Q.1.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ1_SL
Topic: Vectors and scalars
Discuss: Which lists one scalar and two vector quantities?
A. Mass, momentum, potential difference
B. Mass, power, velocity
C. Power, intensity, velocity
D. Power, momentum, velocity
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Power is a scalar quantity, while momentum and velocity are vector quantities.
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option -D}$
Q.2.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ1_SL
Topic: Uncertainties and errors
Given: Two sets of data, shown below with circles and squares, are obtained in two experiments. The size of the error bars is the same for all points.
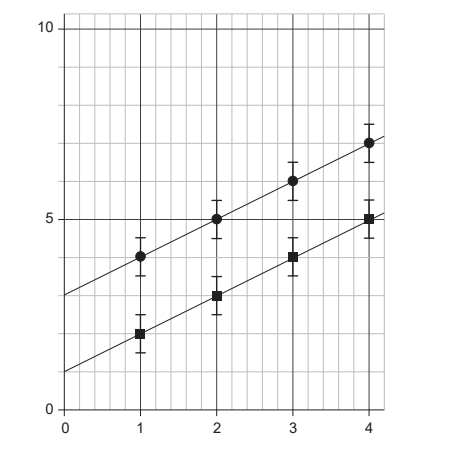
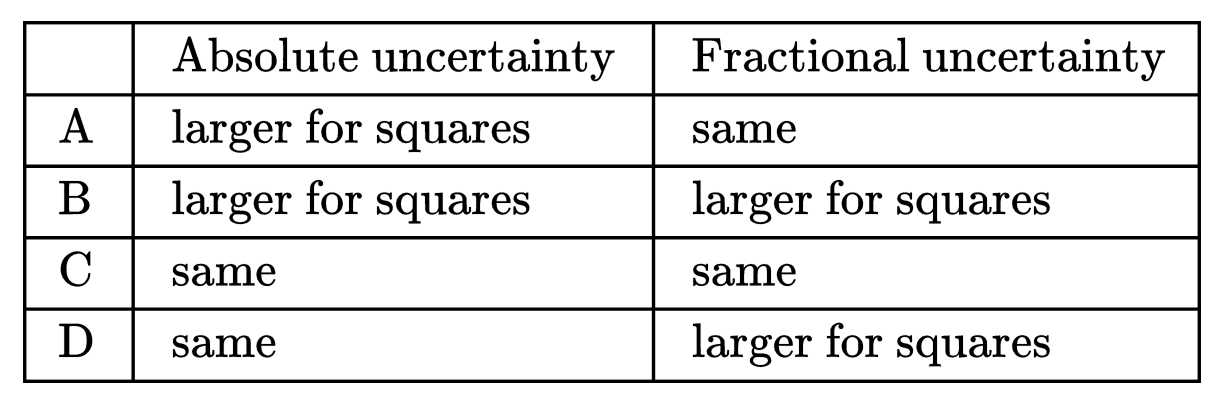
Discuss: What is correct about the absolute uncertainty and the fractional uncertainty of the y intercept of the two lines of best fit?
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
The uncertainty in a measurement can be shown on a graph as an error bar. This bar is drawn above and below the point (or from side to side) and shows the uncertainty in that measurement
The percentage uncertainty in the gradient is given by $=\frac{(m_2)-(m_1)}{m}=\frac{\Delta m}{m} \times 100$.
In above diagram, $\Delta m$ is same, hence absolute uncertainty is same but clearly $m$ is low for squares hence percentage uncertainty is larger.
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option -D}$
Q.3.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ1_SL
Topic: Motion
Given: A large stone is dropped from a tall building.
Discuss: What is correct about the speed of the stone after 1 s?
- It is decreasing at increasing rate.
- It is decreasing at decreasing rate.
- It is increasing at increasing rate.
- It is increasing at decreasing rate.
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Using:$\text{v=u+at}$
here, $u=0$ (dropped from rest) & t=1 sec , $a = g$
As the ball falling on the ground , The velocity will increase as potential energy converted into kinetic. after hitting the ground its velocity will will decrease.
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option -D}$
Q.4.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ1_SL
Topic: Motion
Given: The graph shows how the position of an object varies with time in the interval from 0 to 3 s.
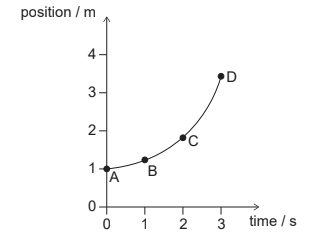
Discuss: At which point does the instantaneous speed of the object equal its average speed over the interval from 0 to 3 s?
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
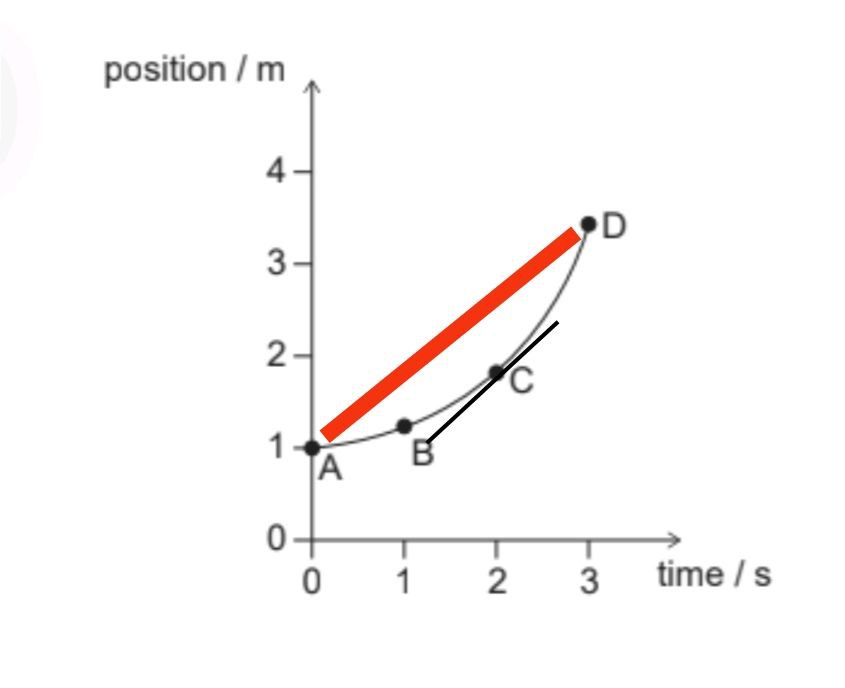
In a graph of position versus time, the instantaneous velocity is the slope of the tangent line at a given point.
The average velocities $=\frac{(x)_f-(x)_i}{(t)_f-(t)_i}$ between times. The slope of line connecting end points (average speed) and slope at C are same.
Slope of red and black line are same
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option -C}$
