Q.1.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ2_SL
Topic: Uncertainties and errors
Given: A student measures the length l and width w of a rectangular table top.
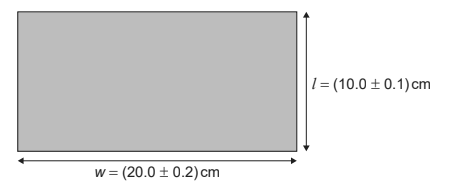
Calculate: What is the absolute uncertainty of the perimeter of the table top?
A. $0.3 \mathrm{~cm}$
B. $ 0.6 \mathrm{~cm}$
C. $ 1.2 \mathrm{~cm}$
D. $2.4 \mathrm{~cm}$
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Absolute uncertainty in perimeter $=\Delta P=\pm 2(\Delta w+\Delta l)$
$
\begin{aligned}
& =\pm 2 \times(0.2+0.1) \\
& =\pm 2 \times(0.3) \\
& =\pm 0.6 \mathrm{~cm}
\end{aligned}
$
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option-B}$
Q.2.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ2_SL
Topic: Physical Quantity
What is the unit of power expressed in fundamental SI units?
A. $\mathrm{kg} \mathrm{ms}^{-3}$
B. $\mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^{-1}$
C. $\mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^2 \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$
D. $\mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^2 \mathrm{~s}^{-3}$
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
The SI unit of power is the watt (W), which is defined as the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. One watt is equal to one joule per second (J/s).
Using the fundamental SI units, the joule is expressed as $\mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^2 \mathrm{~s}^{-2}$ (mass times distance squared per time squared), and the second is simply $\mathrm{s}$. Therefore, substituting these units into the definition of the watt, we get:
\begin{align*}
1~\mathrm{W} &= 1~\mathrm{J/s} \\
&= 1~\mathrm{kg}\mathrm{m}^2\mathrm{s}^{-2}/\mathrm{s} \\
&= 1~\mathrm{kg}\mathrm{m}^2\mathrm{s}^{-3}
\end{align*}
Thus, the unit of power expressed in fundamental SI units is $\mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^2 \mathrm{~s}^{-3}$.
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option-D}$
Q.3.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ2_SL
Topic: Motion
Given: The minute hand of a clock hanging on a vertical wall has length L = 30 cm.
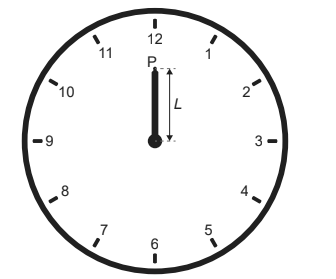
The minute hand is observed pointing at 12 and then again 30 minutes later when the minute hand is pointing at 6.
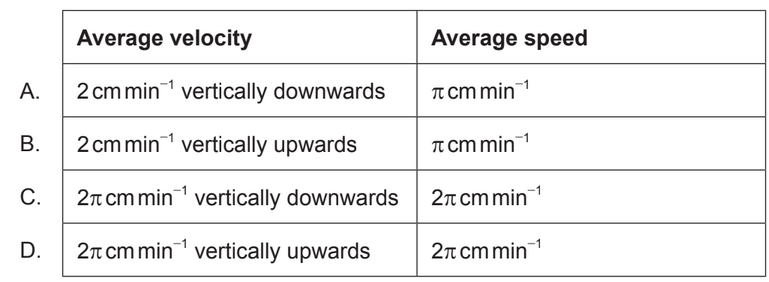
Calculate: What is the average velocity and average speed of point P on the minute hand during this time interval?
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
Average velocity $=\frac{\text { total displacement }}{\text { total time }}$
Total displacement in this interval is $2 \mathrm{~L}$
$
\left\langle v_{a v g}\right\rangle=\frac{2 L}{30 \min }=\frac{2 \mathrm{~cm}}{\min }
$
Speed $_{\text {avg }}=\frac{\text { total distance }}{\text { total time }}$
Total distance in this interval is $\pi L$
Average speed $=\frac{\pi L}{30}=\frac{\pi c m}{\min }$
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option-B}$
Q.4.2021-May-Physics_paper_1__TZ2_SL
Topic: Forces
Given: A person is standing at rest on the ground and experiences a downward gravitational force $W$ and an upward normal force from the ground $N$.
Discuss: Which, according to Newton’s third law, is the force that together with $W$ forms a force pair?
A. The gravitational force $W$ acting upwards on the ground.
B. The gravitational force $W$ acting upwards on the person.
C. The normal force $N$ acting upwards on the person.
D. The normal force $N$ acting downwards on the ground.
Answer/Explanation
Solution:
According to Newton’s third law, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In this case, the person is experiencing a downward gravitational force $W$ due to the Earth’s gravity, and an upward normal force $N$ from the ground, which is in contact with the person’s feet.
The force that forms a force pair with $W$ is the gravitational force $W$ acting upwards on the ground. This is because the force of gravity acting on the person is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity acting on the Earth (ground). In other words, the person and the Earth (ground) are exerting equal and opposite gravitational forces on each other, forming a force pair.
$\colorbox{yellow}{Correct Option-A}$
