Question 1:-
Topic B7.1 (Human Nutrition – Diet)
What do both animals and plants need to meet their nutritional requirements?
(A) carbon dioxide
(B) ions
(C) light
(D) organic compounds
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 2:-
Topic B6.1 (Plant Nutrition – Photosynthesis)
Oxygen produced in palisade mesophyll cells by photosynthesis diffuses into the air spaces in the leaf.
What causes this movement?
(A) osmosis between the leaf cells
(B) evaporation of water from mesophyll cells
(C) difference in oxygen concentration inside and outside the cells
(D) wind blowing over the leaves
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 3:-
Topic B4.1 (Biological Molecules)
A student tests a sample of food to identify its composition.
The results are shown.
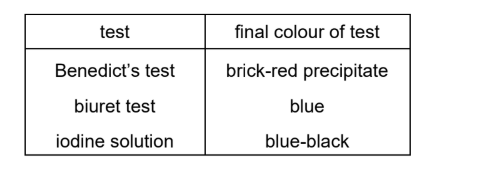
Which substances are shown to be present in the food sample?
(A) protein, reducing sugar and starch
(B) protein and starch only
(C) reducing sugar and starch only
(D) reducing sugar and protein only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 4:-
Topic B5.1 (Enzymes)
The diagram shows a functional human enzyme at 37 °C.
Which row shows the likely shape of this enzyme at 5 °C and 80 °C?
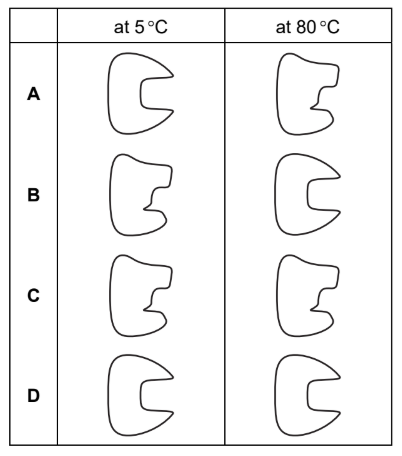
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 5:-
Topic B6.1 (Plant Nutrition – Photosynthesis)
What is the manufacture of carbohydrates from raw materials using light energy called?
(A) growth
(B) photosynthesis
(C) respiration
(D) reproduction
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 6:-
Topic B7.3 (Human Nutrition – Digestion)
Which row about secretions in the alimentary canal is correct?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 7:-
Topic B9.3 (Transport in Animals – Blood Vessels)
Which vessels carry blood towards the heart?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 8:-
Topic B12.1 (Respiration)
Which process releases the most energy?
(A) carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
(B) glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
(C) glucose → alcohol + carbon dioxide
(D) glucose → lactic acid
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 9:-
Topic B13.3 (Coordination and Response – Homeostasis)
The arterioles that supply blood to the skin’s surface capillaries undergo vasodilation.
Which row describes the effect of this on the core body temperature and the volume of blood passing through these capillaries?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 10:-
Topic B15.4 (Reproduction – Sexual Reproduction in Humans)
Which statements about human egg and sperm cells are correct?
1. The egg cell’s membrane changes to prevent other sperm from entering it after fertilisation.
2. The egg and sperm cells have a diploid nucleus.
3. The sperm’s enzymes allow it to penetrate the egg to fertilise it.
4. The process of fertilisation occurs in the ovary.
(A) 1 and 3 (B) 1 and 4 (C) 2 and 3 (D) 2 and 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 11:-
Topic B16.1 (Inheritance – Chromosomes and Genes)
Which row shows the sex chromosomes in humans?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 12:-
Topic B18.2 (Organisms and their Environment – Food Chains and Food Webs)
The diagram shows part of a food web in a rainforest.

Which animals are feeding as quaternary consumers?
(A) crocodile and green anaconda
(B) crocodile and jaguar
(C) green anaconda and tanager
(D) jaguar and tanager
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 13:-
Topic B18.3 (Organisms and their Environment – Carbon Cycle)
The diagram shows part of the carbon cycle.
Which process, due to human activities, has increased the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 14:-
Topic C12.4 (Experimental Techniques and Chemical Analysis – Separation and Purification)
Which process is used to obtain water from a salt solution?
(A) chromatography
(B) crystallisation
(C) distillation
(D) filtration
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 15:-
Topic C2.3 (Atoms, Elements, and Compounds – Isotopes)
One isotope of oxygen is represented by \( _{8}^{16}\textrm{O}\) .
Which diagram represents a different isotope of oxygen?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 16:-
Topic C4.1 (Electrochemistry – Electrolysis)
Which row shows the ionic half-equation for the reaction at the cathode during the electrolysis of the named electrolyte?
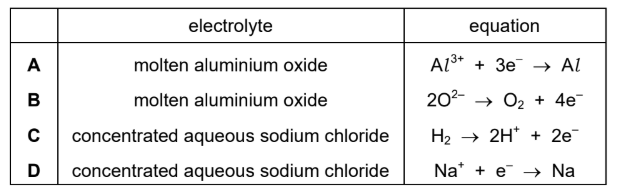
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 17:-
Topic C6.2 (Chemical Reactions – Rate of Reaction)
When dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium carbonate, carbon dioxide is produced.
Which pieces of apparatus are used to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of this reaction?

(A) 1, 2 and 3 (B) 1 and 2 only (C) 1 and 3 only (D) 2 and 3 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 18:-
Topic C6.3 (Chemical Reactions – Redox)
Solid zinc reacts with aqueous copper(II) sulfate. The ionic equation for the reaction is shown.
Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
Which row identifies the substance being oxidised and the reducing agent?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 19:-
Topic C7.2 (Acids, Bases, and Salts – Oxides)
Chromium(III) oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid and with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Which word describes chromium(III) oxide?
(A) acidic
(B) amphoteric
(C) basic
(D) neutral
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 20:-
Topic C12.5 (Experimental Techniques and Chemical Analysis – Identification of Ions and Gases)
Gas X turns limewater milky.
What is X?
(A) carbon dioxide
(B) chlorine
(C) hydrogen
(D) oxygen
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 21:-
Topic C8.3 (The Periodic Table – Group VII Properties)
Which statements about the elements in Group VII of the Periodic Table are correct?
1. Bromine is lighter in colour than chlorine.
2. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine.
3. Chlorine displaces iodide ions from aqueous solution.
4. Iodine displaces bromide ions from aqueous solution.
(A) 1 and 2 (B) 1 and 4 (C) 2 and 3 (D) 3 and 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 22:-
Topic C8.5 (The Periodic Table – Noble Gases)
Neon is in Group Vlll of the Periodic Table.
Which row about neon is correct?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 23:-
Topic C9.6 (Metals – Extraction of Metals)
Which row identifies an ore of aluminium and the method of extraction of aluminium from its ore?
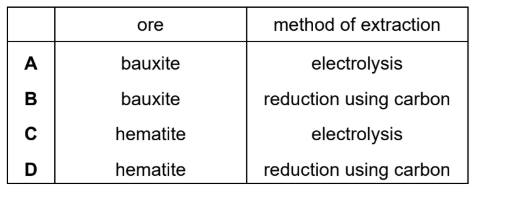
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 24:-
Topic C10.1 (Chemistry of the Environment – Water
Copper(II) sulfate and cobalt(II) chloride are used to test for water.
Which rows show the colour changes for these two substances?

(A) 1 and 2 (B) 1 and 4 (C) 2 and 3 (D) 3 and 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 25:-
Topic C6.2 (Chemical Reactions – Rate of Reaction)
Sulfuric acid is manufactured by the Contact process.
Which reaction in this process uses a catalyst?
(A) S + O2 → SO2
(B) 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
(C) SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
(D) H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 26:-
Topic C10.2 (Chemistry of the Environment – Air Quality and Climate)
What is the main constituent of clean air and of natural gas?
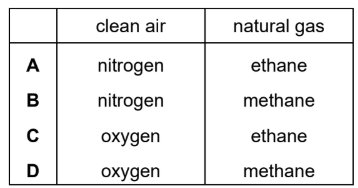
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 27:-
Topic C11.7 (Organic Chemistry – Polymers)
The structure of a monomer is shown.

Which structure represents a section of the addition polymer that is formed from this monomer?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 28:-
Topic P1.2 (Motion, Forces, and Energy – Motion
The speed–time graph represents the motion of a vehicle during the first 10 s of a journey.

How far does the vehicle travel during the 10 s?
(A) 25 m (B) 50 m (C) 75 m (D) 100 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 29:-
Topic P1.5 (Motion, Forces, and Energy – Forces)
The diagram shows a spring without a load and then with a load of mass 500 g suspended from the same spring. The spring obeys Hooke’s law.

The length of the unloaded spring is 30 cm.
When the 500 g load is suspended from the spring, the spring extends to a new length of 35 cm.
The gravitational field strength g is 10 N/ kg.
Which calculation gives the spring constant of the spring?
(A) \(\frac{0.5 \times 10}{35 – 30} N/cm\)
(B) \(\frac{0.5 }{10 \times (35-30)} N/cm\)
(C) \(\frac{10 \times (35-30)}{0.5} N/cm\)
(D) \(0.5 \times 10 \times (35-30) N/cm\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 30:-
Topic P1.5 (Motion, Forces, and Energy – Forces)
A weightless L-shaped beam is pivoted as shown.
A load of mass 2.4 kg is suspended from the beam at point X. The beam is held in equilibrium by a horizontal force F acting at the point shown.

The gravitational field strength g is 10 N/ kg.
What is F?
(A) 4.8 N (B) 48N (C) 72N (D) 720N
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 31:-
Topic P1.6 (Motion, Forces, and Energy – Energy, Work, and Power)
Four different kettles contain different masses of water.
They are used to heat the water from room temperature to boiling point.
The kettles take different times to do this.
Which kettle has the lowest useful power output?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 32:-
Topic P2.1 (Thermal Physics – Kinetic Particle Model of Matter)
A gas in a balloon is heated at constant pressure.
What happens to the gas?
(A) Its density decreases.
(B) Its mass decreases.
(C) Its temperature decreases.
(D) Its volume decreases.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 33:-
Topic P3.2 (Waves – Light)
Which diagram shows a ray of light undergoing total internal reflection?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 34:-
Topic P3.3 (Waves – Electromagnetic Spectrum
Which two types of wave cannot travel at the same speed as each other in a vacuum?
(A) infrared and gamma
(B) ultraviolet and X-rays
(C) light and microwaves
(D) radio waves and sound
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 35:-
Topic P4.2 (Electricity and Magnetism – Electrical Quantities)
The electromotive force (e.m.f.) of a battery is 2.0V.
Which statement is correct?
(A) The battery supplies 0.50 J of energy for every 1.0 C of charge driven around a circuit.
(B) The battery supplies 0.50 J of energy for every 2.0 C of charge driven around a circuit.
(C) The battery supplies 2.0 J of energy for every 1.0 C of charge driven around a circuit.
(D) The battery supplies 2.0 J of energy for every 2.0 C of charge driven around a circuit.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question 36:-
Topic P4.2 (Electricity and Magnetism – Electrical Quantities)
The potential difference (p.d.) across a 60 Ω resistor is 12V.
How much time does it take for a charge of 100 C to pass through the resistor?
(A) 0.0020 s (B) 0.050 s (C) 20 s (D) 500 s
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question 37:-
Topic P4.4 (Electricity and Magnetism – Electrical Safety)
A heater circuit is protected by a 10A fuse.
How does the fuse protect the circuit?
(A) It cuts off the current when the current in the heater is greater than 10A.
(B) It decreases the current in the heater to 10A when the current is more than 10A.
(C) It increases the current in the heater to 10A when the current is less than 10A.
(D) It maintains a constant temperature in the heater.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question 38:-
Topic P4.5 (Electricity and Magnetism – Electromagnetic Effects)
The diagram shows a wire carrying an electric current in the direction shown (towards the bottom of the page). The wire is at right angles to a magnetic field that is directed into the page.
A force acts on the wire because of the current and the magnetic field.
In which labelled direction does this force act?
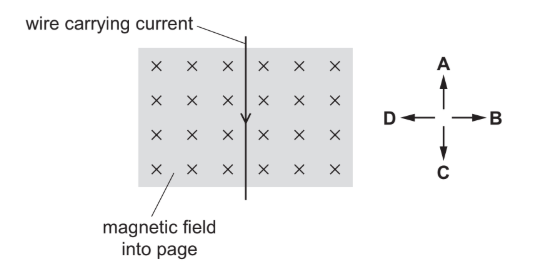
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 39:-
Topic P4.5 (Electricity and Magnetism – Electromagnetic Effects)
Which voltage–time graph shows the output voltage of a simple a.c. generator?

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Question 40:-
Topic P5.2 (Nuclear Physics – Radioactivity)
A beam of different types of ionising radiation passes through an electric field between two metal plates. The diagram shows the direction of each type of radiation as it passes through the field.

What does the beam contain?
(A) alpha (α)-particles, beta (β)-particles and gamma (γ)-rays
(B) alpha (α)-particles and beta (β)-particles only
(C) alpha (α)-particles and gamma (γ)-rays only
(D) beta (β)-particles and gamma (γ)-rays only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
