Question-1(a) :2019-may-Chemistry_paper_2__TZ2_HL
Topic:
Given: Ethyne, $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2$, reacts with oxygen in welding torches.
Write: an equation for the complete combustion of ethyne.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution:
The complete combustion of ethyne can be represented by the following equation:
$$\mathrm{C_2H_2 + 2.5O_2 \rightarrow 2CO_2 + H_2O}$$
In this reaction, ethyne reacts with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water. The stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced equation indicate that two moles of ethyne require 2.5 moles of oxygen to completely react.
Question-1[(b) (i) ] :2019-may-Chemistry_paper_2__TZ2_HL
Topic:
Draw: the Lewis (electron dot) structure of ethyne.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Ethyne is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula $\mathrm{C_2H_2}$. It is also known as acetylene and is a colorless gas with a distinct odor. It is highly flammable and is commonly used as a fuel for welding and cutting torches.
Ethyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon, meaning it contains one or more double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. In the case of ethyne, there is a triple bond between the two carbon atoms. This triple bond is composed of two pi bonds and one sigma bond.
Ethyne is produced naturally by certain bacteria, but it is also synthesized industrially from methane and other hydrocarbons through a process called cracking. It is an important chemical in the production of many organic compounds, including plastics, solvents, and synthetic rubber.
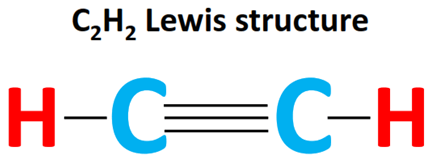
Question-1[(b) (ii)] :2019-may-Chemistry_paper_2__TZ2_HL
Topic:
Compare: giving a reason, the length of the bond between the carbon atoms in ethyne with that in ethane, $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_6$.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution:
The bond length between the carbon atoms in ethyne is shorter than the bond length between the carbon atoms in ethane.
The bond length is the distance between the nuclei of the two atoms that are bonded together. In ethyne, the triple bond between the two carbon atoms consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds. These bonds are shorter and stronger than the single covalent bond between the two carbon atoms in ethane. In addition, the triple bond in ethyne also results in a greater electron density between the two carbon atoms, which further contributes to a shorter bond length.
Therefore, the bond length between the carbon atoms in ethyne is shorter than that in ethane, which only has a single bond between the two carbon atoms.
Question-1[(b) (iii)] :2019-may-Chemistry_paper_2__TZ2_HL
Topic:
Discuss: the type of interaction that must be overcome when liquid ethyne vaporizes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution:
When liquid ethyne vaporizes, the type of interaction that must be overcome is intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular forces are the attractive or repulsive forces that exist between molecules in a substance. In the liquid phase, the molecules of ethyne are held together by intermolecular forces, which keep them close together and in a fixed position. When ethyne vaporizes, these intermolecular forces are overcome and the molecules break away from one another, resulting in the formation of a gas.
In the case of ethyne, the dominant intermolecular force is London dispersion force. This force arises due to temporary fluctuations in electron density that create temporary dipoles, which attract neighboring molecules. The strength of London dispersion force depends on the size and shape of the molecule, as well as the number of electrons. In the case of ethyne, the molecules are small and have a linear shape, so the intermolecular forces are relatively weak, and the boiling point of ethyne is low (-84°C).
Question-1[(c) (i)] :2019-may-Chemistry_paper_2__TZ2_HL
Topic:
Given: Ethyne reacts with steam.
$$
\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_4 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{g})
$$
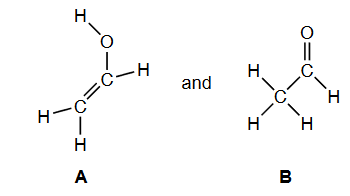
Write: the name of product $\mathbf{B}$, applying IUPAC rules.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Solution:
The name of Product B, applying IUPAC rules, is “ethanal”.
The structure of Product B can be represented as follows:
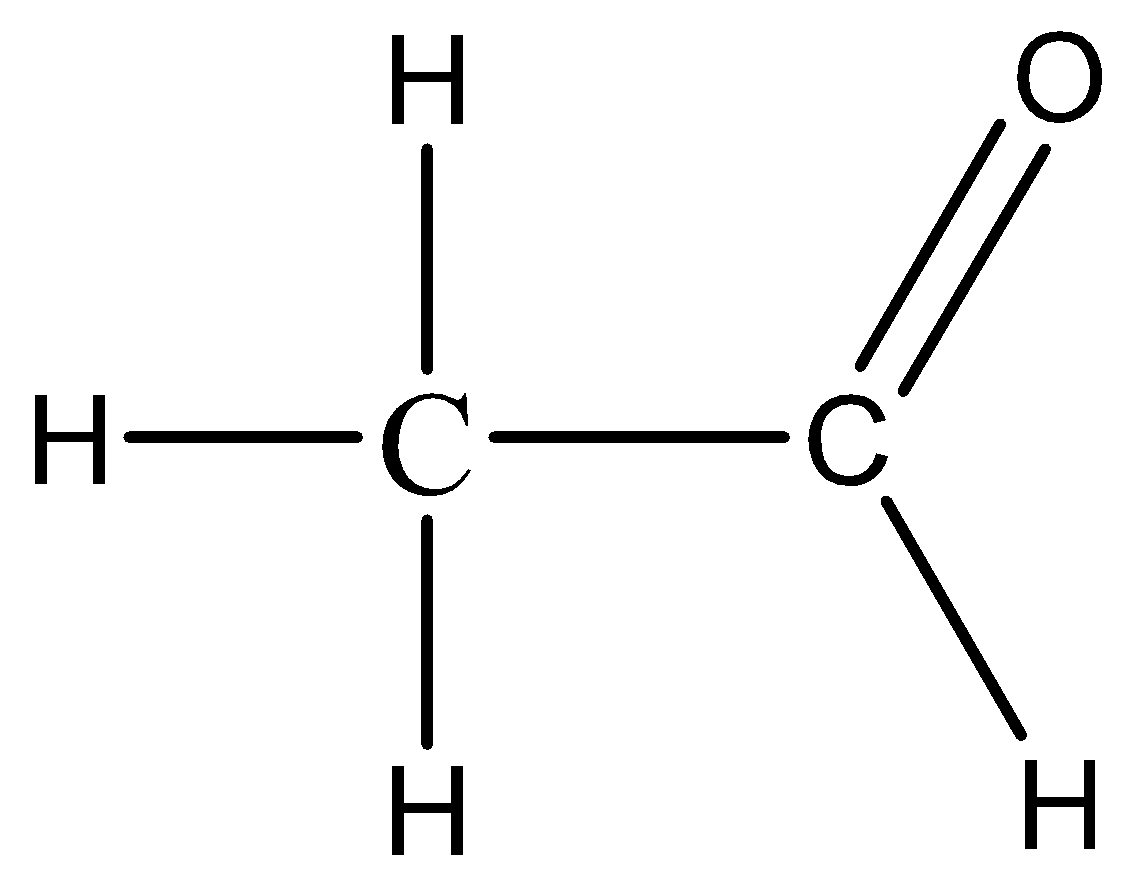
In the IUPAC nomenclature system, aldehydes are named by replacing the “-e” suffix of the corresponding parent alkane with the suffix “-al”. The parent alkane in this case is ethane, so the corresponding aldehyde is named “ethanal”.
