Topic – 1.1
A sample of ethanol is left in an open beaker at room temperature.
After 24 hours, no ethanol remains in the beaker.
What has happened to the ethanol?
A) It has boiled.
B) It has condensed.
C) It has evaporated.
D) It has frozen.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
At room temperature, ethanol is a volatile liquid that will gradually evaporate when left in an open container. Boiling requires heating to the boiling point (78°C for ethanol), condensation is the opposite process (gas to liquid), and freezing would leave solid ethanol behind. Since the ethanol completely disappeared over time without any heating, the correct answer is evaporation.
Topic – 1.1
A gas is in a sealed container with a fixed volume.
Which statements describe what happens to the molecules in the gas when the temperature is increased?
1 They move more slowly.
2 They collide with the walls of the container more frequently.
3 They collide with the walls of the container with less force.
4 They have greater kinetic energy.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
When temperature increases in a fixed volume container:
1. Gas molecules move faster, not slower (statement 1 is wrong).
2. Faster molecules collide with walls more frequently (statement 2 is correct).
3. Faster molecules collide with walls with greater force (statement 3 is wrong).
4. Higher temperature means greater average kinetic energy (statement 4 is correct).
Therefore, only statements 2 and 4 are correct.
Topic – 2.4
What happens when sodium atoms combine with chlorine atoms to form sodium chloride?
A) Sodium atoms each gain one electron, and chlorine atoms each lose one electron.
B) Sodium atoms each lose one electron, and chlorine atoms each gain one electron.
C) Sodium atoms and chlorine atoms share one electron with each other.
D) Sodium atoms and chlorine atoms share two electrons with each other.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Sodium (Na) is in Group I and has 1 valence electron, while chlorine (Cl) is in Group VII and needs 1 more electron to complete its outer shell. In ionic bonding:
– Sodium atoms lose their single valence electron to achieve a stable electron configuration (becoming Na⁺).
– Chlorine atoms gain one electron to complete their outer shell (becoming Cl⁻).
The options describing electron sharing (C and D) refer to covalent bonding, which doesn’t occur in NaCl formation.
Topic – 2.4
The table shows some properties of four substances.
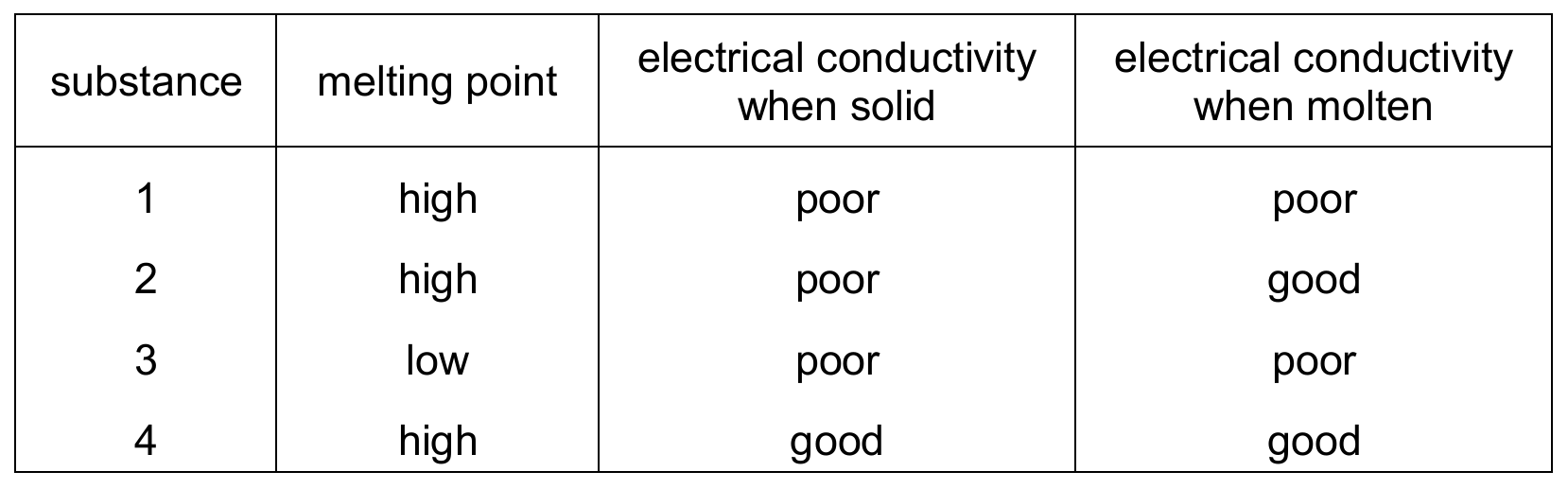
Which substances are ionic?
A) 1, 3 and 4
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Ionic compounds typically have:
1. High melting points (eliminates substance 3)
2. Poor conductivity when solid (ions can’t move)
3. Good conductivity when molten (ions are free to move)
Only substance 2 fits all these criteria. Substance 4 conducts in solid state, suggesting metallic bonding. Substance 1 is likely covalent (poor conductor in both states). Therefore, only substance 2 is ionic.
Topic – 2.5
Which statement about methane is correct?
A) In methane, positive hydrogen ions are attracted to negative carbon ions.
B) In methane, electrons are shared between carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms.
C) Methane has a high boiling point.
D) Methane is a good conductor of electricity.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Methane (CH₄) is a covalent compound where:
– Carbon shares electrons with four hydrogen atoms (statement B is correct).
– There are no ions involved (statement A is wrong).
– As a simple molecular substance, it has low boiling point (statement C is wrong).
– Covalent compounds don’t conduct electricity (statement D is wrong).
The correct statement describes the covalent bonding in methane through electron sharing.
Topic – 2.3
A sample of iridium has a relative atomic mass of 192.29.
The sample contains two isotopes only.
64.50% of the sample is 193Ir.
What is the other isotope in the sample?
A) 189Ir
B) 190Ir
C) 191Ir
D) 192Ir
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let the other isotope be xIr. The percentage of this isotope is 100% – 64.50% = 35.50%. The relative atomic mass is the weighted average of the isotopes:
192.29 = (64.50 × 193 + 35.50 × x)/100
Solving for x: 19229 = 12448.5 + 35.5x → 6780.5 = 35.5x → x ≈ 191
Therefore, the other isotope must be 191Ir (option C). The calculation shows that only this value gives the correct weighted average.
Topic – 3.1
Ammonium iron(III) citrate contains in its formula:
- more than one ammonium ion
- one iron ion
- two C6H4O74- ions.
What is the formula of ammonium iron(III) citrate?
A) (NH4)4Fe(C6H4O7)2
B) (NH4)5Fe(C6H4O7)2
C) (NH4)6Fe(C6H4O7)2
D) (NH4)7Fe(C6H4O7)2
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Each citrate ion (C6H4O74-) carries 4- charge. With two citrate ions, total negative charge is 8-. Iron(III) contributes 3+ charge. To balance, we need 5 NH4+ ions (5 × 1+ = 5+). Total positive charge: 5+ (ammonium) + 3+ (iron) = 8+, balancing the 8- from citrate. Therefore, the correct formula is (NH4)5Fe(C6H4O7)2 (option B).
Topic – 3.1
Silicon(IV) oxide reacts with chlorine and carbon to form liquid silicon(IV) chloride, SiCl4, and carbon dioxide gas.
If the reaction is carried out at r.t.p., which symbol equation represents this reaction?
A) SiO2(l) + 2Cl2(g) + C(s) → SiCl4(l) + CO2(g)
B) SiO2(l) + 2Cl2(g) + C(g) → SiCl4(l) + CO2(g)
C) SiO2(s) + 2Cl2(g) + C(s) → SiCl4(g) + CO2(g)
D) SiO2(s) + 2Cl2(g) + C(s) → SiCl4(l) + CO2(g)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The correct equation must account for the physical states: SiO2 is solid (s), Cl2 is gas (g), carbon is solid (s), SiCl4 is liquid (l) at r.t.p., and CO2 is gas (g). Therefore, option D is correct. Option A incorrectly shows SiO2 as liquid, B shows carbon as gas (unlikely at r.t.p.), and C shows SiCl4 as gas when it should be liquid.
Topic – 3.3
The structure of ethene is shown.

How many hydrogen atoms and how many carbon atoms are in one mole of ethene?
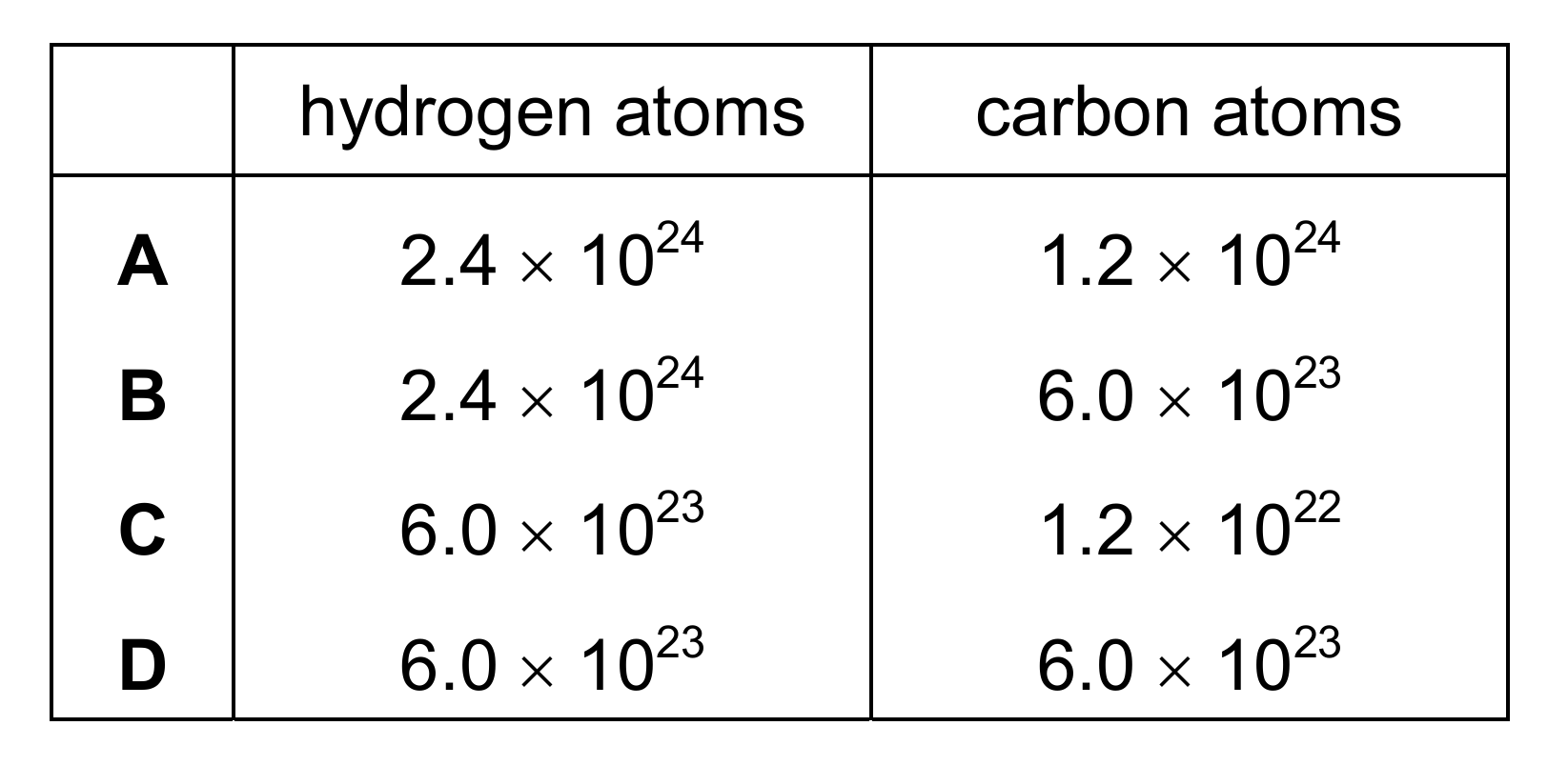
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
One mole of ethene (C2H4) contains 2 moles of carbon atoms and 4 moles of hydrogen atoms. Using Avogadro’s number (6.0 × 1023 particles per mole):
Carbon atoms: 2 × 6.0 × 1023 = 1.2 × 1024
Hydrogen atoms: 4 × 6.0 × 1023 = 2.4 × 1024
Therefore, option A is correct. The other options either miscalculate the number of atoms or don’t account for the molecular formula properly.
Topic – 12.1
A known volume and concentration of aqueous sodium hydroxide is titrated against dilute hydrochloric acid.
The volume of dilute hydrochloric acid needed to exactly neutralise the sodium hydroxide is measured.
Five calculation steps are shown.
- Calculate the amount of hydrochloric acid in moles.
- Calculate the relative formula mass of hydrochloric acid.
- Calculate the concentration of hydrochloric acid in g/dm3.
- Calculate the amount of sodium hydroxide in moles.
- Calculate the concentration of hydrochloric acid in mol/dm3.
What is the order of these steps to calculate the concentration of the hydrochloric acid in g/dm3?
A) 1 → 4 → 3 → 5 → 2
B) 1 → 2 → 4 → 5 → 3
C) 4 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 3
D) 4 → 2 → 1 → 3 → 5
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The correct order is:
- Calculate moles of NaOH (step 4)
- Use stoichiometry to find moles of HCl (step 1)
- Calculate HCl concentration in mol/dm³ (step 5)
- Find Mr of HCl (step 2)
- Convert to g/dm³ (step 3)
Therefore, the sequence is 4 → 1 → 5 → 2 → 3 (option C). You must start with the known quantity (NaOH), use the 1:1 reaction ratio, then convert between units. The other sequences either start incorrectly or perform conversions in the wrong order.
Topic – 4.1
Two different substances are electrolysed using inert electrodes in two separate experiments.
Hydrogen is produced in both experiments.
Which row identifies the two substances and the electrode at which hydrogen is produced?
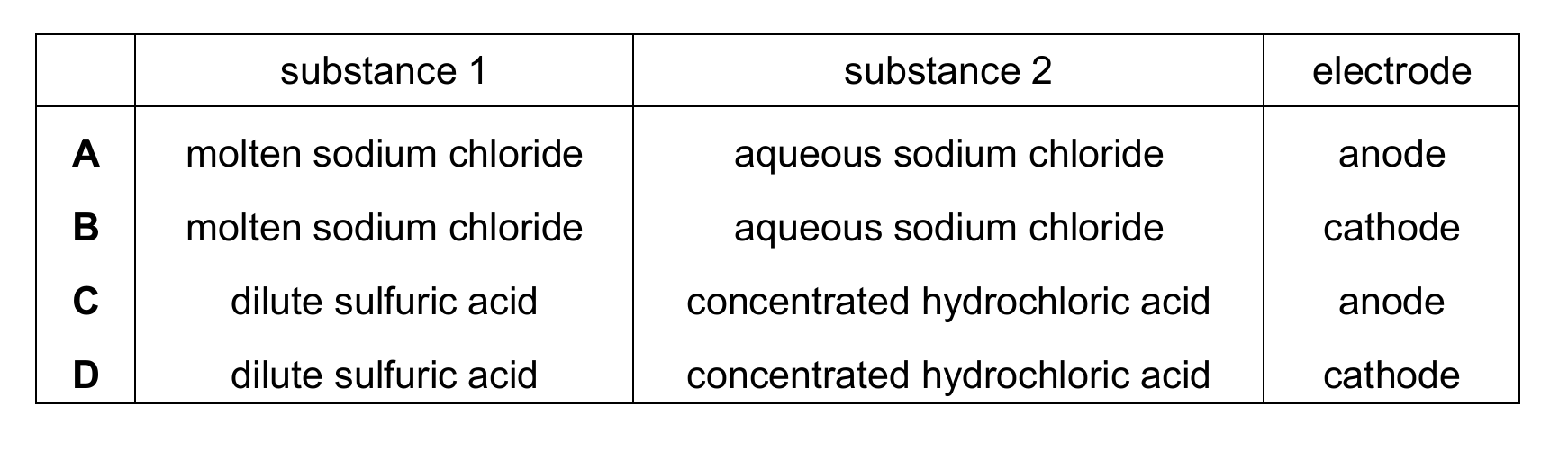
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In electrolysis, hydrogen gas is produced at the cathode through reduction of hydrogen ions (H⁺).
For dilute sulfuric acid: 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂ (at cathode)
For concentrated hydrochloric acid: 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → H₂ (at cathode)
Molten sodium chloride produces sodium metal at the cathode and chlorine gas at the anode, not hydrogen, so options A and B are incorrect.
Option C is incorrect because hydrogen is never produced at the anode.
Therefore, the correct answer is D, where both substances produce hydrogen at the cathode.
Topic – 4.1
Aqueous copper(II) sulfate can be electrolysed using either carbon electrodes or copper electrodes.
Which statement describes what happens at the positive electrode?
A) Copper is deposited if the electrode is made from carbon.
B) Copper is deposited if the electrode is made from copper.
C) Oxygen gas is produced if the electrode is made from carbon.
D) Oxygen gas is produced if the electrode is made from copper.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
In the electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) sulfate:
With inert carbon electrodes:
- At the cathode (negative electrode): Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu (copper is deposited)
- At the anode (positive electrode): 4OH⁻ → O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ (oxygen gas is produced)
With copper electrodes:
- At the cathode: Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu (copper is deposited)
- At the anode: Cu → Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ (copper dissolves)
Option A is incorrect because copper is deposited at the cathode, not the anode.
Option B is incorrect because copper dissolves at the anode when using copper electrodes.
Option D is incorrect because oxygen is only produced when using inert electrodes like carbon.
Therefore, the correct answer is C, as oxygen gas is produced at the positive carbon electrode.
Topic – 4.2
Which statement about a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell is not correct?
A) Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
B) Hydrogen is oxidised.
C) The reaction that takes place is endothermic.
D) Water is the only chemical product.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
In a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell:
1. Chemical energy is indeed converted to electrical energy (A is correct).
2. Hydrogen is oxidized at the anode: H₂ → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ (B is correct).
3. The overall reaction is exothermic, not endothermic (C is incorrect, which makes it the correct answer).
4. The only product is water: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O (D is correct).
The reaction in a fuel cell is exothermic because it releases energy (heat and electricity). The question asks for the statement that is NOT correct, which is C.
Topic – 6.2
Which reaction pathway diagram is correctly labelled?
A) 
B) 
C) 
D) 
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
A correctly labeled reaction pathway diagram should show:
- Reactants at a certain energy level
- Products at a different energy level (lower for exothermic, higher for endothermic)
- Activation energy (Eₐ) as the energy difference between reactants and the transition state
Option A is correct because:
- It clearly shows the reactants at a higher energy level than products (indicating an exothermic reaction)
- The activation energy (Eₐ) is correctly marked as the energy barrier between reactants and the transition state
- The progress of reaction is properly indicated on the x-axis
The other options likely have incorrect labeling of Eₐ or the relative positions of reactants and products.
Topic – 5.1
Which row describes a reaction where the overall energy change is exothermic?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
An exothermic reaction is characterized by:
- More energy being released in bond formation than required for bond breaking (net energy release)
- An increase in temperature of the surroundings (as energy is released to the environment)
Let’s analyze each option:
Option A: 600 kJ in, 300 kJ out → net absorption of 300 kJ (endothermic)
Option B: 600 kJ in, 1200 kJ out → net release of 600 kJ, but temperature decreases (contradicts exothermic behavior)
Option C: 900 kJ in, 300 kJ out → net absorption of 600 kJ (endothermic)
Option D: 900 kJ in, 1200 kJ out → net release of 300 kJ with temperature increase (correct for exothermic)
Therefore, only option D shows both the correct energy relationship (more energy out than in) and the correct temperature effect (increase) for an exothermic reaction.
Topic – 6.1
Which process involves a physical change only?
A) heating calcium carbonate strongly
B) burning wood
C) melting an ice cube
D) mixing an acid and a base
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
A physical change is one where the substance changes its physical state but not its chemical composition. Melting an ice cube (option C) is simply changing water from solid to liquid state without altering its chemical structure. The other options involve chemical changes: heating calcium carbonate decomposes it into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide (A), burning wood involves combustion (B), and mixing acid and base results in neutralization (D).
Topic – 6.3
In the Haber process, an equilibrium is established.
\[ \text{N}_2(g) + 3\text{H}_2(g) \rightleftharpoons 2\text{NH}_3(g) \]
The forward reaction is exothermic.
Which change to the reaction conditions will move the position of equilibrium to the left?
A) decreasing the pressure by 100 atm
B) decreasing the temperature by 100 °C
C) adding more nitrogen gas to the mixture
D) removing the iron catalyst
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, decreasing pressure will shift the equilibrium to the side with more gas molecules. In this case, the left side has 4 gas molecules (1 N₂ + 3 H₂) while the right has 2 (2 NH₃), so decreasing pressure shifts equilibrium left (option A). Decreasing temperature would favor the exothermic reaction (shift right, B is wrong). Adding more nitrogen would shift equilibrium right (C is wrong). A catalyst doesn’t affect equilibrium position (D is wrong).
Topic – 7.2
The flow chart shows some properties of a metal oxide.

What is the metal oxide?
A) aluminium oxide
B) copper(II) oxide
C) iron(III) oxide
D) zinc oxide
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The key clues are that the metal oxide reacts with both acid (HCl) and base (NaOH) to form salt and water (amphoteric behavior), and is a component of brass. Zinc oxide (D) fits both criteria as it’s amphoteric and brass is a copper-zinc alloy. Aluminium oxide (A) is amphoteric but not in brass. Copper(II) oxide (B) and iron(III) oxide (C) are basic oxides that don’t react with NaOH.
Topic – 6.4
Which statement about reactants in redox reactions is correct?
A) An oxidising agent donates electrons, and a reducing agent accepts electrons.
B) When one element gains electrons, the oxidation number of a different element increases.
C) When the oxidation number of one element increases, a different element gains oxygen.
D) When the oxidation number of one element increases, a different element loses electrons.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
In redox reactions, when one species gains electrons (is reduced), another must lose electrons (be oxidized). This means the oxidation number of the element that loses electrons increases (B is correct). Option A is wrong because oxidising agents accept electrons, not donate. Options C and D are incorrect generalizations – oxygen gain or electron loss aren’t necessary for all redox reactions, but oxidation number changes are fundamental.
Topic – 6.4
Aluminium is extracted from aluminium oxide by electrolysis. The ionic half-equation for the reaction at one of the electrodes is shown.
\[ \text{Al}^{3+} + 3\text{e}^- \rightarrow \text{Al} \]
Which row describes the change in oxidation number of the aluminium and the type of reaction at this electrode?
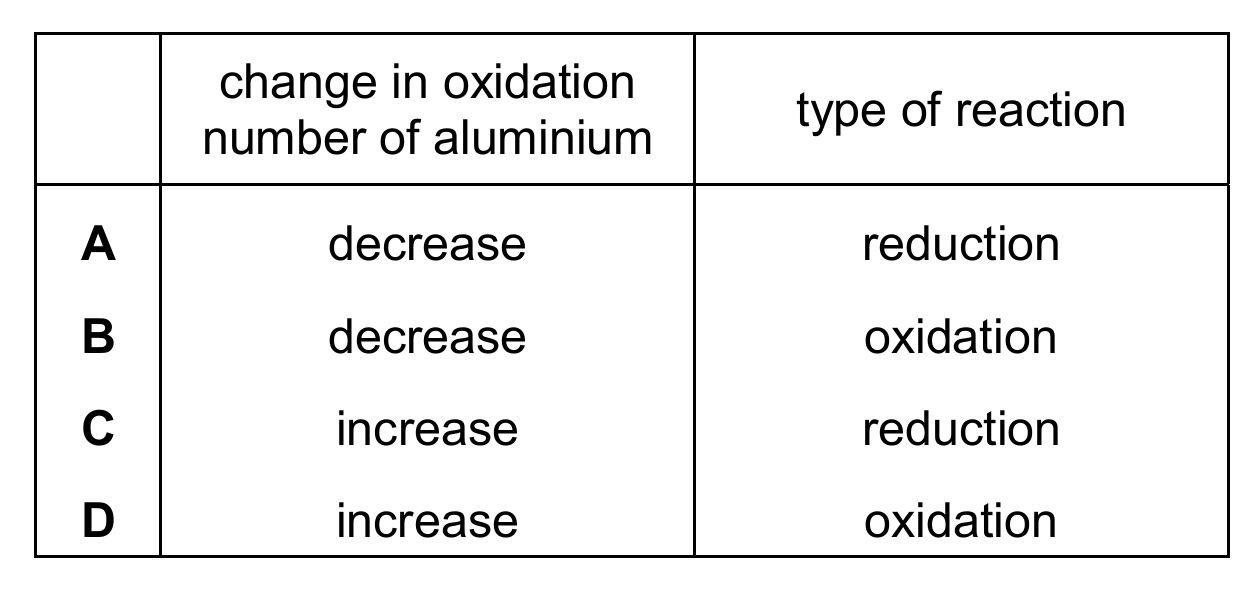
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The half-equation shows Al³⁺ gaining 3 electrons to become Al. This is reduction (gain of electrons), and the oxidation number decreases from +3 to 0. Therefore, option A is correct. Reduction always involves a decrease in oxidation number. Options B and D incorrectly identify the reaction type, while option C incorrectly states the oxidation number increases during reduction.
Topic – 7.1
Which statement about dilute hydrochloric acid is correct?
A) It is a strong acid as it fully dissociates.
B) It is a strong acid as it partially dissociates.
C) It is a weak acid as it fully dissociates.
D) It is a weak acid as it partially dissociates.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, meaning it completely (fully) dissociates in aqueous solution to form H⁺ and Cl⁻ ions. Therefore, option A is correct. The terms “strong” and “weak” refer to the degree of dissociation, not concentration – strong acids fully dissociate regardless of concentration (so B and D are wrong). Option C is contradictory as weak acids don’t fully dissociate.
Topic – 7.3
Which row describes and gives the formula of hydrated copper(II) sulfate?
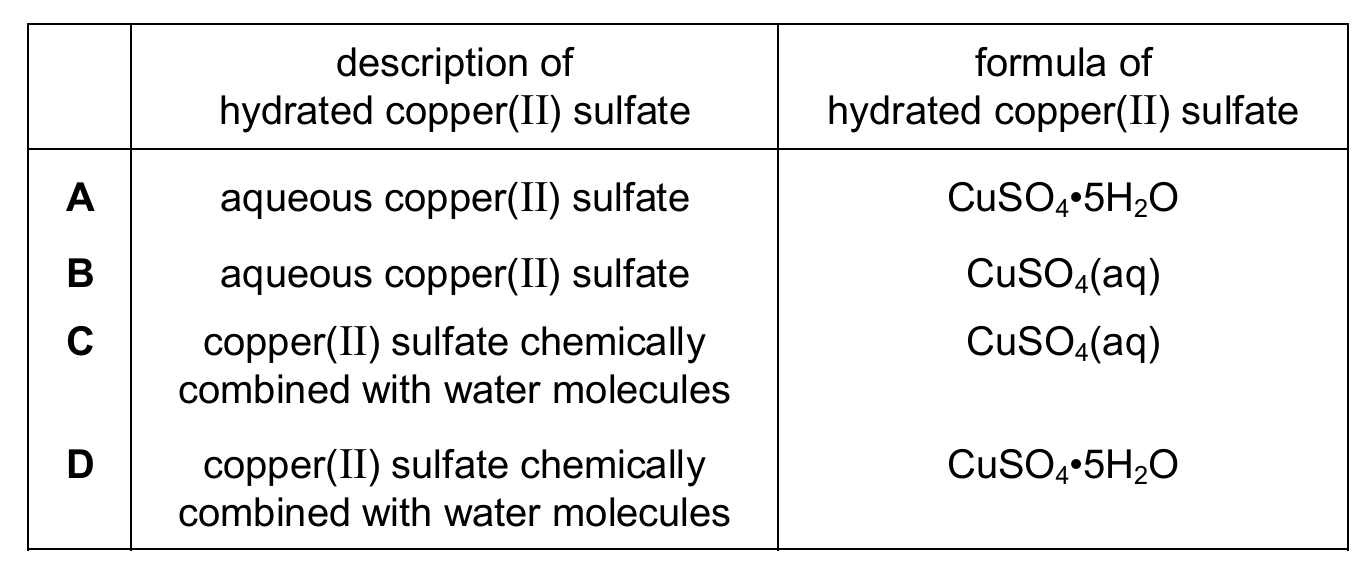
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Hydrated copper(II) sulfate refers to the solid compound where water molecules are chemically bound in the crystal structure (not just dissolved in water). Its correct formula is CuSO₄•5H₂O (the dot indicates water of crystallization). Therefore, option D is correct. Options A and B incorrectly describe it as aqueous (dissolved in water), while option C uses the wrong formula for the hydrated solid.
Topic – 7.3
The equations for three reactions are shown.
1 Pb(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI₂(s) + 2KNO₃(aq)
2 2AgNO₃(aq) + CuI₂(aq) → Cu(NO₃)₂(aq) + 2AgI(s)
3 CuO(s) + H₂SO₄(aq) → CuSO₄(aq) + H₂O(l)
Which reactions are suitable for making a salt by precipitation?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Precipitation reactions involve the formation of an insoluble solid (precipitate) when two solutions are mixed. In reaction 1, PbI₂ is the precipitate. In reaction 2, AgI is the precipitate. Reaction 3 is an acid-base neutralization producing a soluble salt (CuSO₄) and water – no precipitate forms. Therefore, only reactions 1 and 2 are precipitation reactions (option A).
Topic – 8.4
Acidified potassium dichromate(VI), K₂Cr₂O₇, is used to oxidise ethanol, C₂H₅OH.
The ionic equation for the reaction is shown.
\[ 3C_2H_5OH + 2Cr_2O_7^{2-} + 16H^+ \rightarrow 3CH_3COOH + 4Cr^{3+} + 11H_2O \]
Which properties of transition elements are shown by chromium in this reaction?
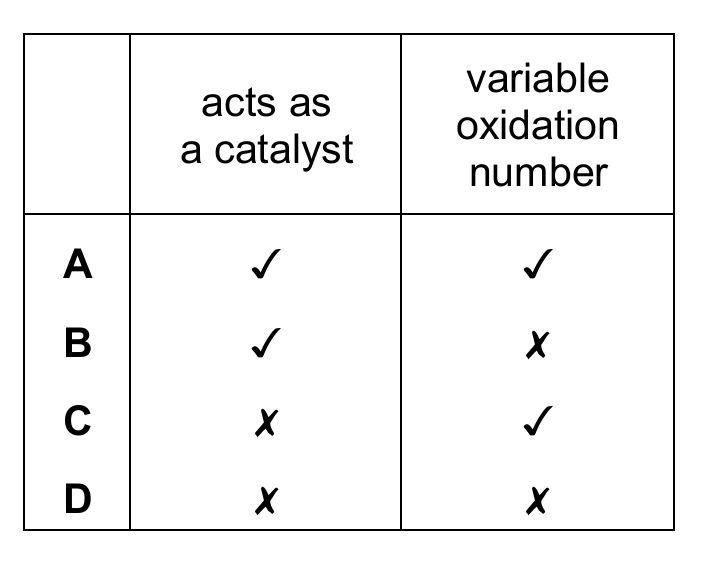
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
In this reaction, chromium changes from Cr₂O₇²⁻ (Cr oxidation number +6) to Cr³⁺, showing variable oxidation number (✓). However, potassium dichromate is not acting as a catalyst here – it’s being used up in the reaction (✗). Therefore, option C is correct. Transition elements often show variable oxidation states, but not all their compounds act as catalysts in every reaction they participate in.
Topic – 8.1
Which statements describe the Periodic Table?
1 The elements are arranged in order of their nucleon number.
2 The elements are arranged in order of their proton number.
3 It is used to predict the properties of elements.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 only
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The Periodic Table arranges elements by increasing atomic (proton) number (statement 2 is correct, 1 is wrong). The periodic arrangement allows prediction of element properties based on their position (statement 3 is correct). Therefore, option C (2 and 3) is correct. Nucleon number (mass number) isn’t the basis for the periodic arrangement, as isotopes would disrupt the periodic trends if it were.
Topic – 9.4
Which row shows the correct order of reactivity of the four named metals?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The correct reactivity series for these metals is: magnesium (most reactive) > zinc > copper > silver (least reactive). Therefore, option B is correct. Magnesium is above zinc in the reactivity series, and both are above hydrogen, while copper and silver are below hydrogen. Options A, C and D all have errors in the relative positions of these metals in the reactivity series.
Topic – 9.4
Four iron nails are added to four different metal sulfate solutions.
In which solution does a displacement reaction occur?
A) copper(II) sulfate
B) magnesium sulfate
C) sodium sulfate
D) zinc sulfate
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
A displacement reaction occurs when a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its compound. Iron is more reactive than copper but less reactive than magnesium, sodium and zinc. Therefore, iron can displace copper from copper(II) sulfate (A), forming iron sulfate and copper metal. No reaction occurs with the other solutions (B, C, D) as those metals are more reactive than iron.
Topic – 10.2
A fertiliser contains ammonium nitrate and potassium phosphate.
Why is the fertiliser described as an NPK fertiliser?
A) It provides nitrogen, which is an essential element for improved plant growth.
B) It contains the element oxygen, which neutralises acidic soil.
C) It contains the elements nitrogen and phosphorus.
D) It provides the three main elements needed for improved plant growth.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
NPK fertilisers provide the three main essential elements for plant growth: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K). Ammonium nitrate provides nitrogen (N), potassium phosphate provides phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). Therefore, option D is correct as it mentions all three elements. Option A mentions only nitrogen, option C misses potassium, and option B is irrelevant (oxygen isn’t a primary nutrient).
Topic – 10.3
What are the approximate percentages of oxygen and nitrogen in clean, dry air?
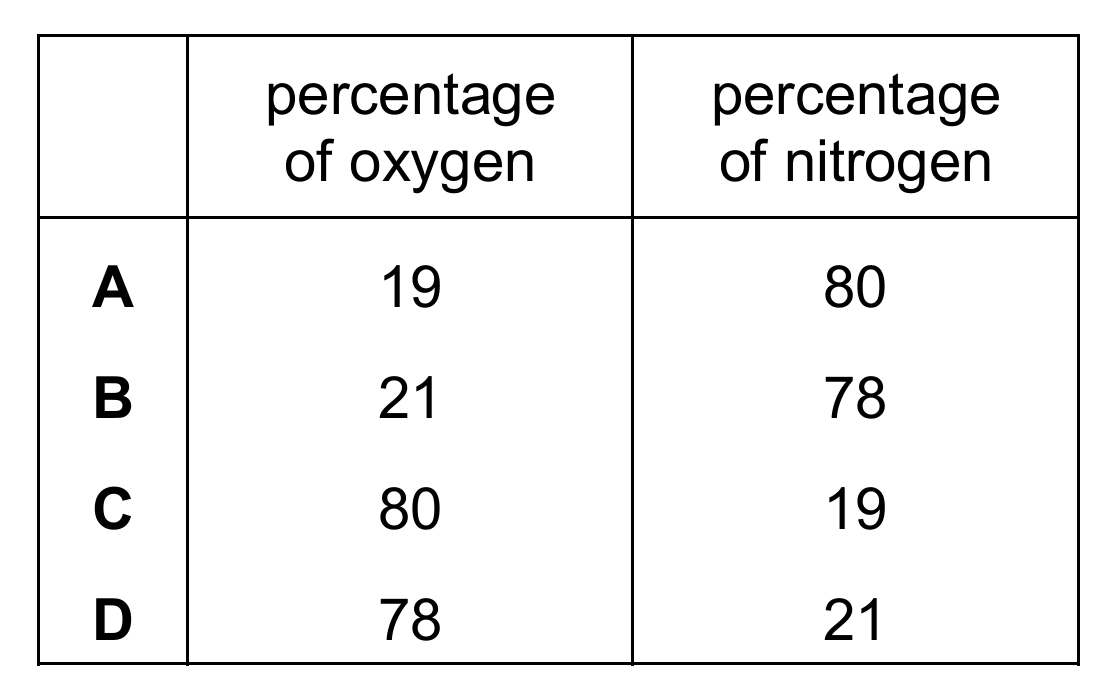
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Clean, dry air is approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen by volume, with the remaining 1% being other gases like argon and carbon dioxide. Therefore, option B is correct. The other options either reverse the percentages (C, D) or provide incorrect values (A). These percentages are fundamental values in atmospheric chemistry.
Topic – 11.1
Which compounds have similar chemical properties?
A) butanol and butanoic acid
B) ethane and ethene
C) methane and butane
D) propene and propanol
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Compounds in the same homologous series have similar chemical properties. Methane and butane are both alkanes (C is correct). The other pairs belong to different functional groups: butanol (alcohol) and butanoic acid (carboxylic acid, A); ethane (alkane) and ethene (alkene, B); propene (alkene) and propanol (alcohol, D). Only option C represents two members of the same homologous series.
Topic – 11.1
Four statements about organic compounds P, Q, R and S are listed.
P is a saturated hydrocarbon.
The formula of Q is CH3CH3.
A molecule of R contains only one oxygen atom.
Compound S is a carboxylic acid.
Which statement about these compounds is correct?
A) P and Q are members of different homologous series.
B) P and S are members of the same homologous series.
C) Q and S are members of the same homologous series.
D) Q, R and S are all members of different homologous series.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s analyze each compound:
P is a saturated hydrocarbon (alkane series).
Q (CH3CH3) is ethane, also an alkane.
R has one oxygen atom – could be an alcohol, ether, or aldehyde (different from P and Q).
S is a carboxylic acid (completely different functional group).
Option D is correct because Q (alkane), R (could be alcohol/ether), and S (carboxylic acid) are indeed from different homologous series.
Topic – 11.2
The structure of an organic compound is shown.
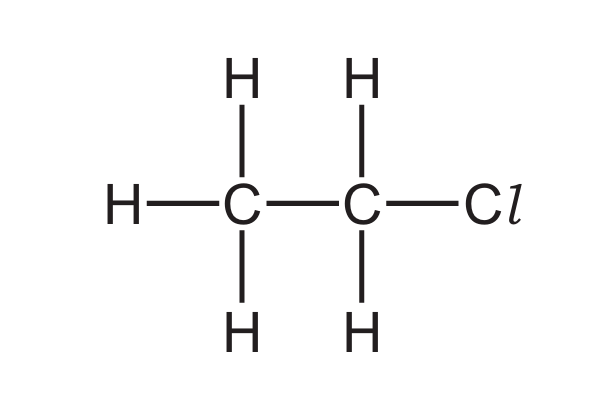
What is the name of the compound?
A) chloroethane
B) chloroethene
C) chloroethanol
D) chloroethanoic acid
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The structure shows a two-carbon chain with single bonds (ethane) with one chlorine substituent:
CH3-CH2Cl
This is chloroethane. Key points:
– It’s not an alkene (no double bond) so not chloroethene
– No OH group present (rules out chloroethanol)
– No carboxyl group (rules out chloroethanoic acid)
The correct IUPAC name is chloroethane.
Topic – 11.5
Which statement about the manufacture of ethene from larger alkane molecules is correct?
A) A low temperature is required.
B) The process is called cracking.
C) The process requires an excess of oxygen.
D) Water is also a product.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The process of breaking down larger hydrocarbons into smaller ones (like ethene) is called cracking.
Key facts:
– Cracking requires high temperatures (around 600-700°C), so A is wrong
– It’s typically done in the absence or limited oxygen to prevent combustion, making C wrong
– The main products are smaller alkanes and alkenes, not water, so D is wrong
B is correct as this is indeed the definition of cracking – breaking long-chain hydrocarbons into shorter ones including alkenes like ethene.
Topic – 11.7
Which processes are used to make ethanoic acid?
1 heating ethanol with acidified aqueous potassium manganate(VII)
2 bacterial oxidation of ethanol
3 distilling ethanol using a fractionating column
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 only
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Ethanoic acid can be produced by:
1. Oxidation of ethanol using acidified potassium manganate(VII) – this is a standard laboratory method
2. Bacterial fermentation of ethanol – this is how vinegar is made commercially
Distillation (process 3) simply purifies ethanol but doesn’t convert it to ethanoic acid.
Therefore, the correct answer is A (1 and 2 only).
Topic – 11.5
Which statement about propene, C3H6, is correct?
A) Propene reacts with bromine in the dark in a substitution reaction.
B) Propene reacts with steam in the presence of an alkaline catalyst, forming an alcohol.
C) Propene undergoes addition polymerisation, forming poly(ethene).
D) Propene undergoes an addition reaction to form an alkane.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Let’s evaluate each option:
A) Wrong – propene reacts with bromine via addition (not substitution) and the reaction is faster in light
B) Wrong – steam addition to propene requires an acid catalyst (not alkaline) to form propan-2-ol
C) Wrong – propene polymerizes to form poly(propene), not poly(ethene)
D) Correct – propene can undergo addition reactions (e.g., hydrogenation) to form propane (an alkane)
The double bond in propene makes addition reactions characteristic of alkenes possible, including hydrogenation to form alkanes.
Topic – 11.1
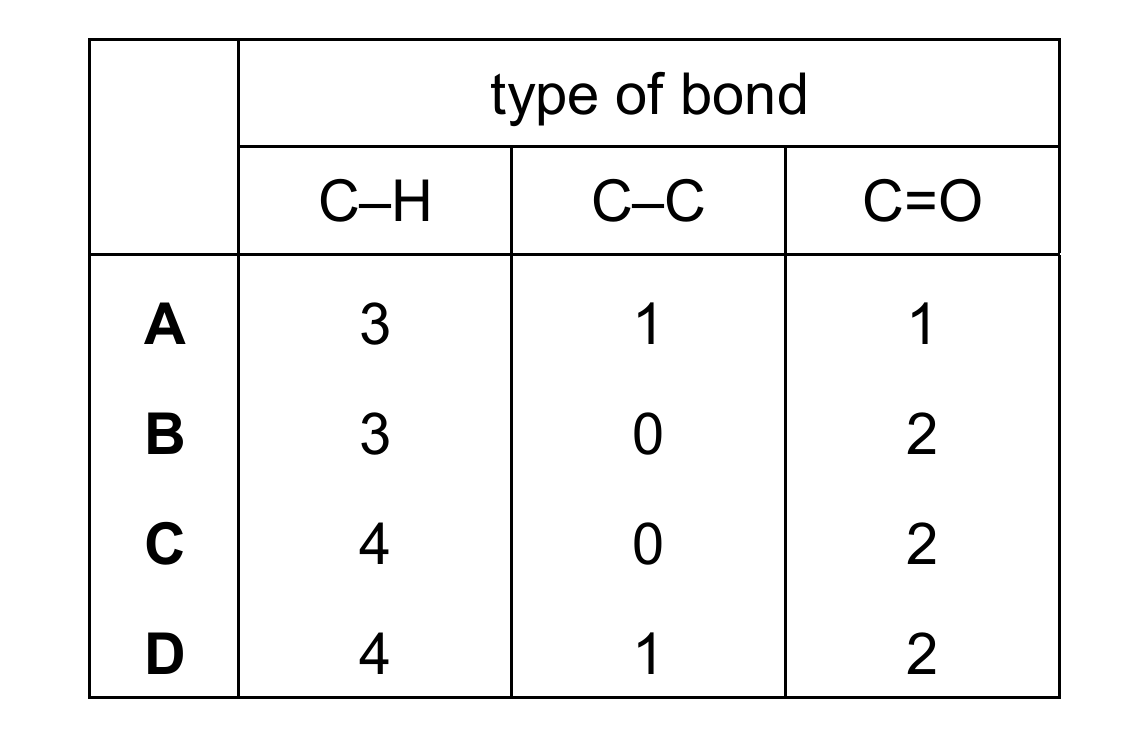
How many of each type of bond are present in ethanoic acid, CH3COOH?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Let’s analyze the structure of ethanoic acid (CH3COOH):
1. The molecule has 3 C-H bonds in the methyl group (CH3)
2. There is 1 C-C bond between the methyl group and the carboxyl group
3. The carboxyl group has 1 C=O bond (the other oxygen is bonded with a single bond and has an OH group)
Therefore, the correct counts are: 3 C-H bonds, 1 C-C bond, and 1 C=O bond, which corresponds to option A.
Topic – 11.8
Which diagram represents the structure of a protein?
A 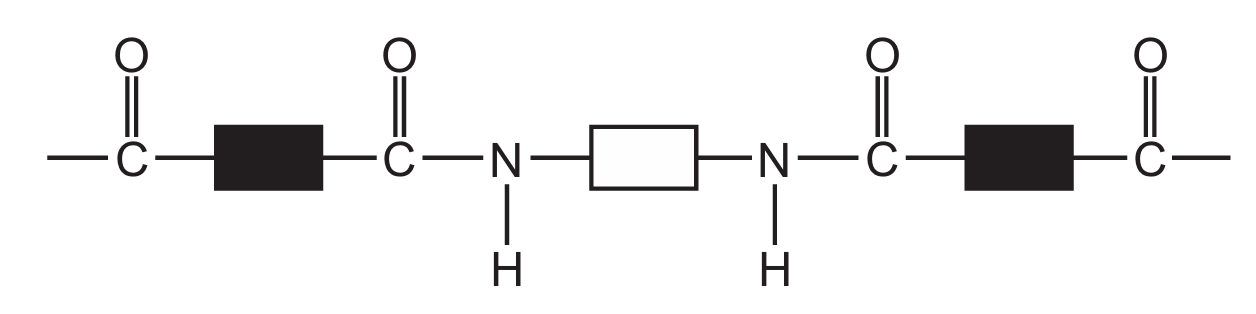
B 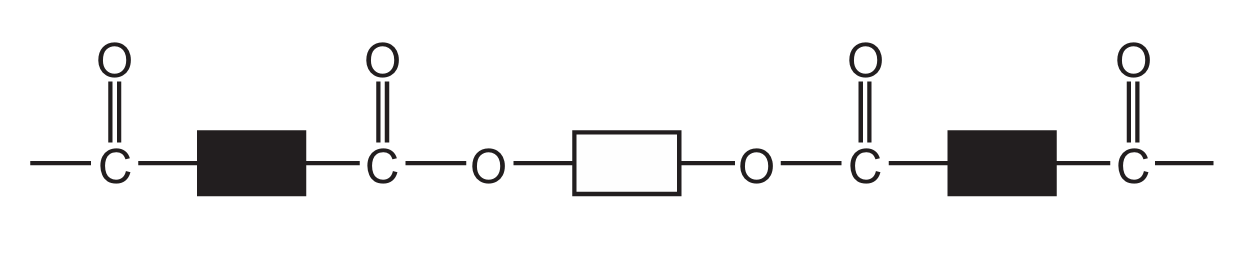
C 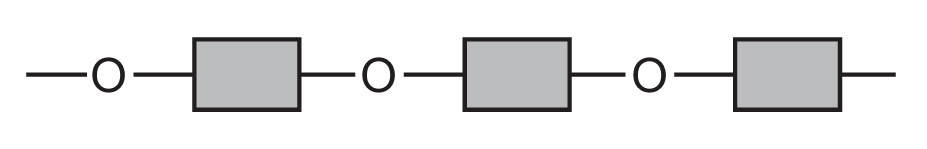
D 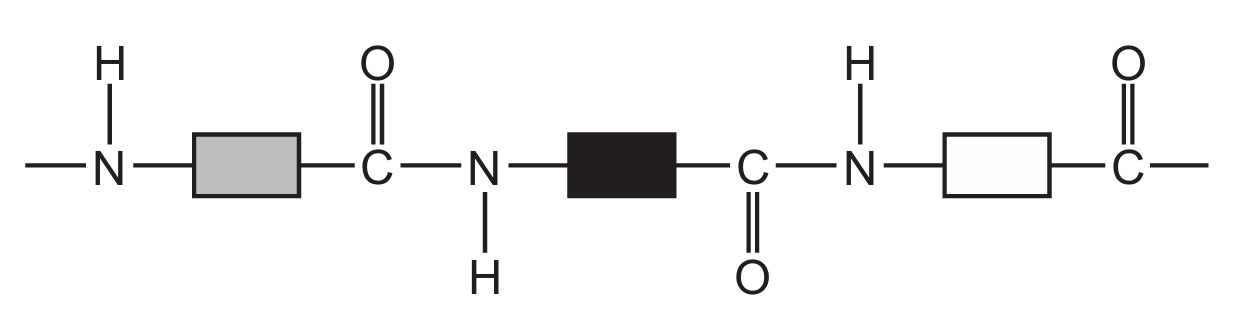
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Proteins have a complex structure with peptide bonds (formed between amino acids) creating long chains that fold into specific 3D shapes. The correct diagram should show:
1. Multiple amino acid units linked together
2. Peptide bonds (C-N bonds between amino acids)
3. A complex three-dimensional structure
Diagram D correctly represents this protein structure, showing the characteristic peptide bonds and complex folding pattern that distinguishes proteins from simpler organic molecules.
Topic – 12.3
The chromatogram of substance S is shown.
Some distances, W, X, Y and Z, are labelled on the diagram.
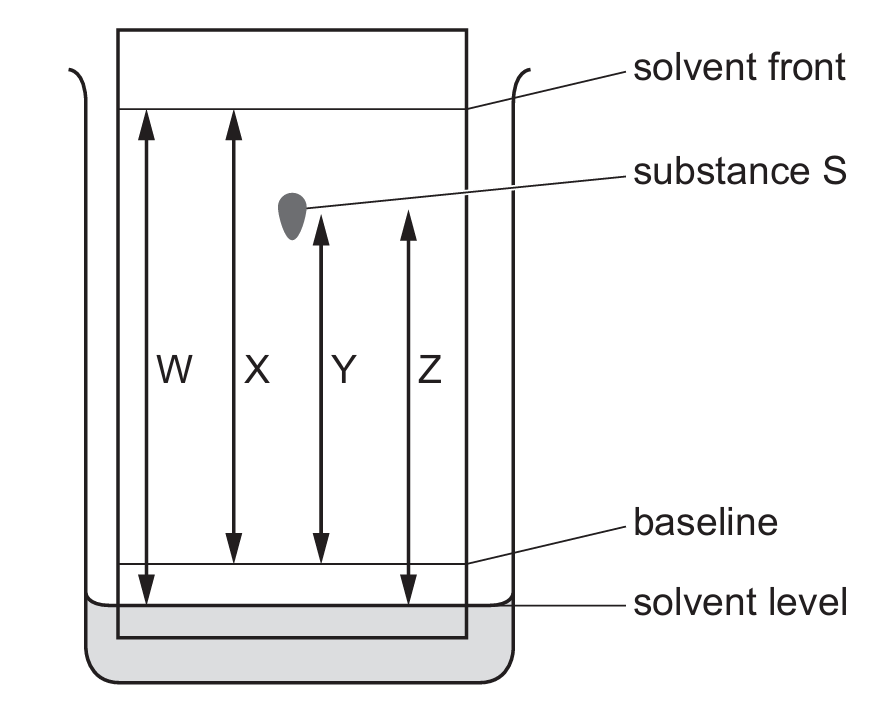
How is the Rf value of substance S calculated?
A \(\frac{X}{Y}\)
B \(\frac{W}{Z}\)
C \(\frac{Y}{X}\)
D \(\frac{Y}{W}\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The Rf (retention factor) value in chromatography is calculated as:
\[ R_f = \frac{\text{distance traveled by substance}}{\text{distance traveled by solvent front}} \]
From the diagram:
– Y represents the distance traveled by the substance from the baseline
– X represents the distance traveled by the solvent front from the baseline
Therefore, the correct calculation is \(\frac{Y}{X}\), which corresponds to option C.
W and Z distances are not relevant for calculating Rf values as they don’t represent the key movement measurements needed.
Topic – 12.4
Some information about solid silver chloride and solid sodium chloride is shown.
- Silver chloride and sodium chloride do not dissolve in kerosene.
- Silver chloride is insoluble in water, but sodium chloride is soluble in water.
- The boiling point of silver chloride is 1547°C and the boiling point of sodium chloride is 1413°C.
Which processes are used to separate a mixture of solid silver chloride and solid sodium chloride?
A add kerosene, stir and then filter
B add water, stir and then filter
C add water, stir and then leave to crystallise
D add water, stir and then perform fractional distillation
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
The key to separation is the difference in solubility:
1. Both compounds don’t dissolve in kerosene, so option A won’t work
2. Sodium chloride dissolves in water while silver chloride doesn’t
3. Therefore, adding water will dissolve NaCl but leave AgCl as solid
4. Filtration can then separate the insoluble AgCl (on filter paper) from the NaCl solution
Crystallization (option C) isn’t needed as we’re not trying to recover the NaCl yet, and fractional distillation (option D) is impractical due to the extremely high boiling points of both solids.
Topic – 12.5
Which statement describes how a flame test is done?
A The tip of a clean wire is dipped into the substance and the wire is placed in a blue Bunsen burner flame.
B The tip of a clean wire is dipped into the substance and the wire is placed in a yellow Bunsen burner flame.
C A wooden splint is lit and is placed above a test-tube containing the gas being tested.
D A wooden splint is lit, blown out and the glowing splint put into a test-tube of the gas being tested.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The correct procedure for a flame test is:
1. Use a clean wire loop (usually platinum or nichrome) to avoid contamination
2. Dip the wire into the test substance (often moistened with hydrochloric acid)
3. Place the wire in the blue (hottest) part of a Bunsen flame
4. Observe the characteristic color produced
Option B is incorrect because the yellow flame contains soot particles that would interfere with the test. Options C and D describe gas tests, not flame tests for metal ions.
