes | 12 |
| B | alkenes | 14 |
| C | alcohols | 32 |
| D | carboxylic acids | 60 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s calculate the relative molecular mass for the first member of each series:
Alkanes (A): Methane (CH4) = 12 + (1×4) = 16 (not 12)
Alkenes (B): Ethene (C2H4) = (12×2) + (1×4) = 28 (not 14)
Alcohols (C): Methanol (CH3OH) = 12 + (1×3) + 16 + 1 = 32 (correct)
Carboxylic acids (D): Methanoic acid (HCOOH) = 1 + 12 + 16 + 16 + 1 = 46 (not 60)
Only option C gives the correct \( M_r \) for the first member of its homologous series (methanol in the alcohol series).
Topic – 11.5
A hydrocarbon decolourises bromine water.
Which statement about the hydrocarbon is correct?
A) It is an alkane.
B) Its molecular formula is \( C_2H_6 \).
C) It is a saturated hydrocarbon.
D) It has the general formula \( C_nH_{2n} \).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The key information here is that the hydrocarbon decolourises bromine water. This is a characteristic reaction of unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkenes) which can undergo addition reactions with bromine. Alkanes (option A) are saturated and don’t react with bromine water. Option B describes ethane which is an alkane. Option C is incorrect because saturated hydrocarbons don’t decolourise bromine water. Option D is correct because alkenes have the general formula \( C_nH_{2n} \) and react with bromine water.
Topic – 11.6
Which statement describes how ethanol is manufactured from ethene?
A) Steam is added to ethene using an acid catalyst at 30 °C.
B) Steam is added to ethene using an acid catalyst at 300 °C.
C) Ethene is fermented using yeast at 30 °C.
D) Ethene is fermented using yeast at 300 °C.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Ethanol can be produced from ethene through hydration, where steam is added to ethene in the presence of an acid catalyst (usually phosphoric acid) at high temperature (around 300°C). This is an industrial method of ethanol production. Options C and D are incorrect because fermentation uses sugars, not ethene. Option A has the right reactants but the temperature is too low – 30°C would be appropriate for fermentation but not for the hydration of ethene.
Topic – 11.7
Ethanoic acid reacts with aqueous sodium carbonate.
Which gas is given off in this reaction?
A) hydrogen
B) carbon dioxide
C) carbon monoxide
D) oxygen
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
When ethanoic acid (a weak acid) reacts with sodium carbonate (a base), a neutralization reaction occurs producing sodium ethanoate, water, and carbon dioxide gas. The reaction can be represented as: \( 2CH_3COOH + Na_2CO_3 \rightarrow 2CH_3COONa + H_2O + CO_2 \). This is a standard test for carboxylic acids – they produce effervescence (bubbles) of carbon dioxide when reacted with carbonates. The other gases listed are not products of this reaction.
Topic – 12.4
A mixture containing an aqueous salt, sand and hot water is stirred.
The mixture is then poured into the apparatus shown.
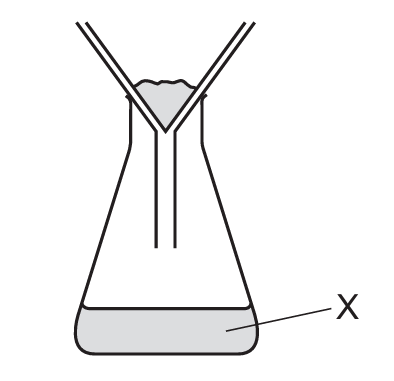
What is X?
A) a filtrate only
B) a residue only
C) a solute only
D) a solvent only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The described process is filtration. When the mixture is poured into the filtration apparatus, the sand (insoluble solid) will be trapped by the filter paper as the residue, while the aqueous salt solution (filtrate) passes through. X refers to what comes through the filter paper, which is the filtrate – the liquid containing the dissolved salt. It’s not just the solvent (water) because it contains the dissolved salt, and it’s not the solute only because that would imply pure salt without water. The residue (sand) remains in the filter paper.
Topic – 12.2
A scientist uses a titration to calculate the concentration of acid in a sample of lemon juice.
A measured volume of aqueous lemon juice and a few drops of an indicator are added to a flask.
The aqueous lemon juice is then titrated against 0.1 mol/dm³ aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Which piece of apparatus is used to add the aqueous sodium hydroxide to the flask?
A) a burette
B) a delivery tube
C) a measuring cylinder
D) a volumetric pipette
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
In a titration, the solution of known concentration (in this case sodium hydroxide) is always added from a burette. A burette allows precise measurement of the volume added, which is essential for calculating the unknown concentration. A delivery tube (B) is used in gas collection, not titrations. A measuring cylinder (C) isn’t precise enough for titration work. A volumetric pipette (D) is used to measure a fixed volume of solution (like the lemon juice being analyzed), not for adding the titrant.
